Abstract
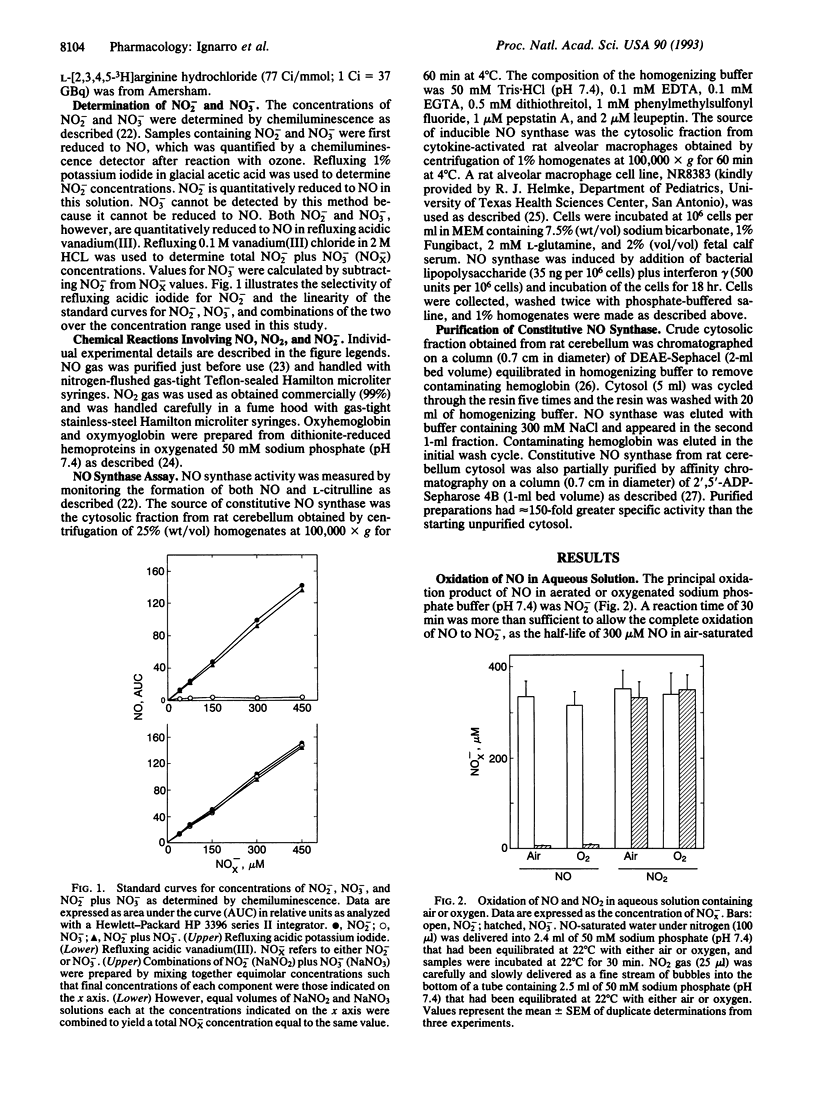
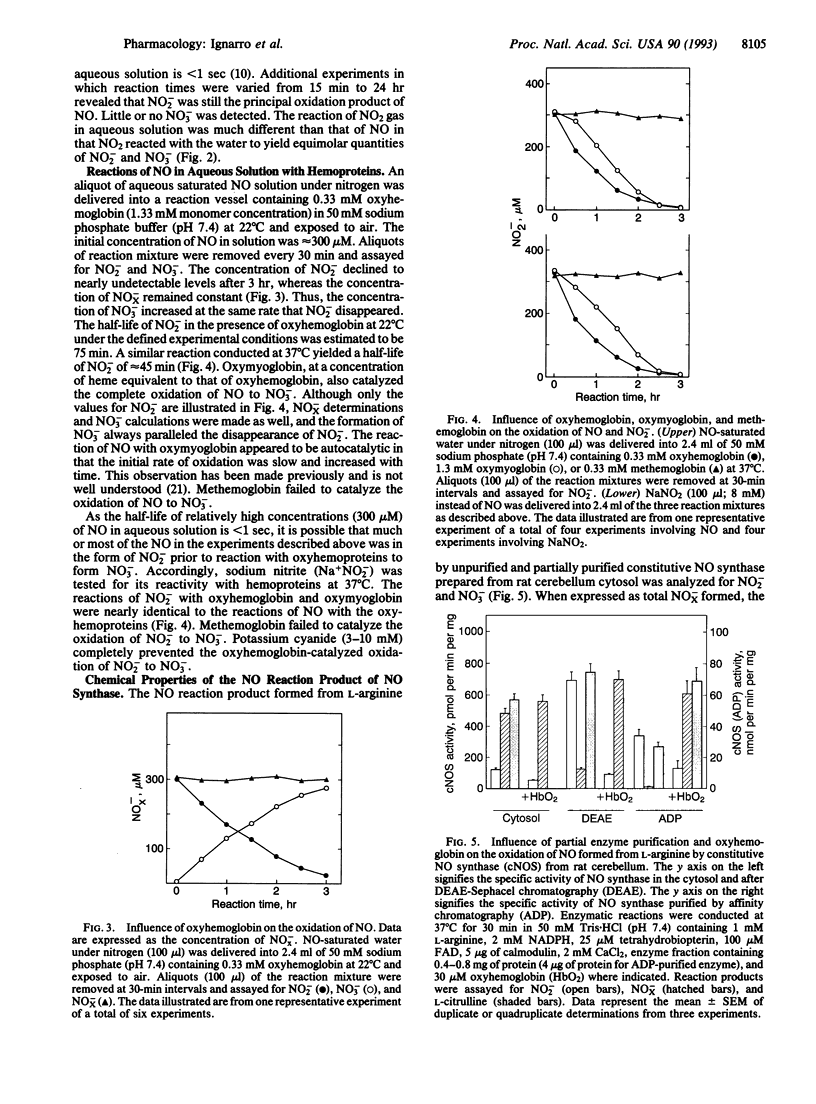
Nitric oxide (NO) in oxygen-containing aqueous solution has a short half-life that is often attributed to a rapid oxidation to both NO2- and NO3-. The chemical fate of NO in aqueous solution is often assumed to be the same as that in air, where NO is oxidized to NO2 followed by dimerization to N2O4. Water then reacts with N2O4 to form both NO2- and NO3-. We report here that NO in aqueous solution containing oxygen is oxidized primarily to NO2- with little or no formation of NO3-. In the presence of oxyhemoglobin or oxymyoglobin, however, NO and NO2- were oxidized completely to NO3-. Methemoglobin was inactive in this regard. The unpurified cytosolic fraction from rat cerebellum, which contains constitutive NO synthase activity, catalyzed the conversion of L-arginine primarily to NO3- (NO2-/NO3- ratio = 0.25). After chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel or affinity chromatography using 2',5'-ADP-Sepharose 4B, active fractions containing NO synthase activity catalyzed the conversion of L-arginine primarily to NO2- (NO2-/NO3- ratio = 5.6) or only to NO2-, respectively. Unpurified cytosol from activated rat alveolar macrophages catalyzed the conversion of L-arginine to NO2- without formation of NO3-. Addition of 30 microM oxyhemoglobin to all enzyme reaction mixtures resulted in the formation primarily of NO3- (NO2-/NO3- ratio = 0.09 to 0.20). Cyanide ion, which displaces NO2- from its binding sites on oxyhemoglobin, inhibited the formation of NO3-, thereby allowing NO2- to accumulate. These observations indicate clearly that the primary decomposition product of NO in aerobic aqueous solution is NO2- and that further oxidation to NO3- requires the presence of additional oxidizing species such as oxyhemoproteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush P. A., Gonzalez N. E., Griscavage J. M., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum catalyzes the formation of equimolar quantities of nitric oxide and citrulline from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):960–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91720-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case G. D., Dixon J. S., Schooley J. C. Interactions of blood metalloproteins with nitrogen oxides and oxidant air pollutants. Environ Res. 1979 Oct;20(1):43–65. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(79)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L., deRojas T. C., Chapman T. E., Vogt J., Burke J. F., Tannenbaum S. R., Young V. R. Splanchnic metabolism of dietary arginine in relation to nitric oxide synthesis in normal adult man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Hoekstra J. W. Oxidation of nitrogen oxides by bound dioxygen in hemoproteins. J Inorg Biochem. 1981 Jul;14(4):351–358. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Gorsky L. D., Pollock J. S., Ishii K., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Hormone-induced biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide-like material in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells requires calcium and calmodulin. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmke R. J., Boyd R. L., German V. F., Mangos J. A. From growth factor dependence to growth factor responsiveness: the genesis of an alveolar macrophage cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;23(8):567–574. doi: 10.1007/BF02620974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Byrns R. E., Buga G. M., Wood K. S. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide radical. Circ Res. 1987 Dec;61(6):866–879. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.6.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Wood K. S., Wolin M. S. Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by protoporphyrin IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2870–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Imaizumi K., Imai K., Tyuma I. Stoichiometry of the reaction of oxyhemoglobin with nitrite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 23;581(1):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Wishnok J. S., Miwa M., Leaf C. D., Tannenbaum S. R. Nitrosation by stimulated macrophages. Inhibitors, enhancers and substrates. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Mar;10(3):563–566. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., John M., Böhme E. Purification of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent nitric oxide synthase from porcine cerebellum. Cofactor-role of tetrahydrobiopterin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80848-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan K., Bredt D. S., Hirsch D. J., Snyder S. H., Clark J. E., Masters B. S. Cloned, expressed rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase contains stoichiometric amounts of heme, which binds carbon monoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11141–11145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodkey F. L. A mechanism for the conversion of oxyhemoglobin to methemoglobin by nitrite. Clin Chem. 1976 Dec;22(12):1986–1990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers N. E., Ignarro L. J. Constitutive nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum is reversibly inhibited by nitric oxide formed from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):242–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91550-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Sakuma I., Levi R., Nathan C. F. Activated murine macrophages secrete a metabolite of arginine with the bioactivity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and the chemical reactivity of nitric oxide. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1011–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Griffith O. W., Feldman P. L., Wiseman J. N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6259–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. A., Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase is a cytochrome P-450 type hemoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6627–6631. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wink D. A., Darbyshire J. F., Nims R. W., Saavedra J. E., Ford P. C. Reactions of the bioregulatory agent nitric oxide in oxygenated aqueous media: determination of the kinetics for oxidation and nitrosation by intermediates generated in the NO/O2 reaction. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993 Jan-Feb;6(1):23–27. doi: 10.1021/tx00031a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]