Abstract
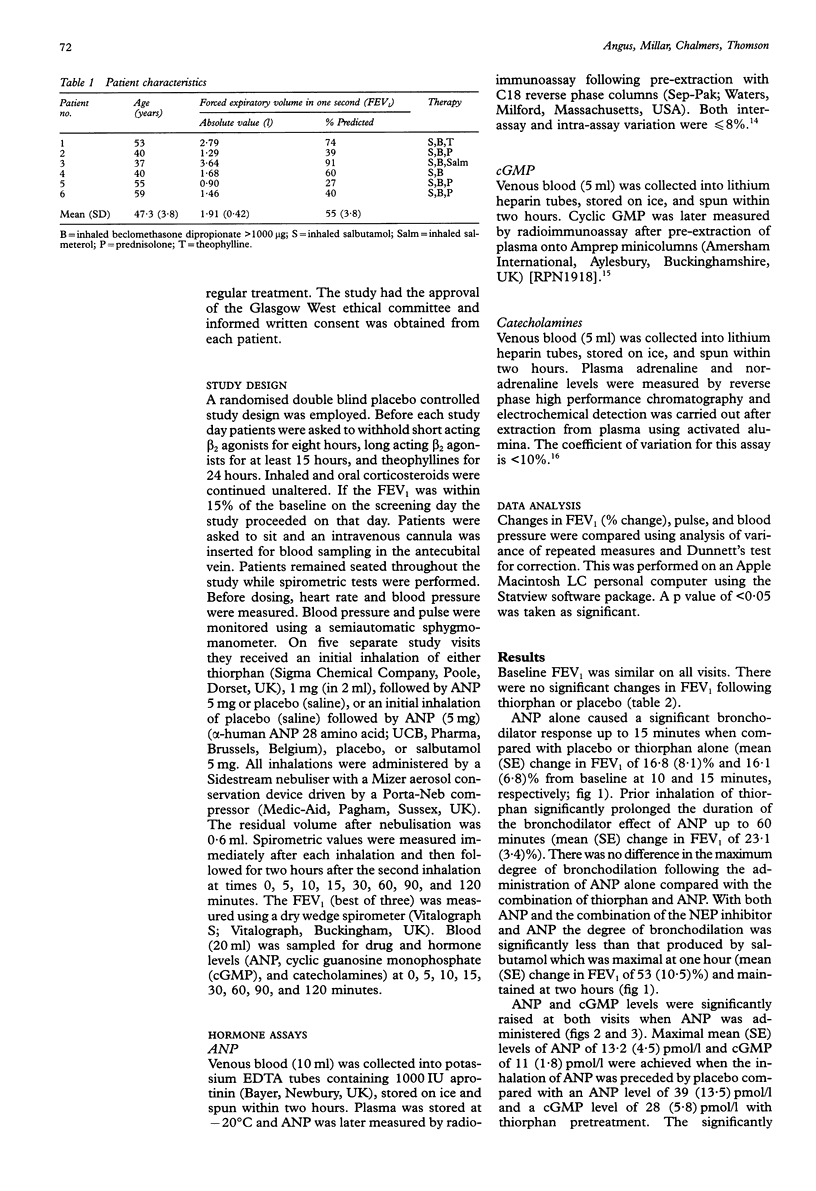
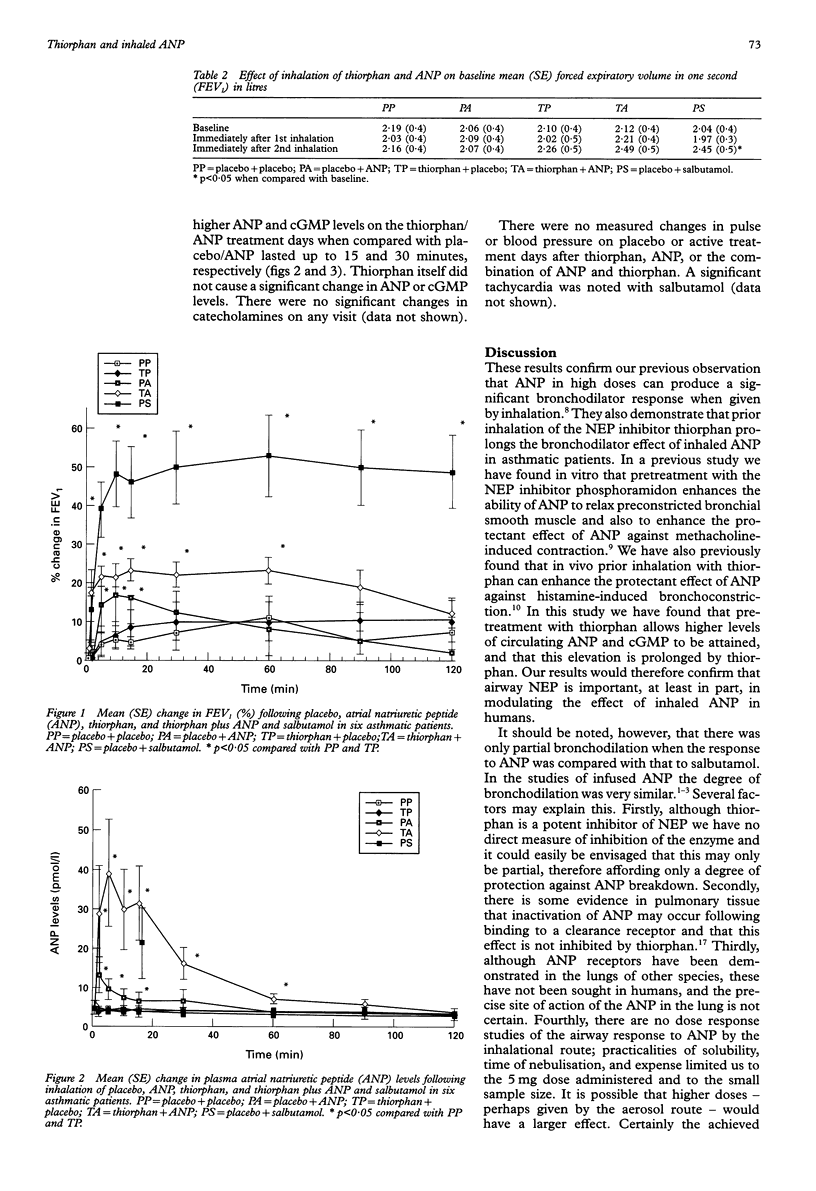
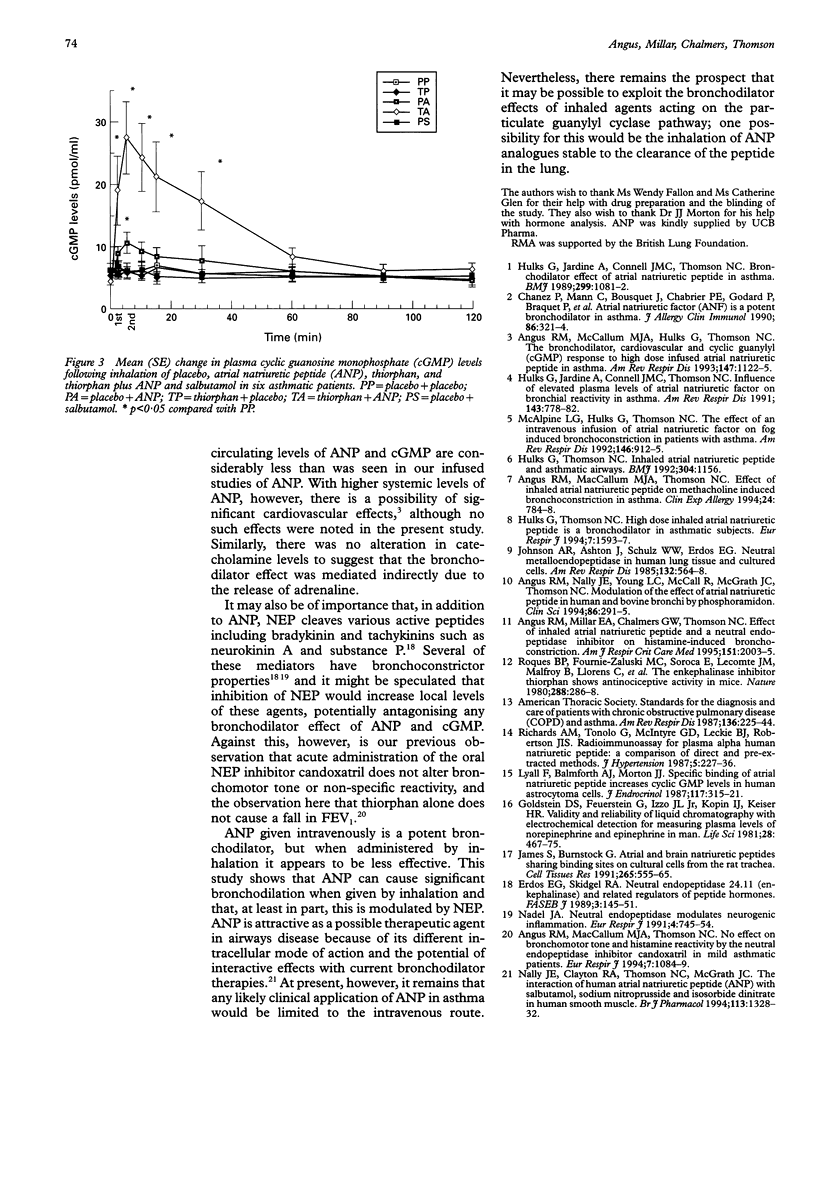
BACKGROUND: The hormone atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) causes bronchodilation and partially protects against direct and indirect bronchial challenges. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have found that the protective effect of ANP against bronchoconstriction is enhanced by inhibition of the enzyme neutral endopeptidase (NEP). It was hypothesised that pretreatment with thiorphan, an NEP inhibitor, might enhance the bronchodilator response to inhaled ANP. METHODS: In a randomised double blind placebo controlled crossover study, six asthmatic patients (one woman) of mean (SD) age 47.3 (3.8) years and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) 1.91 (0.42) 1, 55 (3.8)% predicted, were studied. All were shown at screening to have at least a 25% improvement in FEV1 to inhaled salbutamol. On five study visits the patients received either thiorphan 1 mg (in 2 ml) followed by ANP 5 mg or placebo (saline), or placebo (saline) followed by ANP (5 mg), placebo or salbutamol 5 mg. Spirometric parameters were measured after each inhalation and thereafter for the next two hours. RESULTS: ANP alone caused a bronchodilator response up to 15 minutes when compared with placebo or thiorphan alone with a mean (SE) change in FEV1 of 16.8 (8.1)% and 16.1 (6.8)% at 10 and 15 minutes from baseline, respectively. Prior inhalation of thiorphan prolonged the duration of the bronchodilator effect of ANP up to 60 minutes with a mean (SE) change in FEV1 of 23.1 (3.4)% at 60 minutes. There was no difference in the maximum degree of bronchodilation following the administration of ANP alone compared with the combination of thiorphan and ANP. The degree and duration of the bronchodilator response produced by ANP, or the combination of the NEP inhibitor and ANP, were less than that produced by salbutamol. CONCLUSIONS: These results confirm that, at least in part, the bronchodilator response to inhaled ANP is modulated by NEP. Analogues of ANP which are stable to NEP may have greater bronchodilator activity than ANP in the treatment of asthma.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus R. M., McCallum M. J., Nally J. E., Thomson N. C. No effect of the oral neutral endopeptidase inhibitor candoxatril, on bronchomotor tone and histamine reactivity in asthma. Eur Respir J. 1994 Jun;7(6):1084–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus R. M., McCallum M. J., Thomson N. C. Effect of inhaled atrial natriuretic peptide on methacholine induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994 Aug;24(8):784–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus R. M., Millar E. A., Chalmers G. W., Thomson N. C. Effect of inhaled atrial natriuretic peptide and a neutral endopeptidase inhibitor on histamine-induced bronchoconstriction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jun;151(6):2003–2005. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.6.7767551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus R. M., Nally J. E., McCall R., Young L. C., McGrath J. C., Thomson N. C. Modulation of the effect of atrial natriuretic peptide in human and bovine bronchi by phosphoramidon. Clin Sci (Lond) 1994 Mar;86(3):291–295. doi: 10.1042/cs0860291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanez P., Mann C., Bousquet J., Chabrier P. E., Godard P., Braquet P., Michel F. B. Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is a potent bronchodilator in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Sep;86(3 Pt 1):321–324. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(05)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Skidgel R. A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and related regulators of peptide hormones. FASEB J. 1989 Feb;3(2):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S., Feuerstein G., Izzo J. L., Jr, Kopin I. J., Keiser H. R. Validity and reliability of liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection for measuring plasma levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine in man. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 2;28(5):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulks G., Jardine A. G., Connell J. M., Thomson N. C. Influence of elevated plasma levels of atrial natriuretic factor on bronchial reactivity in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Apr;143(4 Pt 1):778–782. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.4_Pt_1.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulks G., Jardine A., Connell J. M., Thomson N. C. Bronchodilator effect of atrial natriuretic peptide in asthma. BMJ. 1989 Oct 28;299(6707):1081–1082. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6707.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulks G., Thomson N. C. High dose inhaled atrial natriuretic peptide is a bronchodilator in asthmatic subjects. Eur Respir J. 1994 Sep;7(9):1593–1597. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07091593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulks G., Thomson N. C. Inhaled atrial natriuretic peptide and asthmatic airways. BMJ. 1992 May 2;304(6835):1156–1156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6835.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyall F., Balmforth A. J., Morton J. J. Specific binding of atrial natriuretic peptide increases cyclic GMP levels in human astrocytoma cells. J Endocrinol. 1988 May;117(2):315–321. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcalpine L. G., Hulks G., Thomson N. C. Effect of atrial natriuretic peptide given by intravenous infusion on bronchoconstriction induced by ultrasonically nebulized distilled water (fog). Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Oct;146(4):912–915. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.4.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase modulates neurogenic inflammation. Eur Respir J. 1991 Jun;4(6):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nally J. E., Clayton R. A., Thomson N. C., McGrath J. C. The interaction of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) with salbutamol, sodium nitroprusside and isosorbide dinitrate in human bronchial smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1328–1332. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Tonolo G., McIntyre G. D., Leckie B. J., Robertson J. I. Radio-immunoassay for plasma alpha human atrial natriuretic peptide: a comparison of direct and pre-extracted methods. J Hypertens. 1987 Apr;5(2):227–236. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198704000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



