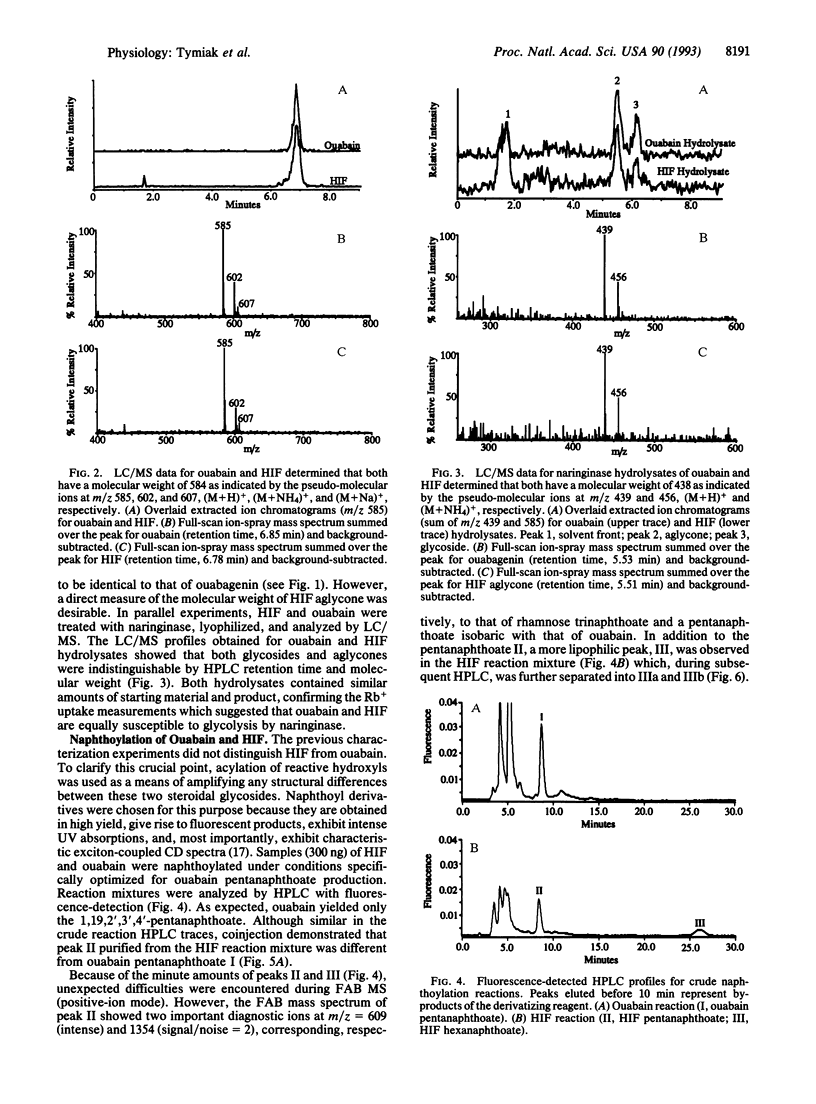
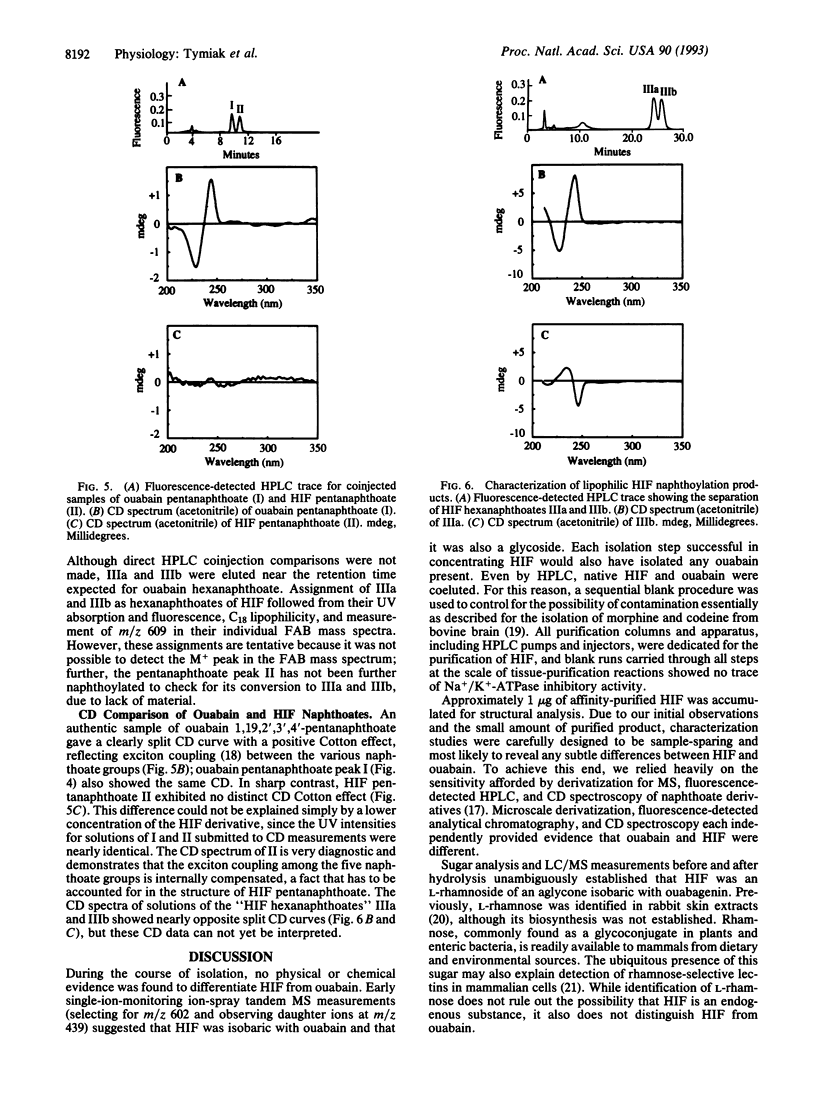
Abstract
Recent reports have shown the presence of a ouabain-like inhibitor of Na+/K(+)-ATPase in humans. We have purified a bovine hypothalamic Na+/K(+)-ATPase inhibitory factor (HIF) by using affinity chromatography combined with HPLC. This inhibitor has a molecular weight of 584 as determined by ion-spray mass spectrometry, making it isobaric with ouabain. Glycosidase treatment or acid hydrolysis of HIF released only L-rhamnose, the hexose isomer found in ouabain, as detected by chiral GC/MS. Additionally, enzymatically generated desrhamnosyl HIF was found to have a molecular weight of 438, as does ouabagenin, the aglycone of ouabain. HIF and its aglycone were indistinguishable from ouabain and ouabagenin, respectively, by reversed-phase HPLC retention times. However, derivatization with naphthoylimidazole followed by HPLC revealed different retention times for naphthoylation products of HIF and ouabain. Subsequent CD spectroscopy on isolated naphthoylation products of HIF and ouabain confirmed that they were different. This study provides chromatographic and spectroscopic evidence that ouabain and HIF are isomeric cardenolides. The structural difference is presumed to account for the significant differences in biological properties observed for HIF and ouabain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anner B. M., Rey H. G., Moosmayer M., Meszoely I., Haupert G. T., Jr Hypothalamic Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase inhibitor characterized in two-sided liposomes containing pure renal Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):F144–F153. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C165–C173. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bova S., Blaustein M. P., Ludens J. H., Harris D. W., DuCharme D. W., Hamlyn J. M. Effects of an endogenous ouabainlike compound on heart and aorta. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):944–950. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butts W. C., Jolley R. L. Gas-chromatographic identification of urinary carbohydrates isolated by anion-exchange chromatography. Clin Chem. 1970 Aug;16(8):722–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Chen E., Ray S., Haupert G. T., Jr Na+ pump in renal tubular cells is regulated by endogenous Na+-K+-ATPase inhibitor from hypothalamus. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F574–F580. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carilli C. T., Berne M., Cantley L. C., Haupert G. T., Jr Hypothalamic factor inhibits the (Na,K)ATPase from the extracellular surface. Mechanism of inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1027–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan D., Grillon C., Monsigny M., Redziniak G., Kieda C. Human keratinocyte membrane lectins: characterization and modulation of their expression by cytokines. Biol Cell. 1991;73(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(91)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandi M., Minotti E., Salardi S., Florio M., Bianchi G., Ferrari P. Ouabainlike factor in Milan hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):F739–F748. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.4.F739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Haupert G. T., Jr The search for a hypothalamic Na+,K+-ATPase inhibitor. Hypertension. 1987 Apr;9(4):315–324. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.4.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy F. J., Overbeck H. W. The role of humoral agents in volume expanded hypertension. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 1;19(7):935–947. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallaq H. A., Haupert G. T., Jr Positive inotropic effects of the endogenous Na+/K(+)-transporting ATPase inhibitor from the hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10080–10084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn J. M., Blaustein M. P., Bova S., DuCharme D. W., Harris D. W., Mandel F., Mathews W. R., Ludens J. H. Identification and characterization of a ouabain-like compound from human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6259–6263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupert G. T., Jr, Carilli C. T., Cantley L. C. Hypothalamic sodium-transport inhibitor is a high-affinity reversible inhibitor of Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 2):F919–F924. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.6.F919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupert G. T., Jr Physiological inhibitors of Na, K-ATPase: concept and status. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268B:297–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupert G. T., Jr, Sancho J. M. Sodium transport inhibitor from bovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4658–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAWISTA I., DAVIDSON E. A. Isolation and identification of rhamnose from rabbit skin. Nature. 1961 Dec 2;192:871–872. doi: 10.1038/192871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Fujii Y., Yamashita E., Niizaki Y., Sato Y. Studies on cardiotonic steroids from the skin of Japanese toad. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1977 Apr;25(4):714–730. doi: 10.1248/cpb.25.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz C. J., Lowney L. I., Faull K. F., Feistner G., Goldstein A. Morphine and codeine from mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9784–9788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wardener H. E., Clarkson E. M. Concept of natriuretic hormone. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jul;65(3):658–759. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.3.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



