Abstract
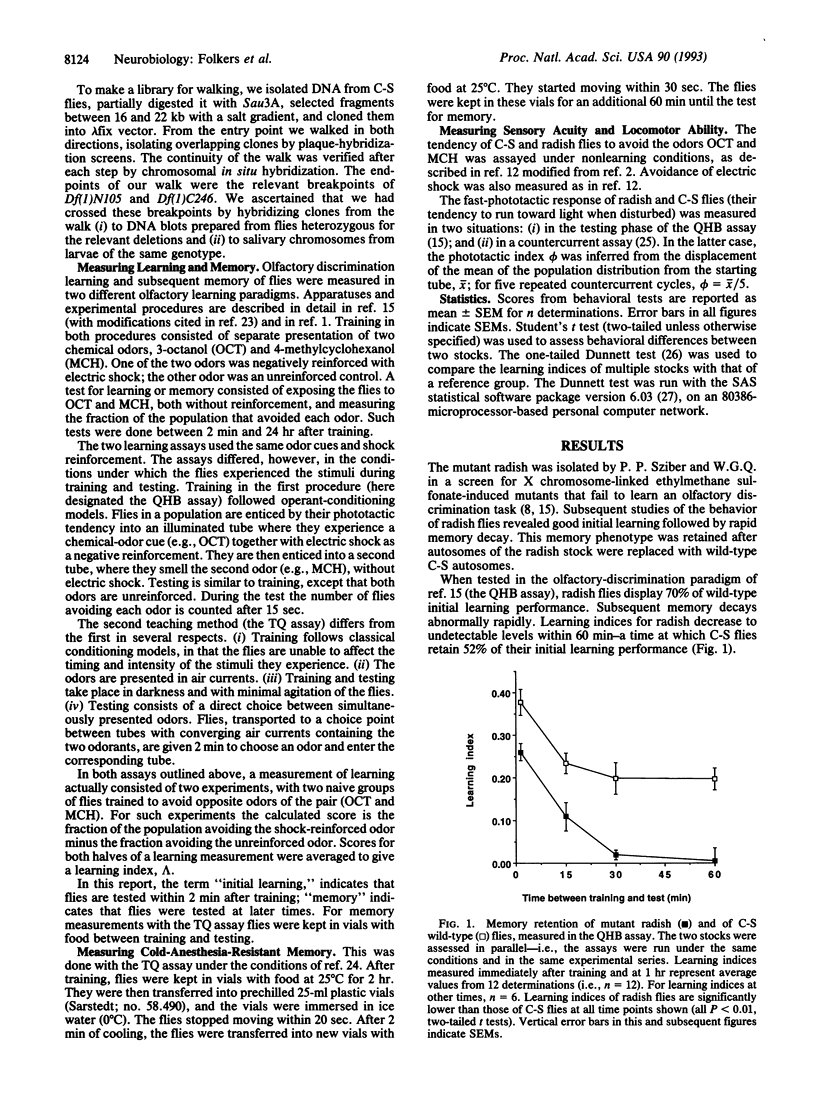
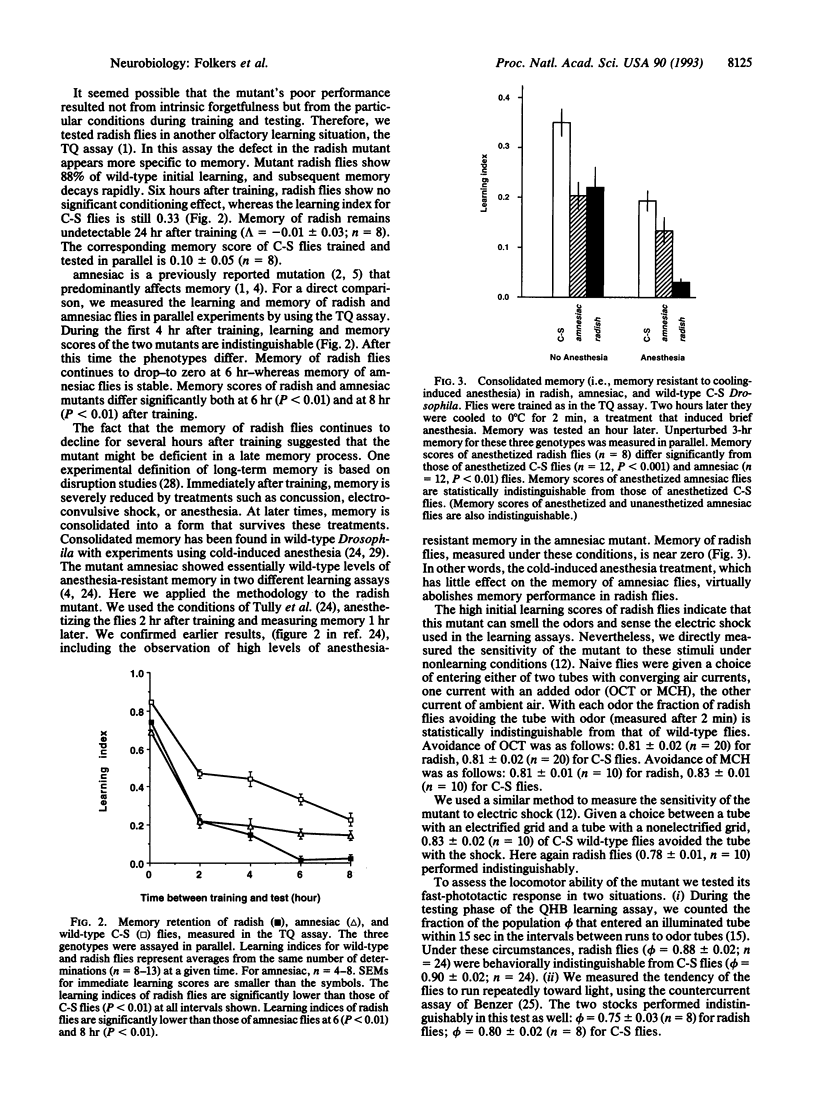
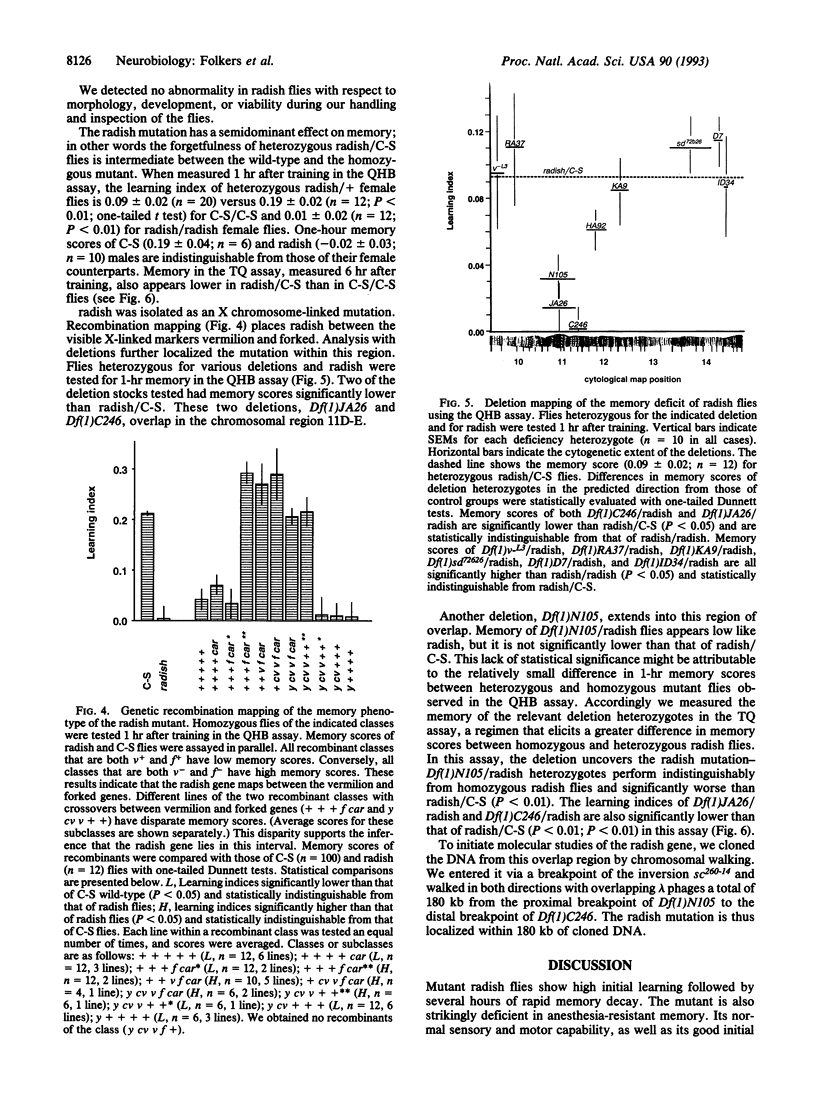
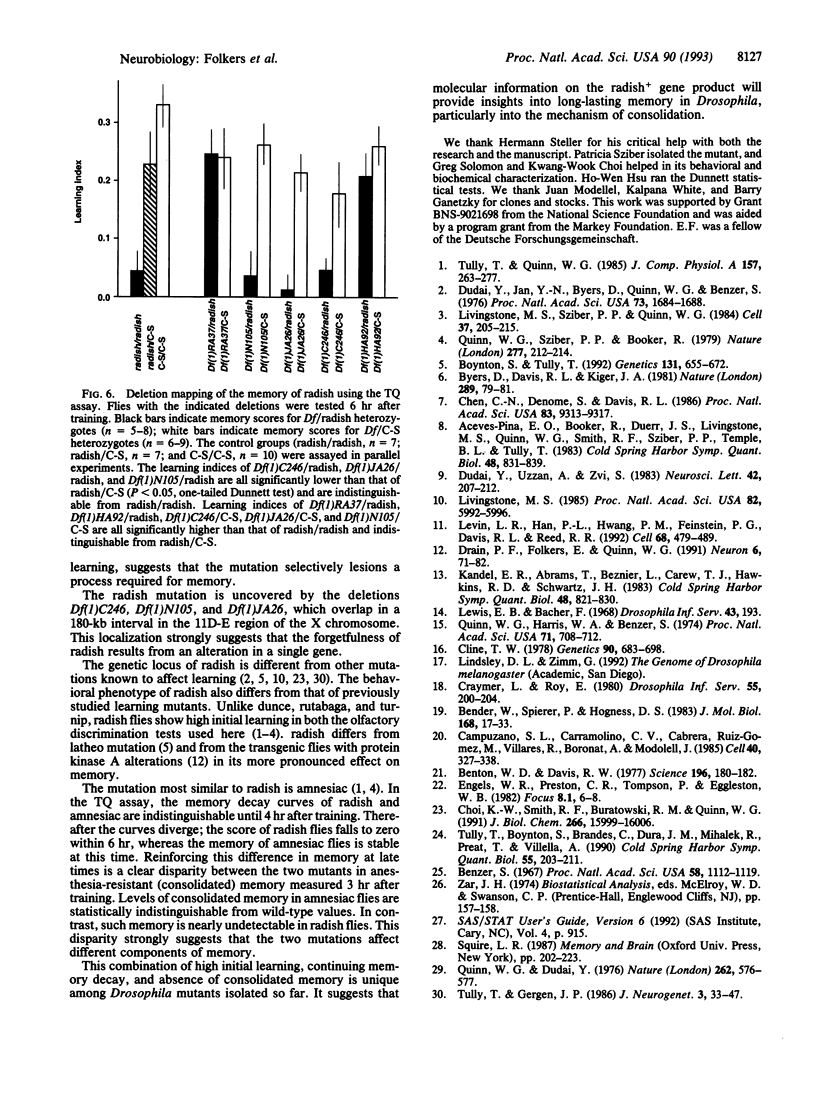
We have characterized the behavior and genetics of the Drosophila mutant radish (rsh gene). Initial learning of radish flies in two olfactory discrimination tests is high, but subsequent memory decays rapidly at both early and late times after training. Anesthesia-resistant memory (consolidated memory) is undetectable in radish flies 3 hr after training. The mutant shows normal locomotor activity and normal sensitivity to the odor cues and electric-shock reinforcement used in the learning tests. The radish gene maps within a 180-kb interval in the 11D-E region of the X chromosome.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves-Piña E. O., Booker R., Duerr J. S., Livingstone M. S., Quinn W. G., Smith R. F., Sziber P. P., Tempel B. L., Tully T. P. Learning and memory in Drosophila, studied with mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. BEHAVIORAL MUTANTS OF Drosophila ISOLATED BY COUNTERCURRENT DISTRIBUTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton S., Tully T. latheo, a new gene involved in associative learning and memory in Drosophila melanogaster, identified from P element mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):655–672. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers D., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Defect in cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase due to the dunce mutation of learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):79–81. doi: 10.1038/289079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Carramolino L., Cabrera C. V., Ruíz-Gómez M., Villares R., Boronat A., Modolell J. Molecular genetics of the achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. N., Denome S., Davis R. L. Molecular analysis of cDNA clones and the corresponding genomic coding sequences of the Drosophila dunce+ gene, the structural gene for cAMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9313–9317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. W., Smith R. F., Buratowski R. M., Quinn W. G. Deficient protein kinase C activity in turnip, a Drosophila learning mutant. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15999–15606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. Two closely linked mutations in Drosophila melanogaster that are lethal to opposite sexes and interact with daughterless. Genetics. 1978 Dec;90(4):683–698. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drain P., Folkers E., Quinn W. G. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the disruption of learning in transgenic flies. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90123-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y., Jan Y. N., Byers D., Quinn W. G., Benzer S. dunce, a mutant of Drosophila deficient in learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudaí Y., Uzzan A., Zvi S. Abnormal activity of adenylate cyclase in the Drosophila memory mutant rutabaga. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Abrams T., Bernier L., Carew T. J., Hawkins R. D., Schwartz J. H. Classical conditioning and sensitization share aspects of the same molecular cascade in Aplysia. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):821–830. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Han P. L., Hwang P. M., Feinstein P. G., Davis R. L., Reed R. R. The Drosophila learning and memory gene rutabaga encodes a Ca2+/Calmodulin-responsive adenylyl cyclase. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90185-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S. Genetic dissection of Drosophila adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5992–5996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Sziber P. P., Quinn W. G. Loss of calcium/calmodulin responsiveness in adenylate cyclase of rutabaga, a Drosophila learning mutant. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn W. G., Dudai Y. Memory phases in Drosophila. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):576–577. doi: 10.1038/262576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn W. G., Harris W. A., Benzer S. Conditioned behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn W. G., Sziber P. P., Booker R. The Drosophila memory mutant amnesiac. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):212–214. doi: 10.1038/277212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully T., Boynton S., Brandes C., Dura J. M., Mihalek R., Preat T., Villella A. Genetic dissection of memory formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:203–211. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully T., Gergen J. P. Deletion mapping of the Drosophila memory mutant amnesiac. J Neurogenet. 1986 Jan;3(1):33–47. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully T., Quinn W. G. Classical conditioning and retention in normal and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Physiol A. 1985 Sep;157(2):263–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01350033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



