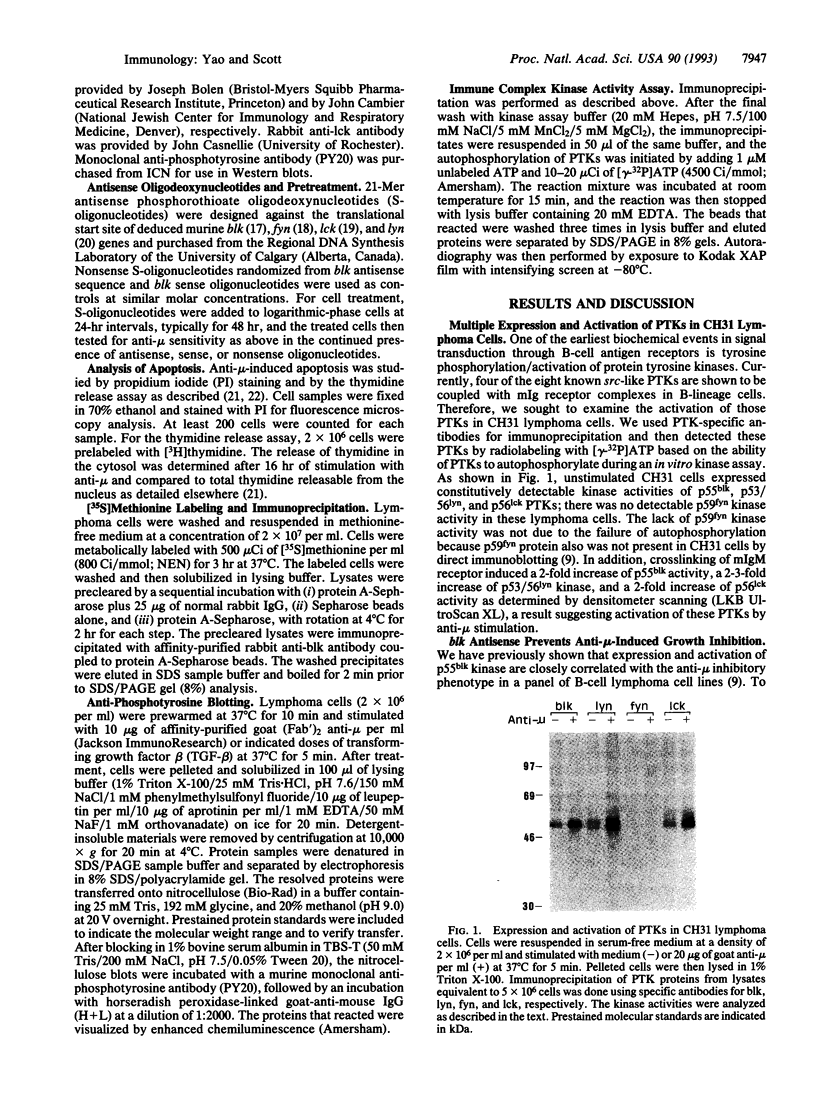
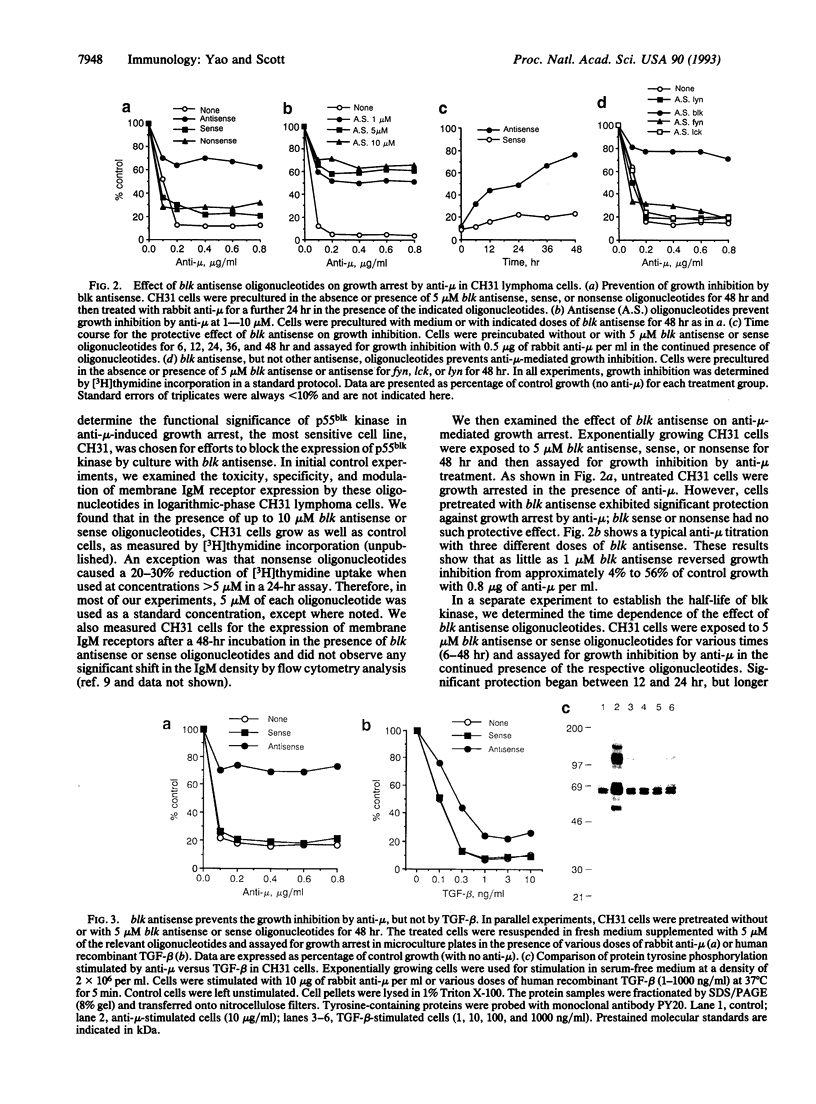
Abstract
Crosslinking of membrane immunoglobulin (mIg) receptors by anti-Ig causes growth inhibition and subsequent cell death due to apoptosis in a murine B-cell lymphoma model. The earliest signal transduction via mIg has recently been shown to be dependent on the activation of one or more protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). In this study, we utilized the CH31 lymphoma, which is extremely sensitive to growth inhibition by anti-Ig, to examine the role of PTKs in cell cycle arrest. This cell line expresses multiple PTKs, whose activities are stimulated by crosslinking mIg. To determine whether PTK activity is essential for the inhibition of cell growth, we exposed CH31 cells to antisense oligodeoxynucleotides for the blk PTK prior to the growth inhibition assay. We found that exposure of CH31 cells to blk antisense effectively prevented anti-mu-chain-mediated growth inhibition and subsequent apoptosis. Corresponding blk sense or antisense oligonucleotides for other PTKs had no protective effect against anti-mu. Moreover, antisense blk oligonucleotides had no effect on transforming growth factor beta-mediated growth arrest and apoptosis. Further experiments showed significantly reduced endogenous p55blk in blk antisense-treated cells. In addition, anti-mu stimulation of antisense-treated cells failed to induce any detectable increase in kinase activity of p55blk, a result suggesting the uncoupling of blk proteins from normal signal pathways that are essential for growth inhibition. These results implicate a role of blk kinase in anti-mu-mediated pathway to cell cycle arrest.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Campbell K. S. Membrane immunoglobulin and its accomplices: new lessons from an old receptor. FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3207–3217. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Association between B-lymphocyte membrane immunoglobulin and multiple members of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2315–2321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., McHugh J. C., Altman A. Predominant expression and activation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5660–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dymecki S. M., Niederhuber J. E., Desiderio S. V. Specific expression of a tyrosine kinase gene, blk, in B lymphoid cells. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):332–336. doi: 10.1126/science.2404338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Crowley M. T., Martin G. A., McCormick F., DeFranco A. L. Targets of B lymphocyte antigen receptor signal transduction include the p21ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and two GAP-associated proteins. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce apoptosis in immature B cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel W. M., Schatzman R. C., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 upon cross-linking of membrane Ig on murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., deRiel J. K., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Inhibition of cellular proliferation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to PCNA cyclin. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2897717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. A., Gold M. R., DeFranco A. L. Examination of B lymphoid cell lines for membrane immunoglobulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and src-family tyrosine kinase mRNA expression. Mol Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;29(7-8):917–926. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90130-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Justement L. B. The MB-1/B29 heterodimer couples the B cell antigen receptor to multiple src family protein tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1548–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuki M., Massagué J. Evidence for the involvement of protein kinase activity in transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):261–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell C. A., Scott D. W. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. IV. Growth inhibition by anti-Ig of CH31 and CH33 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Livnat D., Pennell C. A., Keng P. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. III. Cell cycle dependence for negative signalling of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells by anti-mu. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., O'Garra A., Warren D., Klaus G. G. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. VI. Reversal of anti-Ig-mediated negative signaling by T cell-derived lymphokines. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):3924–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora G., Clair T., Cho-Chung Y. S. An antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeted against the type II beta regulatory subunit mRNA of protein kinase inhibits cAMP-induced differentiation in HL-60 leukemia cells without affecting phorbol ester effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):705–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner G. L., Ludlow J. W., Nelson D. A., Gaur A., Scott D. W. Anti-immunoglobulin treatment of murine B-cell lymphomas induces active transforming growth factor beta but pRB hypophosphorylation is transforming growth factor beta independent. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Mar;3(3):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukui Y., Wongsasant B., Kinoshita Y., Ichimori Y., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Activation of Src-like protein-tyrosine kinase Lyn and its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase upon B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao X. R., Scott D. W. Expression of protein tyrosine kinases in the Ig complex of anti-mu-sensitive and anti-mu-resistant B-cell lymphomas: role of the p55blk kinase in signaling growth arrest and apoptosis. Immunol Rev. 1993 Apr;132:163–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Bolen J. B., Ihle J. N. Hematopoietic cells express two forms of lyn kinase differing by 21 amino acids in the amino terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2391–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]