Abstract
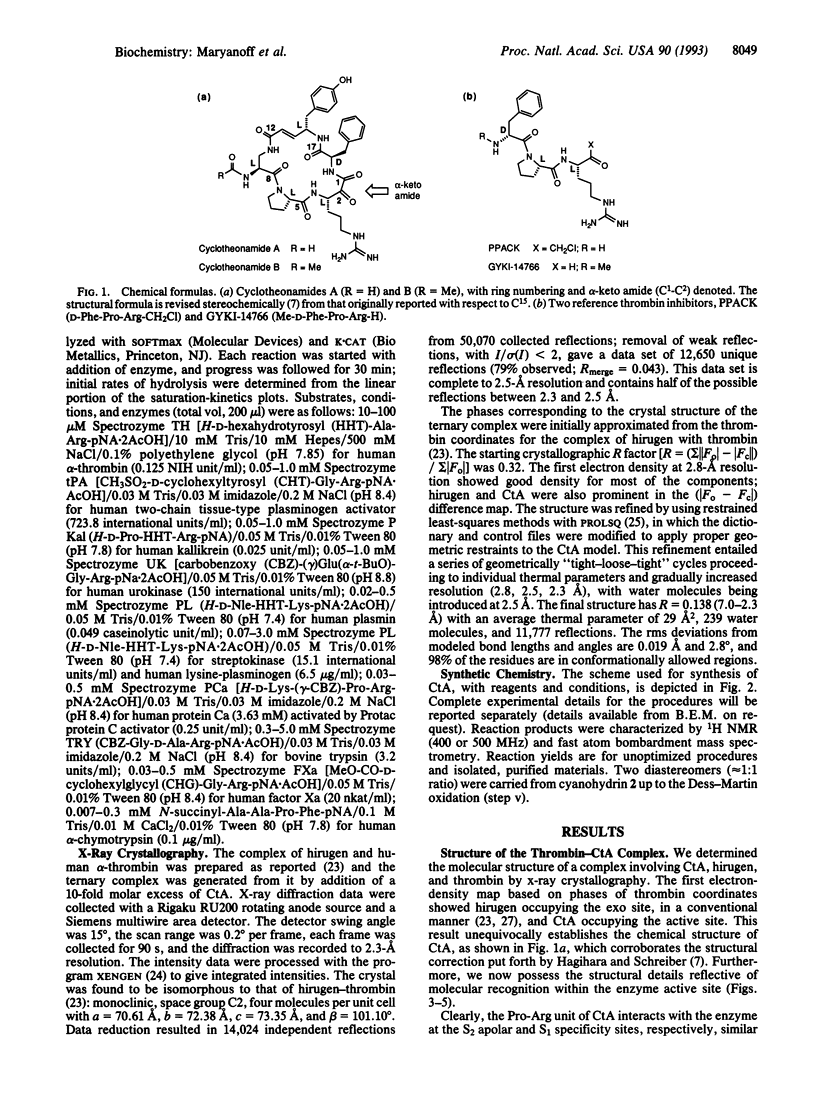
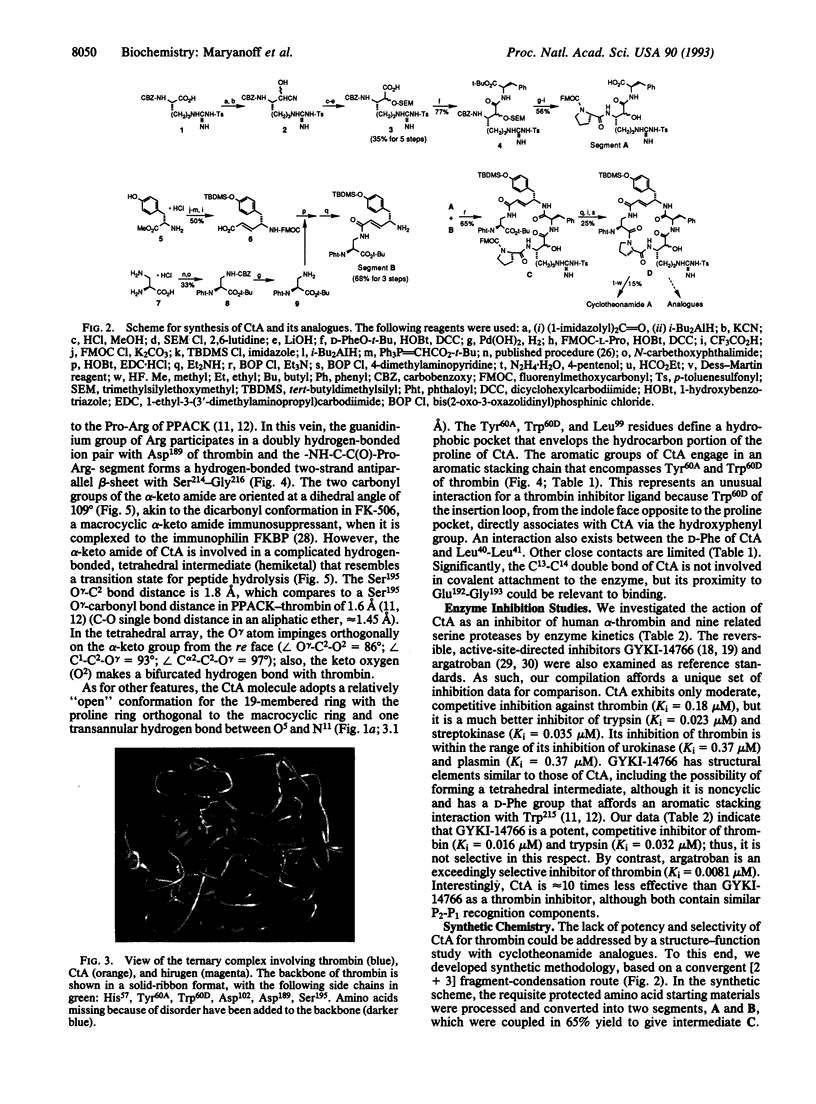
The macrocyclic peptide cyclotheonamide A (CtA), isolated from the marine sponge Theonella sp., represents an unusual class of serine protease inhibitor. A complex of this inhibitor with human alpha-thrombin, a protease central to the bioregulation of thrombosis and hemostasis, was studied by x-ray crystallography. This work (2.3-A resolution) confirms the structure of CtA and reveals intimate details about its molecular recognition within the enzyme active site. Interactions due to the "Pro-Arg motif" (Arg occupancy of the S1 specificity pocket; formation of a hydrogen-bonded two-strand antiparallel beta-sheet with Ser214-Gly216) and the alpha-keto amide group of CtA are primarily responsible for binding to thrombin, with the alpha-keto amide serving as a transition-state analogue. A special interaction with the "insertion loop" of thrombin (Tyr60A-Thr60I) is manifested through engagement of the hydroxyphenyl group of CtA with Trp60D as part of an "aromatic stacking chain." Biochemical inhibition data (Ki values at 37 degrees C) were obtained for CtA with thrombin and a diverse collection of serine proteases. Thus, CtA is just a moderate inhibitor of human alpha-thrombin (Ki = 0.18 microM) but a potent inhibitor of trypsin (Ki = 0.023 microM) and streptokinase (Ki = 0.035 microM). The relative lack of potency of CtA as a thrombin inhibitor is discussed with respect to certain structural features of the enzyme complex. We also report the total synthesis of CtA, by a convergent [2 + 3] fragment-condensation approach, to serve the preparation of cyclotheonamide analogues for structure-function studies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajusz S., Szell E., Bagdy D., Barabas E., Horvath G., Dioszegi M., Fittler Z., Szabo G., Juhasz A., Tomori E. Highly active and selective anticoagulants: D-Phe-Pro-Arg-H, a free tripeptide aldehyde prone to spontaneous inactivation, and its stable N-methyl derivative, D-MePhe-Pro-Arg-H. J Med Chem. 1990 Jun;33(6):1729–1735. doi: 10.1021/jm00168a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Turk D., Karshikov A. The refined 1.9-A X-ray crystal structure of D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone-inhibited human alpha-thrombin: structure analysis, overall structure, electrostatic properties, detailed active-site geometry, and structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1992 Apr;1(4):426–471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. Y., Abeles R. H. Inhibition of cathepsin B and papain by peptidyl alpha-keto esters, alpha-keto amides, alpha-diketones, and alpha-keto acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Sep;281(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. R. HIV protease: a novel chemotherapeutic target for AIDS. J Med Chem. 1991 Aug;34(8):2305–2314. doi: 10.1021/jm00112a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. V., Crowe V. G., Frank J. D., Wilson H. C., Coffman W. J., Utterback B. G., Jakubowski J. A., Smith G. F. Pharmacological assessment of the antithrombotic activity of the peptide thrombin inhibitor, D-methyl-phenylalanyl-prolyl-arginal (GYKI-14766), in a canine model of coronary artery thrombosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Moolenaar W. H. Thrombin receptor activation causes rapid neural cell rounding and neurite retraction independent of classic second messengers. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):411–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Inactivation of trypsin-like enzymes with peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):826–842. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikumoto R., Tamao Y., Tezuka T., Tonomura S., Hara H., Ninomiya K., Hijikata A., Okamoto S. Selective inhibition of thrombin by (2R,4R)-4-methyl-1-[N2-[(3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-8-quinolinyl++ +) sulfonyl]-l-arginyl)]-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):85–90. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. A new link in the brain's defenses. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1278–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.1445531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokotoff M., Logue L. W. Potential inhibitors of L-asparagine biosynthesis. 5. Electrophilic amide analogues of (S)-2,3-diaminopropionic acid. J Med Chem. 1981 May;24(5):554–559. doi: 10.1021/jm00137a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocain T. D., Rich D. H. alpha-Keto amide inhibitors of aminopeptidases. J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 7;35(3):451–456. doi: 10.1021/jm00081a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peet N. P., Burkhart J. P., Angelastro M. R., Giroux E. L., Mehdi S., Bey P., Kolb M., Neises B., Schirlin D. Synthesis of peptidyl fluoromethyl ketones and peptidyl alpha-keto esters as inhibitors of porcine pancreatic elastase, human neutrophil elastase, and rat and human neutrophil cathepsin G. J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):394–407. doi: 10.1021/jm00163a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H. Pepstatin-derived inhibitors of aspartic proteinases. A close look at an apparent transition-state analogue inhibitor. J Med Chem. 1985 Mar;28(3):263–273. doi: 10.1021/jm00381a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen M. K., Standaert R. F., Galat A., Nakatsuka M., Schreiber S. L. Inhibition of FKBP rotamase activity by immunosuppressant FK506: twisted amide surrogate. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):863–866. doi: 10.1126/science.1693013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R. Refined structure of the hirudin-thrombin complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):583–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Naughton M. A., Teng W., Hung D. T., Rose J., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Turck C. W., Coughlin S. R. Tethered ligand agonist peptides. Structural requirements for thrombin receptor activation reveal mechanism of proteolytic unmasking of agonist function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13146–13149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A. Thrombin-cellular interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:228–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypczak-Jankun E., Carperos V. E., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Westbrook M., Maraganore J. M. Structure of the hirugen and hirulog 1 complexes of alpha-thrombin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1379–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duyne G. D., Standaert R. F., Karplus P. A., Schreiber S. L., Clardy J. Atomic structure of FKBP-FK506, an immunophilin-immunosuppressant complex. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1709302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]