Abstract
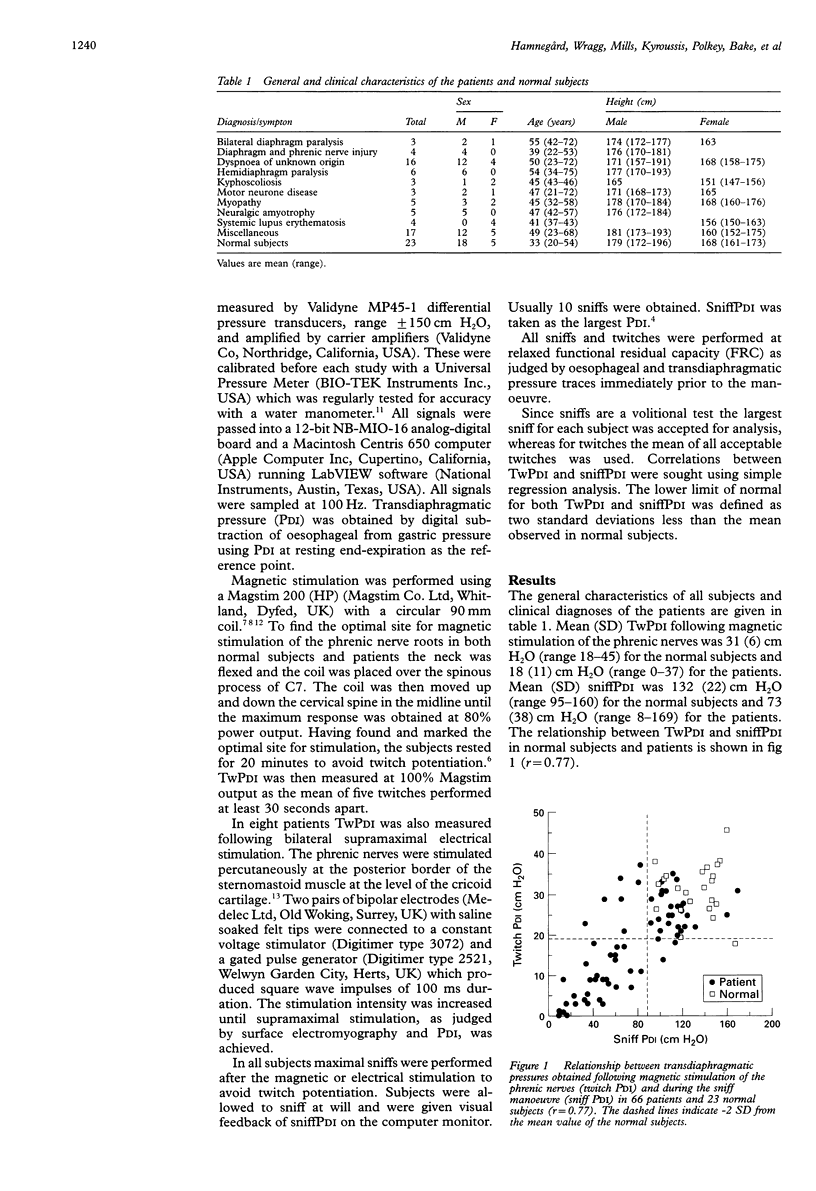
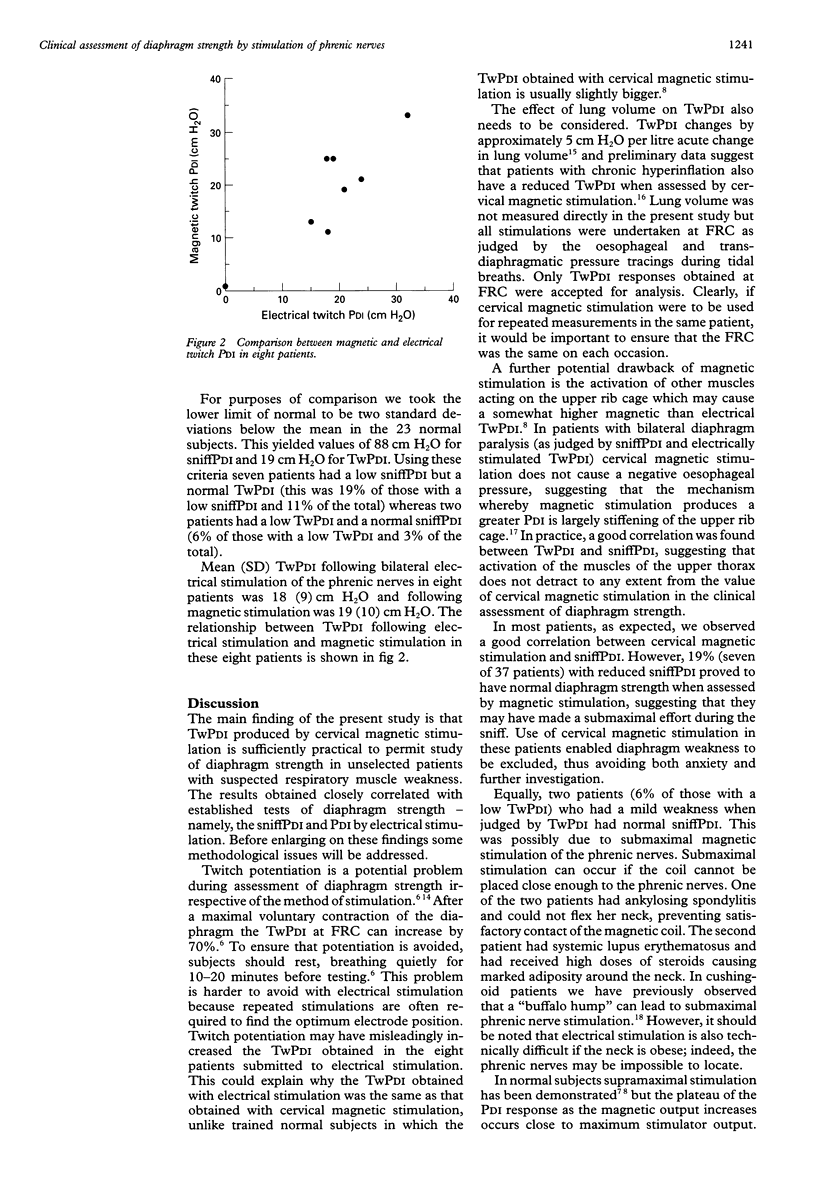
BACKGROUND: Accurate assessment of diaphragm strength can be difficult. Transdiaphragmatic pressure (PDI) measurements during volitional manoeuvres are useful but it may be difficult to ensure maximum patient effort. Magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves is easy to perform and the results are reproducible in normal subjects. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the usefulness of magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves in the assessment of diaphragm weakness in patients. METHODS: Sixty-six patients referred for assessment of respiratory muscle strength and 23 normal subjects were studied. Twitch PDI (TwPDI) following magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves and sniffPDI were obtained in all individuals. TWPDI following bilateral electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves was also obtained in eight patients. RESULTS: Mean (SD) TwPdi for the normal subjects was 31 (6) cm H2O and 18 (11) cm H2O for the patients. TwPDI and sniffPDI were correlated (r = 0.77). Seven of the 37 patients (19%) with a reduced sniffPDI had a TwPDI within the normal range whereas two of the 32 patients (6%) with a reduced TwPDI had a normal sniffPDI. TwPDI was similar with magnetic and electrical stimulation. CONCLUSIONS: TwPDI following magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves is a clinically useful measurement when assessing diaphragm weakness.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. M., Gandevia S. C., McKenzie D. K. Reliability of measurements of muscle strength and voluntary activation using twitch interpolation. Muscle Nerve. 1995 Jun;18(6):593–600. doi: 10.1002/mus.880180605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. M., Hunt B., Green M. Fall in vital capacity with posture. Br J Dis Chest. 1985 Jul;79(3):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker A. T., Freeston I. L., Jalinous R., Jarratt J. A. Magnetic stimulation of the human brain and peripheral nervous system: an introduction and the results of an initial clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):100–109. doi: 10.1097/00006123-198701000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baydur A., Behrakis P. K., Zin W. A., Jaeger M., Milic-Emili J. A simple method for assessing the validity of the esophageal balloon technique. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):788–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N. Phrenic nerve conduction in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Oct;30(5):420–426. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.5.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamnegård C. H., Wragg S., Mills G., Kyroussis D., Road J., Daskos G., Bake B., Moxham J., Green M. The effect of lung volume on transdiaphragmatic pressure. Eur Respir J. 1995 Sep;8(9):1532–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lekven J. Myocardial blood flow distribution. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Jan;36(1):1–6. doi: 10.1080/00365517609068011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mador M. J., Magalang U. J., Kufel T. J. Twitch potentiation following voluntary diaphragmatic contraction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Mar;149(3 Pt 1):739–743. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.8118645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier-Jedrzejowicz A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Assessment of diaphragm weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):877–883. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Moxham J., Green M. The maximal sniff in the assessment of diaphragm function in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Jul;69(1):91–96. doi: 10.1042/cs0690091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. H., Kyroussis D., Hamnegard C. H., Wragg S., Moxham J., Green M. Unilateral magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerve. Thorax. 1995 Nov;50(11):1162–1172. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.11.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similowski T., Fleury B., Launois S., Cathala H. P., Bouche P., Derenne J. P. Cervical magnetic stimulation: a new painless method for bilateral phrenic nerve stimulation in conscious humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1311–1318. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Aquilina R., Moran J., Ridding M., Hamnegard C., Fearn T., Green M., Moxham J. Comparison of cervical magnetic stimulation and bilateral percutaneous electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves in normal subjects. Eur Respir J. 1994 Oct;7(10):1788–1792. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07101788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Hamnegard C., Road J., Kyroussis D., Moran J., Green M., Moxham J. Potentiation of diaphragmatic twitch after voluntary contraction in normal subjects. Thorax. 1994 Dec;49(12):1234–1237. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.12.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


