Abstract
AIM: To detect infection rate of GBV-C/HGV in hepatitis C patients, to determine the methods of higher sensitivity and the primers of higher efficiency for GBV-C/HGV RNA detection and to study the dominant subtype and mutation of GBV-C/HGV.
METHODS: Quantitative RT-PCR for detection pf HCV RNA concentration in serum samples, RT-nested PCR with two sets of primers for detection of GBV-CRNA, RT-PCR ELISA with two sets of primers for detection of HGV RNA, nucleotide sequence and putative amino acid sequence analysis.
RESULTS: The positive rates of GBV-C RNA at the 5’-NCR and NS3 region in 211 serums amples from the patients with HCV infection were 31.8% and 22.8% respectively. The positive rates of HGV RNA at the 5’-NCR and NS5 region in the same samples were 47.9% and 31.8% respectively. The total positive rate of GBV-C/HGV RNA was as high as 55.5%. HCV copy numbers in the patients without GBV-C/HGV coinfection were statistically higher than that in the patients with GBV-C/HGV coinfection (P < 0.01). Frequent mutation of nucleotide residue was present in the amplification products. Frameshift mutation was found in two samples with GBV-C NS3 region nucleotide sequences. All nucleotide sequences from amplification products showed higher homology to HGV genome than to GBV-C genome even though part of the sequences were amplified with GBV-C primers.
CONCLUSION: A high frequency of GBV-C/HGV coinfection existed in the hepatitis C patients. RT-PCR ELISA was more sensitive than RT-nested PCR for detection of GBV-C/HGV RNA. The primers derived from the 5’-NCR was more efficient than those derived from the NS3 and NS5 regions. A reverse relationship was found to exist between HCV RNA concentration and GBV-C/HGV infection frequency. HGV was the dominant subtype of the virus in the local area. The major mutations of GBV-C/HGV genomes were random mutation of nucleotide residue.
Keywords: GB Virus C; hepatitis G virus; hepatitis C virus; coinfection; polymerase chain reaction; sequencing; dominant viral subtype, Germany
INTRODUCTION
Hepatitis GV virus C (GBV-C) and hepatitis G virus (HGV) were recently identified as novel member of Flaviviridae family associated with human non A-E hepatitis[1-5]. The two viral agents are different isolates of the same virus because of their high homology in nucleotide sequences and putative amino acid sequences[6,7]. GBV-C/HGV can be transmitted parenterally through transfusions of blood, blood products, intravenous drug user, hemodialysis and vertical transmission[8-19]. Although GBV-C/HGV were considered to be the major causative agent of human non A-E hepatitis, many later investigative data revealed that GBV-C/HGV infection rates in non A-E hepatitis patients were lower than 15%[20-25]. GBV-C genome does not have the gene responsible for encoding core protein[26,27]. HGV capsid protein is absent or defective and the capsid may be provided by another virus[2,28]. Therefore, coinfection of GBV-C/HGV with other viruses is an interesting and important subject for investigation. The reported GBV-C/GV infection rates in hepatitis C patients were approximate 20%[29-32] but a quite lower coinfection rate of HGV and HCV (5.6%) was also reported[33]. Contradictory data about the clinical importance of GBV-C/HGV infection and nucleotide sequence mutation of the viral isolates indicated that the pathogenes is and variability of the virus are not fully understood[34-44].
In this study, GBV-C/HGV RNAs in the 211 serum samples of hepatitis C patients were detected by RT-nested PCR and RT-PCR ELISA with four different sets of primers. The GBV-C/HGV RNA positive amplification products from part of the serum samples were cloned and then sequenced. The results of this study may contribute to the determination of GBV-C/HGV coinfection frequency in hepatitis C patients, choice of the methods with high sensitivity and the primers with high efficiency for GBV-C/HGV RNA detection and understanding the mutation of GBV-C/HGV genomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
211 serum samples of hepatitis C patients were obtained from the hospitals in Leubeck and in Koln of Germany. The 211 samples were confirmed to be HCV RNA positive by using HCV Monitor-TM Test Kit (Hoffmann LaRoche). This test is a routine work in our laboratory for quantitative detection of HCV RNA. HCV RNA concentration in the 211 samples ranged from 200 to 4166000 copies per milliliter of serum. All serum samples were HBV negative by using EIA and PCR. T-A Cloning Kit was purchased from Invitrogen. All other materials used in this study were purchased from Boehringer Mannheim.
Methods
Total serum RNA isolation Highly Pure RNA Isolation Kit was used to prepare total RNA from the samples according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
Reverse transcription (RT) reaction Ten μL total RNA preparation was mixed with 10 μL RT master mixture containing 0.2 mmol/L dNTP, 50 nmol/L hexanucleotide, 20 U M-MuLV-reverse transcr-iptase, 20 U RNA inhibitor and 4 μL 5 × RT buffer (pH8.3), and incubated at 37 °C for 45 min.
RT-nested PCR for GBV-C RNA detection Two sets of primers derived from GBV-C 5’NCR and NS3 region were used in the RT-nested PCR[45]. 5’-NCR external primers: 5’-ATGACAGGGTTGGTAGGTCGTAAATC-3’ (sense), 5’-CCCCACTGGTC-CTTGTCAACTCGCCG-3' (antisense). 5'-NCR internal primers: 5'-TGGTAGCCACTATAGGTGG-GTCTTAA-3' (sense), -5’-ACATTGAAGGGCGACG-TGGACCGTAC-3’ (antisense). NS3 region external primers: 5’-GCTCGCCTATGACTCAGCAT-3’ (sense), 5’-GTCACCTCAACGACCTCCTC-3’ (anti sense). NS3 region internal primers: 5’-ATCCATAATTGAGACAAAGCTGGA-3’ (sense), 5’-CCACCAACCCACAGTCGGTG-3’ (antisense). For the first PCR round, 10 μL- RT product was mixed with PCR master mixture containing 20 pmol/L primers, 0.2 mmol/L dNTP, 3 U Tag polymerase and 10 μL 10 × PCR buffer (pH9.1) and 25 mmol/L MgCl2. For the second PCR round, 5 μL product from the first PCR round was used as template and the other reaction reagents were the same as that in the first PCR round except the primers. The volume per reaction in the two rounds was 100 μL. The PCR parameters were described as the following: 94 °C 3 min (× 1); 94 °C 30 s, 56 °C 30 s, 72 °C 30 s, (× 10); 94 °C 30 s, 56 °C 30 s, 72 °C 35 s, (× 25, 5 s in addition for each of the following cycle); and 72 °C 7 min (× 1). The products of RT-nested PCR were detected by 2% ethidium bromide stained agarose gel electrophoresis.
RT-PCR ELISA for HGV RNA detection HGV RNA in the samples was detected by Hepatitis G Virus Primer and Capture Probe Set Kit according to the manufacturer’s instruction. This kit contains two sets of primers for detection of HGV 5’-NCR and NS5 RNA and two sets of capture probes for detecting PCR products. 5’-NCR primers: 5’-CGGCCAAAAGGTGGTGGATG-3’ (sense), 5’-CGACGAGCCTGACGTCGGG-3’ (antisense). NS5 region primers: 5’-CTCTTTGTGGTAGTAGC-CGAGAGAT-3’ (sense), 5’-CGAATGAGTCAG-AGGACGGGGTAT-3’ (antisense). 5’-NCR capture probe: 5’-Biotin-GGTAGCCACTATAGGTGGG-3’. NS5 region capture probe: 5’-Biotin-GTTACTGAGAGCAGCTCAGAT-3’. Taq and two polymerase mix in this kit was used in PCR to allow DIG-11-dUTP incorporating the products during amplification process. The PCR parameters were described as the following: 94 °C 3 min (1 ×); 94 °C 30 s, 55 °C 30 s, 72 °C 30 s (10 ×); 94 °C 30 s, 55 °C 30 s, 72 °C 35 s (5 s in addition for each of the following cycle, 30 ×); 72 °C 7 min (1 ×).
The RT-PCR products were detected by using PCR ELISA DIG Detection Kit according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The PCR ELISA is a liquid phase hybridization/DIG detection system. It was found that DNA fragments amplified from HGV RNA could also be seen in 2% ethidium bromide stained agarose gel if the OD value at 405 nm by RT-PCR ELISA was higher than 1.0.
Analysis of nucleotide sequences and putative amino acid sequences The target DNA fragments in GBV-C RT-nested PCR products or HGV RT-PCR products (DIG-11-dUTP replaced by dTTP) were cloned into PCR2.1 plasmid by using T-A Cloning Kit according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The plasmid was amplified in E. coli and then recovered by the Sambrook’s method[46]. The inserted sequences were analyzed by MWG-BIOTECH. The homology of the nucleotide sequences and putative amino acid sequences was compared with the those thow reported[1,2].
RESULTS
GBV-C and HGV RNA detection rates Seventy-four of the 211 serum samples (35.1%) were GBV-C RNA positive, 41 of the 74 samples (55.4%) were GBV-C RNA positive for both the 5’-NCR and NS3 region, 26 of the 74 samples (35.1%) were only 5’-NCR RNA positive and only 7 of the 74 samples (9.5%) detected NS3 region RNA. A statistically significant difference (χ² = 4.32, P < 0.05) was found to exist between the positive rates of GBV-C 5’-NCR (67/211) and those of NS3 region (48/211).
One hundred and five (49.8%) of the 211 serum samples were HCV RNA positive, 63 of 105 samples (60.0%) were HGV RNA positive for both the 5’-NCR and NS5 regions, 38 of the 105 samples (36.2%) were only 5’-NCR RNA positive and 4 of the 105 samples (3.8%) were only detectable for NS5 region RNA. A statistic ally significant difference (χ² = 11.43, P < 0.01) was also found between the positive rates of HGV 5’-NCR (101/211) and NS5 region (67/211). The respective target fragments amplified from GBV-C 5’-NCR, NS3 region and HGV 5’-NCR, NS5 region are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2.
Figure 1.
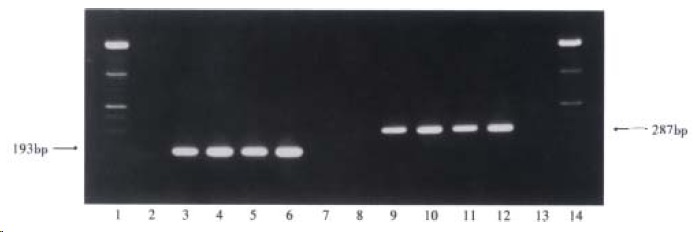
Target amplification fragments from GBV-C 5’-NCR and NS3 region. (1 and 14: markers; 2 and 8: negative serum samples; 7 and 13: blanks; 3-6: four GBV-C 5’-NCR RNA positive serum samples; 9-12: four GBV-C NS3 region RNA positive serum samples)
Figure 2.
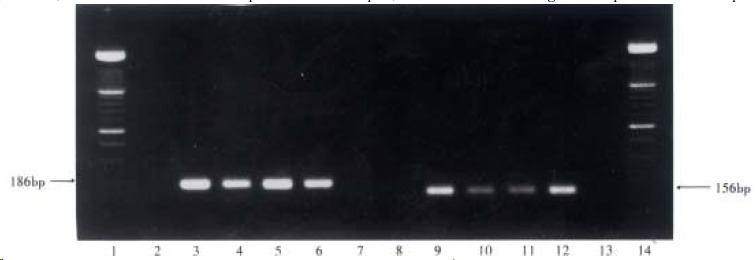
Target amplification fragments from HGV 5’-NCR and NS5 region. (1 and 14: markers; 2 and 8: negative serum samples; 7 and 13: blanks; 3-6: four HGV 5’-NCR RNA positive serum samples; 9-12: four HGV NS5 region RNA positive serum samples)
Total positive rate of GBV-C/HGV and distribution of the positive samples One hundred and seventeen (55.5%) of the 211 serum samples were GBV-C and/or HGV RNA positive and 94 of the 211 samples (44.5%) were negative for both viral RNAs, 62, 12 and 43 of the 117 samples were positive for both viral RNAs, GBV-C RNA positive and detectable HGV RNA respectively. The distribution of the 117 samples is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Distribution of 117 GBV-C and/or HGV positive samples
| GBV-C | HGV |
Positive cases |
Positive rate (%) |
||
|
5’-NCR |
NS5 |
5’-NCR |
NS5 |
||
| +* | + | + | + | 26 | 12.3 |
| + | + | + | -** | 7 | 3.3 |
| + | + | - | + | 3 | 1.4 |
| + | - | + | + | 9 | 4.3 |
| - | + | + | + | 3 | 1.4 |
| + | - | + | - | 11 | 5.2 |
| - | + | + | - | 3 | 1.4 |
| + | + | - | - | 5 | 2.4 |
| - | - | + | + | 25 | 11.9 |
| + | - | - | - | 6 | 2.8 |
| - | - | + | - | 17 | 8.1 |
| - | + | - | - | 1 | 0.5 |
| - | - | - | + | 1 | 0.5 |
| 117 | 55.5 | ||||
+: the viral RNA was detectable.
-: the viral RNA was undetectable.
Relationship between HCV RNA concentration and GBV-C/HGV infection frequency The range of HCV RNA concentrations of the 211 serum samples was 200-4166000 copies/mL. A statistically significant difference (t’ = 2.559, P < 0.01) was present in the HCV RNA copy numbers of the group with GBV-C and/or HGV RNA positive samples (mean = 344000 HCV RNA copies/mL) and the group with both viral RNA negative samples (mean = 556000 HCV RNA copies/mL). In addition, HCV RNA concentration in each of 21 cases of the 211 samples was higher than 1000000 copies/mL. Six of the 21 cases distributed in GBV-C and/or HGV RNA positive group and the other 15 cases belonged to the negative group. In comparison with the two percentages (6/211 and 15/211), a statistically significant difference was also found (χ² = 4.06, P < 0.05).
Nucleotide sequence analysis The homology of the nucleotide sequences of GBV-C 5’-NCR RT-nested PCR products from 3 serum samples compared with the reported GBV-C sequence[1] and the reported HGV sequence[2] was 81.8%, 81.1%, 82.5% and 97.6%, 97.2%, 99.3% respectively. The homology of the two reported sequences at the 5’-NCR was 81.8%. The homology of the nucleotide sequences of GBV-C NS3 region RT-nested PCR products from 6 samples compared with the reported GBV-C sequence[1] and the reported HGV sequence[2] was 80.2%, 82.3%, 81.5%, 84.4%, 85.6%, 85.2% and 86.8%, 88.1%, 88.1%, 88.1%, 86.8%, 87.7% respectively. The homology of the two reported nucleotide sequences at the NS3 region was 84.4%. Although the primers used in the RT-nested PCR derived from GBV-C genome, each of the 9 nucleotide sequences showed a higher homology to HGV than to GBV-C. These nucleotide sequences are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4.
Figure 3.

Homology of the nucleotide sequences from GBV-C 5’-NCR RT-nested PCR products from 3 serum samples as compared with the reported sequences. (1) the reported GBV-C 5’-NCR sequence, (2) the reported HGV 5’-NCR sequence, (3)-(5) the sequences of GBV-C 5’-NCR RT-nested PCR product from 3 samples. Underlined areas indicated the primers’position.
Figure 4.
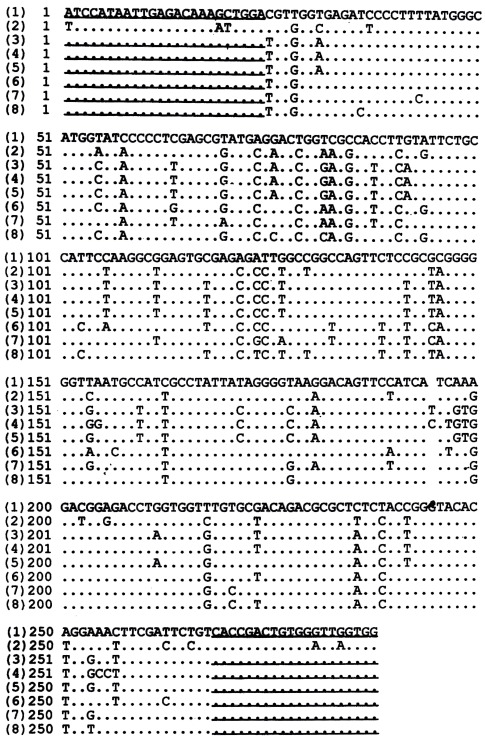
Homology of the sequences from GBV-C NS3 RT-nested PCR products from 6 serum samples compared with the reported sequences. (1) the reported GBV-C NS3 region sequence, (2) the reported HGV NS3 region sequence, (3)-(8) the sequences from GBV-C NS3 region RT-nested PCR products from 6 serum samples. Underlined areas indicated the primers’position.
The homology of the nucleotide sequences of HGV 5’-NCR RT-PCR products from 3 samples compared with the reported HGV sequence[2] and the reported GB V-C sequence[1] was 95.2%, 99.3%, 98.6% and 86.4%, 87.1%, 87.8% respectively. The homology of the two reported sequences at the 5’-NCR was 86.4%, whereas the homology of the nucleotide sequences of HGV NS5 region RT-PCR products from 3 serum samples compared with the reported HGV[2] sequence and the reported GBV-C sequence[1] was 95.3%, 96.3%, 96.3% and 94.4%, 94.4%, 93.4% respectively. The homology of the two reported sequences at the NS5 region was 93.4%. These nucleotide sequences are shown in Figure 5, Figure 6.
Figure 5.

Homology of the nucleotide sequences of HGV 5’-NCR RT-PCR products from 3 serum samples compared to the reported sequences. (1) the reported HGV 5’-NCR sequence, (2) the reported GBV-C 5’-NCR sequence, (3)-(5) the sequences of HGV 5’-NCR RT-PCR products from 3 samples. Underlined indicated the primers’ position.
Figure 6.

Homology of the nucleotide sequences from HGV NS5 RT-PCR products from 3 serum samples compared to the reported sequences. (1) the reported HGV NS5 region sequence, (2) the reported GBV-C NS5 region sequence, (3)-(5) the sequences from HGV NS5 region RT-PCR products from 3 serum samples. Underlined areas indicated the primers’ position.
The homology in comparison of these sequences mentioned above did not contain the primer sequences.
The putative amino acid sequence analysis Putative amino acid sequences translated from the 6 nucleotide sequences from GBV-C NS3 region and the 3 nucleotide sequences from HGV NS5 region were respectively compared with the reported HGV and GBV-C sequences[1,2]. These putative amino acid sequences were shown in Figure 7, Figure 8.
Figure 7.

Comparison of the putative amino acid sequences from GBV-C NS3 RT-nested PCR products from 9 serum samples with the reported sequences. (1) the reported GBV-C sequence, (2) the reported HGV sequence, (3)-(8) putative amino acid sequences translated from the 6 nucleotide sequences from GBV-C NS3 region. Underlined are indicated the primers’ position.
Figure 8.

Comparison of the putative amino acid sequences from HGV NS5 RT-PCR products from 3 serum samples with the reported sequences. (1) the reported HGV sequence, (2) the reported GBV-C sequence, (3)-(5) putative amino acid sequences translated from the 3 nucleotide sequences from HGV NS5 region. Underlined areas indicated the primers’ position.
DISCUSSION
As mentioned in the introduction, the reported GBV-C/HGV infection rates in non A-E hepatitis patients were lower than 15% and the reported GBV-C/HGV and HCV coinfection rates were approximate 20%. In this study, a high total positive rate (55.5%) of GBV-C and/or HGV RNA in hepatitis C patients was found. Such a high frequency of GBV-C and/or HGV and HCV coinfection including most of the reported coinfection rates, suggested that GBV-C/HGV coinfected with HCV may be one of the features of its prevalence.
GBV-C RNA positive rate in the 211 samples by using RT-nested PCR was 35.1%. HGV RNA positive rate in the same samples by RT-PCR ELISA was as high as 49.8%. Statistical analysis of the two positive rates indicated that RT-PCR ELISA is more sensitive than RT-nested PCR (χ² = 9.32, P < 0.01).
In the 211 serum samples, the positive rate (31.8%) of GBV-C 5’-NCR was higher than that (22.8%) of GBV-C NS3 region (χ² = 4.32, P < 0.05) and the positive rate (47.9%) of HGV 5’-NCR was also higher than that (31.8%) of HGV NS5 region (χ² = 11.43, P < 0.01).These data led to the conclusion that the primers derived from the 5’-NCRs were more efficient than those derived from the NS regions[47]. According to the results of nucleotide sequence analysis, this efficiency difference of primers was probably due to the higher conservation of sequences within the 5’-NCRs. In addition, only 26 of the 117 GBV-C and/or HGV RNA positive samples were positive for all the four viral genomic regions. It suggested that application of multiple primers is helpful to increase positive rate of GBV-C/HGV RNA detection.
A reverse relationship of HCV RNA concentration and GBV-C/HGV infection frequ ency was found in this study. This finding suggested that GBV-C/HGV and HCV might suppress each other in vivo. This reverse relationship seemed to be contradictory to the high GBV-C/HGV and HCV coinfection rate. However, this kind of situation of cocurrence and competition is a normal phenomenon among microorganisms. For example, HBV and HCV coinfection is frequent in Asia but HCV was found to suppress the replication of HBV and vice versa to a lesser extent[48-50].
In this study, the homology of nucleotide sequences in the products amplified with the primers derived from HGV genome was higher in the reported HGV sequence than in the reported GBV-C sequence. Such results could be expected, however, all nucleotide sequences in the products amplified with the primers derived from GBV-C genome also showed higher homology with the reported HGV sequence. These data reveal the fact that: HGV and not the GBV-C, is the dominant subtype in the local area. Besides, these existed random mutations in a large number of nucleotide residue in all amplification products and two showed frameshift mutation which indicate that mutation of GBV-C/HGV genomic sequences occurs easily at the subtype level.
Footnotes
Edited by Wu XN
Verified by Ma JY
This study was completed in Medical University of Leubeck, Germany.
References
- 1.Leary TP, Muerhoff AS, Simons JN, Pilot-Matias TJ, Erker JC, Chalmers ML, Schlauder GG, Dawson GJ, Desai SM, Mushahwar IK. Sequence and genomic organization of GBV-C: a novel member of the flaviviridae associated with human non-A-E hepatitis. J Med Virol. 1996;48:60–67. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199601)48:1<60::AID-JMV10>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simons JN, Leary TP, Dawson GJ, Pilot-Matias TJ, Muerhoff AS, Schlauder GG, Desai SM, Mushahwar IK. Isolation of novel virus-like sequences associated with human hepatitis. Nat Med. 1995;1:564–569. doi: 10.1038/nm0695-564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Linnen J, Wages J, Zhang-Keck ZY, Fry KE, Krawczynski KZ, Alter H, Koonin E, Gallagher M, Alter M, Hadziyannis S, et al. Molecular cloning and disease association of hepatitis G virus: a transfusion-transmissible agent. Science. 1996;271:505–508. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kim JP, Fry KE. Molecular characterization of the hepatitis G virus. J Viral Hepat. 1997;4:77–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.1997.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang XT, Zhuang H, Song HB, Li HM, Zhang HY, Yu Y. Partial sequencing of 5' noncoding region of 7 HGV strains isolated from different areas of China. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:432–434. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i5.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zanetti AR, Tanzi E, Romanò L, Galli C. GBV-C/HGV: a new human hepatitis-related virus. Res Virol. 1997;148:119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(97)89895-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heringlake S, Tillmann HL, Manns MP. New hepatitis viruses. J Hepatol. 1996;25:239–247. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moaven LD, Hyland CA, Young IF, Bowden DS, McCaw R, Mison L, Locarnini SA. Prevalence of hepatitis G virus in Queensland blood donors. Med J Aust. 1996;165:369–371. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb125019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Casteling A, Song E, Sim J, Blaauw D, Heyns A, Schweizer R, Margolius L, Kuun E, Field S, Schoub B, et al. GB virus C prevalence in blood donors and high risk groups for parenterally transmitted agents from Gauteng, South Africa. J Med Virol. 1998;55:103–108. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9071(199806)55:2<103::aid-jmv4>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goubau P, Andrade FB, Liu HF, Basilio FP, Croonen L, Barreto-Gomes VA. Prevalence of GB virus C/hepatitis G virus among blood donors in north-eastern Brazil. Trop Med Int Health. 1999;4:365–367. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.1999.00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jarvis LM, Davidson F, Hanley JP, Yap PL, Ludlam CA, Simmonds P. Infection with hepatitis G virus among recipients of plasma products. Lancet. 1996;348:1352–1355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)04041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ling BH, Zhuang H, Cui YH, An WF, Li ZJ, Wang SP, Zhu WF. A cross-sectional study on HGV infection in a rural population. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4:489–492. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i6.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Masuko K, Mitsui T, Iwano K, Yamazaki C, Okuda K, Meguro T, Murayama N, Inoue T, Tsuda F, Okamoto H, et al. Infection with hepatitis GB virus C in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1485–1490. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199606063342301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Thomas DL, Nakatsuji Y, Shih JW, Alter HJ, Nelson KE, Astemborski JA, Lyles CM, Vlahov D. Persistence and clinical significance of hepatitis G virus infections in injecting drug users. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:586–592. doi: 10.1086/514078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Noguchi S, Sata M, Suzuki H, Ohba K, Mizokami M, Tanikawa K. GB virus C (GBV-C)/hepatitis G virus (HGV) infection among intravenous drug users in Japan. Virus Res. 1997;49:155–162. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(97)01470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aikawa T, Sugai Y, Okamoto H. Hepatitis G infection in drug abusers with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:195–196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199601183340316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Feucht HH, Zollner B, Polywka S, Laufs R. Vertical transmission of hepatitis G. Lancet. 1996;347:615–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moaven LD, Tennakoon PS, Bowden DS, Locarnini SA. Mother-to-baby transmission of hepatitis G virus. Med J Aust. 1996;165:84–85. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb124854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Viazov S, Riffelmann M, Sarr S, Ballauff A, Meisel H, Roggendorf M. Transmission of GBV-C/HGV from drug-addicted mothers to their babies. J Hepatol. 1997;27:85–90. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang JH, Wei L, Du SC, Wang H, Sun Y, Tao QM. Hepatitis G virus infection in patients with chronic non A E hepatitis. China Natl J New Gastroenterol. 1997;3:143–146. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i3.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang JT, Tsai FC, Lee CZ, Chen PJ, Sheu JC, Wang TH, Chen DS. A prospective study of transfusion-transmitted GB virus C infection: similar frequency but different clinical presentation compared with hepatitis C virus. Blood. 1996;88:1881–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sarrazin C, Herrmann G, Roth WK, Lee JH, Marx S, Zeuzem S. Prevalence and clinical and histological manifestation of hepatitis G/GBV-C infections in patients with elevated aminotransferases of unknown etiology. J Hepatol. 1997;27:276–283. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cheung RC, Keeffe EB, Greenberg HB. Hepatitis G virus: is it a hepatitis virus. West J Med. 1997;167:23–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kondo Y, Mizokami M, Nakano T, Kato T, Ueda R, Mukaide M, Hikiji K, Ishida T, Dorjsuren D, Dashnyam B, et al. Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of GB virus C/hepatitis G virus infection in Mongolia. J Med Virol. 1997;52:143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Park YM, Mizokami M, Nakano T, Choi JY, Cao K, Byun BH, Cho CH, Jung YT, Paik SY, Yoon SK, et al. GB virus C/hepatitis G virus infection among Korean patients with liver diseases and general population. Virus Res. 1997;48:185–192. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(97)01450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Simons JN, Desai SM, Schultz DE, Lemon SM, Mushahwar IK. Translation initiation in GB viruses A and C: evidence for internal ribosome entry and implications for genome organization. J Virol. 1996;70:6126–6135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.9.6126-6135.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muerhoff AS, Simons JN, Leary TP, Erker JC, Chalmers ML, Pilot-Matias TJ, Dawson GJ, Desai SM, Mushahwar IK. Sequence heterogeneity within the 5'-terminal region of the hepatitis GB virus C genome and evidence for genotypes. J Hepatol. 1996;25:379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pickering JM, Thomas HC, Karayiannis P. Predicted secondary structure of the hepatitis G virus and GB virus-A 5'untranslated regions consistent with an internal ribosome entry site. J Viral Hepat. 1997;4:175–184. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1997.00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tsuda F, Hadiwandowo S, Sawada N, Fukuda M, Tanaka T, Okamoto H, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M. Infection with GB virus C (GBV-C) in patients with chronic liver disease or on maintenance hemodialysis in Indonesia. J Med Virol. 1996;49:248–252. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199607)49:3<248::AID-JMV15>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Francesconi R, Giostra F, Ballardini G, Manzin A, Solforosi L, Lari F, Descovich C, Ghetti S, Grassi A, Bianchi G, et al. Clinical implications of GBV-C/HGV infection in patients with "HCV-related" chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1997;26:1165–1172. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nagayama R, Miyake K, Okamoto H. Effect of interferon on GB virus C and hepatitis C virus in hepatitis patients with the co-infection. J Med Virol. 1997;52:156–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sauleda S, Reesink HJ, Esteban JI, Hess G, Esteban R, Guardia J. Profiles of GBV-C/hepatitis G virus markers in patients coinfected with hepatitis C virus. J Med Virol. 1999;59:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sáiz JC, Ampurdanés S, Olmedo E, López-Labrador FX, Forns X, Guilera M, Tassies D, Costa J, Sánchez-Tapias JM, Jiménez de Anta MT, et al. Hepatitis G virus infection in chronic hepatitis C: frequency, features and response to interferon therapy. J Hepatol. 1997;26:787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cotler SJ, Gretch DR, Bronner MP, Tateyama H, Emond MJ, dela Rosa C, Perkins JD, Carithers RL. Hepatitis G virus co-infection does not alter the course of recurrent hepatitis C virus infection in liver transplantation recipients. Hepatology. 1997;26:432–436. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sugai Y, Nakayama H, Fukuda M, Sawada N, Tanaka T, Tsuda F, Okamoto H, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M. Infection with GB virus C in patients with chronic liver disease. J Med Virol. 1997;51:175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sallie R, Shaw J, Mutimer D. GBV-C virus and fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet. 1996;347:1552. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yoshiba M, Okamoto H, Mishiro S. Detection of the GBV-C hepatitis virus genome in serum from patients with fulminant hepatitis of unknown aetiology. Lancet. 1995;346:1131–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Heringlake S, Osterkamp S, Trautwein C, Tillmann HL, Böker K, Muerhoff S, Mushahwar IK, Hunsmann G, Manns MP. Association between fulminant hepatic failure and a strain of GBV virus C. Lancet. 1996;348:1626–1629. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)04413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kao JH, Chen PJ, Hsiang SC, Chen W, Chen DS. Phylogenetic analysis of GB virus C: comparison of isolates from Africa, North America, and Taiwan. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:410–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fukushi S, Kurihara C, Ishiyama N, Okamura H, Hoshino FB, Oya A, Katayama K. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of hepatitis G virus isolated from Japanese patients: comparison with reported isolates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;226:314–318. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.López-Alcorocho JM, Castillo I, Tomás JF, Carreño V. Identification of a novel GB type C virus/hepatitis G virus subtype in patients with hematologic malignancies. J Med Virol. 1999;57:80–84. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9071(199901)57:1<80::aid-jmv12>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Smith DB, Cuceanu N, Davidson F, Jarvis LM, Mokili JL, Hamid S, Ludlam CA, Simmonds P. Discrimination of hepatitis G virus/GBV-C geographical variants by analysis of the 5' non-coding region. J Gen Virol. 1997;78(Pt 7):1533–1542. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-7-1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Muerhoff AS, Smith DB, Leary TP, Erker JC, Desai SM, Mushahwar IK. Identification of GB virus C variants by phylogenetic analysis of 5'-untranslated and coding region sequences. J Virol. 1997;71:6501–6508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.9.6501-6508.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Khudyakov YE, Cong ME, Bonafonte MT, Abdulmalek S, Nichols BL, Lambert S, Alter MJ, Fields HA. Sequence variation within a nonstructural region of the hepatitis G virus genome. J Virol. 1997;71:6875–6880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.9.6875-6880.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Muerhoff AS, Simons JN, Erker JC, Desai SM, Mushahwar IK. Identification of conserved nucleotide sequences within the GB virus C 5'-untranslated region: design of PCR primers for detection of viral RNA. J Virol Methods. 1996;62:55–62. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(96)02088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning, a laboratory manual. 2nd Edn, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 1989. pp. pp1.25–1.28. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cantaloube JF, Charrel RN, Attoui H, Biagini P, De Micco P, De Lamballarie X. Evaluation of four PCR systems amplifying different genomic regions for molecular diagnosis of GB virus C infections. J Virol Methods. 1997;64:131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(96)02154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pontisso P, Ruvoletto MG, Fattovich G, Chemello L, Gallorini A, Ruol A, Alberti A. Clinical and virological profiles in patients with multiple hepatitis virus infections. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:1529–1533. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liaw YF, Tsai SL, Chang JJ, Sheen IS, Chien RN, Lin DY, Chu CM. Displacement of hepatitis B virus by hepatitis C virus as the cause of continuing chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:1048–1053. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90766-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Koike K, Yasuda K, Yotsuyanagi H, Moriya K, Hino K, Kurokawa K, Iino S. Dominant replication of either virus in dual infection with hepatitis viruses B and C. J Med Virol. 1995;45:236–239. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890450222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


