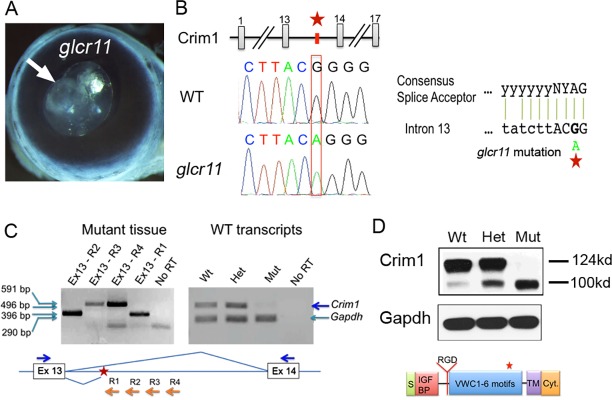
Fig. 1.
WGS identifies an intronic mutation in Crim1glcr11 mouse cataract mutants. (A) glcr11 mutant mice exhibit cataract (arrow). (B) Sequencing shows a G→A mutation in Crim1 intron 13, which creates a perfect cryptic consensus splice acceptor by creating a required A at the −2 position. (C) RT-PCR shows that the cryptically spliced transcripts continue at least 370 bp downstream of the mutation, truncating the exon 13 open reading frame and appending a short nonsense peptide. Upper blue line, normal splicing pattern; lower blue line, aberrant splicing pattern in the Crim1glcr11 mutant. R1-R4, reverse primers used for RT-PCR; RT, reverse transcriptase. (D) Western blot shows the full-length Crim1glcr11 protein at ∼124 kDa and a small amount of known proteolytic product (Wilkinson et al., 2003) at ∼100 kDa in the wild-type lens. In the Crim1glcr11 mutant, Crim1 is truncated via a stop codon shortly after exon 13, and hence the full-length 124 kDa form is absent. The truncated Crim1glcr11 protein is almost the same size (∼100 kDa) as the naturally occurring proteolytic form. Beneath is shown the Crim1 protein domains; the red asterisk indicates the truncation position in the Crim1glcr11 mutant. Panels A-D are representative of six independent experiments. IGFBP, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein motif; vWC, von Willebrand factor C repeats; TM, transmembrane domain; Cyt., cytoplasmic domain; RGD, Arg-Gly-Asp motif; S, signal peptide.