Abstract
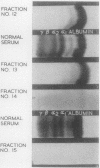
In view of the possible relationship to thrombosis the `anti-heparin' activity of blood protein fractions was studied. Serum and plasma were separated by continuous paper curtain electrophoresis and two different groups of fractions with anti-heparin activity found. One group was associated with the fast γ globulins and the other with the α globulins. The fast γ activity appeared to be identical with the contact activation product (activated factors XI and XII). The α globulin activity is different from any of the known serum clotting factors. This activity may be due to a previously unrecognized clotting factor or may be a coagulant property of certain blood proteins which act by binding heparin.
The clinical implications of these findings are discussed. It is suggested that the fast γ globulin anti-heparin fraction may be identical with Wessler's serum thrombotic accelerator and the α globulin activity is a separate entity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELL W. N., ALTON H. G. A brain extract as a substitute for platelet suspensions in the thromboplastin generation test. Nature. 1954 Nov 6;174(4436):880–881. doi: 10.1038/174880a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGGS R., DOUGLAS A. S. The thromboplastin generation test. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Feb;6(1):23–29. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNOR W. E., HOAK J. C., WARNER E. D. Massive thrombosis produced by fatty acid infusion. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jun;42:860–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI104778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONSDEN R., POWELL M. N. The use of borate buffer in paper electrophoresis of serum. J Clin Pathol. 1955 May;8(2):150–152. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENSON K. W. The specific assay of Prower-Stuart factor and factor VII. Acta Haematol. 1961 Feb;25:105–120. doi: 10.1159/000206523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P., RAPAPORT S. I., OWREN P. A. A simple, specific one-stage prothrombin assay using Russell's viper venom in cephalin suspension. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jul;46(1):89–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS J. H., WALTERS D., DIDISHEIM P., MERCHANT W. R. Application of continuous flow electrophoresis to the study of the blood coagulation proteins and the fibrinolytic enzyme system. I. Normal human materials. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1323–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI103721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLER L. A heparin-retarded plasma clotting test. Angiology. 1954 Feb;5(1):21–26. doi: 10.1177/000331975400500104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOULIER J. P., LE BOLLOCH A. G. The "in vitro" heparin tolerance test in the control of dicumarol therapy. Acta Med Scand. 1951 Jul 15;140(2):132–139. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1951.tb10163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S. Studies in intravascular coagulation. I. Coagulation changes in isolated venous segments. J Clin Invest. 1952 Nov;31(11):1011–1014. doi: 10.1172/JCI102685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh T. R., Ruddick D. W. A Test for Increased Coagulability of the Blood. Can Med Assoc J. 1944 Jun;50(6):547–549. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]