Abstract
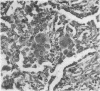
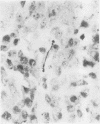
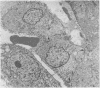
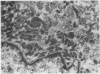
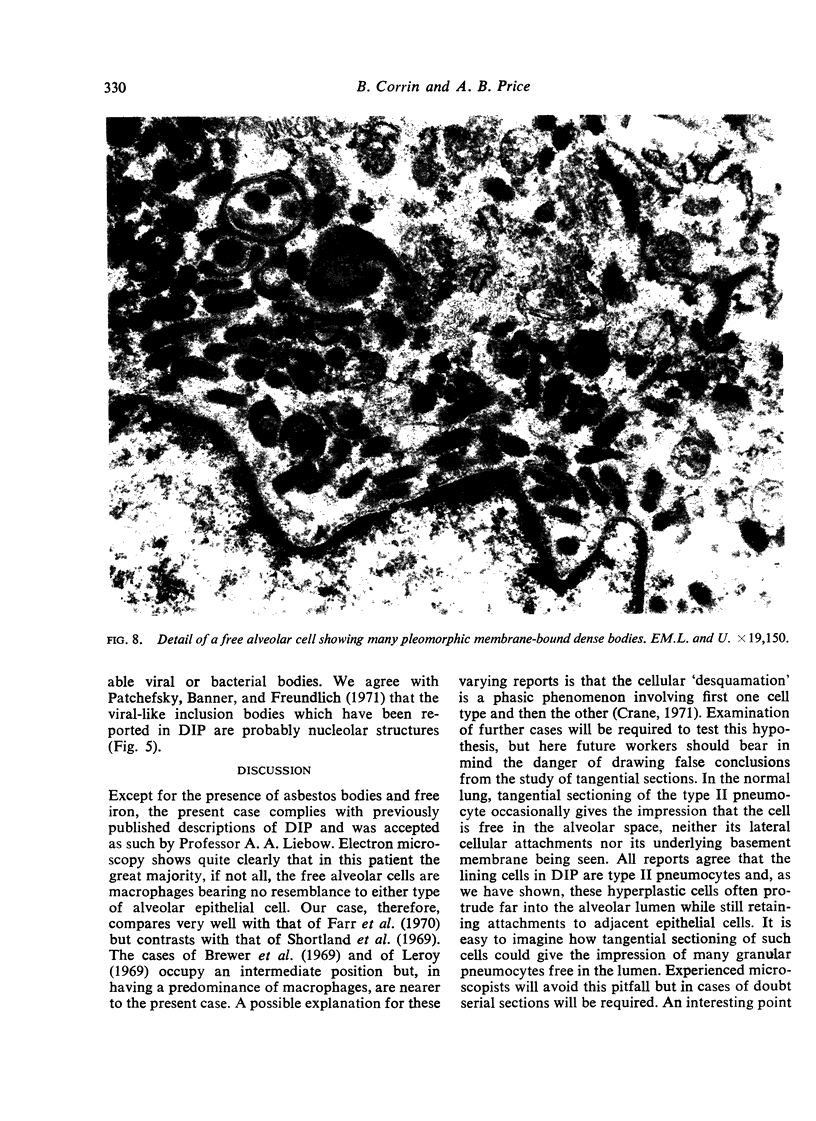
A case of desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) has been studied by electron microscopy in order to determine the nature of the alveolar cells. Those lining the alveolar walls proved to be granular pneumocytes (type II alveolar epithelial cells) while cells free in the lumen were alveolar macrophages. The brief literature describing the electron microscopic findings in DIP is reviewed. All workers agree that the lining cells are granular pneumocytes and most report a mixed free cell population with the emphasis shifting from desquamated epithelial cells to macrophages. In the present case asbestos bodies were also found in the lung, suggesting that DIP is not a specific disease entity.
Full text
PDF

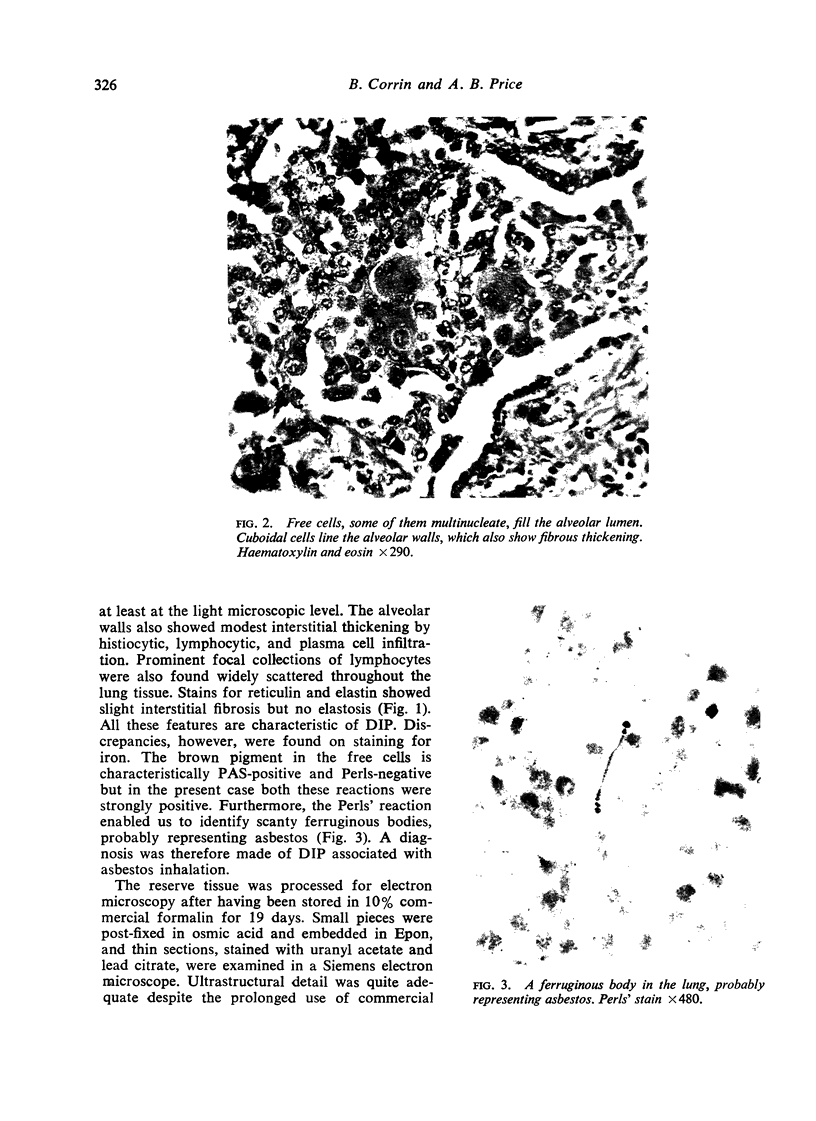
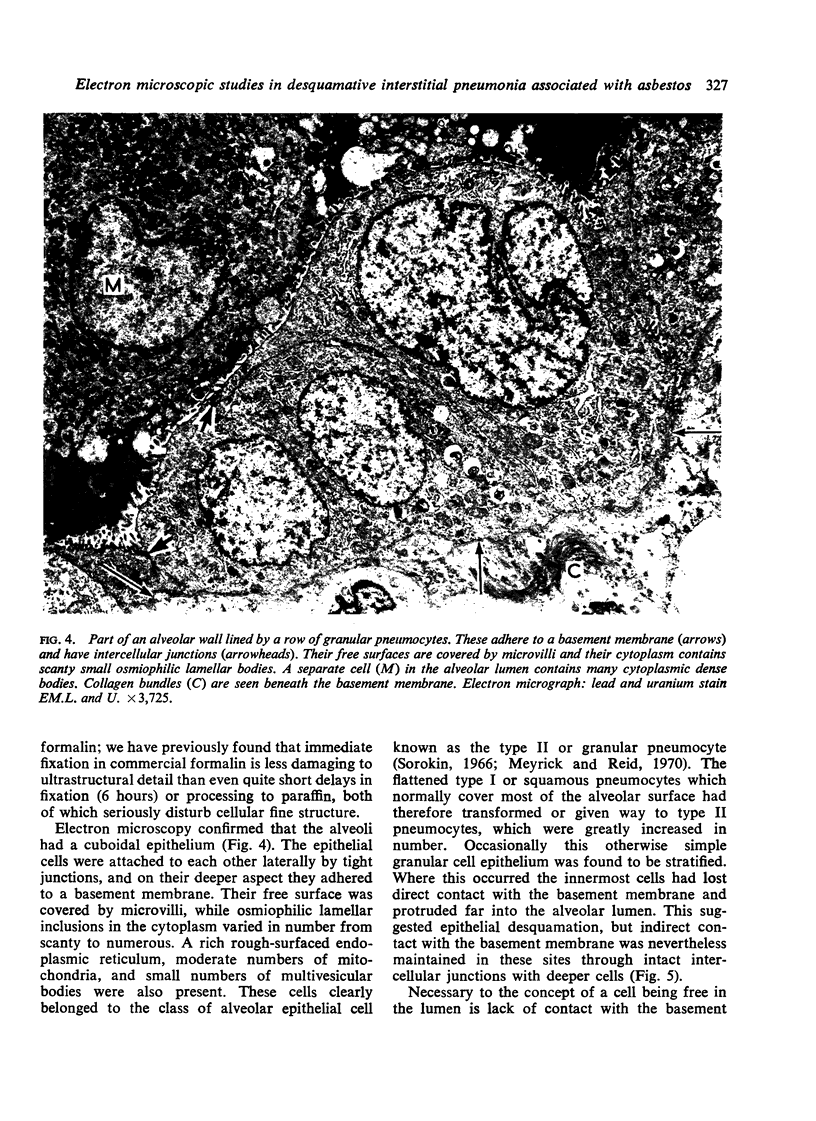
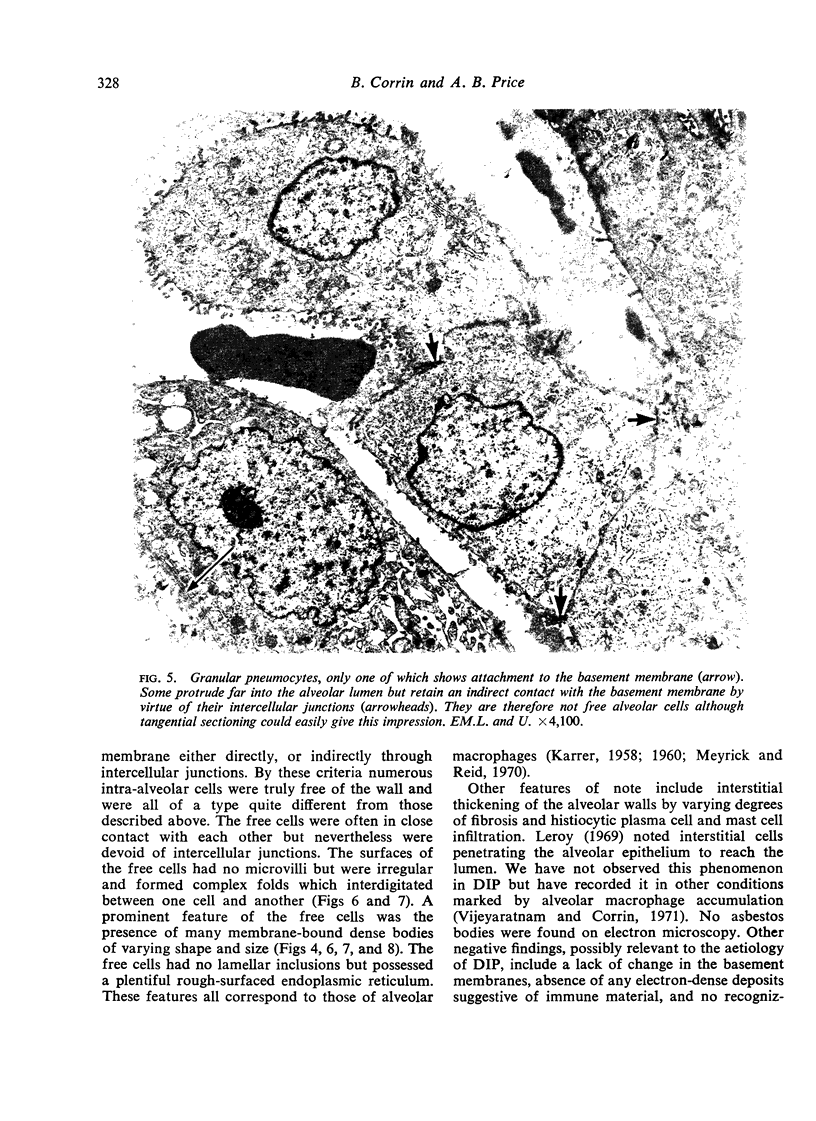
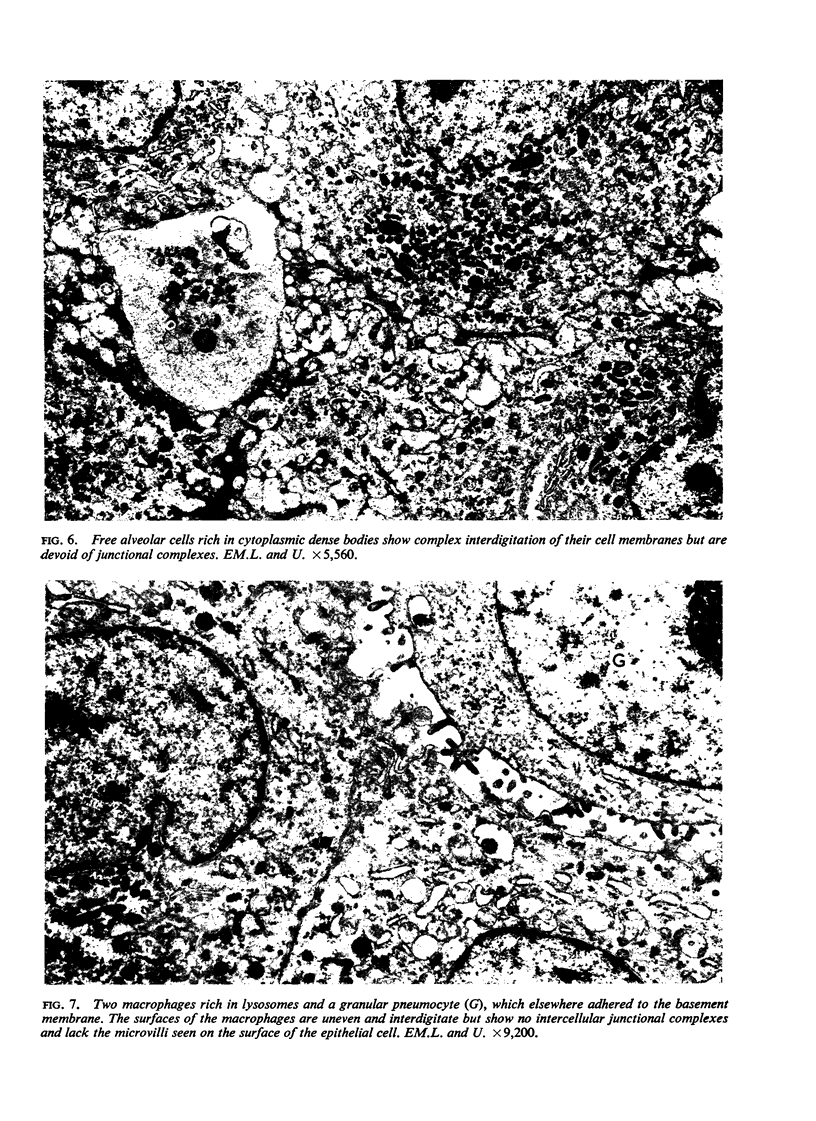

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhagwat A. G., Conen P. E. Characterization of "free alveolar cells" in experimental adjuvant induced pneumonia. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jul;88(1):21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer D. B., Heath D., Asquith P. Electron microscopy of desquamative interstitial pneumonia. J Pathol. 1969 Feb;97(2):317–323. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr G. H., Harley R. A., Hennigar G. R. Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1970 Sep;60(3):347–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff A. M., McNary W. F., Jr, Gaensler E. A. Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Med Thorac. 1967;24(5):317–329. doi: 10.1159/000192536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. The ultrastructure of mouse lung: the alveolar macrophage. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):693–700. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBOW A. A., STEER A., BILLINGSLEY J. G. DESQUAMATIVE INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIA. Am J Med. 1965 Sep;39:369–404. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy E. P. The blood-air barrier in desquamative interstitial pneumonia (D.I.P.). Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1969;348(2):117–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00544319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The alveolar wall. Br J Dis Chest. 1970 Jul;64(3):121–140. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(70)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchefsky A. S., Banner M., Freundlich I. M. Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Significance of intranuclear viral-like inclusion bodies. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Mar;74(3):322–327. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-3-322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding J. G., Hinson K. F. Diffuse fibrosing alveolitis (diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lungs). Correlation of histology at biopsy with prognosis. Thorax. 1967 Jul;22(4):291–304. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortland J. R., Darke C. S., Crane W. A. Electron microscopy of desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Thorax. 1969 Mar;24(2):192–208. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.2.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin S P. A morphologic and cytochemical study on the great alveolar cell. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Dec;14(12):884–897. doi: 10.1177/14.12.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol. 1971 Feb;103(2):123–129. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]