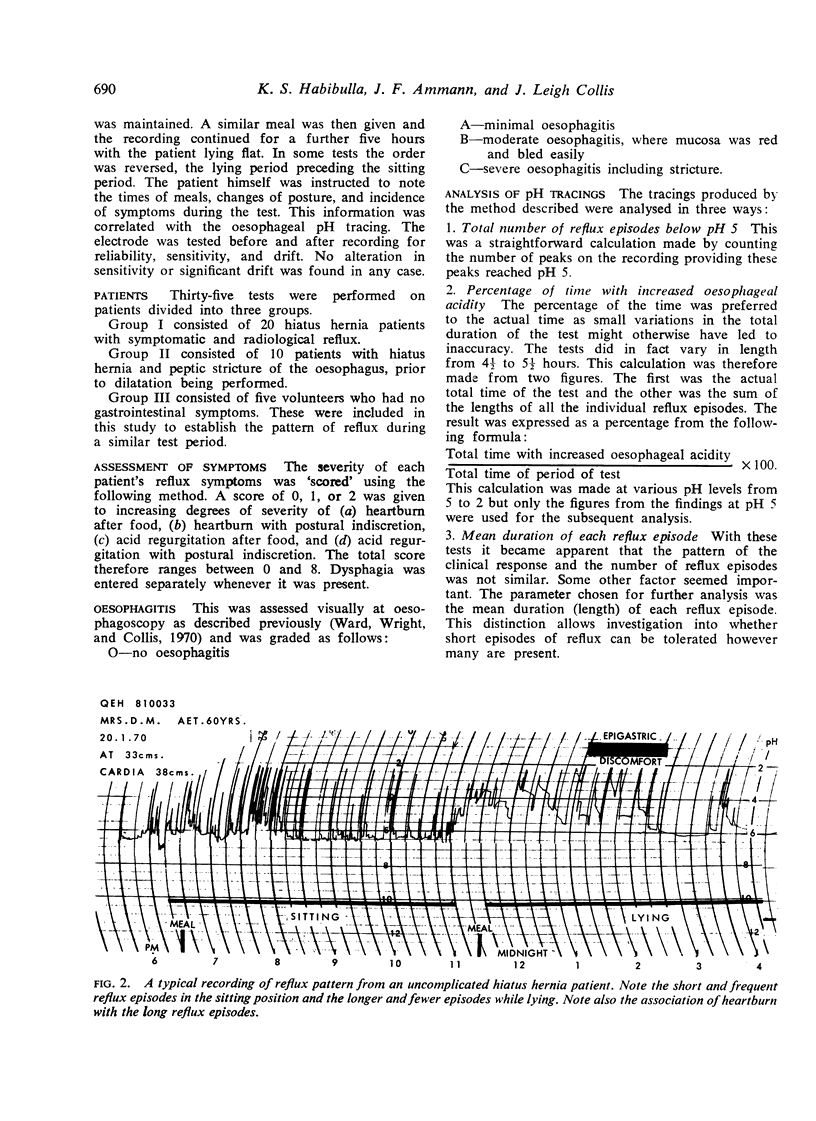
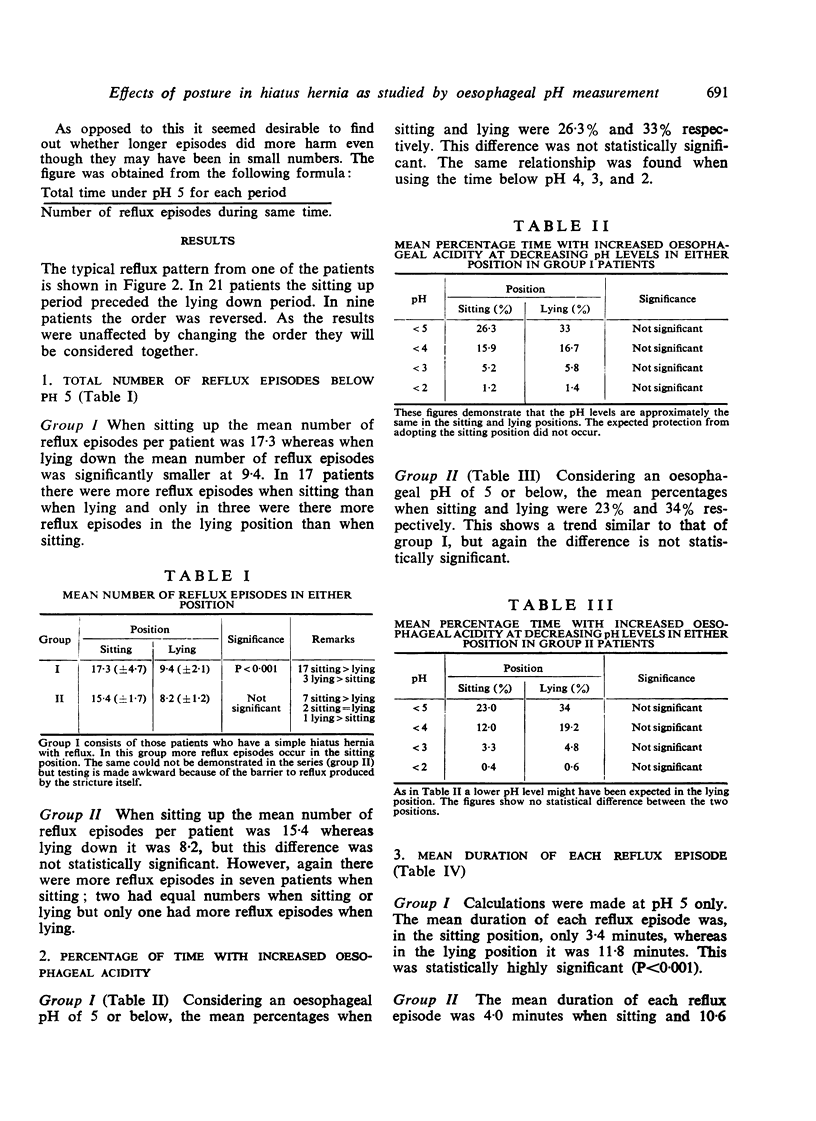
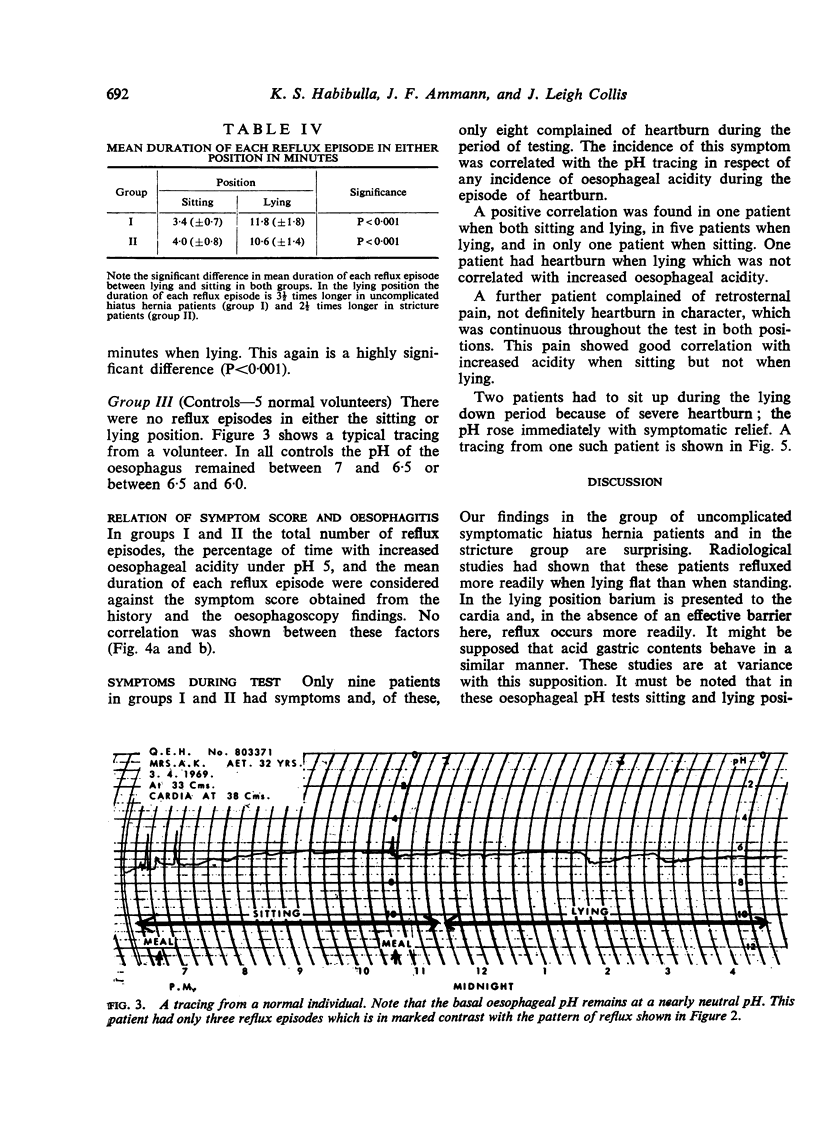
Abstract
The use of postural restriction in the treatment of patients with hiatus hernia has been analysed using continuous oesophageal pH measurements. It appears that it is not effective in the prevention of reflux of acid. The percentage of the time during which oesophageal pH remains below 5 is not significantly different when comparison is made during periods of sitting and lying. The frequency of reflux episodes is actually greater in the sitting position, but the duration of each reflux episode is significantly shorter than when lying. It is suggested that the undoubted symptomatic benefit derived by hiatus hernia patients from adopting the sitting position is explained by improved clearance of regurgitated acid.
Full text
PDF
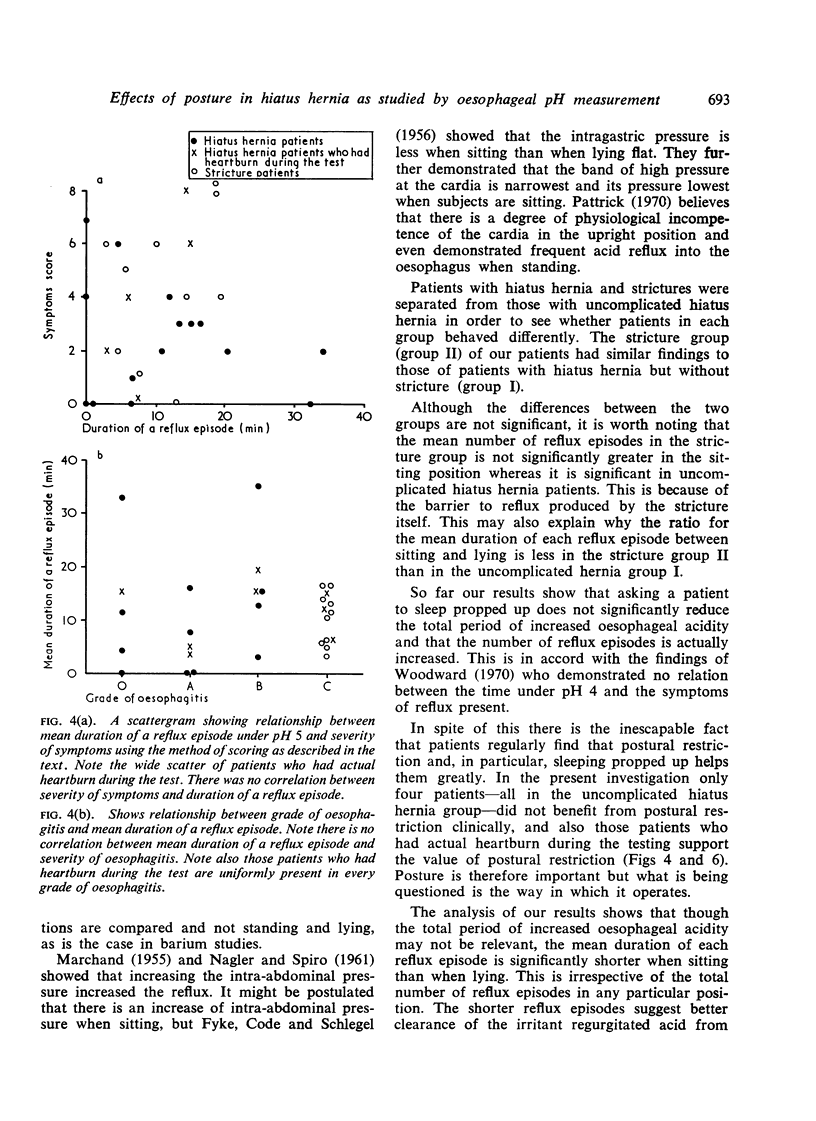
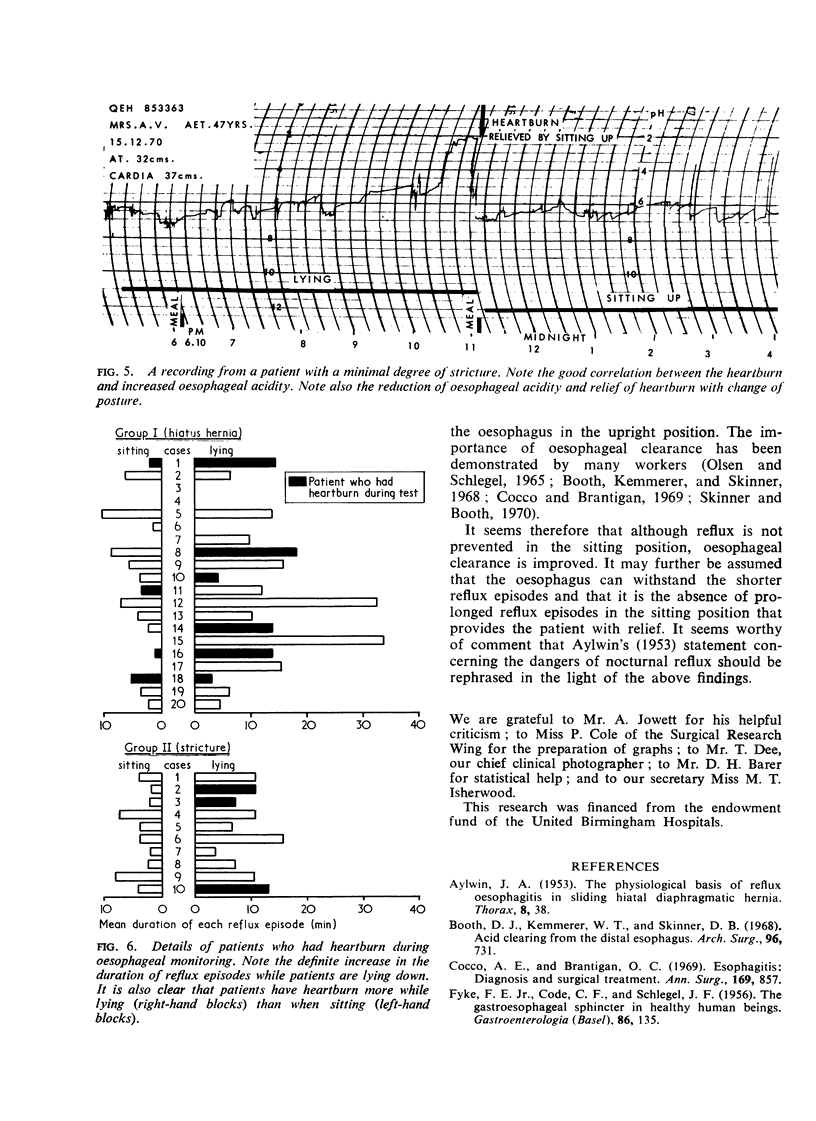

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYLWIN J. A. The physiological basis of reflux oesophagitis in sliding hiatal diaphragmatic hernia. Thorax. 1953 Mar;8(1):38–45. doi: 10.1136/thx.8.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth D. J., Kemmerer W. T., Skinner D. B. Acid clearing from the distal esophagus. Arch Surg. 1968 May;96(5):731–734. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330230039006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., FYKE F. E., Jr, SCHLEGEL J. F. The gastroesophageal sphincter in healthy human beings. Gastroenterologia. 1956;86(3):135–150. doi: 10.1159/000200544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco A. E., Brantigan O. C. Esophagitis: diagnosis and surgical treatment. Ann Surg. 1969 Jun;169(6):857–866. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196906000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELM W. J., SCHLEGEL J. F., CODE C. F., SUMMERSKILL W. H. IDENTIFICATION OF THE GASTROESOPHAGEAL MUCOSAL JUNCTION BY TRANSMUCOSAL POTENTIAL IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH HIATAL HERNIA. Gastroenterology. 1965 Jan;48:25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHAND P. The gastro-oesophageal sphincter and the mechanism of regurgitation. Br J Surg. 1955 Mar;42(175):504–513. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004217510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER R., SPIRO H. M. Heartburn in late pregnancy. Manometric studies of esophageal motor function. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:954–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI104335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen A. M., Schlegel J. F. Motility disturbances caused by esophagitis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965 Nov;50(5):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICCONE V. A., GUTELIUS J. R., MCCORRISTON J. R. A MULTIPHASE ESOPHAGEAL PH TEST FOR GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX. Surgery. 1965 May;57:638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattrick F. G. Investigation of gastroesophageal reflux in various positions with a two-lumen pH electrode. Gut. 1970 Aug;11(8):659–667. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.8.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Booth D. J. Assessment of distal esophageal function in patients with hiatal hernia and-or gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1970 Oct;172(4):627–637. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197010000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. Prolonged pH recording in the study of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1969 Dec;56(12):912–914. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800561211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUTTLE S. G., GROSSMAN M. I. Detection of gastro-esophageal reflux by simultaneous measurement of intraluminal pressure and pH. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jun;98(2):225–227. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. S., Wright D. H., Collis J. L. The assessment of oesophagitis in hiatus hernia patients. Thorax. 1970 Sep;25(5):568–572. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward D. A. Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis. Thorax. 1970 Jul;25(4):459–464. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.4.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]