Abstract
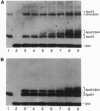
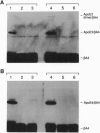
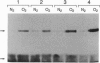
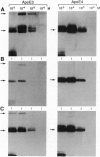
Apolipoprotein E (apoE), a plasma apolipoprotein that plays a central role in lipoprotein metabolism, is localized in the senile plaques, congophilic angiopathy, and neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease. Late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer disease patients have an increased frequency of one of the three common apoE alleles, epsilon 4, suggesting apoE4 is associated with increased susceptibility to disease. To follow up on this suggestion, we compared the binding of synthetic amyloid beta (beta/A4) peptide to purified apoE4 and apoE3, the most common isoform. Both isoforms bound synthetic beta/A4 peptide, the primary constituent of the plaque and angiopathy, forming a complex that resisted dissociation by boiling in SDS. Oxygen-mediated complex formation was implicated because binding was increased in oxygenated buffer, reduced in nitrogen-purged buffer, and prevented by reduction with dithiothreitol or 2-mercaptoethanol. Binding of beta/A4 peptide was saturable at 10(-4) M peptide and required residues 12-28. Examination of apoE fragments revealed that residues 244-272 are critical for complex formation. Both oxidized apoE4 and apoE3 bound beta/A4 peptide; however, binding to apoE4 was observed in minutes, whereas binding to apoE3 required hours. In addition, apoE4 did not bind beta/A4 peptide at pH < 6.6, whereas apoE3 bound beta/A4 peptide from pH 7.6 to 4.6. Together these results indicate differences in the two isoforms in complexing with the beta/A4 peptide. Binding of beta/A4 peptide by oxidized apoE may determine the sequestration or targeting of either apoE or beta/A4 peptide, and isoform-specific differences in apoE binding or oxidation may be involved in the pathogenesis of the intra- and extracellular lesions of Alzheimer disease.
Full text
PDF
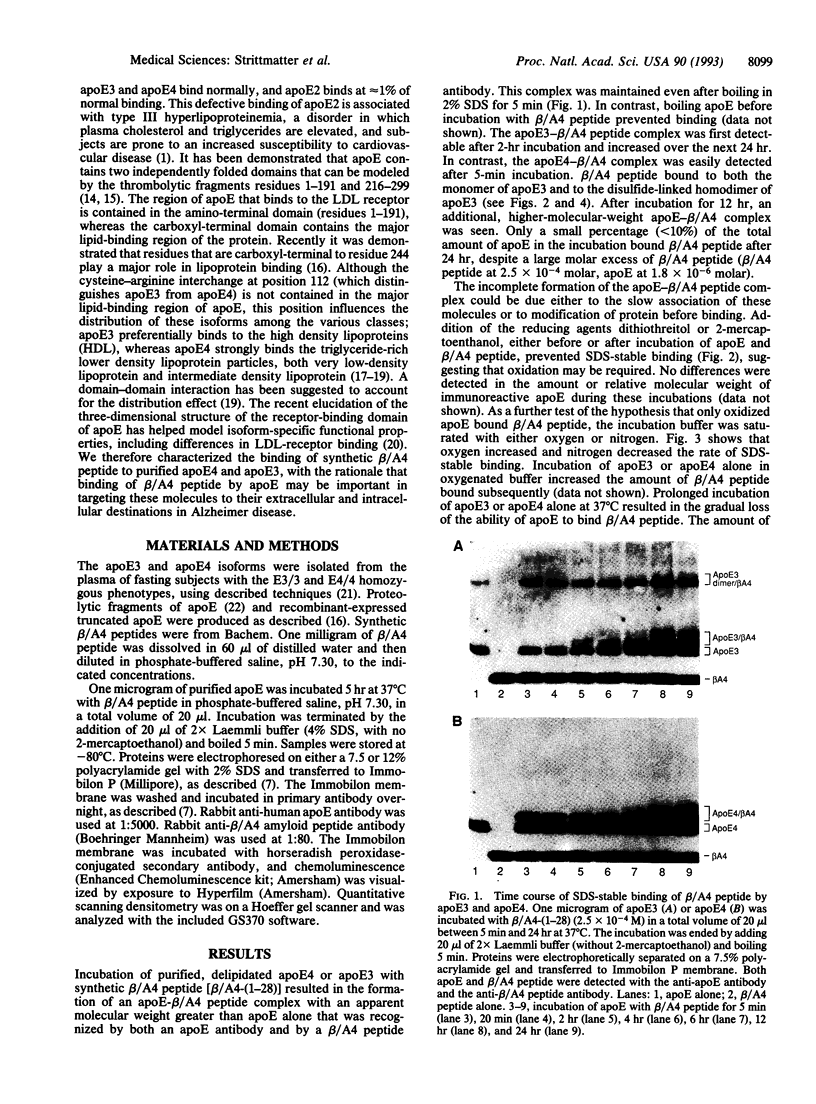
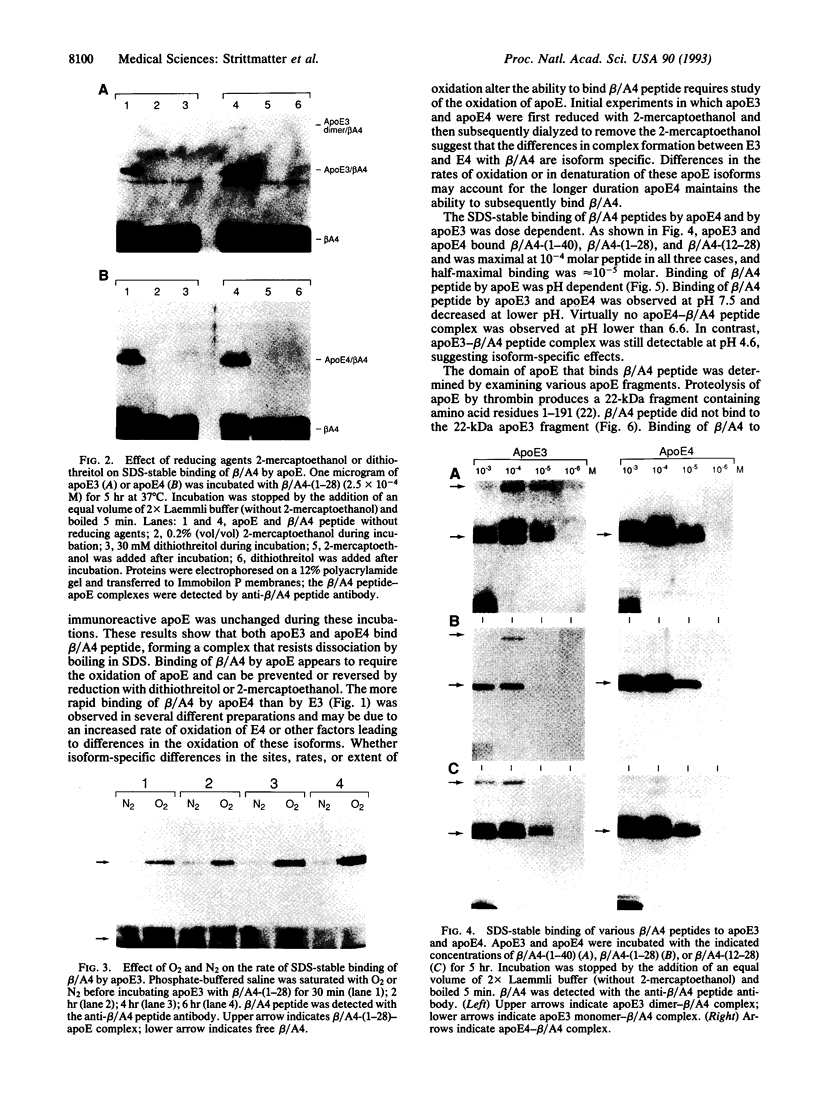


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck L. P., Wetterau J. R., Weisgraber K. H., Wu C. S., Lindgren F. T. Human apolipoprotein E3 in aqueous solution. II. Properties of the amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6249–6258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Hughes T. A., Iqbal M., Gawish A., Neame P. J., Medley M. F., Segrest J. P. Effect of oxidation on the properties of apolipoproteins A-I and A-II. J Lipid Res. 1988 Mar;29(3):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham K. B., Schickler M., Sapoznikov D., Yarom R., Groner Y. Down's syndrome: abnormal neuromuscular junction in tongue of transgenic mice with elevated levels of human Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyles J. K., Zoellner C. D., Anderson L. J., Kosik L. M., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Hui D. Y., Mahley R. W., Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Ignatius M. J. A role for apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein A-I, and low density lipoprotein receptors in cholesterol transport during regeneration and remyelination of the rat sciatic nerve. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1015–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI113943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Stone P. J., El Hag A., Calore J. D., Franzblau C. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed inactivation of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3348–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallongeville J., Lussier-Cacan S., Davignon J. Modulation of plasma triglyceride levels by apoE phenotype: a meta-analysis. J Lipid Res. 1992 Apr;33(4):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich J. F., Minnigan H., Carp R. I., Whitaker J. N., Race R., Frey W., 2nd, Haase A. T. Neuropathological changes in scrapie and Alzheimer's disease are associated with increased expression of apolipoprotein E and cathepsin D in astrocytes. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4759–4768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4759-4768.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Liao W. S., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Apolipoprotein E mRNA is abundant in the brain and adrenals, as well as in the liver, and is present in other peripheral tissues of rats and marmosets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):203–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein EBethesda: a new variant of apolipoprotein E associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):969–974. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelmann G. E., Boyles J. K., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Pitas R. E. Effects of apolipoprotein E, beta-very low density lipoproteins, and cholesterol on the extension of neurites by rabbit dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1992 Nov;33(11):1677–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignatius M. J., Gebicke-Härter P. J., Skene J. H., Schilling J. W., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Shooter E. M. Expression of apolipoprotein E during nerve degeneration and regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1125–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Friedlander E. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Binding of apolipoprotein E fragments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12341–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Travis J. The oxidative inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Further evidence for methionine at the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4022–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Bebout J. L., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Yamaoka L. H., Hung W. Y., Alberts M. J., Walker A. P., Bartlett R. J., Haynes C. A., Welsh K. A. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1034–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of apolipoprotein E. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:273–287. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Siddique T., Patterson D., Figlewicz D. A., Sapp P., Hentati A., Donaldson D., Goto J., O'Regan J. P., Deng H. X. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):59–62. doi: 10.1038/362059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Carney J. M., Starke-Reed P. E., Oliver C. N., Stadtman E. R., Floyd R. A., Markesbery W. R. Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10540–10543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes G. J., McGuire C. B., Norden J. J., Freeman J. A. Nerve injury stimulates the secretion of apolipoprotein E by nonneuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R. Protein oxidation and aging. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1220–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.1355616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A., Jakobs C., Motzny S., Kaffarnik H. Differential distribution of apolipoprotein E isoforms in human plasma lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):405–411. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Kawarabayasi Y., Nakai T., Sakai J., Yamamoto T. Rabbit very low density lipoprotein receptor: a low density lipoprotein receptor-like protein with distinct ligand specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9252–9256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E distribution among human plasma lipoproteins: role of the cysteine-arginine interchange at residue 112. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Apoprotein (E--A-II) complex of human plasma lipoproteins. I. Characterization of this mixed disulfide and its identification in a high density lipoprotein subfraction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6281–6288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Shinto L. H. Identification of the disulfide-linked homodimer of apolipoprotein E3 in plasma. Impact on receptor binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12029–12034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Aggerbeck L. P., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Human apolipoprotein E3 in aqueous solution. I. Evidence for two structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6240–6248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Agard D. A. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1817–1822. doi: 10.1126/science.2063194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein A., Walter M., Holz H., Benninghoven A., Assmann G. Site-specific methionine sulfoxide formation is the structural basis of chromatographic heterogeneity of apolipoproteins A-I, C-II, and C-III. J Lipid Res. 1991 Sep;32(9):1465–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]