Abstract
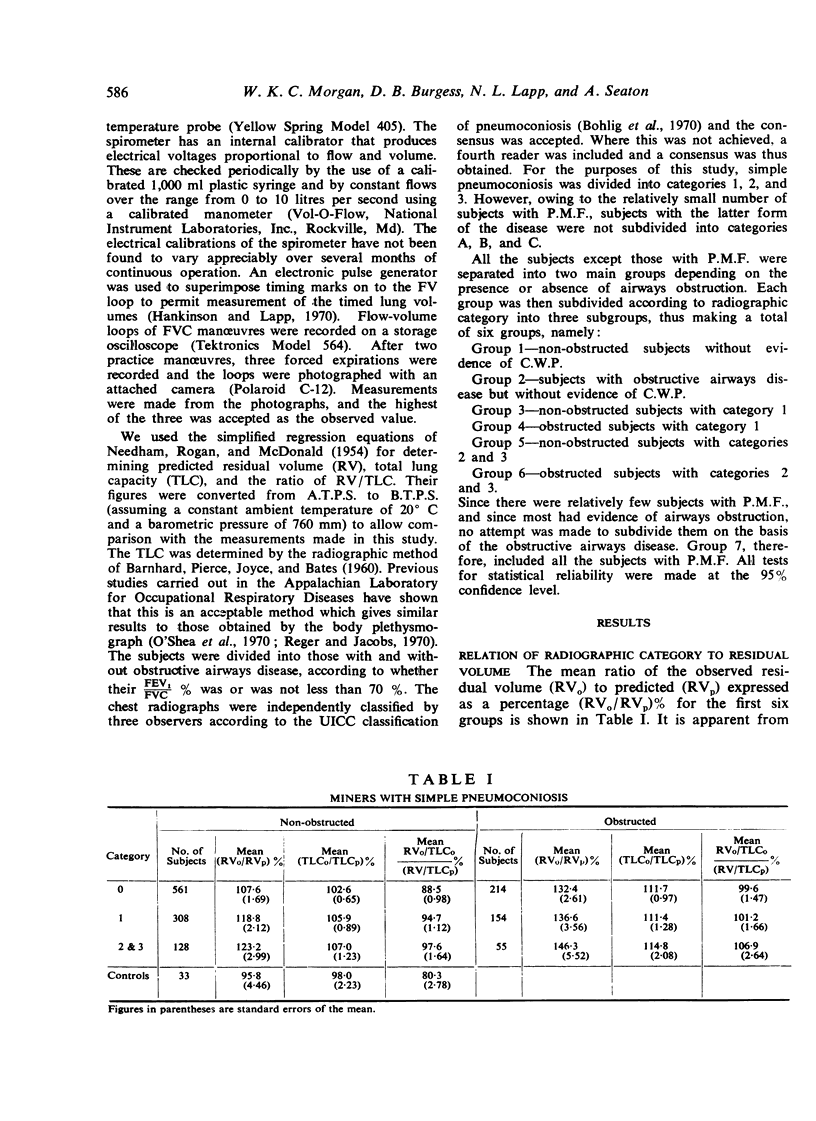
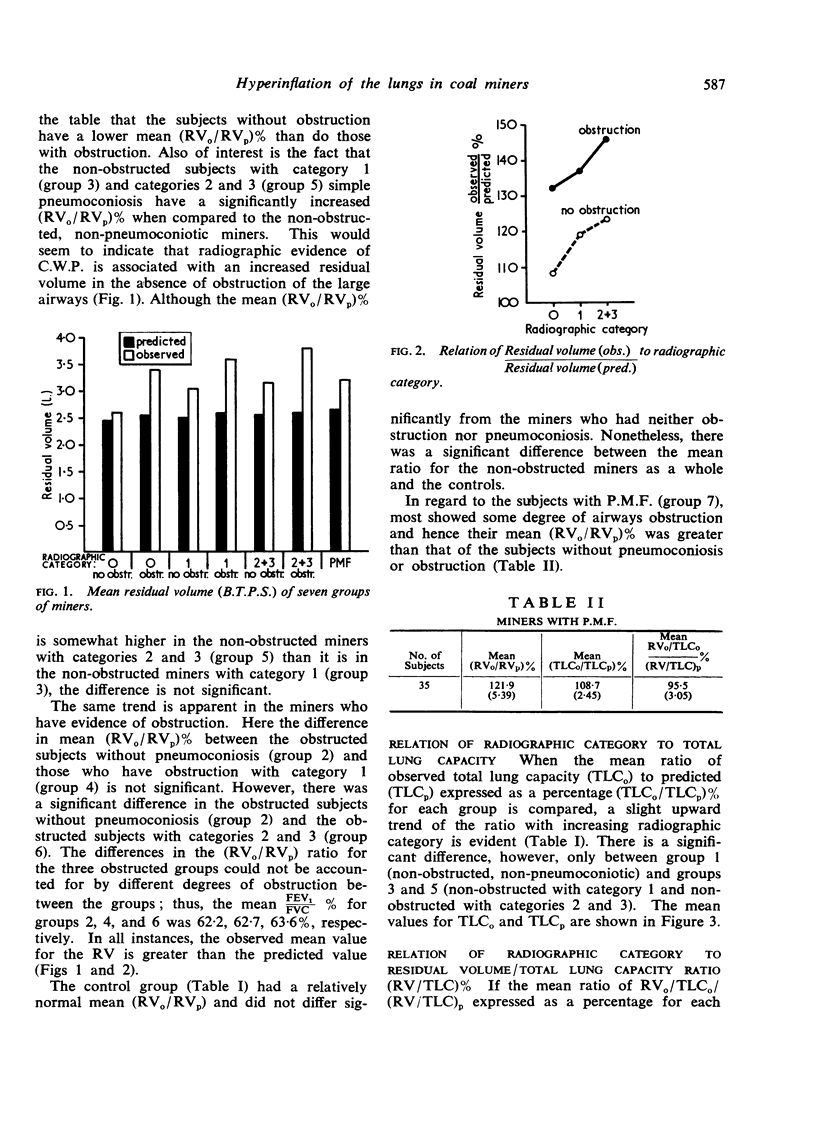
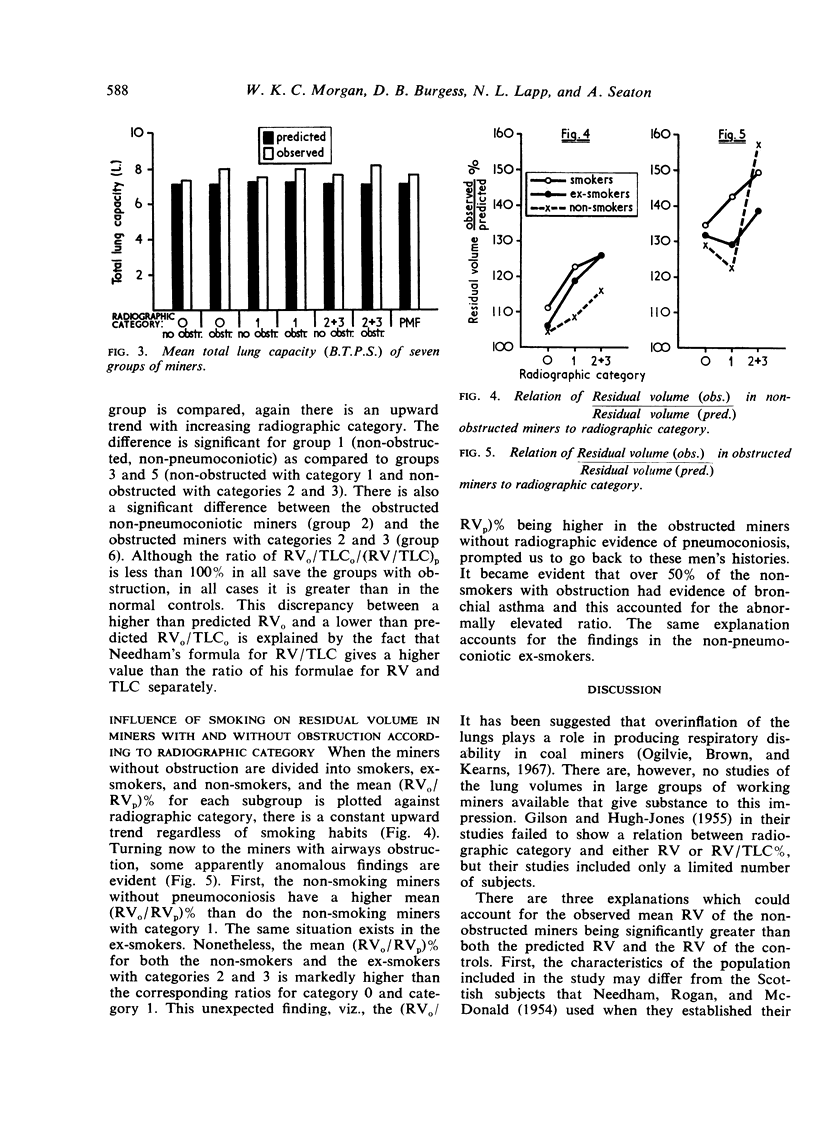
The residual volume and total lung capacity of 1,455 working Pennsylvania coal miners were determined as part of a larger epidemiological study. The age of the subjects varied between 18 and 65 with a mean of 48·7 years. The total lung capacity of the subjects was determined from standard posteroanterior and lateral chest films while the forced vital capacity was determined by spirometry (O'Shea et al., 1970). The effect of increasing radiographic category of simple coal workers' pneumoconiosis on lung volumes was investigated. It was shown that the residual volume increased with radiographic category and that this occurred whether or not the miners had obstructive airways disease. The presence of obstruction had an additional effect over and above that due to coal dust alone, so that the largest increase in residual volume was found in miners who had both obstruction and radiographic evidence of simple coal workers' pneumoconiosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNHARD H. J., PIERCE J. A., JOYCE J. W., BATES J. H. Roentgenographic determination of total lung capacity. A new method evaluated in health, emphysema and congestive heart failure. Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The pathological anatomy of simple pneumokoniosis in coal workers. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):235–246. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson J. L., Lapp N. L. Time-pulse generator for flow-volume curves. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Jul;29(1):109–110. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C., Macklem P. T., Thurlbeck W. M. Site and nature of airway obstruction in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 20;278(25):1355–1360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806202782501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklem P. T., Mead J. Resistance of central and peripheral airways measured by a retrograde catheter. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):395–401. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J., Lapp N. L., Russakoff A. D., Reger R., Morgan W. K. Determination of lung volumes from chest films. Thorax. 1970 Sep;25(5):544–549. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.5.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie C., Brown K., Kearns W. E. Overinflation of the lungs in coal miners. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 1;3(5556):10–14. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5556.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reger R. B., Jacobs A. C. Analysis of components of variation in a radiological method for determining total lung capacity. Arch Environ Health. 1970 Dec;21(6):778–783. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1970.10667331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



