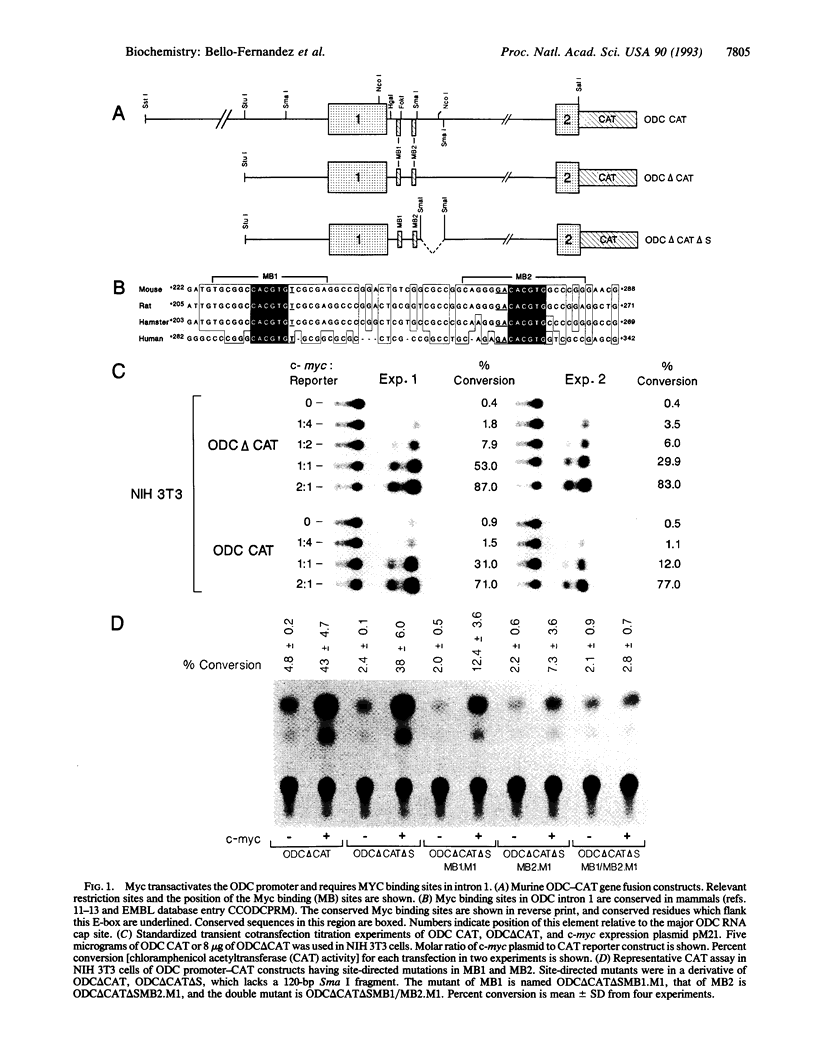
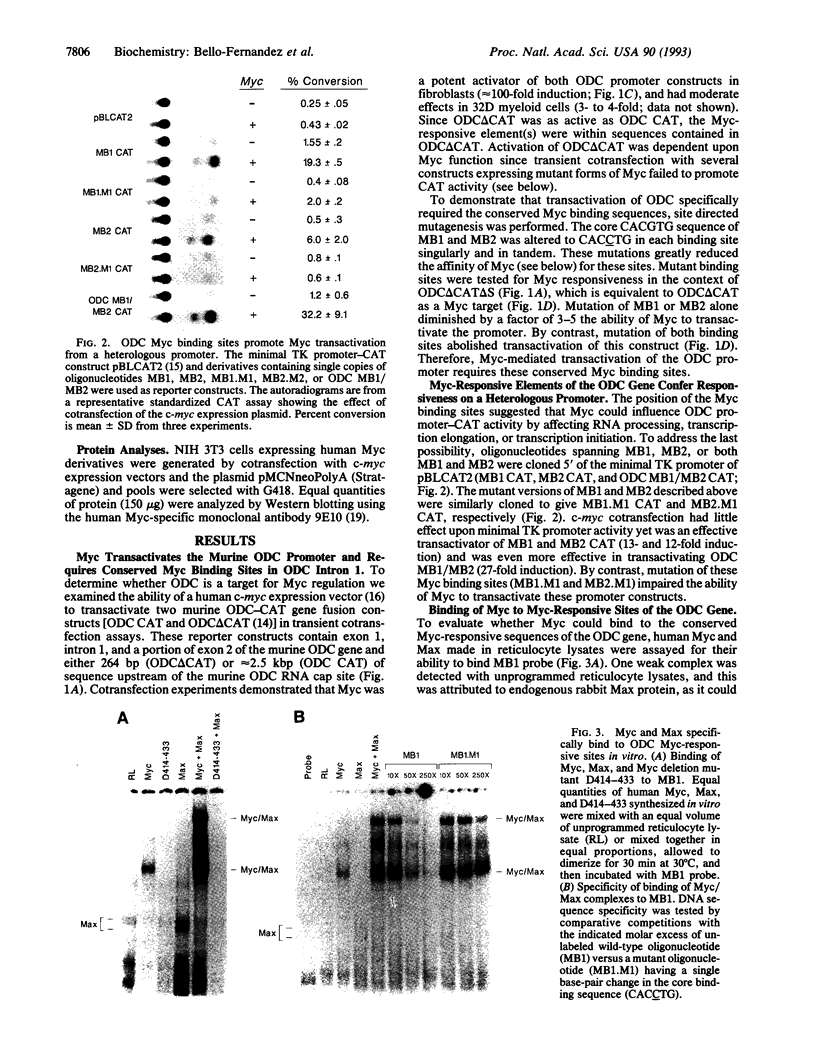
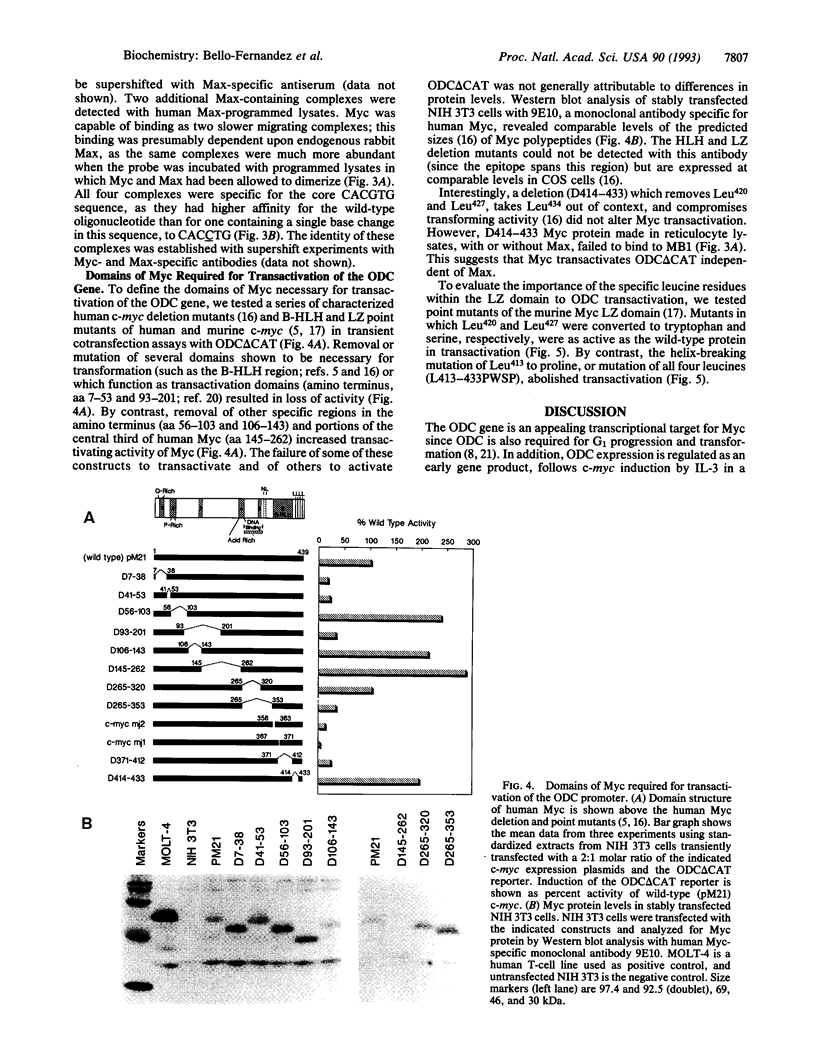
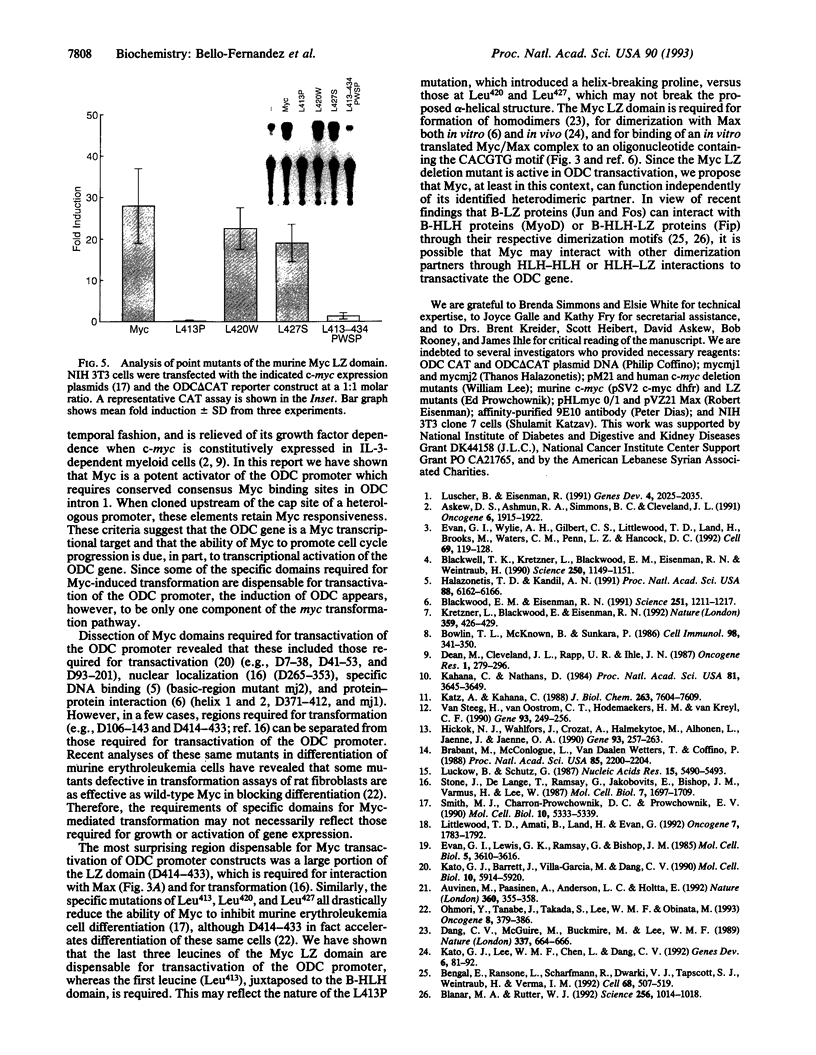
Abstract
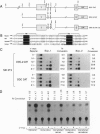
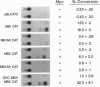
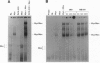
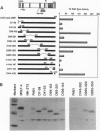
Constitutive c-myc expression suppresses cell cycle arrest, promotes entry into S phase, and results in the growth factor-independent expression of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC; EC 4.1.1.17). The ODC gene contains a conserved repeat of the Myc binding site, CACGTG, in intron 1. In this report, we demonstrate that c-Myc is a potent transactivator of ODC promoter-reporter gene constructs in fibroblasts that requires the CACGTG repeat. These sites conferred Myc responsiveness on heterologous promoter constructs, suggesting that ODC is regulated by Myc at the level of transcription initiation. Analysis of deletion and point mutants of c-myc revealed that domains required for transactivation of the ODC promoter did not include the leucine zipper of the Myc protein. This suggests that Myc may interact with transcription factors other than Max to transactivate the ODC gene.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auvinen M., Paasinen A., Andersson L. C., Hölttä E. Ornithine decarboxylase activity is critical for cell transformation. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):355–358. doi: 10.1038/360355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowlin T. L., McKown B. J., Sunkara P. S. Ornithine decarboxylase induction and polyamine biosynthesis are required for the growth of interleukin-2- and interleukin-3-dependent cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabant M., McConlogue L., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Mouse ornithine decarboxylase gene: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2200–2204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Cleveland J. L., Rapp U. R., Ihle J. N. Role of myc in the abrogation of IL3 dependence of myeloid FDC-P1 cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Aug;1(3):279–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Determination of the c-MYC DNA-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickok N. J., Wahlfors J., Crozat A., Halmekytö M., Alhonen L., Jänne J., Jänne O. A. Human ornithine decarboxylase-encoding loci: nucleotide sequence of the expressed gene and characterization of a pseudogene. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90233-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Nathans D. Isolation of cloned cDNA encoding mammalian ornithine decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3645–3649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Kahana C. Isolation and characterization of the mouse ornithine decarboxylase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7604–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood T. D., Amati B., Land H., Evan G. I. Max and c-Myc/Max DNA-binding activities in cell extracts. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1783–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori Y., Tanabe J., Takada S., Lee W. M., Obinata M. Functional domains of c-Myc involved in the commitment and differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Charron-Prochownik D. C., Prochownik E. V. The leucine zipper of c-Myc is required for full inhibition of erythroleukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5333–5339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg H., van Oostrom C. T., Hodemaekers H. M., van Kreyl C. F. Cloning and functional analysis of the rat ornithine decarboxylase-encoding gene. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90232-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]