Abstract
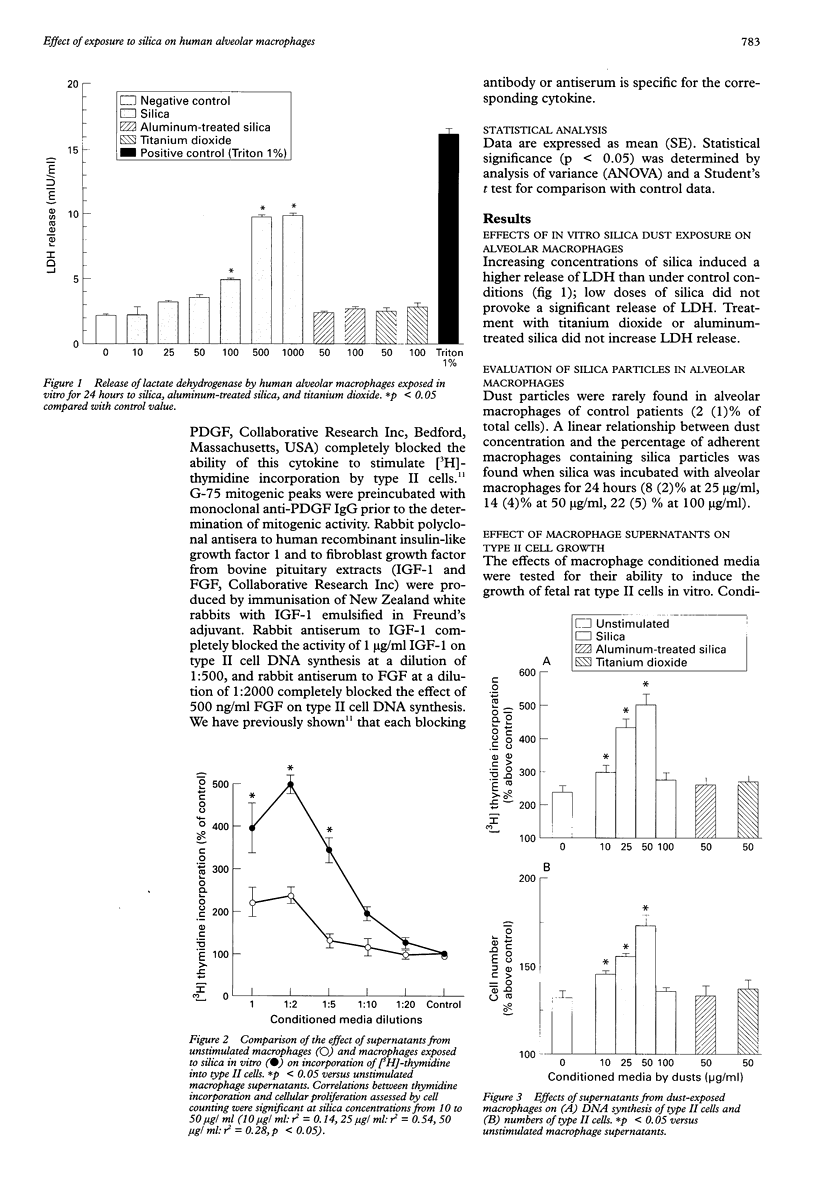
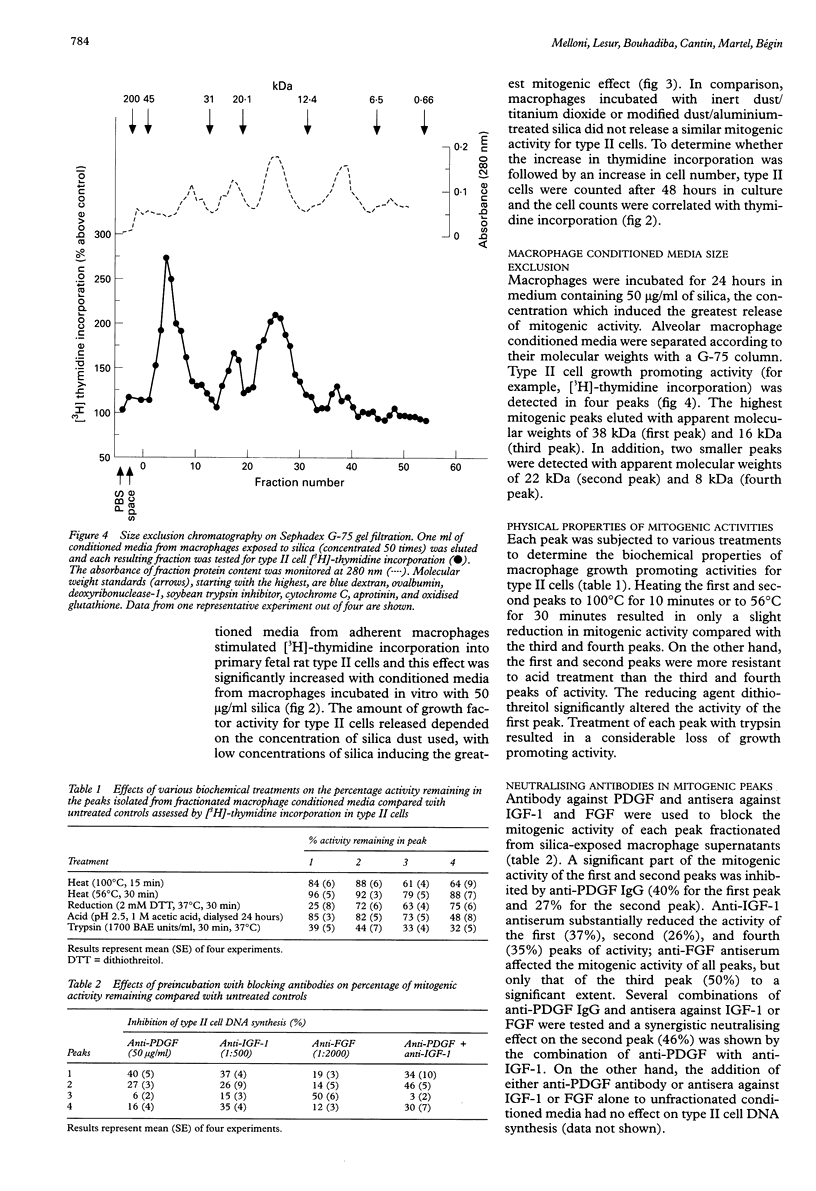
BACKGROUND: The proliferative response of type II cells is an important event following silica-induced lung injury. Alveolar macrophages, when activated by fibrogenic agents, secrete various biological mediators which affect cell growth. METHODS: Human alveolar macrophages from normal volunteers were incubated in serum-free medium or in the presence of increasing concentrations of silica. Alveolar macrophage conditioned media were diluted and added to type II cell cultures for proliferation studies. Purified type II pneumocytes were isolated from fetal rat lungs for bioassays. Growth factor activities were partially characterised by size exclusion chromatography. Each fractionated mitogenic peak was preincubated with monoclonal antibody against platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) or antisera against insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) or fibroblast derived growth factor (FGF) in order to study the nature of each activity. RESULTS: Conditioned media from alveolar macrophages exposed to silica induced an increase in type II cell DNA synthesis and cell number over that seen when type II cells were incubated with unstimulated alveolar macrophage supernatants. Size exclusion of alveolar macrophage supernatants exposed to silica showed four peaks of type II cell stimulating activity with apparent molecular weights of 38, 22, 16, and 8 kDa. Anti-PDGF antibody significantly reduced the activity of the first and second peaks, antiserum against IGF-1 partially reduced the activity of the first and fourth peaks, and antiserum against FGF reduced only the third peak of activity. CONCLUSIONS: Human alveolar macrophages exposed to silica in vitro release mitogens for type II pneumocytes including PDGF-like, IGF-1-like, and FGF-like molecules. These agents are likely to be involved in the epithelial repair and type II cell hyperplasia observed in silicosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauman M. D., Jetten A. M., Bonner J. C., Kumar R. K., Bennett R. A., Brody A. R. Secretion of a platelet-derived growth factor homologue by rat alveolar macrophages exposed to particulates in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin R. O., Cantin A. M., Boileau R. D., Bisson G. Y. Spectrum of alveolitis in quartz-exposed human subjects. Chest. 1987 Dec;92(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin R., Massé S., Rola-Pleszczynski M., Martel M., Desmarais Y., Geoffroy M., LeBouffant L., Daniel H., Martin J. Aluminum lactate treatment alters the lung biological activity of quartz. Exp Lung Res. 1986;10(4):385–399. doi: 10.3109/01902148609058289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S. Pathogenesis of silicosis: current concepts and hypotheses. Lung. 1986;164(3):139–154. doi: 10.1007/BF02713638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. Cytokines of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):765–788. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R. K., O'Grady R., Li W., Velan G. M. Mitogenic activity for fibroblasts induced by silica and titanium dioxide particles in vitro and in vivo. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Oct;73(5):573–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. C., McCormick-Shannon K., Cook J. L., Mason R. J. Macrophages stimulate DNA synthesis in rat alveolar type II cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Dec;132(6):1246–1252. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.6.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. C., McCormick-Shannon K., Mason R. J. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from normal rats stimulates DNA synthesis in rat alveolar type II cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):360–366. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesur O., Cantin A. M., Tanswell A. K., Melloni B., Beaulieu J. F., Bégin R. Silica exposure induces cytotoxicity and proliferative activity of type II pneumocytes. Exp Lung Res. 1992 Mar-Apr;18(2):173–190. doi: 10.3109/01902149209031679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesur O., Melloni B., Cantin A. M., Bégin R. Silica-exposed lung fluids have a proliferative activity for type II epithelial cells: a study on human and sheep alveolar fluids. Exp Lung Res. 1992 Sep-Oct;18(5):633–654. doi: 10.3109/01902149209031699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Kumar R. K., O'Grady R., Velan G. M. Role of lymphocytes in silicosis: regulation of secretion of macrophage-derived mitogenic activity for fibroblasts. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Dec;73(6):793–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni B., Lesur O., Bouhadiba T., Cantin A., Bégin R. Partial characterization of the proliferative activity for fetal lung epithelial cells produced by silica-exposed alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 May;55(5):574–580. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.5.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni B., Lesur O., Cantin A., Bégin R. Silica-exposed macrophages release a growth-promoting activity for type II pneumocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Mar;53(3):327–335. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. E., Dethloff L. A., Gladen B. C., Hook G. E. Progression of type II cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia during silica-induced pulmonary inflammation. Lab Invest. 1987 Nov;57(5):546–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M., Smith B. T. Histochemical and immunocytochemical identification of alveolar type II epithelial cells isolated from fetal rat lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):525–530. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Basset P., Fells G. A., Nukiwa T., Trapnell B. C., Crysal R. G. Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1685–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI113781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Cantin A., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the lower respiratory tract inflammation of nonsmoking individuals with interstitial lung disease associated with chronic inhalation of inorganic dusts. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):591–614. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheule R. K., Holian A. Immunologic aspects of pneumoconiosis. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jul-Aug;17(4):661–685. doi: 10.3109/01902149109062872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R., Gaumer H. R., Stankus R. P., Kaimal J., Hoffmann E., Salvaggio J. E. Bronchoalveolar lavage in silicosis. Evidence of type II cell hyperplasia. Lung. 1980;157(2):95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles A. D., Smith B. T., Post M. Reciprocal autocrine and paracrine regulation of growth of mesenchymal and alveolar epithelial cells from fetal lung. Exp Lung Res. 1986;11(3):165–177. doi: 10.3109/01902148609064294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura T., Rom W. N., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Morphologic characterization of alveolar macrophages from subjects with occupational exposure to inorganic particles. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1674–1685. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhee D., Gosset P., Wallaert B., Voisin C., Tonnel A. B. Mechanisms of fibrosis in coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Increased production of platelet-derived growth factor, insulin-like growth factor type I, and transforming growth factor beta and relationship to disease severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Oct;150(4):1049–1055. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.4.7921435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





