Abstract
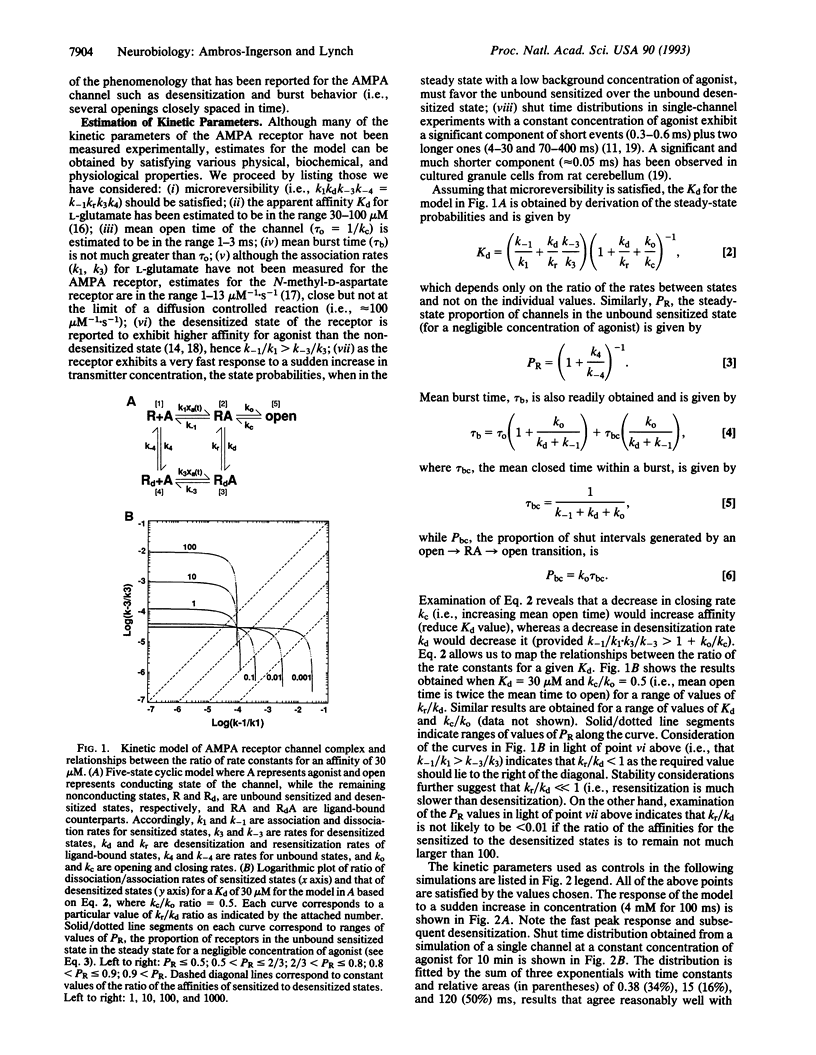
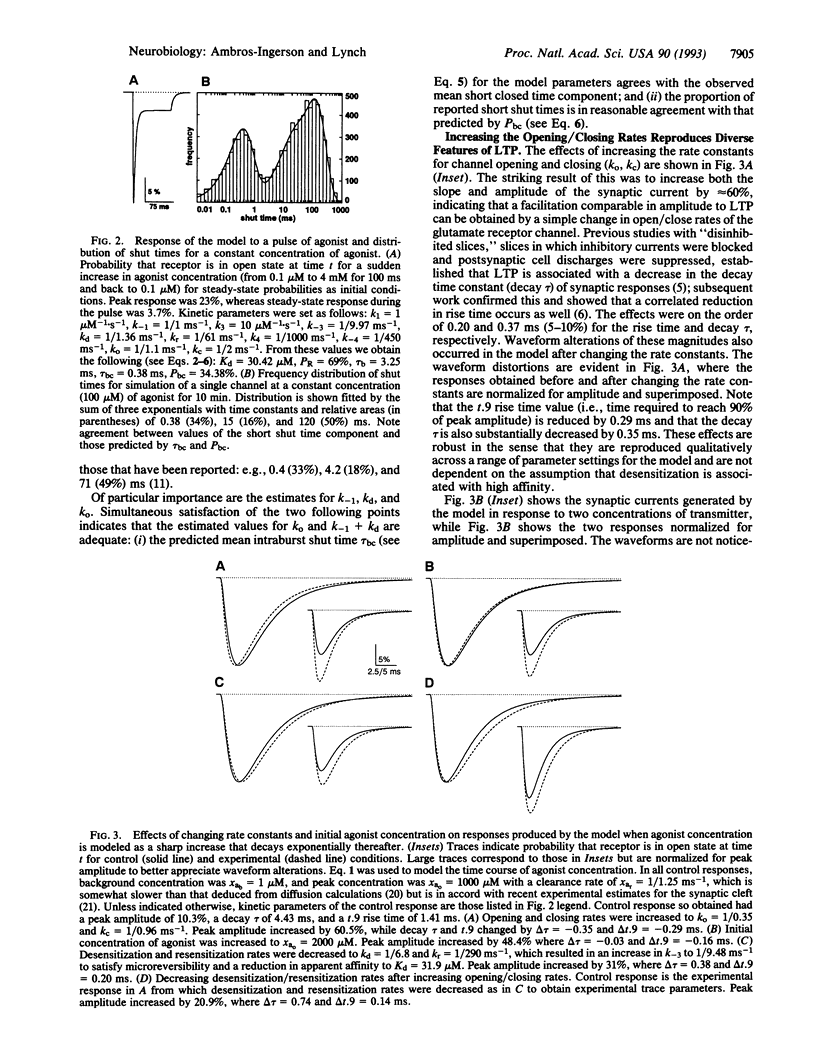
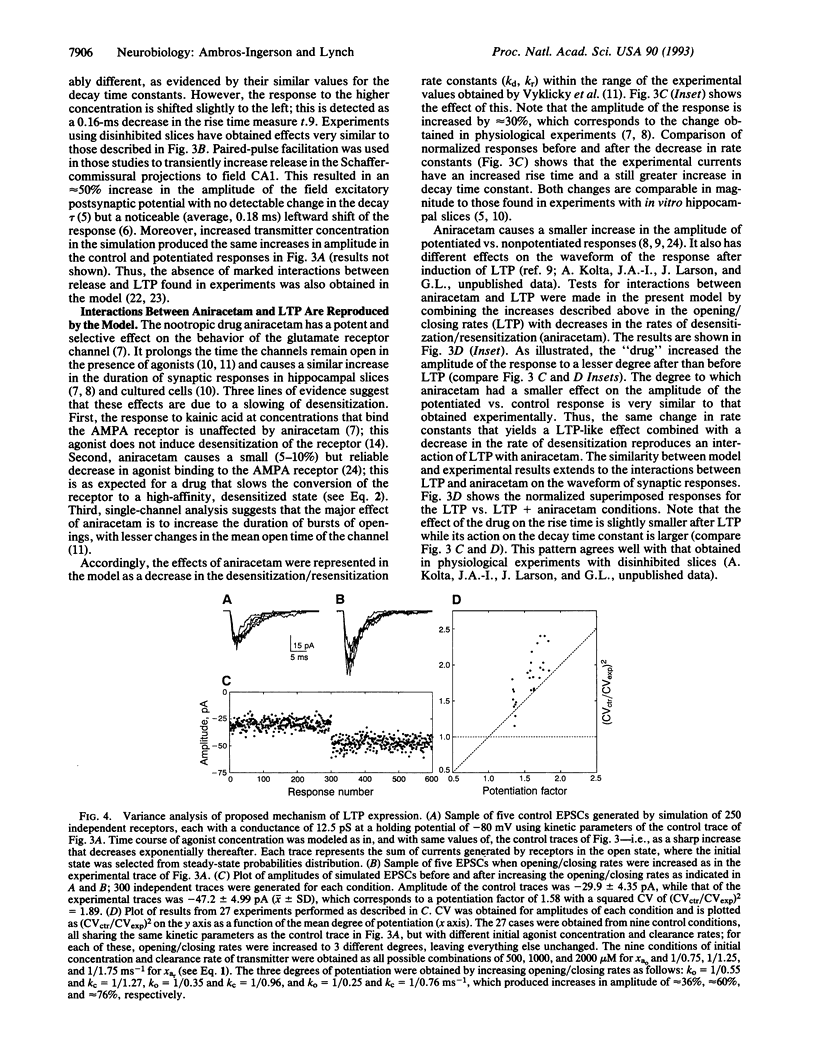
A kinetic model of the glutamate DL-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor/channel complex was used to test whether changes in the rate constants describing channel behavior could account for various features of long-term potentiation (LTP). Starting values for the kinetic parameters were set to satisfy experimental data (e.g., affinity, mean open time, mean burst length, etc.) and physical constraints (i.e., microreversibility). The resultant model exhibited a variety of dynamic properties known to be associated with the receptor. Increasing the rate constants governing opening/closing of the channel produced an unexpected increase in the probability of the channel being open shortly after transmitter binding. This would account for the enhanced response size with LTP. Increases in rate constants produced two other aspects of LTP: (i) an alteration of the waveform of the synaptic response and (ii) an interaction with changes in desensitization kinetics. The results obtained with the model corresponded closely to those found in LTP experiments. Thus, an increase in opening/closing rates for the postsynaptic receptor channel provides a single explanation for diverse characteristics of LTP. Finally, the kinetic manipulation reduced the coefficient of variation of synaptic currents in a model involving 250 receptors. This calls into question the use of variance measures for distinguishing pre- vs. postsynaptic sites of potentiation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros-Ingerson J., Larson J., Xiao P., Lynch G. LTP changes the waveform of synaptic responses. Synapse. 1991 Dec;9(4):314–316. doi: 10.1002/syn.890090406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros-Ingerson J., Xiao P., Larson J., Lynch G. Waveform analysis suggests that LTP alters the kinetics of synaptic receptor channels. Brain Res. 1993 Aug 27;620(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. Presynaptic mechanism for long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):724–729. doi: 10.1038/346724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste M., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of antagonist action at N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. Two binding sites each for glutamate and glycine. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):560–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82272-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lester R. A., Tong G., Jahr C. E., Westbrook G. L. The time course of glutamate in the synaptic cleft. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.1359647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., JAEGER J. C. The relationship between the mode of operation and the dimensions of the junctional regions at synapses and motor end-organs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):38–56. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. C., McNaughton B. L. Long-term enhancement of CA1 synaptic transmission is due to increased quantal size, not quantal content. Hippocampus. 1991 Jan;1(1):79–91. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honore T., Drejeŕ J., Nielsen E. O., Nielsen M. Non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist 3H-CNOX binds with equal affinity to two agonist states of quisqualate receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 1;38(19):3207–3212. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Colquhoun D., Cull-Candy S. G. On the kinetics of large-conductance glutamate-receptor ion channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 May 23;233(1273):407–422. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Tanabe S., Kohda A., Sugiyama H. Allosteric potentiation of quisqualate receptors by a nootropic drug aniracetam. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:533–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G., Baudry M. The biochemistry of memory: a new and specific hypothesis. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1057–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.6144182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Tsien R. W. Presynaptic enhancement shown by whole-cell recordings of long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):177–180. doi: 10.1038/346177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Lynch G. Evidence that changes in presynaptic calcium currents are not responsible for long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 13;479(2):290–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of interactions between kainate and AMPA: evidence for activation of a single receptor in mouse hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):785–798. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90175-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahi K., Baudry M. Increasing binding affinity of agonists to glutamate receptors increases synaptic responses at glutamatergic synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6881–6885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staubli U., Ambros-Ingerson J., Lynch G. Receptor changes and LTP: an analysis using aniracetam, a drug that reversibly modifies glutamate (AMPA) receptors. Hippocampus. 1992 Jan;2(1):49–57. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450020107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Shi Q. Y., Katchman A., Lynch G. Modulation of the time course of fast EPSCs and glutamate channel kinetics by aniracetam. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):288–290. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Fischbach G. D. Glutamate receptor desensitization and its role in synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklicky L., Jr, Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by drugs that reduce desensitization at AMPA/kainate receptors. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):971–984. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90342-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao P., Staubli U., Kessler M., Lynch G. Selective effects of aniracetam across receptor types and forms of synaptic facilitation in hippocampus. Hippocampus. 1991 Oct;1(4):373–380. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalutsky R. A., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of two forms of long-term potentiation in single hippocampal neurons. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1619–1624. doi: 10.1126/science.2114039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



