Abstract
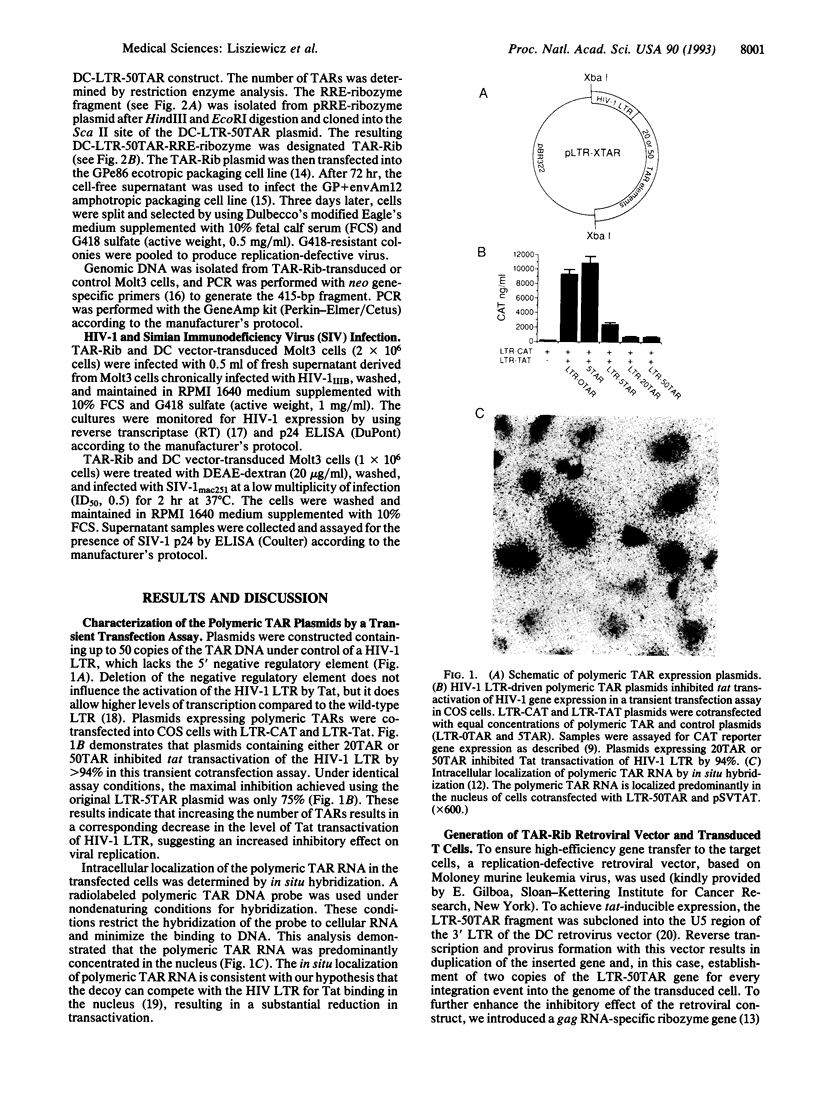
We are investigating a strategy for somatic gene therapy to treat human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection by intracellular expression of an RNA decoy and a ribozyme. The RNA decoy, consisting of polymeric Tat activation response elements (TARs), is designed to compete for Tat binding in an equilibrium with viral TAR RNA, thereby inhibiting viral replication. The expression of polymeric TAR is regulated by the HIV long terminal repeat (LTR) and transcriptional activation is dependent on the presence of HIV Tat. Our initial studies indicated that plasmids expressing up to 50 tandem copies of TAR RNA (50TAR) inhibited tat-mediated gene expression by > 90% in a transient transfection assay. A HIV LTR-driven 50TAR construct was subcloned into a replication-defective retroviral vector to ensure high-efficiency gene transfer into T lymphocytes. In addition, a gag RNA-specific ribozyme gene was introduced into the 50TAR containing retroviral vector to enhance the inhibitory effect of the construct (designated TAR-Rib). A human T-cell line (Molt3) was infected (transduced) with the TAR-Rib recombinant retrovirus and challenged with either HIV-1 or simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). HIV-1 replication was inhibited by 99% in the TAR-Rib-transduced T cells and was maintained over a 14-month period, suggesting that this antiviral strategy represses the formation of escape mutants. Interestingly, the TAR-Rib also inhibited SIV replication in transduced T cells, which suggests that polymeric TAR is a general inhibitor of primate lentiviruses; therefore, the macaque model could be used for further in vivo testing of this antiviral gene therapy strategy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F. Human gene therapy. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):808–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1589762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Beaver B., Jagodzinski L., Ensoli B., Kanki P. J., Albert J., Fenyo E. M., Biberfeld G., Zagury J. F., Laure F. New human and simian HIV-related retroviruses possess functional transactivator (tat) gene. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):548–550. doi: 10.1038/328548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerkoel C. F., Kung H. J. Transcriptional interaction between retroviral long terminal repeats (LTRs): mechanism of 5' LTR suppression and 3' LTR promoter activation of c-myc in avian B-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4814–4823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4814-4823.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonaguro L., Barillari G., Chang H. K., Bohan C. A., Kao V., Morgan R., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7159–7167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7159-7167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan S., Streicher H. Z., Wahl L. M., Miller N., Louie A. T., Goldfarb I. S., Jackson W. L., Casali P., Notkins A. L. Model for studying virus attachment. II. Binding of biotinylated human T cell leukemia virus type I to human blood mononuclear cells potential targets for human T cell leukemia virus type I infection. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Buonaguro L., Barillari G., Fiorelli V., Gendelman R., Morgan R. A., Wingfield P., Gallo R. C. Release, uptake, and effects of extracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on cell growth and viral transactivation. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):277–287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.277-287.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari G., Rossini S., Giavazzi R., Maggioni D., Nobili N., Soldati M., Ungers G., Mavilio F., Gilboa E., Bordignon C. An in vivo model of somatic cell gene therapy for human severe combined immunodeficiency. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1363–1366. doi: 10.1126/science.1848369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantzopoulos P. A., Sullenger B. A., Ungers G., Gilboa E. Improved gene expression upon transfer of the adenosine deaminase minigene outside the transcriptional unit of a retroviral vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Rappaport J., Dhar R. Tat-regulated production of multimerized TAR RNA inhibits HIV-1 gene expression. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Human gene therapy comes of age. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):455–460. doi: 10.1038/357455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Lee S. J., Khalili K., Wong-Staal F. The acidic amino-terminal region of the HIV-1 Tat protein constitutes an essential activating domain. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Sun D., Thornton A., Müller W. E. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Apr;78(4):663–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Josephs S. F., Dukovich M., Peffer N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of the HIV-1 LTR by T cell mitogens and the trans-activator protein of HTLV-I. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2825351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






