Abstract
In cultured vertebrate neurons, axons have a uniform arrangement of microtubules with plus-ends distal to the cell body (plus-end-out), whereas dendrites contain mixed polarity orientations with both plus-end-out and minus-end-out oriented microtubules. Rather than non-uniform microtubules, uniparallel minus-end-out microtubules are the signature of dendrites in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans neurons. To determine whether mixed microtubule organization is a conserved feature of vertebrate dendrites, we used live-cell imaging to systematically analyze microtubule plus-end orientations in primary cultures of rat hippocampal and cortical neurons, dentate granule cells in mouse organotypic slices, and layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in the somatosensory cortex of living mice. In vitro and in vivo, all microtubules had a plus-end-out orientation in axons, whereas microtubules in dendrites had mixed orientations. When dendritic microtubules were severed by laser-based microsurgery, we detected equal numbers of plus- and minus-end-out microtubule orientations throughout the dendritic processes. In dendrites, the minus-end-out microtubules were generally more stable and comparable with plus-end-out microtubules in axons. Interestingly, at early stages of neuronal development in nonpolarized cells, newly formed neurites already contained microtubules of opposite polarity, suggesting that the establishment of uniform plus-end-out microtubules occurs during axon formation. We propose a model in which the selective formation of uniform plus-end-out microtubules in the axon is a critical process underlying neuronal polarization.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Live-cell imaging was used to systematically analyze microtubule organization in primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons, dentate granule cells in mouse organotypic slices, and layer 2/3 pyramidal neuron in somatosensory cortex of living mice. In vitro and in vivo, all microtubules have a plus-end-out orientation in axons, whereas microtubules in dendrites have mixed orientations. Interestingly, newly formed neurites of nonpolarized neurons already contain mixed microtubules, and the specific organization of uniform plus-end-out microtubules only occurs during axon formation. Based on these findings, the authors propose a model in which the selective formation of uniform plus-end-out microtubules in the axon is a critical process underlying neuronal polarization.
Keywords: cytoskeleton, dendrites, development, microtubule dynamics, neuron, polarity
Introduction
Neurons are polarized cells that have a long axonal process and several branched dendrites and strongly depend on the microtubule cytoskeleton for their integrity and organelle transport (Conde and Cáceres, 2009; Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2015). Microtubule-based motor proteins recognize the intrinsic asymmetry of the microtubule lattice and drive transport to either the microtubule plus end or minus end (Hirokawa et al., 2010; Maday et al., 2014). In various model systems, it has been shown that microtubule arrays within axon and dendrites are highly organized with respect to their intrinsic polarity, and this specific microtubule organization is essential to direct polarized cargo transport (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2011; Rolls, 2011). For instance, studies in primary hippocampal neurons have demonstrated that microtubule plus-end-directed motor kinesin-1 selectively transports cargoes into the axon along plus-end-out microtubules (Nakata and Hirokawa, 2003; Hammond et al., 2010; Kapitein et al., 2010a; Nakata et al., 2011; Huang and Banker, 2012). In addition, the selective presence of minus-end-out oriented microtubules in dendrites enables the minus-end-directed motor dynein to selectively transport cargoes into dendrites (Kapitein et al., 2010b). Although the importance of the microtubule cytoskeleton for proper intracellular trafficking and cargo sorting is unambiguous, how the microtubules in axon and dendrites are organized in developing and mature neurons is essentially unknown.
The hook-decoration technique was used originally to determine the orientation of microtubules in axons and dendrites by electron microscopy (EM; Baas and Lin, 2011). Using this approach, uniformly plus-end-out microtubule polarity orientations were observed in axons of various types of cultured vertebrate neurons (Baas et al., 1987; Baas et al., 1988). In contrast, proximal dendrites contained non-uniformly oriented microtubules that were found to be approximately half plus-end-out and half minus-end-out (Baas et al., 1988; Burton, 1988). In olfactory bulb mitral cells, the mixed population of microtubules remained constant throughout the dendritic processes, although microtubules in distal dendritic segments in hippocampal neurons appeared primarily oriented plus-end-out (Baas et al., 1988; Burton, 1988). The different microtubule polarity orientations in axons and dendrites were confirmed using fluorescently labeled microtubule plus-end binding proteins in living hippocampal and Purkinje cell cultures (Stepanova et al., 2003). Nevertheless, the fraction of inward-growing comets is typically twofold lower than outward-growing comets. In addition, some evidence for mixed microtubule arrays in mouse brain tissue have been presented by both second-harmonic generation microscopy and live-cell imaging of microtubule growth (Kwan et al., 2008; Kleele et al., 2014). In invertebrate neurons, microtubules in axons are also arranged with their plus ends distal to the cell body, whereas in dendrites most microtubules are arranged with their minus ends distal to the cell body, although mixed orientation microtubules have also been observed (Stone et al., 2008; Goodwin et al., 2012; Maniar et al., 2012). These results suggest that the presence of minus-end-out oriented microtubules is a unique property of dendrites.
In this study, we use a combination of cell-biological approaches, quantitative microscopy, laser microsurgery, organotypic slice cultures, and in vivo imaging in living mice to determine microtubule orientations in axons and dendrites. In mature neurons, non-uniformly oriented microtubules are present in dendrite in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. Equal numbers of plus- and minus-end-out microtubule orientations are present throughout mature dendritic processes. During early stages of neuronal development, minus-end-out microtubules were already detected in growing neurites before neuronal polarization. These data suggest that mixed microtubule polarity is established before axon formation and neuronal polarization.
Materials and Methods
Animals
All experiments with animals were performed in compliance with the guidelines for the welfare of experimental animals issued by the government of The Netherlands or the Swiss Federal Act on Animal Protection and were approved by the Animal Ethical Review Committee of Utrecht University or the University of Geneva and the Geneva Cantonal Veterinary Office.
DNA constructs
CAMSAP2–shRNA (ttgcatgtgctcaacagt) has been described previously (Yau et al., 2014). The GFP–MT+TIP construct contains the general microtubule plus-tip localization signal (SxIP motif) of human MACF2, which is recognized by the end binding (EB) protein. It was generated by fusing the two-stranded leucine zipper coiled-coil sequence corresponding to GCN4-p1 (RMKQLEDKVEELLSKNYHLENEVARLKKLVGER) to N-terminal 18 aa peptide of human MACF2 (Gly5468-Lys5485; NP_899236) by PCR-based strategy (Honnappa et al., 2009). A glycine rich-linker sequence (GAGG) was inserted between GCN4 pl and MACF18 and subcloned into pβactin-16 pl expression vector to generate pβactin–GFP–GCN4–MACF18. For stage 2–3 neurons, we used MACF43 that is identical to MACF18 except for the 43 N-terminal amino acids of human MACF2 (Glu5455–Arg5497). Because we used GFP–GCN4–MACF18/43 as a general marker to analyze the dynamics of microtubule growing plus ends, we named this construct GFP–MT+TIP. pβactin–GFP and pβactin–mRFP have been described previously (Kapitein et al., 2010a). The volume marker MARCKS–TagRFP-T was adapted from MARCKS–GFP (De Paola et al., 2003). The first 41 aa of MARCKS (MGCQFSKTAAKGEAAAERPGEAAVASSPSKANGQENGHVKV) containing an Ala-Cys mutation were fused to TagRFP-T spaced by a GS-linker (PCR). MARCKS–TagRFP-T was cloned upstream and GFP–GCN4–MACF18 downstream of an attenuated ECMV internal ribosome entry site (pIRES), resulting in high expression of the volume marker and low expression of GFP–MT+TIP. The bicistronic construct was either subcloned into pCAGGS vector for single-cell electroporation or into the lentivirus vector pSIN–TRE–mSEAP–hPGK–rtTA2sM2 (kind gift from Dr. Didier Trono, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland). The human PGK promotor was replaced for a short rat synapsin (0.5 kb) promotor to restrict the expression primarily to neurons. Lentiviral particles were generated as described previously (Yau et al., 2014).
Primary cortical and hippocampal neuron cultures, transfection, and infections
Primary cortical and hippocampal cultures were prepared from embryonic day 18 rat brains (of either sex). Cells were plated on coverslips coated with poly-l-lysine (37.5 μg/ml) and laminin (1.25 μg/ml) at a density of 75,000/well. Dissociated neurons were cultured in Neurobasal medium (NB) supplemented with 2% B27 (Gibco), 0.5 mm glutamine (Gibco), 15.6 μm glutamate (Sigma), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco).
Transfections.
Hippocampal neurons were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). Briefly, DNA (1.8 μg/well, for a 12-wells plate) was mixed with 3.3 μl of Lipofectamine 2000 in 200 μl of NB, incubated for 30 min, and then added to the neurons in NB at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 45 min. Next, neurons were washed with NB and transferred to their original medium at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 2–4 d.
Nucleofections.
Primary cortical neurons (1.3 × 106 cells) were nucleofected with 0.5 μg of GFP–MACF43 or GFP plasmid and 2.5 μg of empty plasmid or shRNA using the Amaxa Rat Neuron Nucleofector kit (Lonza) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Cells were grown for 18–24 h at 37°C in 5% CO2 before imaging.
Lentivirus infections.
Hippocampal neurons were transduced with lentivirus 7–10 d before experiments. The tetracycline-dependent expression was induced 2 d before imaging by supplementing the medium with 500 ng/ml doxycycline.
Organotypic slice cultures and lentivirus infections
Mouse hippocampal slices (350 μm) were prepared from postnatal day 5–6 pups (of either sex). Slices were transferred on small patches of FHLC membrane (0.45 μm; Millipore) positioned on Millicell culture inserts (Millipore). Hippocampal slices were transduced with lentivirus directly after plating by pouring a drop of concentrated virus solution over the culture. Medium exchange and maintenance of the cultures followed the method described previously (Stoppini et al., 1991). Experiments were performed after 14–21 d in vitro (DIV). Slice culture medium was supplemented with doxycycline (500 ng/ml) at least 5 d before imaging.
In vivo single-cell electroporation
In vivo single-cell DNA electroporation was performed as described previously (Pagès et al., 2015). Briefly, young male mice (4–6 weeks old) were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of MMF [a mixture of medetomidin (Dorbene, 0.2 mg/kg), midazolam (Dormicum, 5 mg/kg), and fentanyl (Duragesic, 0.05 mg/kg) in saline]. A craniotomy was performed above the somatosensory cortex. A 15–20 MΩ glass pipette (GC150F-7.5; Harvard Apparatus) was filled with internal solution [in mm: 266 KMeSO4, 14 KCl, 20 Na-HEPES, 4 MgATP, 4 Na2ATP, 1 Na2GFP, and 0.1 EGTA, pH 7.2 (280–290 mOsm)], containing 30 ng/μl plasmid DNA and Alexa Fluor 488 hydrazide (50 μm; Life Technologies). Under visual guidance, cortical layer 2/3 (L2/3) pyramidal cells were targeted and electroporated (10 pulses, −12 V, 500 us, 50 Hz) using a head stage (AP-1AX1MU) attached to an Axoporator 800A (Molecular Devices). Successful electroporations resulted in fast filling of cell bodies by Alexa. Finally, the pipette was withdrawn gently, and a glass coverslip (3 μm diameter) was implanted to cover the craniotomy. Imaging was started after 1 week of recovery.
Live-cell confocal imaging and laser-induced severing
Spinning-disk confocal microscopy was performed on an inverted microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti with Perfect Focus System) with a Plan Apo VC 100×, 1.4 numerical aperture (NA) oil-immersion objective or an S Fluor 100×, 0.5–1.3 NA oil-immersion objective (Nikon) for laser-induced severing (LS) experiments. MetaMorph software was used to control the Evolve 512 EMCCD camera (Photometrics) and all motorized parts. The microscope has been further outfitted with an ASI motorized stage MS-2000-XYZ with piezo top plate, ILas system (Roper Scientific France/PICT-IBiSA, Curie Institute), and Shutter LB10-3. For fluorescence excitation, a Calypso 491 nm, 100 mW laser and Jive 561, 100 mW laser (Cobolt) were used. A Teem Photonics 355 nm Q-switched pulsed laser was used for LS (Botvinick et al., 2004; Colombelli et al., 2005). ET-GFP/mCherry dichroic (59022; Chroma Technology) or sequential ET-GFP (49002; Chroma Technology) and ET-mCherry (49008; Chroma Technology) were used for wavelength selection. All imaging was performed in full conditioned medium for hippocampal neuron cultures. A Tokai Hit Stage Top Incubator (INUBG2E-ZILCS) was used to maintain neurons at 37°C with 5% CO2.
Imaging stage 1–2 neurons.
Time-lapse acquisition was performed for 6 min (without LS) or for 1 min before LS and 5 min after, with a time interval of 1 s. LS was performed at 10 μm from the soma. Regions of 10 μm before and behind the position of LS were used for the quantifications. In neurites shorter than 20 μm, LS was performed in the neurite midpoint.
Imaging stage 3–5 neurons.
Microtubule plus-tip imaging in neuron cultures was performed with 6 × 0.5 μm steps and sequential channel recordings. Time-lapse recordings were performed in a single plane when LS was conducted sequentially.
Imaging taxol-treated neurons.
Hippocampal neurons were incubated with DMSO or 10 nm taxol at DIV1 for 72 h. For microtubule LS experiments, control and taxol-treated neurons were transfected at DIV3 with GFP–MT+TIP using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). At DIV4, neurons were fixed for immunostaining or imaged for live-cell experiments.
Imaging organotypic slices.
Slice cultures were imaged in ACSF [126 mm NaCl, 3 mm KCl, 2.5 mm CaCl2, 1.3 mm MgCl2, 1.25 mm Na2HPO4, 26 mm NaHCO3, 20 mm glucose, and 1 mm Trolox (bubbled with 95% O2, 5% CO2)]. Dendrites were imaged with z-stacks of 6–8 × 0.5 μm steps, unless for LS experiments (single plane). Imaging positions along the dendrites were defined as follows: proximal <25%; middle between 25 and 60%; distal >60% of total dendritic length.
In vivo two-photon laser scanning microscopy
Imaging was performed using a custom-built two-photon laser-scanning microscope (https://openwiki.janelia.org/wiki/display/shareddesigns/Shared+Two-photon+Microscope+Designs) and data acquisition software Scanimage (https://openwiki.janelia.org/wiki/display/ephus/ScanImage). Anesthetized mice (with MMF; see above) were head fixed under the microscope, and their temperature was kept constant by a feedback-controlled heating pad. Fluorophores were excited using a titanium:sapphire laser (Chameleon Ultra II; Coherent) tuned at 950 nm. Emitted fluorescence was collected using a 16× multiphoton objective (0.8 NA, N16XLWD-PF; Nikon), spectrally separated using two bandpass filters (HC530/55, HC607/70, BrightLine; Semrock) and detected using two photomultiplier tubes (10770PB-40 for green, and R3896 for red; Hamamatsu). Images were recorded at 0.2 Hz (512 × 512 pixels, 2 ms/line, 5 s interimage interval). Typical fields of view spanned from 30–50 μm square. The average excitation power was kept below 50 mW as measured under the objective.
Immunofluorescence staining
Neurons were fixed in ice-cold 100% methanol/1 mm EGTA for 10 min at −20°C. After fixation, cells were washed three times for 5 min in PBS and incubated with the primary antibody in GDB buffer (0.2% BSA, 0.8 m NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 30 mm phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) overnight at 4°C. After extensive washing with PBS, neurons were incubated with secondary antibodies in GDB buffer for 1 h at room temperature and then washed again. Coverslips were mounted in Vectashield (Vector Laboratories) and sealed with nail polish. The following primary and secondary antibodies were used: rabbit anti-CAMSAP2 (17880-1-AP; Proteintech), mouse anti-α-tubulin (B-5-1-2; Sigma), mouse anti-Tau (MAB3420; Millipore Bioscience Research Reagents), βIII tubulin (PRB-435P; Covance), mouse anti-GFP (1814460; Roche), and Alexa Fluor 488- and Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated secondary antibodies (Invitrogen).
Image processing and quantifications
Image analysis was performed using FIJI, and data processing and statistical analysis were done in Excel and GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software).
MT+TIP analysis.
Time-lapse recordings were low-pass filtered and subtracted with an average projection of the complete time lapse (Kapitein et al., 2010b). Kymography was performed on the filtered images using the FIJI “KymoResliceWide” plugin. Starting and end positions of the traces were marked by the “Cell Counter” plugin, and coordinates were exported for additional analysis. The number of microtubule plus-tip comets, comet growth speed, and distances to the cutting position were calculated from the starting and end coordinates of the microtubule traces. To produce comparable data of microtubule plus-tip dynamics between the different model systems, we quantified comets that were detectable over 1 min within 20 μm of axonal or dendritic segment (if not indicated differently). In LS experiments, the place of cutting was positioned in the center of this observation area.
MT stability analysis.
Similar imaging and analysis was performed as described above. The starting points of comets relative to the site of LS within a time window of 1 min (before or after LS) were put into bins of 2 μm and averaged with each DIV15 dendrite or axon. Multiple minutes were averaged for each dendrite and axon after LS. The median indicates 50% of the data points.
Analysis of CAMSAP2 distribution.
Images from a wide-field fluorescence microscope (Eclipse 80i; Nikon) were used to quantify CAMSAP2 distribution. Localization of CAMSAP2 only at the tip of the neurite was classified as “tip,” homogenous distribution along the neurite as “equal,” and scattered accumulations along the neurite as “random.”
Analysis of CAMSAP2 staining.
Cortical neurons were nucleofected with GFP and either pSuper control or CAMSAP2 shRNA before plating. Neurons were fixed 72 h after transfection and stained for CAMSAP2. Confocal images were taken with a Zeiss LSM 700. Mean intensities of CAMSAP2 signals were quantified in neurites of control and CAMSAP2 depleted neurons at 15 μm distance from the soma using FIJI software.
Results
Mixed microtubule organization in dendrites in vitro and in vivo
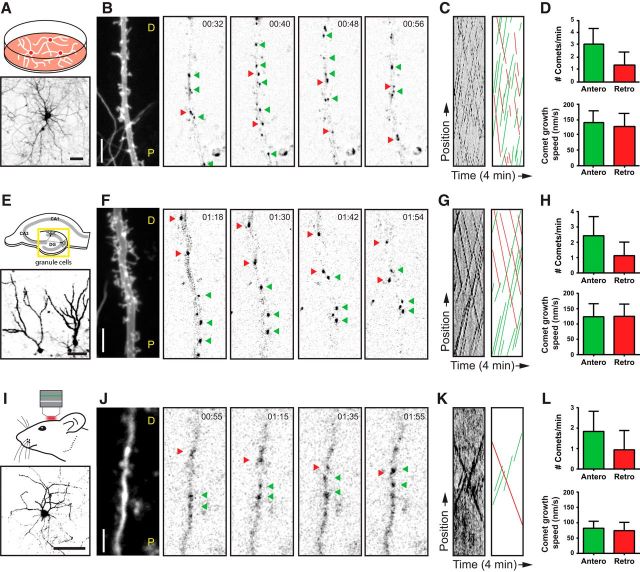
To determine the microtubule organization in vertebrate dendrites in vitro and in vivo, we systematically analyzed microtubule plus-end dynamics and orientations in primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons, dentate granule cells in mouse organotypic slices, and L2/3 pyramidal neuron in somatosensory cortex of living mice. We first performed two-color live-cell imaging in differentiated (DIV18) hippocampal neurons in culture. We generated a bicistronic construct expressing the microtubule plus-end marker GFP–MT+TIP (Yau et al., 2014) and MARCKS–TagRFP to highlight neuronal morphology and used lentivirus to transduce the dissociated cultures. In cases when the expression level was low, we observed unidirectional displacement of GFP–MT+TIP comets in axons, whereas in dendrites the movements were bidirectional, reflecting the different MT organization in axons and dendrites (Stepanova et al., 2003; Jaworski et al., 2009). Consistent with previous reports using EB3–GFP as +TIP marker (Jaworski et al., 2009; Kapitein et al., 2011), the total number of comets in DIV18 cultured hippocampal neurons was 4.4 ± 1.6 comets/min/20 μm (mean ± SD; n = 32 dendrites), and the average velocity of comet movements was 132 ± 53 nm/s (mean ± SD; n > 600 comets). Next, we analyzed in detail the direction of GFP–MT+TIP comets that were recorded in middle segments of primary dendrites, calculated as the half-length of the total dendrite measured from the cell body to the dendritic tip (Fig. 1A–C; Movie 1). We found on average 31% of labeled plus ends moving retrogradely toward the cell body, whereas the comet growth speed did not significantly differ between both directions (Fig. 1D). These results indicate that one-third of the dynamic microtubules in dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons are oriented with the plus end inward.
Figure 1.
Mixed dendritic microtubule organization in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. A, Schematic drawing of dissociated neuron cultures (top) and a representative example expressing a volume marker (bottom). Neurons have been transduced with lentivirus expressing a bicistronic cassette of GFP–MT+TIP and the volume marker MARCKS–TagRFP. B, Time-lapse acquisitions from a DIV18 neuron. The first frame shows an average projection of the volume marker. Dendrite orientation is indicated by P (proximal) and D (distal). All the following represent selected frames from the GFP–MT+TIP time-lapse. Green arrowheads point to individual anterograde moving GFP–MT+TIP comets, and red arrowheads point to retrograde moving comets. C, Kymographs made from the complete time-lapse recording shown in B. The left shows the original kymograph, and the right shows an illustration of the manually traced comets displacements for better visualization. D, Quantification of microtubule properties in dissociated cultures. The top diagram shows the number of GFP–MT+TIP comets within a defined observation window of 1 min and 20 μm (n = 32 dendrites). The bottom diagram displays the average speeds of anterograde and retrograde moving comets (n > 500 comets). E, Schematic drawing of a hippocampal slice (top) and two representative granule cells (bottom) imaged in organotypic slice cultures. The yellow box indicates the dentate gyrus region that has been analyzed exclusively in this study. Slices have been transduced with the same lentivirus used for dissociated neurons. F, Recordings from a granule cell dendrite at 18 d in culture. The first frame displays the dendritic profile labeled by the volume marker. Subsequent frames show the GFP–MT+TIP channel acquired from the same dendrite. G, Original and illustrated kymographs of the time-lapse recording shown in F. H, Quantification of the average comet number (top diagram; n = 38 dendrites) and growth speed (bottom diagram; n > 300 comets) in organotypic slice cultures. The method of quantification was identical to the data on dissociated cultures. I, Schematic illustration of the in vivo imaging through a cranial window (top) and a representative example of a neuron at low magnification expressing the volume marker (bottom). Neurons were transfected by single-cell electroporation using the same bicistronic expression construct on which the lentivirus was based on. J, In vivo two-photon time-lapse imaging of an L2/3 pyramidal neuron. The dendritic dimensions were visualized by an average projection of the GFP–MT+TIP channel (first frame), and the following frames represent selected time points of the same channel. Bidirectional microtubule displacements are indicated by colored arrowheads. K, Original and illustrated kymographs of the time-lapse recording shown in J. L, Quantification of the average comet number (top diagram; n = 12 dendrites) and growth speed (bottom diagram; n > 100 comets) of the observed in vivo microtubule dynamics. Scale bars: A, E, I, 50 μm; B, F, J, 5 μm. Error bars indicate SD. See also Movie 1.
Mixed dendritic microtubule organization in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. GFP-MT+TIP comets were imaged in middle dendritic regions of a dissociated neuron culture (left), organotypic slice culture (middle), and mouse neocortex (right). All dendrites show anterograde and retrograde displacement of the comets. The scale bar is applicable for all recordings. Frame rates were adjusted in order to compensate for acquisition at different time intervals (dissociated neurons = 4 s; slice cultures = 6 s; in vivo = 5 s intervals). GFP-MT+TIP signals were corrected for bleaching and convoluted to enhance signal to noise. The movie has been accelerated (40×).
Next, we determined microtubule dynamics and growth direction in mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Using the same live-cell imaging approach, we then focused primarily on the dendrites of the granule cells, the principal neurons of the dentate gyrus (Fig. 1E–G; Movie 1). Similar to the dissociated hippocampal neurons, middle segments of granule cell dendrites have on average 32% of the GFP–MT+TIP comets moving retrogradely toward the cell body (Fig. 1H). In slice cultures, both the total number of comets and the comet growth speed were slightly reduced in both directions (Fig. 1H).
Finally, we recorded microtubule dynamics and orientation in dendrites of L2/3 pyramidal cells in the somatosensory cortex of living mice (Fig. 1I–K; Movie 1). The bicistronic construct expressing GFP–MT+TIP and MARCKS–TagRFP was delivered by single-cell electroporation into the neocortex of 6-week-old mice and in vivo two-photon laser scanning microscopy (2PLSM) imaging was performed through a cranial window (Cane et al., 2014; Pagès et al., 2015). Transfected neurons that were sufficiently bright in both channels were selected for imaging at high magnification. In dendrites, we observed clear displacements of GFP–MT+TIP comets in both anterograde and retrograde directions. Similar to the culture systems, pyramidal cell dendrites had on average 34% of the GFP–MT+TIP comets moving retrogradely toward the cell body (Fig. 1L). The total number of comets and the comet growth speed were further reduced in dendrites in vivo compared with in vitro systems (Fig. 1L). Together, these data demonstrate that a mixed microtubule organization is present in mature dendrites from different neuron types, both in vitro and in vivo. Although the number of dynamic microtubules and growth speed is markedly decreased in vivo, the ratio of dynamic plus-end-in (1:3) and plus-end-out (2:3) microtubules in dendrites is a constant parameter in all analyzed model systems.
Gradual increase in minus-end-out microtubules during dendrite development
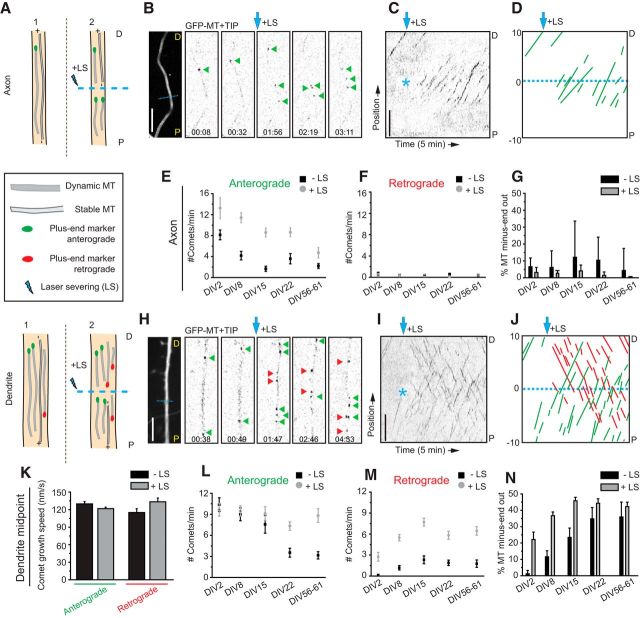
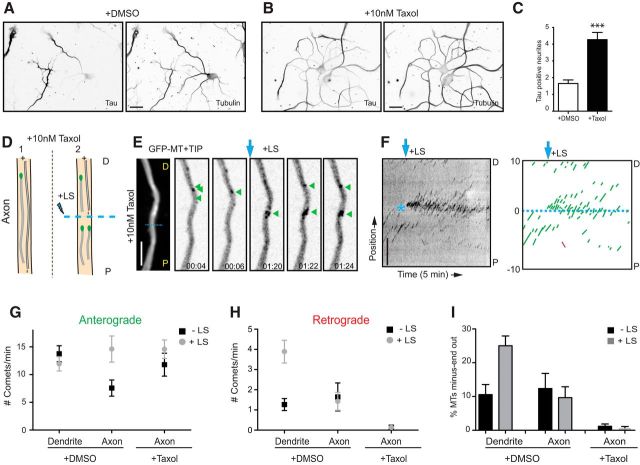
Imaging of plus-tip markers provides information about the dynamic ends of microtubules but not about the length of the remaining portion behind the plus end. Therefore, the fraction of comets moving in a specific direction does not directly reflect the fraction of corresponding microtubule orientations in a certain section, because microtubules of different orientations could have different lengths (Fig. 2A). To elucidate in more detail the orientations within a bundle of microtubules, we used live-cell imaging in combination with laser-based microsurgery (Yau et al., 2014). Cutting a microtubule bundle with a short-pulsed laser creates new microtubule ends and allows analysis of the newly generated growing microtubule plus ends (Fig. 2A). By observing the growth direction of GFP–MT+TIP comets before and after LS, this assay permits a direct readout of the orientations of microtubules within specific cellular regions, regardless of length or plus-end dynamicity (Fig. 2B–D, H–J). An increased fraction of comets moving in one direction indicates that the microtubules with corresponding orientations are on average longer or nondynamic, both suggesting increased stability. Analyzing the growth direction of GFP–MT+TIP comets before and after LS in axons at different developmental stages (from DIV2 until DIV61) revealed that, in all cases, the majority of the GFP–MT+TIP comets (>95%) showed anterograde displacement (Fig. 2G). We also found that the total number of comets was decreased in more mature axons both before and after LS (Fig. 2E,F). The observed decrease in axonal plus ends suggests the following: (1) the total number of microtubules in the axon shaft decreases during differentiation; or (2) the total number of axonal microtubules remains constant, and shorter microtubules are gradually replace by longer ones.
Figure 2.
Differential microtubule organization during neuronal development. A, Schematic representation of microtubule LS in axon (top) and dendrite (bottom). P indicates the proximal region and D the distal region. B, Stills from a spinning-disk time-lapse recording of an axon (DIV15) transfected with mRFP and GFP–MT+TIP at DIV13. The first still on the left is an average projection of the axon in which the dashed cyan line is the region of LS. Green arrowheads indicate GFP–MT+TIP comets pointing in an anterograde direction during the time-lapse recording. Cyan arrow indicates when LS is performed. The time-lapse recording is low-pass filtered and background subtracted. C, Kymograph of the time-lapse recording shown in B. Asterisk indicates time and location of LS. D, Schematic representation of the kymograph shown in C. Dashed cyan line separates the regions 10 μm before and 10 μm after LS. Green lines represent comets pointing in the anterograde direction. E, F, Quantification of the number of comets per minute pointing in the anterograde (E) or retrograde (F) direction, 10 μm before and after the position of LS. Black square data points are before LS, and the gray circles are after LS; n = 13 axons. G, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends pointed out in axons before (black columns) and after (gray columns) LS. H, Stills from a spinning-disk time-lapse recording of a dendrite middle region (DIV15) transfected with mRFP and GFP–MT+TIP at DIV13. The first still on the left is an average projection of the axon in which the dashed cyan line is the region of LS. Green and red arrowheads indicate comets moving in anterograde or retrograde direction. The cyan arrow indicates when LS is performed. The time-lapse recording is low-pass filtered and background subtracted. I, Kymograph of the time-lapse recording shown in H. Asterisk indicates time and location of LS. J, Schematic representation of the kymograph shown in I. Dashed cyan line separates the regions 10 μm before and 10 μm after LS. Green and red lines represent comets pointing in the anterograde or retrograde direction, respectively. K, Growth speed of comets extending in anterograde or retrograde direction along the dendrite. Black bars are before LS and gray bars are after; n = 163, n = 475, n = 41, n = 335 number of comets. L, M, Quantification of the number of comets per minute pointing in the anterograde (L) or retrograde (M) direction, 10 μm before and after the position of LS. Black square data points are before LS, and the gray circles are after LS. N, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends pointed out in dendrites before (black columns) and after (gray columns) LS; DIV2, n = 7 axons and 8 dendrites; DIV8, n = 11 axons and 17 dendrites; DIV15, n = 13 axons and 16 dendrites; DIV22, n = 12 axons and 17 dendrites; DIV56–DIV61, n = 10 axons and 13 dendrites. Scale bars, 5 μm. Error bars indicate SEM.
Next, we analyzed the growth direction and speed of GFP–MT+TIP comets in middle segments of primary dendrites and found both anterograde and retrograde moving comets at all developmental stages (DIV2–DIV61; Fig. 2H–K). The ratio plus-end-in and plus-end-out microtubules changes markedly during early dendrite development (DIV2–DIV15) but remains constant in more mature dendrites (older than DIV22; Fig. 2N). In young dendrites (DIV2), the majority of the GFP–MT+TIP comets show predominantly anterograde displacement, whereas additional retrograde comets were observed after LS (Fig. 2M,N), demonstrating that stable (long or nondynamic) minus-end-out microtubules are present in dendrites at these early developmental stages. In more differentiated dendrites at later stages of development (DIV2–DIV15), the relative fraction of plus-end-in comets increased during LS, suggesting again that minus-end-out microtubules are on average more stable (i.e., longer or nondynamic; Fig. 2L,M). At later stages (older than DIV22), the fraction of plus-end-in comets before LS increased because the number of plus-end-out comets decreased, indicating that, in mature dendrites, microtubules of both orientations are more stable (i.e., longer or nondynamics; Fig. 2L,M). These results indicate that mature dendrites contain equal numbers of plus- and minus-end-out microtubule orientations.
Mixed microtubule orientations are present throughout the dendrites
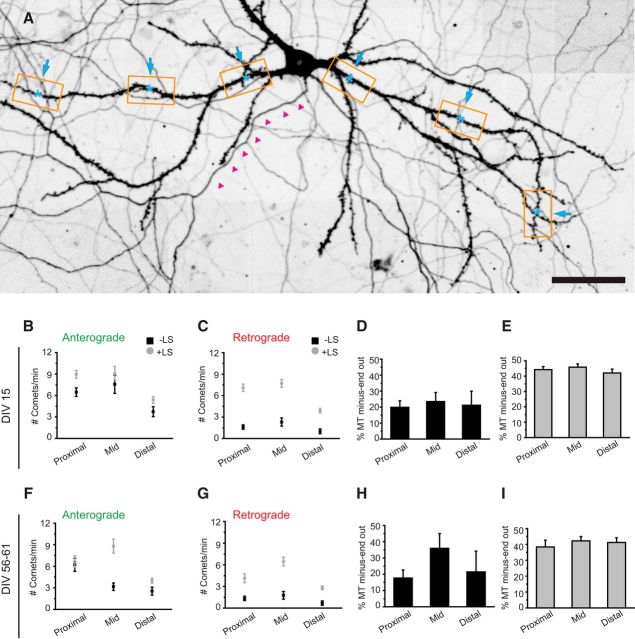
Previous EM studies suggested differences in microtubule orientation between distinct dendritic regions, with a gradual increase in plus-end-out microtubules in the more distal parts of the dendrites (Baas et al., 1989). Because all analysis was done on the middle segments of primary dendrites, we extended our live-cell imaging and LS study to proximal and distal regions of the dendrite (Fig. 3A). In dendrites of DIV15 neurons, we observed mixed microtubule orientation in all dendritic regions with constant ratios of ∼20% minus-end-out for dynamic microtubules (Fig. 3B–D). During LS, the fraction of minus-end microtubule increased twofold, suggesting that minus-end-out microtubules are more stable (i.e., longer or nondynamic), whereas plus-end-out microtubules are dynamic throughout the whole dendrite. Similarly, LS in mature neurons (DIV55–DIV61) revealed that 40% of microtubules are oriented minus-end-out (Fig. 3F–I). Next, we analyzed microtubule dynamics in proximal, middle, and distal regions of granule cells in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures (Fig. 4A–C). Dynamic minus-end-out microtubules were present in different numbers in all three dendritic segments (Fig. 4D; Movie 2). In agreement with our data on mature dissociated cultures, we found an increased ratio of dynamic minus-end-out microtubules in the middle segment compared with other regions (Fig. 4E). Because the analyzed granule cells varied in the length of their dendritic trees, we tested for potential position effects. Within the middle segments, defined as 25–60% of total dendritic length, we found no indication for differential microtubule organization with regard to absolute or relative dendritic length (Fig. 4F). This suggests a continuous microtubule organization within the middle segments of dendrites. LS in the same region confirmed that the majority of minus-end-out microtubules are also stable in slice cultures (Fig. 4H,I). These results show that microtubule orientations are mixed throughout the dendrites and confirm the previous findings on differential stability of anterograde and retrograde microtubules in dendrites.
Figure 3.
Microtubule organization is maintained throughout dendritic regions. A, Hippocampal neuron at DIV18 (stitched image of 20× recordings). The axon is highlighted by magenta arrowheads. Orange boxes show examples of proximal, middle, and distal regions along the dendrites. Laser-induced severing of microtubules was performed in proximal regions with a distance of 20 μm to the soma and in distal regions with 20 μm to the end of the dendrite (cyan asterisk). B, C, DIV15 quantification of the number of comets per minute pointing in the anterograde (B) and retrograde (C) direction, 10 μm before and after the position of LS. Black square data points are before LS, and the gray circles are after LS. D, E, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends pointed out in dendrites before (black columns; D) and after (gray columns; E) LS; DIV15, proximal dendrite n = 30, middle dendrite n = 16, distal dendrite n = 19. F, G, DIV56–DIV61 quantification of the number of comets per minute pointing in the anterograde (F) and retrograde (G) direction, 10 μm before and after the position of LS. Black square data points are before LS, and the gray circles are after LS. H, I, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends pointed out in dendrites before (black columns; H) and after (gray columns; I) LS; DIV56–DIV61, proximal dendrite n = 15, middle dendrite n = 13, distal dendrite n = 13, n = 10 axons. Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bars indicate SEM.
Figure 4.
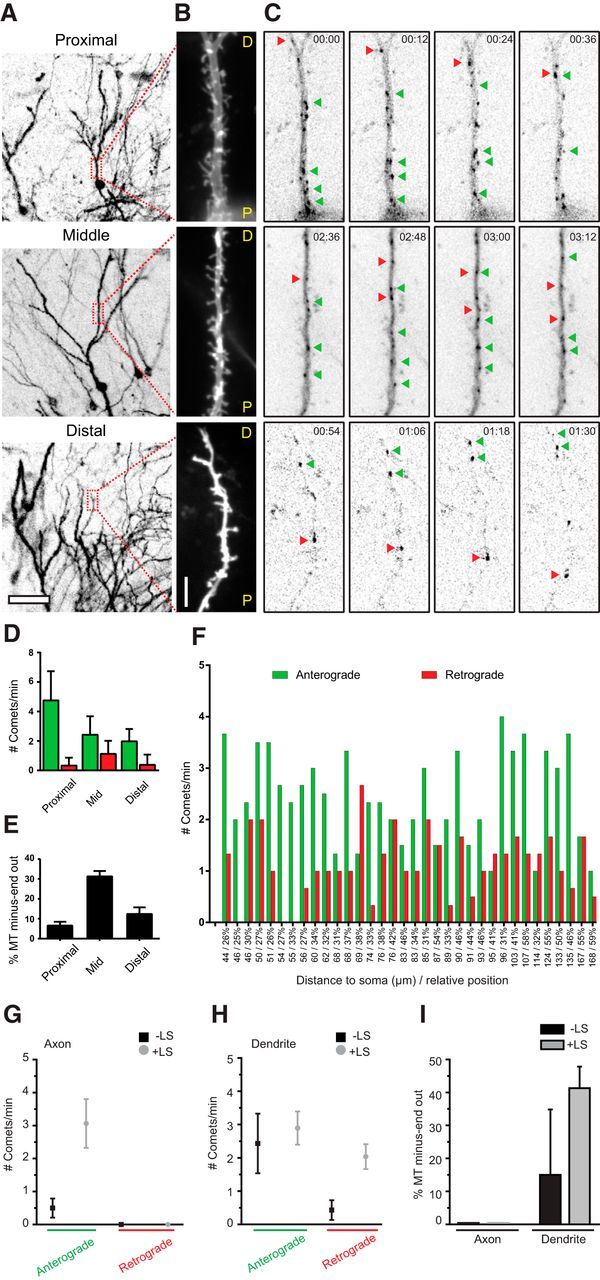
Hippocampal slice cultures exhibit similar microtubule organization as mature dissociated cultures. A, Lentivirus transduced hippocampal slice cultures expressing GFP–MT+TIP and a volume marker. Low-magnification overview images show dendritic tree recorded with the volume marker. Boxes label regions that were used for high-resolution imaging and localize at proximal, medial, or distal regions as indicated. B, Average projection of volume channels recorded sequentially to GFP–MT+TIP time-lapse imaging. C, Single still frames of a GFP–MT+TIP time-lapse recording acquired from the adjacent dendrite shown in B. Arrowheads point on individual comets moving in anterograde (green) or retrograde (red) direction. Recordings were performed at 6 s intervals. See also Movie 2. D, Quantification of microtubule plus tips moving in anterograde or retrograde direction analyzed for indicated dendritic regions (counted within a time window of 1 min and 20 μm dendrite length); proximal dendrite n = 14, middle dendrite n = 34, distal dendrite n = 21. E, Percentage of microtubules with minus-end-out orientation in proximal, middle, and distal dendrites. F, Quantification of comets direction in middle regions of individual dendrites (n = 34). Numbers on the x-axis show the distance of the imaging position center to the soma and the relative distance compared with the total dendritic length in percentage. The average number of comets/min/20 μm moving anterograde (green) and retrograde (red) are presented for each dendrite. G, H, Quantification of GFP–MT+TIP moving anterograde or retrograde in axons and dendrites of hippocampal slice cultures. Black square data points are before LS, and gray circle data points are after LS; axon, n = 7; dendrite, n = 8. I, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends pointed outward in axons and dendrites before (black columns) and after (gray columns) LS. Scale bars: A, 50 μm; B, 5 μm. Error bars indicate SD (D) and SEM (E, G, H, I).
Bidirectional microtubules are found in all dendritic regions. Lentivirus-infected organotypic slice cultures were imaged in proximal (top), middle (middle), and distal (bottom) dendritic regions. Left columns show live recordings of the volume marker channel and right columns the corresponding GFP-MT+TIP channel. Anterograde and retrograde moving comets are observable in all three dendritic regions at different ratios. Time-lapse images were acquired at 6 s intervals and the movie has been accelarated (∼50×).
Stable minus-end-out microtubules in dendrites
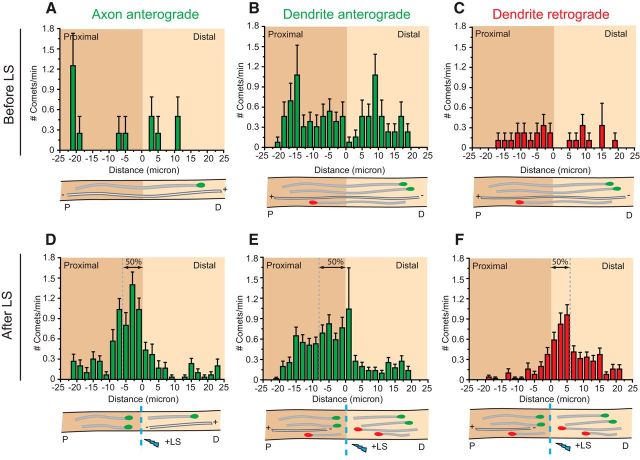
The increased fraction of plus-end-in comets during LS suggested that minus-end-out microtubules are either longer or less dynamic, both suggesting increased stability. To verify in more detail the difference in stability between plus- and minus-end-out microtubules, we analyzed the precise position of the new plus-end microtubules generated after LS. Cutting microtubules induces a quick depolymerization, followed by a rescue event and the formation of a new microtubule plus end from which we determine microtubule orientations. The positions from which new comets appear are a relative measurement of microtubule depolymerization before rescue and also reveal the resistance of a microtubule to depolymerization, allowing us to report on microtubule stability in different neuronal compartments. As stated above, using LS we cannot discriminate between different stable microtubule populations, such as nondynamic microtubules and long microtubules with a dynamic plus end. As expected, before LS, the GFP–MT+TIP comets are distributed randomly throughout the axon and dendrites in cultured hippocampal neurons at DIV15 (Fig. 5A–C). The newly formed comets after cutting axonal microtubules start at 0–10 μm proximal to the cut site, with a median at 5.7 μm (Fig. 5D). Similar to stable axonal microtubules, newly formed retrograde comets in dendrites are concentrated in close proximity to the LS position (median at 5.7 μm; Fig. 5F). However, the newly formed anterograde comets in dendrites start at a greater distance from the cut site (median at 7.9 μm; Fig. 5E), which is indicative of increased microtubule depolymerization caused by less stable anterograde microtubules in dendrites. These results suggest that the minus-end-out microtubules in dendrites exhibit similar stability as axonal microtubules and the plus-end-out microtubules in dendrites are relatively less stable.
Figure 5.
Dendrites contain stable minus-end-out microtubules. A–C, Histograms of anterograde comet starting positions in axons (A) and dendritic middle region (B) before LS in green and retrograde comet starting positions in red (C). D–F, Histograms of anterograde comet starting positions in axons (D) and dendritic middle region (E) after LS in green and retrograde comet starting positions in red (F). Below the histograms are schematic representations of comets going anterograde (green) and retrograde (red). Error bars indicate SEM.
Minus-end-out microtubules are present in neurites before neuronal polarization
Previous EM studies have suggested that the mixed microtubule organization in dendrites appears after axon initiation and neuronal polarization (Baas et al., 1989). Because we found minus-end-out microtubules in DIV2 neurons (Fig. 2M,N), we next studied at which neurodevelopmental stage mixed microtubule polarity is established. Therefore, we extended our study to stage 2 (nonpolarized cells with only neurites) and stage 3 (neurons with an extended axon and minor neurites, which later will differentiate into dendrites; Dotti et al., 1988). Cortical neurons were nucleofected directly after dissociation with GFP–MT+TIP, and microtubule growth dynamics was imaged 18–24 h after transfection before and after LS (Fig. 6A–E). Analysis of the growth direction of GFP–MT+TIP comets revealed that mixed polarity microtubules are already present in neurites before neuronal polarization. Although most comets moved outward, we observed ∼10% of dynamic minus-end-out microtubules in the neurites of stage 2 neurons, which increased approximately twofold after LS (Fig. 6G,H). Similar dynamic effects were found in minor neurites of stage 3 neurons (Fig. 6G,H). However, the ∼10% minus-end-out microtubules in axons were unaffected by LS, demonstrating that all axonal minus-end-out microtubules are dynamic in stage 3 neurons. These results suggest that the stable minus-end-out microtubule population, present in the neurites in nonpolarized cells, is lost from the axon directly after neuronal polarization.
Figure 6.
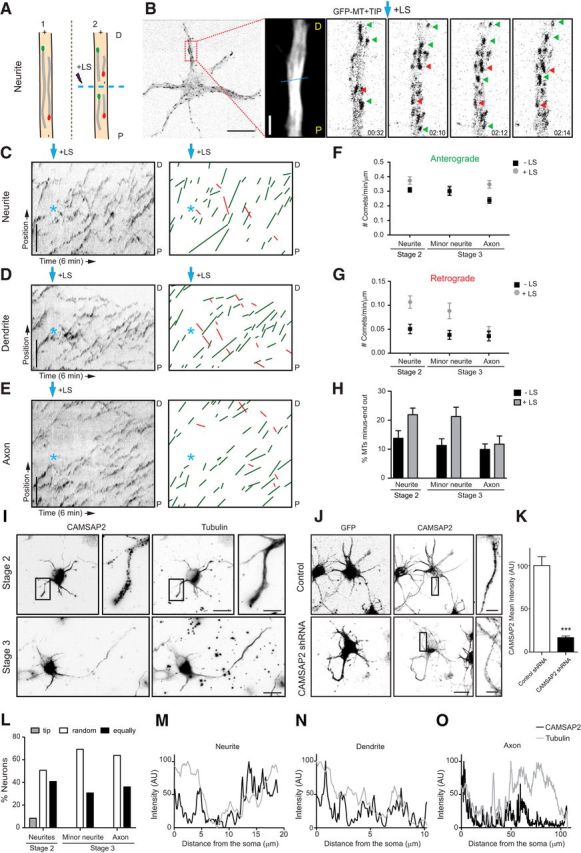
Microtubule orientation in neurons before and after polarization. A, Schematic representation of the microtubule LS procedure in a neurite. P indicates the proximal region and D the distal region. B, A representative DIV1 cortical neuron expressing GFP–MT+TIP, followed by the maximum projection and stills from a time-lapse recording of the indicated neurite. The dashed cyan line represents the region of LS, and the cyan arrow indicates the moment of laser severing. Green and red arrows mark selected plus- and minus-end-out microtubules, respectively. C–E, Kymographs and illustration of microtubule tracings from representative time-lapse recordings of a neurite (C) from a nonpolarized neuron, dendrite (D), and axon (E) of a polarized neuron. Green lines represent plus-end-out microtubules and red lines minus-end-out microtubules. Cyan asterisk and arrow indicate time and location of LS. F, G, Quantification of anterograde (F) and retrograde (G) growing GFP–MT+TIP comets, with and without LS (n = 10–18 neurons) in DIV1 cortical neurons. H, Percentage of microtubules with their minus ends out in unpolarized and polarized DIV1 neurons, before (black columns) and after (gray columns) LS; n = 10–18 neurons. I, Representative images of nonpolarized (top) and polarized (bottom) DIV1 hippocampal neurons stained for both CAMSAP2 (left; I, L) and α-tubulin (right). J, Representative images of stage 2 neurons transfected with GFP and control pSuper (top) or CAMSAP2 shRNA (bottom) and stained for both GFP (left) and CAMSAP2 (right). K, Quantification of CAMSAP2 intensity in neurites in control and CAMSAP2 shRNA transfected neurons (n = 19 neurites). ***p < 0.001 using t test. L, Quantification of CAMSAP2 localization in hippocampal neurons before and after polarization (n > 100 neurites). CAMSAP2 distribution within the neurites is classified in indicated categories. M–O, Representative examples of endogenous CAMSAP2 intensity profiles in neurites (M), before polarization, dendrites (N), and axons (O) from DIV1 hippocampal neurons. Scale bars: B, 2 and 10 μm; C–E, I, J, 5 μm; I, J, 20 μm. Error bars indicate SEM.
Because CAMSAP2 binds and stabilizes minus ends of non-centrosomal microtubules and is essential for neuronal polarization (Yau et al., 2014), we next determined the precise localization of CAMSAP2 in neurons before and after axon outgrowth (Fig. 6I). A variety of small CAMSAP2 clusters and distinct (punctated) stretches were scattered throughout the neurites in developing neurons (Fig. 6I–M). Knocking down of CAMSAP2 using previously published shRNAs (Yau et al., 2014) strongly decreased the antibody signal in stage 2 neurons (Fig. 6J,K), confirming the specificity of the CAMSAP2 staining in neurites. Interestingly, in nonpolarized neurons, we observed that CAMSAP2 stretches were enriched at some of the neurite tips (Fig. 6I–M), suggesting that CAMSAP2 may be involved in setting up minus-end-out microtubules in neurites. At later stages of development, CAMSAP2 was found along the axon and minor neurites (Fig. 6I–O). Together, our results demonstrate that the mixed microtubule organizations are present in neurites of nonpolarized cells and that stable uniform plus-end-out microtubules are formed during the early steps of axon polarization.
Taxol-induced axonal processes contain uniform plus-end-out microtubules
Our data suggest that the selective formation of uniform plus-end-out microtubules occurs during axon polarization. To further evaluate microtubule changes during neuronal polarization, we used the microtubule-stabilizing drug taxol to induce the formation of multiple axons in cultured neurons (Witte et al., 2008) and analyzed the orientation of microtubules in newly formed axonal processes. In the presence of low concentrations of taxol (10 nm) for 3 d, the number of Tau-positive processes per cell was increased more than fourfold compared with control neurons (Fig. 7A–D). Next, neurons were treated with taxol at DIV1 and transfected with GFP–MT+TIP at DIV3, and microtubule growth was analyzed before and after LS at DIV4 (Fig. 7D–F). Consistent with our analysis in DIV2 and DIV8 neurons (Fig. 2E–G,L,M), in nontreated cultures, GFP–MT+TIP comets in dendrites showed both anterograde and retrograde displacements, whereas in axons mainly anterograde moving comets were observed (Fig. 7D–I). In the axon-like processes after taxol treatment, the majority of GFP–MT+TIP comets showed anterograde displacement and almost no retrograde comets were observed, both before and after LS (Fig. 7G,H). Quantification revealed that only a few microtubules remain oriented minus-end-out in taxol-treated neurons, whereas the large majority of microtubules stay plus-end-out (Fig. 7I), very similar to what we found in axons of control cells at the various developmental stages (Fig. 2E–G). These data show that taxol nearly completely abolishes retrograde microtubules in the newly induced axonal processes. Thus, in addition to microtubule stabilization (Witte et al., 2008), the axon-inducing effect of taxol appears to be linked to the selective formation of uniform plus-end-out microtubules.
Figure 7.
Microtubule orientation changes in neurons after taxol treatment. A, B, Representative examples of DIV4 neurons treated for 72 h with DMSO (A) or 10 nm taxol (B) and stained for both Tau (left) and βΙΙΙ-tubulin (right). C, Quantification of Tau-positive neurites in control and taxol-treated neurons. Neurons treated with taxol showed a significant increase in the number of Tau-positive neurites (***p < 0.001 using t test). D, Schematic representation of the microtubule LS procedure in an axon, after taxol treatment. P indicates the proximal region and D the distal region. E, Maximum projection and stills from a representative time-lapse recording of a hippocampal neuron expressing GFP–MT+TIP and treated with taxol for 72 h. F, Kymographs and schematic tracings from a representative time-lapse recording of an axon after taxol treatment. Green lines represent plus-end-out microtubules and red lines minus-end-out microtubules. Cyan asterisk and arrow indicate time and location of LS. G, H, Quantification of GFP–MT+TIP moving anterograde (G) and retrograde (H), with (black squares) and without (gray circles) LS in DIV4 hippocampal neurons treated with DMSO or 10 nm taxol for 72 h. I, Percentage of minus-ends-out microtubules in control and taxol-treated neurons, before (black columns) and after (gray columns) LS. n = 14 axons and 31 dendrites in control neurons, and n = 27 axons after taxol treatment (>3 axons analyzed per neuron). Scale bars: A, B, 50 μm; E, F, 5 μm. Error bars indicate SEM.
Discussion
It is well known that the microtubule organization is different in axons and dendrites and has direct implications for neuronal cargo transport (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2011; Rolls, 2011). In axons, microtubules are typically arranged with their plus ends outward, whereas in dendrites, a mixed microtubule polarity is observed in mammalian neurons (Baas and Lin, 2011). Previous studies have reported unipolar microtubule arrays in apical dendrites from acute hippocampal slices using second-harmonic generation microscopy (Dombeck et al., 2003; Kwan et al., 2008) and demonstrated a predominantly microtubule minus-end-out orientation in dendrites of invertebrate neurons (Stone et al., 2008; Goodwin et al., 2012; Maniar et al., 2012). These findings motivated us to systematically analyze and compare neuronal microtubule dynamics in various mouse and rat model systems.
Microtubule orientations are approximately equally mixed throughout the dendrites
So far, most studies on neuronal microtubule organization focused on primary cultured neurons. Here, we presented a comprehensive study on mammalian in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo model systems that was based on fluorescent microscopic imaging of the growing microtubule plus ends. We found that dendrites in organotypic slice cultures and in the cortex of living mice possess a slight decrease in the number of dynamic microtubule plus ends and growth speed compared with neuron cultures. However, the ratio of dynamic plus-end-out microtubules (2:3) and plus-end-in microtubules (1:3) in dendrites is a constant factor in various model systems. After LS of microtubules, we found an approximately equal ratio (1:1) of plus-end-out and plus-end-in microtubule organization in dendrites. Our findings are in agreement with early EM data obtained by the hook-decoration technique of olfactory bulb mitral cells, in which the mixed microtubule pattern remained constant throughout the entire dendrite (Burton, 1988). However, our data are inconsistent with early EM results in dendrites of hippocampal neurons, which were reported to contain uniform plus-end-out microtubule arrays in distal dendritic parts (Baas et al., 1988, 1989). Importantly, we did observe a great variation in microtubule orientations in some of the dendrites (Fig. 4F). Therefore, it is possible that, because of the low number of dendrites (n = 3 for the position dependent orientations) used in the original EM analysis (Baas et al., 1988, 1989), a sampling bias may have occurred and that the reported dendrites are not representative of the general population. Alternatively, because the distal regions of dendrites are similar in size and diameter to axons (Baas et al., 1988, 1989), identification of distal dendrites in EM samples on size measurements only is challenging and may not be a reliable method.
Although mature Drosophila neurons have dendrites that contain minus-end-out microtubules, it is also important to note that developing Drosophila dendrites initially contain mixed microtubule polarity (Hill et al., 2012). Over a period of several days, this mixed microtubule array gradually matures to a minus-end-out array. In this study, we show in different neuronal cell types from distinct mammalian model systems that microtubules in mature dendrites remain in an antiparallel organization. Thus, it is now clear that dendrites of Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans neurons have a different organization of microtubules. Why mature mammalian dendrites still have plus-end-out microtubules and do not completely switch to minus-end-out polarity, like in Drosophila dendrites, remains an open question. Having opposite polarity microtubules in dendrites may increase the efficiency of polarized transport by coordinating the activity of both dynein and specific kinesin family members.
Differential stabilities of specific microtubule orientations in axons and dendrites
Our results demonstrate that the majority of axonal microtubules are stable and orientated with their plus-end-out during different stages of neuronal development, which is consistent with previous reports (Baas et al., 1991; Kollins et al., 2009). The data also show a marked difference in the stability of anterograde and retrograde directed microtubules in dendrites. Our approach of combining live imaging with LS of microtubules allowed us to quantitatively discriminate between stable and dynamic microtubules. Based on these data, we can distinguish at least three stages of microtubule organization in dendrites. (1) Growing dendrites in young neurons (DIV2) have a 1:4 ratio of plus-end-in/out microtubule orientations, with stable minus-end-out microtubules and dynamic microtubules plus-end-out. (2) Although there are more dynamic plus-end-out microtubules, overall dendrites in developing neurons (DIV8–DIV15) have an almost 1:1 ratio of microtubule orientations. (3) Dendrites in mature neurons (DIV22–DIV61 and slice cultures) contain slightly more stable plus-end-out microtubules, but the equal ratio of mixed microtubule orientations is unaffected. Microtubule stability in neurons is related to many different parameters (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2015) and most likely depends on the combined action of many microtubule regulatory proteins, such as plus-end tracking proteins and minus-end targeting proteins (Akhmanova and Steinmetz, 2008; Akhmanova and Hoogenraad, 2015), microtubule-associated proteins (Dehmelt and Halpain, 2005; Subramanian and Kapoor, 2012), enzymes that sever preexisting microtubules (Roll-Mecak and McNally, 2010; Sharp and Ross, 2012), and tubulin-modifying enzymes that through posttranslational modifications can regulate microtubule stability (Janke and Kneussel, 2010). Future studies should focus on the mechanisms responsible for setting up and selectively stabilizing minus-end-out microtubules during dendrite development.
Mixed microtubules are present in neurites before neuronal polarization
Using the same hook-decoration technique, it was found that, in nonpolarized cells, the microtubule orientation in the newly formed neurites was plus-end-out and that only after axon initiation and neuronal polarization minus-end-out microtubules appeared in dendritic processes (Baas et al., 1989). The EM data suggested that formation of mixed microtubule organization is important for differentiation into dendrites and establishing neuronal polarity (Baas and Lin, 2011). However, this model has never been tested in living neurons at early stages of development. Our results reveal that mixed polarity microtubules are already present in neurites before the neuron becomes polarized. We found that nonpolarized neurons contain ∼20% minus-end-out microtubules in their neurites. At stage 3 neurons, directly after axon outgrowth, the polarity orientation of microtubules in axons changed: 10% of the axonal microtubules are oriented minus-end-out, whereas 20% of the minor neurites microtubules remain minus-end-out. Taxol treatments confirmed this observation and also showed a marked reduction of retrograde microtubules in newly induced axonal processes. At later stages of development, the difference in microtubule orientation in axons and dendrites is even more extreme: almost all minus-end-out microtubules in the axon disappear and minus-end-out microtubules in dendrites increase up to ∼45%. These different microtubule orientations have been shown to facilitate polarized cargo trafficking in mature neurons (Kapitein and Hoogenraad, 2011; Rolls, 2011). For instance, uniform plus-end-out microtubules in axons facilitate the selective sorting of kinesin-driven vesicles, whereas minus-end-out microtubules allow dynein motors to drive specific cargo to dendrites (Nakata and Hirokawa, 2003; Kapitein et al., 2010b). Importantly, a recent study argued against a contribution of dynein to dendrite-specific transport because selective (non-axonal) transport was observed already in stage 3, during which microtubule orientations were long believed to be uniformly plus-end-out (Petersen et al., 2014). However, in this study, we show the following: (1) nonpolarized stage 2 neurons already contain a significant number of minus-end-out microtubules in their neurites, allowing for dynein-based transport at all developmental stages; and (2) axons reduce the number of stable minus-end-out microtubules in stage 3 neurons by ∼50%, allowing dynein motors to exclude dendritic cargos from the axon and drive polarized cargo transport into future dendrites.
The observation that neurites in nonpolarized neurons contain a mixed population of microtubules raises several other questions. First, how are minus-end-out microtubules generated in these newly growing neurites? It is possible that microtubules are (1) nucleated at the centrosome, subsequently released, and transported into the neurites, (2) severed by local katanin or spastin activity, or (3) nucleated at noncentrosomal sites, such as Golgi membranes, local γ-tubulin complexes, or from preexisting microtubules (Kuijpers and Hoogenraad, 2011). In addition, several motor proteins have been reported to contribute to the establishment or maintenance of the minus-end-out microtubule organizations in dendrites. For instance, depletion of kinesin-5 increases the proportion of dynamic minus-end-out microtubules in neurons, whereas downregulation of kinesin-6 or kinesin-12 reduces the number of retrograde microtubules in dendrites (Lin et al., 2012; Kahn et al., 2015). Moreover, kinesin-1 and kinesin-2 have been reported to establish the uniform minus-end-out microtubules in C. elegans and Drosophila, respectively (Mattie et al., 2010; Yan et al., 2013). Second, how are uniform plus-end-out microtubules formed in axons? It is likely that axons eliminate their minus-end-out microtubules. Retrograde axonal microtubules may be specifically depolymerized, selectively destabilized, or actively severed. Interestingly, it has been demonstrated that Tau can regulate microtubule severing via controlling spastin and katanin activity (Yu et al., 2008; Zempel et al., 2013). Alternatively, it is possible that axons selectively stabilize their plus-end-out microtubules. Microtubule stabilization in axons is consistent with previous reports in which high levels of acetylated tubulin and stable axonal microtubules are observed in stage 3 neurons (Witte et al., 2008). Most importantly, it has been shown that local stabilization of microtubules using a photoactivatable analog of the microtubule-stabilizing drug taxol induces axon formation in unpolarized neurons (Witte et al., 2008). Consistently, we found that treatment of cultured neurons with low doses of taxol generates uniform plus-end-out microtubules by reducing the number of retrograde microtubules in the newly formed axonal processes. We propose a model in which the selective formation of uniform plus-end-out microtubules in the axon is a critical processes underlying neuronal polarization. A major challenge for future research is to determine the multiple molecular players that associate with the microtubule cytoskeleton and directly control selective microtubule organization, stabilization, and remodeling to drive axon formation and neuronal polarization.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO-ALW-VICI; C.C.H.; NWO-ALW-VIDI; L.C.K.), the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development (ZonMW-TOP; C.C.H.), the European Science Foundation (ESF-EURYI; C.C.H.), the European Research Council (ERC-StG; L.C.K.), Swiss National Science Foundation Grant 31003A_135631 (A.H.), the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) SYNAPSY financed by Swiss National Science Foundation Grant 51AU40_125759 (A.H., S.P.), the International Foundation for Research on Paraplegia (A.H.), and the Hans Wilsdorf Foundation (A.H., S.P.). P.S. is supported by an FP7 European Union Marie Curie postdoctoral fellowship and a fellowship of the Swiss National Science Foundation. E.T. received support by the Spanish Education Ministry and a FP7 European Union Marie Curie postdoctoral fellowship. We thank Dr. Akhmanova for helpful discussions and Phebe Wulf for help with cloning constructs. We are grateful to Dr. Didier Trono and Dr. Isabel Bade for providing pSIN-TRE-mSEAP-hPGK-rtTA2sM2 lentivirus vector.
References
- Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC. Microtubule minus-end-targeting proteins. Curr Biol. 2015;25:R162–R171. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:309–322. doi: 10.1038/nrm2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas PW, Lin S. Hooks and comets: the story of microtubule polarity orientation in the neuron. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71:403–418. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas PW, White LA, Heidemann SR. Microtubule polarity reversal accompanies regrowth of amputated neurites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:5272–5276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas PW, Deitch JS, Black MM, Banker GA. Polarity orientation of microtubules in hippocampal neurons: uniformity in the axon and nonuniformity in the dendrite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85:8335–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas PW, Black MM, Banker GA. Changes in microtubule polarity orientation during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989;109:3085–3094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas PW, Slaughter T, Brown A, Black MM. Microtubule dynamics in axons and dendrites. J Neurosci Res. 1991;30:134–153. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490300115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botvinick EL, Venugopalan V, Shah JV, Liaw LH, Berns MW. Controlled ablation of microtubules using a picosecond laser. Biophys J. 2004;87:4203–4212. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.049528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton PR. Dendrites of mitral cell neurons contain microtubules of opposite polarity. Brain Res. 1988;473:107–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cane M, Maco B, Knott G, Holtmaat A. The relationship between PSD-95 clustering and spine stability in vivo. J Neurosci. 2014;34:2075–2086. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3353-13.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombelli J, Reynaud EG, Rietdorf J, Pepperkok R, Stelzer EH. In vivo selective cytoskeleton dynamics quantification in interphase cells induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser nanosurgery. Traffic. 2005;6:1093–1102. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde C, Cáceres A. Microtubule assembly, organization and dynamics in axons and dendrites. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:319–332. doi: 10.1038/nrn2631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehmelt L, Halpain S. The MAP2/Tau family of microtubule-associated proteins. Genome Biol. 2005;6:204. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-6-1-204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paola V, Arber S, Caroni P. AMPA receptors regulate dynamic equilibrium of presynaptic terminals in mature hippocampal networks. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:491–500. doi: 10.1038/nn1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombeck DA, Kasischke KA, Vishwasrao HD, Ingelsson M, Hyman BT, Webb WW. Uniform polarity microtubule assemblies imaged in native brain tissue by second-harmonic generation microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:7081–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0731953100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotti CG, Sullivan CA, Banker GA. The establishment of polarity by hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1988;8:1454–1468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01454.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin PR, Sasaki JM, Juo P. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulates the polarized trafficking of neuropeptide-containing dense-core vesicles in Caenorhabditis elegans motor neurons. J Neurosci. 2012;32:8158–8172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0251-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond JW, Huang CF, Kaech S, Jacobson C, Banker G, Verhey KJ. Posttranslational modifications of tubulin and the polarized transport of kinesin-1 in neurons. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:572–583. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-01-0044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill SE, Parmar M, Gheres KW, Guignet MA, Huang Y, Jackson FR, Rolls MM. Development of dendrite polarity in Drosophila neurons. Neural Dev. 2012;7:34. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N, Niwa S, Tanaka Y. Molecular motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease. Neuron. 2010;68:610–638. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honnappa S, Gouveia SM, Weisbrich A, Damberger FF, Bhavesh NS, Jawhari H, Grigoriev I, van Rijssel FJ, Buey RM, Lawera A, Jelesarov I, Winkler FK, Wüthrich K, Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. An EB1-binding motif acts as a microtubule tip localization signal. Cell. 2009;138:366–376. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang CF, Banker G. The translocation selectivity of the kinesins that mediate neuronal organelle transport. Traffic. 2012;13:549–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke C, Kneussel M. Tubulin post-translational modifications: encoding functions on the neuronal microtubule cytoskeleton. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:362–372. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski J, Kapitein LC, Gouveia SM, Dortland BR, Wulf PS, Grigoriev I, Camera P, Spangler SA, Di Stefano P, Demmers J, Krugers H, Defilippi P, Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC. Dynamic microtubules regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 2009;61:85–100. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn OI, Sharma V, González-Billault C, Baas PW. Effects of kinesin-5 inhibition on dendritic architecture and microtubule organization. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:66–77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-08-1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC. Which way to go? Cytoskeletal organization and polarized transport in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011;46:9–20. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC. Building the neuronal microtubule cytoskeleton. Neuron. 2015;87:492–506. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.05.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitein LC, Schlager MA, van der Zwan WA, Wulf PS, Keijzer N, Hoogenraad CC. Probing intracellular motor protein activity using an inducible cargo trafficking assay. Biophys J. 2010a;99:2143–2152. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.07.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitein LC, Schlager MA, Kuijpers M, Wulf PS, van Spronsen M, MacKintosh FC, Hoogenraad CC. Mixed microtubules steer dynein-driven cargo transport into dendrites. Curr Biol. 2010b;20:290–299. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitein LC, Yau KW, Gouveia SM, van der Zwan WA, Wulf PS, Keijzer N, Demmers J, Jaworski J, Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC. NMDA receptor activation suppresses microtubule growth and spine entry. J Neurosci. 2011;31:8194–8209. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6215-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleele T, Marinković P, Williams PR, Stern S, Weigand EE, Engerer P, Naumann R, Hartmann J, Karl RM, Bradke F, Bishop D, Herms J, Konnerth A, Kerschensteiner M, Godinho L, Misgeld T. An assay to image neuronal microtubule dynamics in mice. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4827. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollins KM, Bell RL, Butts M, Withers GS. Dendrites differ from axons in patterns of microtubule stability and polymerization during development. Neural Dev. 2009;4:26. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-4-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers M, Hoogenraad CC. Centrosomes, microtubules and neuronal development. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011;48:349–358. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan AC, Dombeck DA, Webb WW. Polarized microtubule arrays in apical dendrites and axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:11370–11375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805199105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S, Liu M, Mozgova OI, Yu W, Baas PW. Mitotic motors coregulate microtubule patterns in axons and dendrites. J Neurosci. 2012;32:14033–14049. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3070-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maday S, Twelvetrees AE, Moughamian AJ, Holzbaur EL. Axonal transport: cargo-specific mechanisms of motility and regulation. Neuron. 2014;84:292–309. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.10.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniar TA, Kaplan M, Wang GJ, Shen K, Wei L, Shaw JE, Koushika SP, Bargmann CI. UNC-33 (CRMP) and ankyrin organize microtubules and localize kinesin to polarize axon-dendrite sorting. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:48–56. doi: 10.1038/nn.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie FJ, Stackpole MM, Stone MC, Clippard JR, Rudnick DA, Qiu Y, Tao J, Allender DL, Parmar M, Rolls MM. Directed microtubule growth, +TIPs, and kinesin-2 are required for uniform microtubule polarity in dendrites. Curr Biol. 2010;20:2169–2177. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T, Hirokawa N. Microtubules provide directional cues for polarized axonal transport through interaction with kinesin motor head. J Cell Biol. 2003;162:1045–1055. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200302175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T, Niwa S, Okada Y, Perez F, Hirokawa N. Preferential binding of a kinesin-1 motor to GTP-tubulin-rich microtubules underlies polarized vesicle transport. J Cell Biol. 2011;194:245–255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201104034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès S, Cane M, Randall J, Capello L, Holtmaat A. Single cell electroporation for longitudinal imaging of synaptic structure and function in the adult mouse neocortex in vivo. Front Neuroanat. 2015;9:36. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen JD, Kaech S, Banker G. Selective microtubule-based transport of dendritic membrane proteins arises in concert with axon specification. J Neurosci. 2014;34:4135–4147. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3779-13.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roll-Mecak A, McNally FJ. Microtubule-severing enzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolls MM. Neuronal polarity in Drosophila: sorting out axons and dendrites. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71:419–429. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp DJ, Ross JL. Microtubule-severing enzymes at the cutting edge. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:2561–2569. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepanova T, Slemmer J, Hoogenraad CC, Lansbergen G, Dortland B, De Zeeuw CI, Grosveld F, van Cappellen G, Akhmanova A, Galjart N. Visualization of microtubule growth in cultured neurons via the use of EB3-GFP (end-binding protein 3-green fluorescent protein) J Neurosci. 2003;23:2655–2664. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02655.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone MC, Roegiers F, Rolls MM. Microtubules have opposite orientation in axons and dendrites of Drosophila neurons. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:4122–4129. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-10-1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 1991;37:173–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90128-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian R, Kapoor TM. Building complexity: insights into self-organized assembly of microtubule-based architectures. Dev Cell. 2012;23:874–885. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte H, Neukirchen D, Bradke F. Microtubule stabilization specifies initial neuronal polarization. J Cell Biol. 2008;180:619–632. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200707042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan J, Chao DL, Toba S, Koyasako K, Yasunaga T, Hirotsune S, Shen K. Kinesin-1 regulates dendrite microtubule polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans. eLife. 2013;2:e00133. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau KW, van Beuningen SF, Cunha-Ferreira I, Cloin BM, van Battum EY, Will L, Schätzle P, Tas RP, van Krugten J, Katrukha EA, Jiang K, Wulf PS, Mikhaylova M, Harterink M, Pasterkamp RJ, Akhmanova A, Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC. Microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP2 controls axon specification and dendrite development. Neuron. 2014;82:1058–1073. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W, Qiang L, Solowska JM, Karabay A, Korulu S, Baas PW. The microtubule-severing proteins spastin and katanin participate differently in the formation of axonal branches. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:1485–1498. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-09-0878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zempel H, Luedtke J, Kumar Y, Biernat J, Dawson H, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM. Amyloid-beta oligomers induce synaptic damage via Tau-dependent microtubule severing by TTLL6 and spastin. EMBO J. 2013;32:2920–2937. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Mixed dendritic microtubule organization in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. GFP-MT+TIP comets were imaged in middle dendritic regions of a dissociated neuron culture (left), organotypic slice culture (middle), and mouse neocortex (right). All dendrites show anterograde and retrograde displacement of the comets. The scale bar is applicable for all recordings. Frame rates were adjusted in order to compensate for acquisition at different time intervals (dissociated neurons = 4 s; slice cultures = 6 s; in vivo = 5 s intervals). GFP-MT+TIP signals were corrected for bleaching and convoluted to enhance signal to noise. The movie has been accelerated (40×).
Bidirectional microtubules are found in all dendritic regions. Lentivirus-infected organotypic slice cultures were imaged in proximal (top), middle (middle), and distal (bottom) dendritic regions. Left columns show live recordings of the volume marker channel and right columns the corresponding GFP-MT+TIP channel. Anterograde and retrograde moving comets are observable in all three dendritic regions at different ratios. Time-lapse images were acquired at 6 s intervals and the movie has been accelarated (∼50×).