Abstract
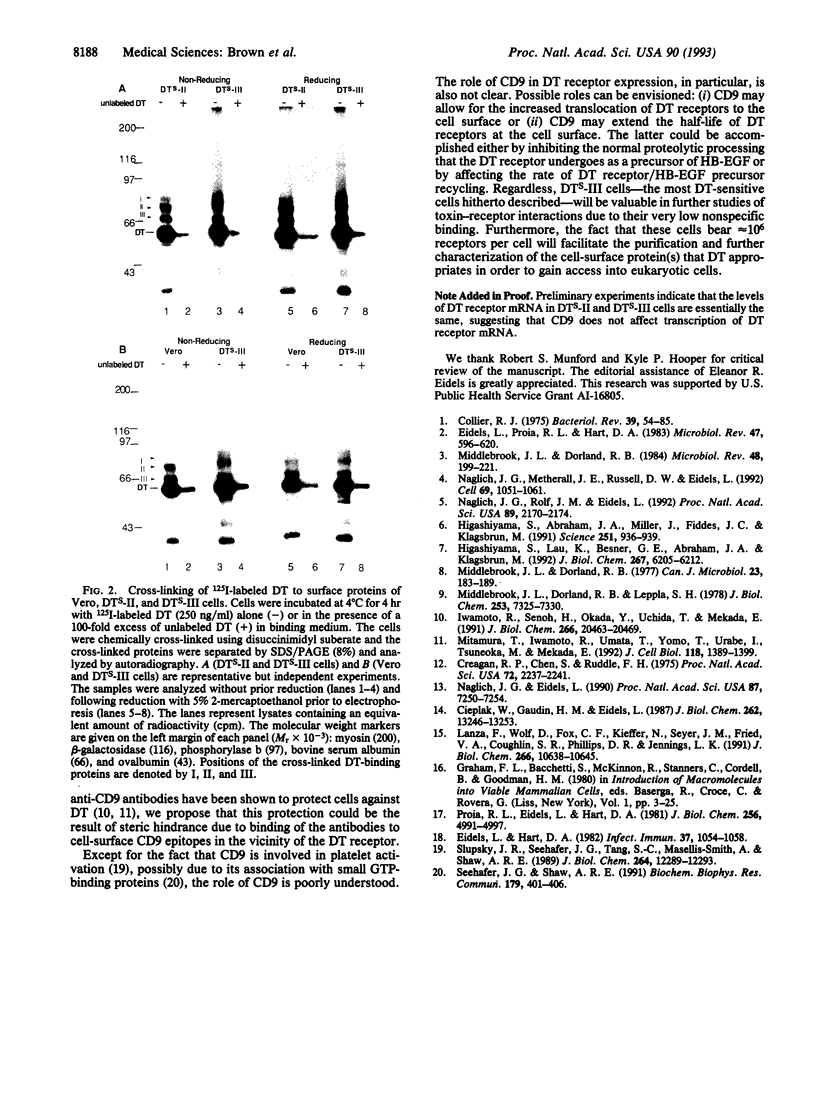
DTS-II is a highly diphtheria toxin (DT)-sensitive cell line previously isolated by transfection of wild-type DT-resistant mouse L-M(TK-) cells with the cDNA encoding a monkey Vero cell DT receptor. DTS-II cells are as toxin-sensitive as Vero cells, have approximately 3-fold more receptors than Vero cells, and have approximately 10-fold lower affinity for DT than Vero cells. We now cotransfected DTS-II cells with a plasmid containing the Vero cell cDNA coding for CD9 antigen (pCD9) and with a plasmid containing the gene for hygromycin resistance (pHyg). The stably transfected hygromycin-resistant colonies were screened for DT hypersensitivity employing a replica plate system. A DT-hypersensitive colony was isolated and purified. The purified DT-hypersensitive cells, DTS-III, (i) are approximately 10-fold more toxin-sensitive than DTS-II and Vero cells and (ii) bear approximately 10(6) DT receptors per cell (i.e., approximately 20-fold and approximately 60-fold more receptors than DTS-II and Vero cells, respectively), but their receptor affinity is still approximately 10-fold lower than that of Vero cells. Cross-linking experiments employing 125I-labeled DT demonstrated that DTS-II and DTS-III cells have essentially the same profile of DT-binding cell-surface protein(s), suggesting that CD9 antigen, although expressed on the cell surface of DTS-III cells, may not be in close proximity to the DT-binding domain of the receptor. CD9 may affect DT receptor expression by increasing receptor density at the cell surface. By employing DTS-III cells it should be possible to purify and characterize the DT cell-surface receptor protein(s).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cieplak W., Gaudin H. M., Eidels L. Diphtheria toxin receptor. Identification of specific diphtheria toxin-binding proteins on the surface of Vero and BS-C-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13246–13253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagan R. P., Chen S., Ruddle F. H. Genetic analysis of the cell surface: association of human chromosome 5 with sensitivity to diphtheria toxin in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2237–2241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidels L., Hart D. A. Effect of polymers of L-lysine on the cytotoxic action of diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1054-1058.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Abraham J. A., Miller J., Fiddes J. C., Klagsbrun M. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.1840698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Lau K., Besner G. E., Abraham J. A., Klagsbrun M. Structure of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Multiple forms, primary structure, and glycosylation of the mature protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6205–6212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto R., Senoh H., Okada Y., Uchida T., Mekada E. An antibody that inhibits the binding of diphtheria toxin to cells revealed the association of a 27-kDa membrane protein with the diphtheria toxin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20463–20469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F., Wolf D., Fox C. F., Kieffer N., Seyer J. M., Fried V. A., Coughlin S. R., Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K. cDNA cloning and expression of platelet p24/CD9. Evidence for a new family of multiple membrane-spanning proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10638–10645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitamura T., Iwamoto R., Umata T., Yomo T., Urabe I., Tsuneoka M., Mekada E. The 27-kD diphtheria toxin receptor-associated protein (DRAP27) from vero cells is the monkey homologue of human CD9 antigen: expression of DRAP27 elevates the number of diphtheria toxin receptors on toxin-sensitive cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1389–1399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Eidels L. Isolation of diphtheria toxin-sensitive mouse cells from a toxin-resistant population transfected with monkey DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7250–7254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Metherall J. E., Russell D. W., Eidels L. Expression cloning of a diphtheria toxin receptor: identity with a heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor precursor. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90623-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Rolf J. M., Eidels L. Expression of functional diphtheria toxin receptors on highly toxin-sensitive mouse cells that specifically bind radioiodinated toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Eidels L., Hart D. A. Diphtheria toxin:receptor interaction. Characterization of the receptor interaction with the nucleotide-free toxin, the nucleotide-bound toxin, and the B-fragment of the toxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4991–4997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seehafer J. G., Shaw A. R. Evidence that the signal-initiating membrane protein CD9 is associated with small GTP-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91384-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slupsky J. R., Seehafer J. G., Tang S. C., Masellis-Smith A., Shaw A. R. Evidence that monoclonal antibodies against CD9 antigen induce specific association between CD9 and the platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12289–12293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]