Abstract
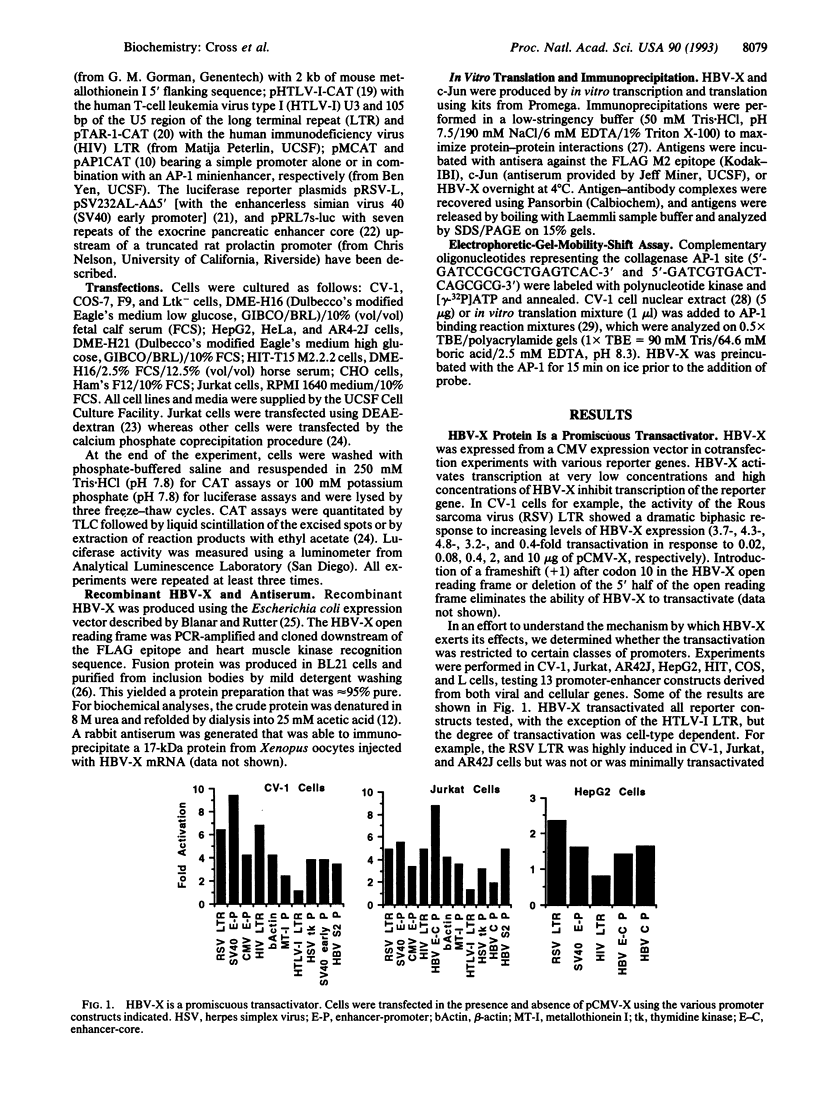
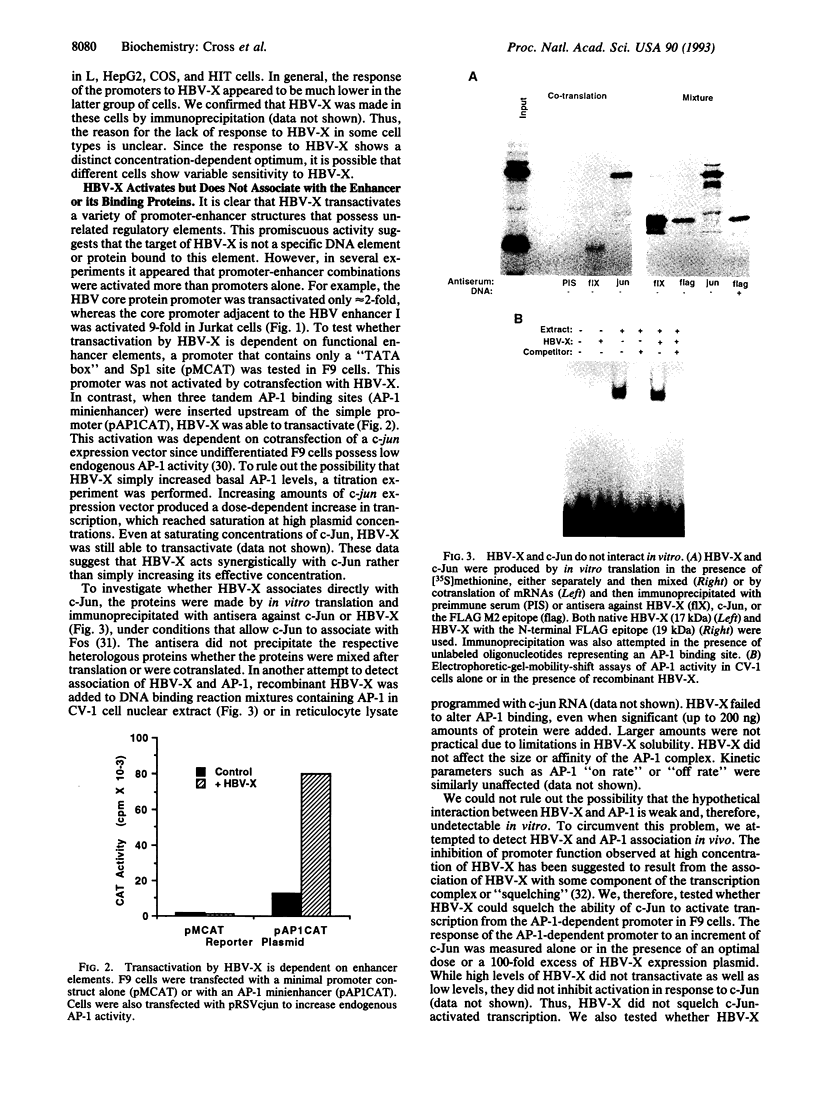
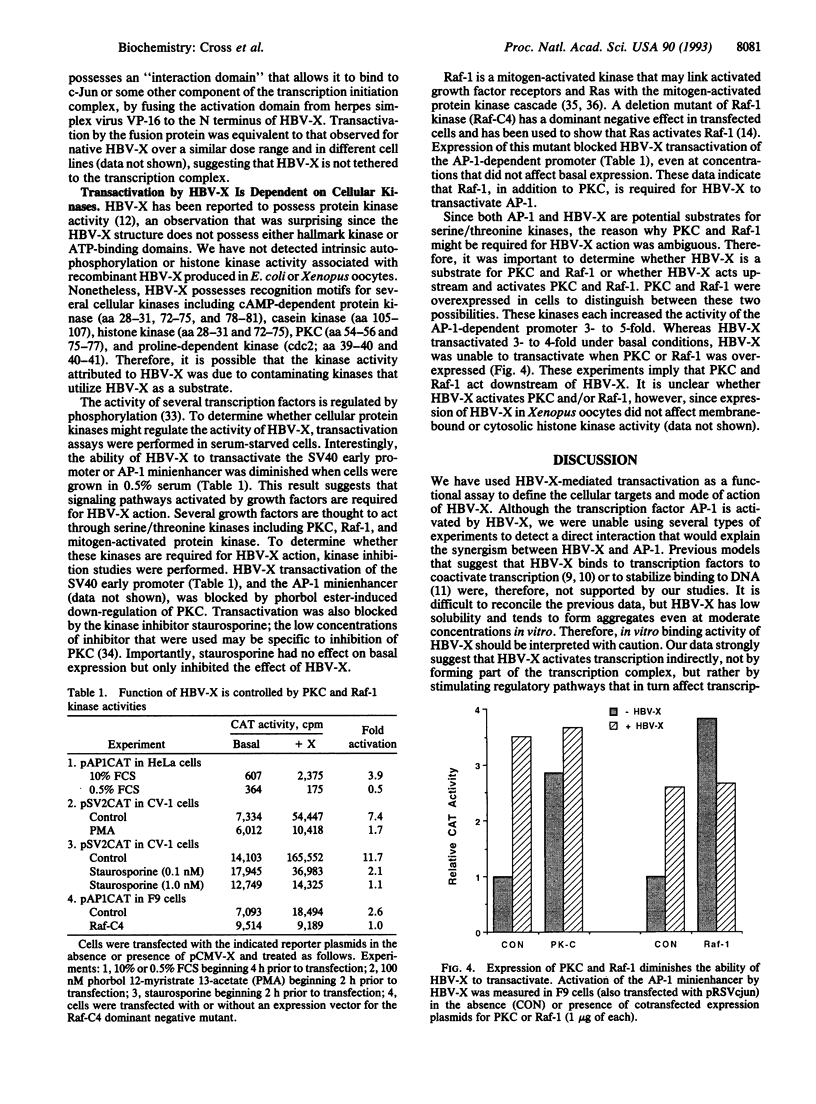
The X protein of hepatitis B virus (HBV-X) can act as a transactivator of transcription but its mechanism of action remains obscure. We have analyzed HBV-X transactivation in several cell types using 13 unrelated viral and cellular promoters and found that transactivation is more or less apparent in most cell types and is promiscuous and unrelated to specific sequence motifs within the target promoters. In general, though, HBV-X appears to act on enhancer elements since HBV-X had no effect on a minimal promoter, whereas HBV-X was able to transactivate after insertion of an AP-1 minienhancer. Several lines of evidence exclude the possibility that HBV-X interacts directly with the AP-1 enhancer or its binding proteins and suggest that the proximal target of HBV-X is peripheral to the transcription complex. This hypothesis is supported by the observation that inhibition of serine/threonine kinases, which regulate AP-1 activity (phorbol ester down-regulation or staurosporine inhibition of protein kinase C and a dominant negative mutant of Raf-1), blocked the ability of HBV-X to transactivate without affecting basal promoter activity. Furthermore, basal transcription from the AP-1-dependent promoter was increased by overexpression of protein kinase C and Raf-1 but HBV-X was unable to further stimulate, indicating that these kinases act subsequently to HBV-X. These data suggest that transactivation by HBV-X is an indirect result of the activation of cellular serine/threonine kinases including protein kinase C and Raf-1. This mode of action implies that HBV-X may affect other cellular processes, besides transcription, that are regulated by these kinases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonucci T. K., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) promoters are regulated by the HBV enhancer in a tissue-specific manner. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):579–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.579-583.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R. Serum-, TPA-, and Ras-induced expression from Ap-1/Ets-driven promoters requires Raf-1 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):545–556. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekulé A. S., Lauer U., Weiss L., Luber B., Hofschneider P. H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBx uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):742–745. doi: 10.1038/361742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Koike K., Saito I., Miyamura T., Jay G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):317–320. doi: 10.1038/351317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucito R., Schneider R. J. Hepatitis B virus X protein activates transcription factor NF-kappa B without a requirement for protein kinase C. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.983-991.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megidish T., Mazurek N. A mutant protein kinase C that can transform fibroblasts. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):807–811. doi: 10.1038/342807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Weinrich S. L., Nelson C., Rutter W. J. The chymotrypsin enhancer core. Specific factor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20744–20751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. MAP kinases: charting the regulatory pathways. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1382311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R. Role of Raf-1 serine/threonine protein kinase in growth factor signal transduction. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schek N., Bartenschlager R., Kuhn C., Schaller H. Phosphorylation and rapid turnover of hepatitis B virus X-protein expressed in HepG2 cells from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1735–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Gaynor R., Srinivasan A., Mapoles J., Farr R. W. trans-activation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starksen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat responds to T-cell activation signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6845–6849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene can transactivate heterologous viral sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Shaul Y. The X protein of the hepatitis B virus acts as a transcription factor when targeted to its responsive element. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1889–1895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chiu R., Karin M. Elevation of AP1 activity during F9 cell differentiation is due to increased c-jun transcription. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):351–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





