Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by rapid and potentially reversible decline in renal function; however, the current management for AKI is nonspecific and associated with limited supportive care. Considering the need for more novel therapeutic approaches, we believe that lectins from Dioclea violacea (Dvl), based on their anti-inflammatory properties, could be beneficial for the treatment of AKI induced by renal ischemia/reperfusion (IR). Dvl (1 mg/kg, i.v.) or vehicle (100 µL) was administered to Wistar rats prior to the induction of bilateral renal ischemia (45 min). Following 24 hours of reperfusion, inulin and para-aminohippurate (PAH) clearances were performed to determine glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), renal blood flow (RBF) and renal vascular resistance (RVR). Renal inflammation was assessed using myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. Kidney sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin to evaluate morphological changes. Intracellular superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide, peroxynitrite, nitric oxide and apoptosis were analyzed using flow cytometry. IR resulted in diminished GFR, RPF, RBF, and increased RVR; however, these changes were ameliorated in rats receiving Dvl. AKI-induced histomorphological changes, such as tubular dilation, tubular necrosis and proteinaceous casts, were attenuated by Dvl administration. Treatment with Dvl resulted in diminished renal MPO activity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats submitted to IR. Our data reveal that Dvl has a protective effect in the kidney, improving renal function after IR injury, probably by reducing neutrophil recruitment and oxidative stress. These results indicate that Dvl can be considered a new therapeutic approach for AKI-induced kidney injury.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury, ischemia reperfusion, renal function, plant lectin, Dioclea violacea
Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by rapid and potentially reversible decline in renal function, including a rapid decrease in glomerular filtration rate and retention of nitrogenous waste, a common complication in critically ill patients who have been hospitalized [1]. Important components of the injury process include apoptosis, necrosis, increased reactive oxygen species production, and micro-vessel damage causing local ischemia, endothelial dysfunction, leaks, and inflammation [2].
AKI is associated with increased risk of death and prolonged hospitalization, typically in intensive care units, resulting in increased costs [3]. AKI may occur as a result of several conditions that can decrease renal perfusion, such as sepsis [4], burns [5], cardiac surgery [6], contrast agents [7], trauma [8] and post-renal transplantation [9,10]. The current management for AKI is nonspecific and associated with limited supportive care; thus, the need for more novel approaches is imperative [11]. The difficulty in finding a new therapeutic target can be attributed to several factors, such as multiple causes of AKI, limited knowledge about the processes involved in the development of AKI, and lack of renal function markers which can identify AKI in its early stages [3].
Among the potential agents that may have a beneficial effect on AKI, we can highlight lectins, which are proteins or glycoproteins of nonimmune origin. Lectins are capable of specific recognition and reversibly binding to carbohydrate-containing compounds. Lectins are distributed in nature in practically all living organisms, but the most studied lectins are derived from plants, especially from the Leguminosae family [12]. Lectins from this family participate in numerous biological processes, such as vasomodulation [13], erythrocyte agglutination [14], and immunological [12] and antinociceptive activity [15]. Studies with Dioclea violacea (Dvl), a lectin from the Leguminosae family, Diocleinae subtribe, showed that neutrophil migration was inhibited in different models of inflammation when applied intravenously [16,17], indicating that the lectin from Dvl could be a promising substance for use in ameliorating the effects of AKI. Therefore, the goal of the present study was to evaluate if treatment with Dvl lectin could improve the renal function of rats with AKI induced by renal IR.
Materials and methods
Lectin extraction
Lectin was extracted from the seeds of Dioclea violacea (Dvl) by affinity chromatography as previously described [18]. Briefly, the seeds were ground into a fine powder and stirred with 0.15 mol/L of NaCl (1:10 w/v) at room temperature for 4 h. The extract was centrifuged at 20000 g for 20 min at 5°C, and the supernatant was applied to a Sephadex G-50 column (Amersham-Biosciences, USA) pre-equilibrated with 0.15 mol/L NaCl containing 5 mmol/L CaCl2 and 5 mmol/L MnCl2. After removal of unbound material, Dvl was eluted with 0.1 mol/L glucose in equilibration solution. Then, this fraction was submitted to a 1 h dialysis against 0.1 mol/L acetic acid, followed by a 24 h dialysis against distilled water. Finally, the lectin was freeze-dried and stored at 5°C. For the experiments, Dvl was dissolved in saline solution (0.9% NaCl).
Animals
Experiments were performed using 11- to 13-week-old male Wistar rats obtained from the animal facilities of the Health Sciences Center at the Federal University of Espirito Santo. Rats received a normal chow diet and water at libitum and were housed in temperature-controlled rooms (22°C) under a 12:12 h light-dark cycle. All experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the protocols were previously approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee for Use of Animals (CEUA-UFES, protocol #58/2013).
Dvl treatment and AKI induction
Treatment with Dvl lectin was performed prior to the induction of AKI. The animals were anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine (91.0/9.1 mg/kg, i.p.), placed on a heated surgical table, and either Dvl lectin (1 mg/kg, i.v.) or vehicle (VH; 100 µL of 0.9% NaCl, i.v.) was administered in penile vein. Thirty minutes after treatment, rats were submitted to renal ischemia reperfusion surgery. Briefly, a midline abdominal incision was made, and the blood supply to the kidneys was interrupted for 45 min by clamping the renal pedicles of both kidneys with a suture line (endocort, nº0, Laboratório Bruneau S.A.). The suture line was then released, and the kidneys were reperfused during 24 hours. In sham surgery, kidneys were exposed, but not clamped. Postoperative dehydration was prevented by subcutaneous administration of 1.0 mL of 0.9% NaCl [19,20].
Renal function studies
Twenty-four hours after kidney reperfusion, renal function was determined using inulin and sodium para-aminohippurate (PAH) clearances to estimate glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow (RPF), respectively. The animals were anesthetized with sodium thiopental (50 mg/kg, i.p.), and a tracheostomy was performed to facilitate breathing, followed by insertion of polyethylene catheters into the femoral artery for collection of blood samples and into the femoral vein for the infusion of saline containing 3% mannitol. A catheter was inserted into the bladder for urine collection. The arterial catheter was connected to a pressure transducer (Cobe Laboratories, USA), which was plugged into a pressure-processor amplifier and data acquisition system (MP100, Biopac Systems, USA) for continuous monitoring of arterial pressure and heart rate.
A 30 min infusion with saline containing 3% mannitol at a rate of 0.06 ml/min was performed, followed by a priming injection of 1 ml of saline containing inulin (300 mg/kg) and PAH (6.66 mg/kg). After that, an infusion at the rate of 0.1 ml/min containing saline, inulin (15 mg/ml), PAH (4 mg/ml), and 3% mannitol was started. Four urine and blood samples were collected at 30 min intervals, starting 30 min after injection of the priming solution for a total of 4 samples. Hematocrit was measured using a heparinized capillary tube. Plasma and urinary inulin and PAH concentrations were measured using a colorimetric assay [21]. Blood samples were also used for plasma urea quantification through spectrophotometry.
Renal blood flow (RBF) and renal vascular resistance (RVR) were determined as previously described [22]. Briefly, RBF was calculated by the equation RBF=RPF/(1-hematocrit), and RVR was calculated using the equation RVR=MAP/RBF.
Renal histology
At the end of the experiments, the animals were euthanized with an overdose of sodium thiopental and perfused via the left ventricle with Krebs HEPES buffer (pH 7.4). The left kidney was removed, cleaned of connective tissue, and renal tissue samples were fixed in 10% formalin, dehydrated in ethanol, embedded in paraffin and cut into 4 µm sections. Then, the sections were deparaffinized with xylene and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were blinded before observation for histopathological changes, such as tubular dilation, tubular necrosis and the presence of proteinaceous casts [23].
Myeloperoxidase assay
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was measured as an index of inflammation, as described previously [24,25]. One hundred mg of kidney was homogenized in 2000 µL of potassium phosphate buffer 0.05 M containing 5 mg/mL of hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and 1.85 mg/mL of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (pH 6.0), using a homogenizer. The homogenate was centrifuged at 12500 g for 15 min at 4°C to obtain the supernatant, which was used to measure MPO activity. Seventy-five microL of supernatant was mixed with 1425 µL of phosphate buffer containing 0.167 mg/mL of o-dianisidine hydrochloride and 0.05% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The change in absorbance was measured at 460 nm for 10 min. Results are expressed as units of MPO activity per gram of tissue, where 1 unit is the quantity of enzyme able to convert 1 mM of H2O2 to water in 1 min at 25°C.
Cell samples
Enriched kidney cell fractions from different groups were prepared as standardized in our laboratory based on previous studies [26,27]. The kidney was divided into cortex and medulla, grossly triturated with surgical scissors, and incubated with an extraction solution containing trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) to dissociate the cells. The cell extract was filtered through a nylon screen (BD Falcon 70 µm) to remove cell debris. The samples were washed twice in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and stored at -80°C until further analysis.
NO intracellular detection
The measurement of nitric oxide (NO) was performed as previously described [28]. Briefly, a NO-sensitive fluorescent probe, 4,5-diaminofluorescein-2/diacetate (DAF-2/DA: 2 μM), was added to the cell suspension (106 cells) and incubated at 37°C for 180 minutes in the dark. For positive control, samples were treated with 100 μM sodium nitroprusside. Cells were then washed, resuspended in PBS and immediately analyzed by flow cytometry (FACSCanto II, Becton Dickinson, CA). Data were analyzed using the FACSDiva software (Becton Dickinson), and overlay histograms were constructed using FCS Express software (De Novo). For quantification of DAF fluorescence, samples were acquired in duplicate, and 10,000 events were used for each measurement. Cells were excited at 488 nm, and fluorescence was detected using a 530/30 band-pass filter. Data were expressed as geometric mean fluorescence intensity.
ROS detection
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) analysis was performed by flow cytometry as previously described [29,30]. Dihydroethidium (DHE) and 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA) were used to detect intracellular superoxide anion (•O2 -) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), respectively. By its ability to freely permeate cell membranes, DHE is extensively used to monitor •O2 - production. Upon reaction with •O2 -, DHE is rapidly oxidized forming ethidium, a red fluorescent product that intercalates with DNA and amplifies the red fluorescence signal. DCF-DA is a cell permeant indicator for H2O2 production. It is nonfluorescent until oxidation occurs within the cell, converting it to the fluorescent form that remains trapped in the cell. DHE (160 mM) and DCF-DA (20 mM) were added to the cell suspension (106 cells) and incubated at 37°C for 30 min, in the dark, to estimate intracellular •O2 - or H2O2 concentration [30]. For positive control, samples were treated for 5 min with 10 μM doxorubicin or 50 mM H2O2 to create oxidative stress, but without toxicity to the cells, whereas for negative control, the cells were incubated with ethanol. Cells were then washed, resuspended in PBS, and kept on icefor immediate detection by flow cytometry (FACSCanto II, Becton Dickinson, CA). Data were analyzed using the FACSDiva software (Becton Dickinson), and overlay histograms were constructed using FCS Express software. For quantification of DHE and DCF fluorescence, samples were acquired in duplicate, and 10,000 events were used for each measurement. Cells were excited at 488 nm, and DHE and DCF fluorescence were detected using, respectively, 585/42 and 530/30 band-pass filters. Data were expressed as geometric mean fluorescence intensity.
hROS detection
Highly reactive oxygen species (hROS), such as hydroxyl radical (•OH) and peroxynitrite anion (ONOO-), were selectively detected by 2-[6-(4’-hydroxy)phenoxy-3H-xanthen-3-on-9-yl] benzoic acid (HPF), as described [31]. In brief, renal cells (106 cells) were incubated with HPF (10 μM) at 37°C for 30 minutes in the dark. For positive control, samples were treated with 100 μM sodium nitroprusside and 10 μM doxorubicin. Cells were then washed, resuspended in PBS, and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACSCanto II, Becton Dickinson, CA). Data were analyzed using the FACSDiva software (Becton Dickinson), and overlay histograms were constructed using FCS Express software (De Novo). For quantification of HPF fluorescence, samples were acquired in duplicate, and 10,000 events were used for each measurement. Cells were excited at 488 nm, fluorescence was detected using a 530/30 band-pass filter, and data were expressed as geometric mean fluorescence intensity.
Apoptosis
Apoptotic cells were quantified by Annexin V-FITC and Propidium iodide (PI) double staining, using an Annexin V-FITC apoptosis detection kit (Becton Dickinson, CA). In brief, renal cells were washed twice with PBS, adjusted to 500 µl of binding buffer (5×105 cells). Then, 2 µl of Annexin V-FITC and 2 µl of PI were added, and cells were gently vortexed. Cells were then incubated for 15 min at room temperature (25°C) in the dark. Finally, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (FACSCanto II, Becton Dickinson). Cells showing as Annexin V-/PI+ were recognized as necrotic, and those showing as Annexin V+/PI+ were interpreted as late apoptotic, or secondary apoptotic, while Annexin V+/PI- cells were recognized as early or primary apoptotic cells [32].
Statistical analyses
Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. Statistical comparisons between the different groups were performed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Statistical analyses were performed using Prism software (Prism 6, GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). A value of p<0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
Results
Figure 1 shows the effects of Dvl treatment on renal hemodynamics, demonstrating glomerular filtration rate, as assessed by inulin clearance (A), and renal plasma flow, as assessed by PAH clearance (B), as well as renal blood flow (C) and vascular resistance (D). Treatment with Dvl did not modify inulin clearance in the sham group (7.3 ± 0.4 mL/min/Kg), when compared with vehicle-treated animals (8.3 ± 0.6 mL/min/Kg). As expected, IR resulted in decreased GFR (2.9 ± 0.4 mL/min/Kg, p<0.05), but Dvl administration prior to IR caused a significant improvement in this parameter (6.0 ± 0.6 mL/min/Kg, p<0.05). PAH clearance was unaffected by Dvl treatment in the sham group (VH: 24.5 ± 0.7 vs. Dvl: 21.6 ± 2.9 mL/min/Kg); however, IR-induced reduction of RPF (4.4 ± 0.6 mL/min/Kg, p<0.05) was ameliorated in IR animals receiving Dvl (15.0 ± 2.0 mL/min/Kg, p<0.05). Since all groups presented the same hematocrit values (data not shown), renal blood flow pattern responses were similar to RPF responses, with no changes in sham animals (VH: 38.6 ± 0.9 vs. Dvl: 32.6 ± 3.2 mL/min/Kg) and a Dvl-induced improvement in RBF in the IR group (VH: 6.6 ± 0.9 vs. Dvl: 22.9 ± 2.8 mL/min/Kg, p<0.05). Renal vascular resistance was increased in IR vehicle-treated animals (16.3 ± 2.8 a.u., p<0.05) when compared to both sham VH (2.7 ± 0.2 a.u.) and sham Dvl (3.8 ± 0.3 a.u.). Once again, Dvl treatment had a positive effect on renal hemodynamics by decreasing RVR in IR Dvl animals (5.2 ± 0.7 a.u, p<0.05).
Figure 1.
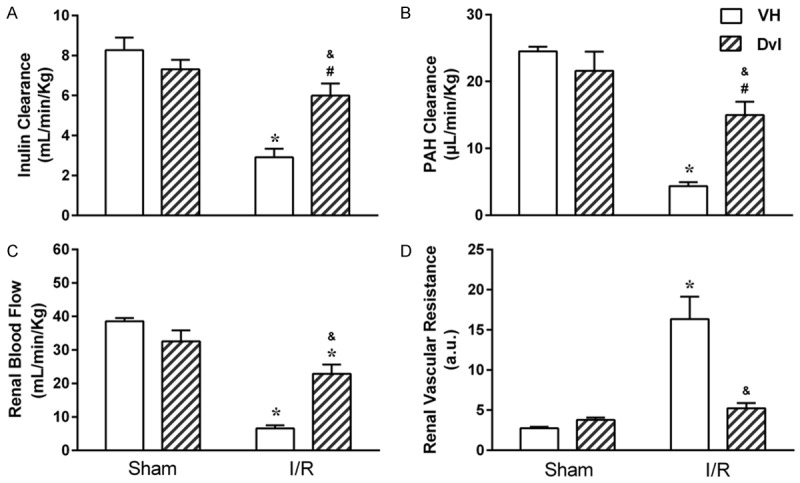
Effect of Dvl treatment on renal function of IR-induced AKI rats. Renal hemodynamics evaluation through determination of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), as assessed by inulin clearance (A) and renal plasma flow (RPF), as assessed by PAH clearance (B), as well as renal blood flow (C) and vascular resistance (D) in sham and IR animals treated with vehicle (white bars) or Dvl (cross-hatched bars). GFR, RPF and renal blood flow (RBF) were significantly decreased in vehicle-treated IR animals. Dvl intravenous injection prior to IR resulted in an amelioration of these parameters. Renal vascular resistance (RVR) was increased in the IR VH group, and Dvl treatment normalized RVR. N=6-7. Values are means ± SEMs. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH; #p<0.05 vs. sham VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
We also evaluated renal function using plasma concentration of urea and histopathologic changes in kidney. Uremia values (Figure 2A) were similar between vehicle (47.9 ± 4.4 mg/dL) and Dvl- (41.7 ± 5.2 mg/dL) treated sham animals. As expected, the IR group presented a marked elevation in plasma urea (166.6 ± 35.0 mg/dL, p<0.05), which was significantly reduced by Dvl treatment (61.6 ± 13.0 mg/dL, p<0.05). In the histopathological evaluation (Figure 2B), no morphological changes were observed in the kidneys of sham rats treated with vehicle and Dvl, but severe and extensive acute tubular damage was observed in the kidneys of IR vehicle rats. These changes were manifested as tubular dilation, tubular necrosis, and the presence of proteinaceous casts. Pretreatment with Dvl was able to reduce the extent and severity of injury.
Figure 2.
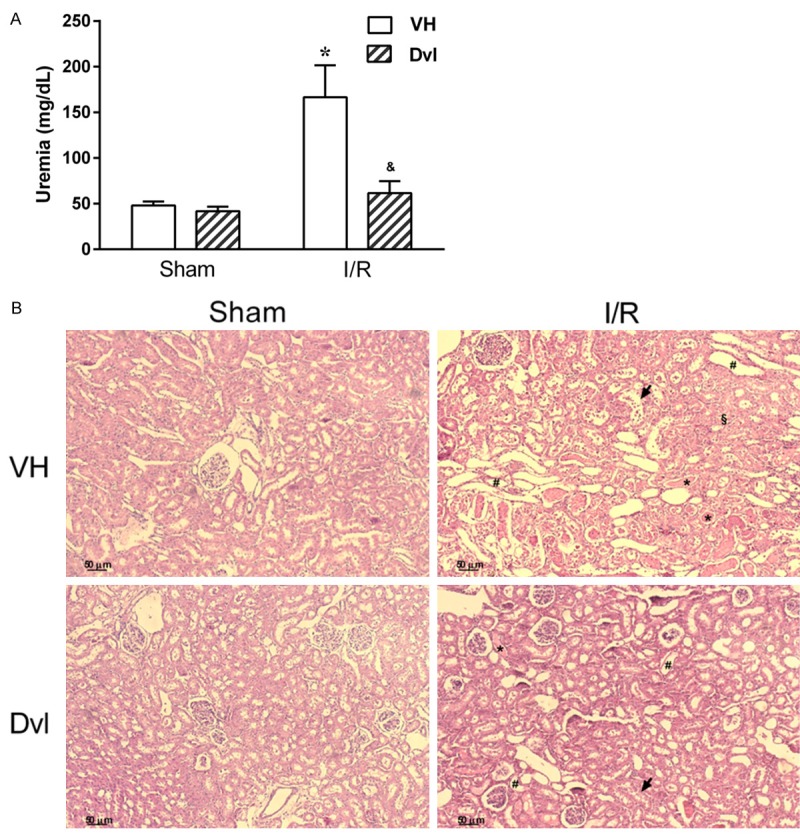
Effect of Dvl treatment on plasma urea and kidney morphology. A. Renal function evaluation using plasma levels of urea in sham and IR-induced AKI animals receiving vehicle (white bars) or Dvl (cross-hatched bars). Note a significant increase in uremia in IR vehicle-treated animals, which was prevented by Dvl administration. N=5-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. B. Representative photomicrographs of kidney histology in sham (left) and rats submitted to ischemia-reperfusion (right) treated with vehicle (top) or Dvl (bottom). Dvl reduced renal damage following renal IR injury. Normal morphology in sham vehicle and in sham Dvl rats. Vehicle-treated rats following IR injury presented severe tubular damage, including tubular dilation (#), proteinaceous cast (*), tubular necrosis (§) and loss of brush border (arrow). Treatment with Dvl reduced the extent of tubular damage. Original magnification × 100.
After IR injury, neutrophils mediate acute inflammatory response. Infiltration of neutrophils following IR injury was evaluated by MPO activity (Figure 3). IR injury significantly increased MPO activity in vehicle-treated animals (13.7 ± 2.6 a.u./g, p<0.05) compared to sham vehicle (1.1 ± 0.2 a.u./g) and sham Dvl animals (1.3 ± 0.3 a.u./g). Importantly, Dvl significantly blocked neutrophil accumulation in the IR group (1.8 ± 0.9 a.u./g, p<0.05) compared to saline-treated animals.
Figure 3.
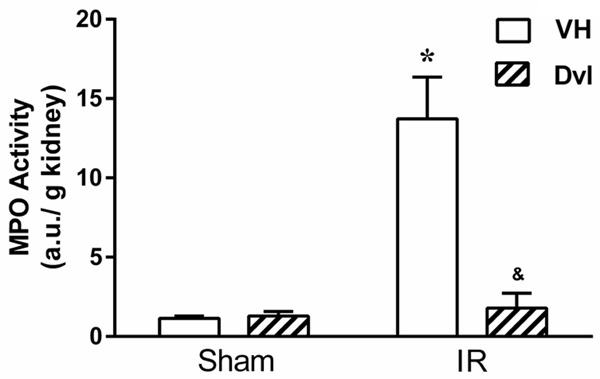
Dvl reduces neutrophil infiltration in kidney of IR-induced AKI rats. Neutrophil infiltration into the kidney was assessed by MPO activity in sham and IR-induced AKI animals receiving vehicle (white bars) or Dvl (cross-hatched bars). Dvl significantly reduced MPO activity. N=5. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
In order to clarify the mechanisms involved in Dvl-induced amelioration of renal function, we performed flow cytometry analyses to evaluate superoxide anion (DHE fluorescence), hydrogen peroxide (DCF fluorescence), peroxynitrite and hydroxyl (HPF fluorescence), and nitric oxide (DAF fluorescence) production in renal cortex and medulla, as well as apoptosis (annexin fluorescence) in the whole kidney. Figure 4 demonstrates typical DHE flow cytometry histograms (top) and quantification of superoxide anion production (bottom) in sham and IR animals in the renal cortex (A) and medulla (B). In the renal cortex, no changes in DHE fluorescence were observed (Sham VH: 2248 ± 143, Sham Dvl: 2072 ± 73, IR VH: 2414 ± 109, IR Dvl: 2433 ± 135 a.u.). As expected, IR vehicle-treated animals presented an increased superoxide anion production in medulla (3012 ± 40 a.u., p<0.05) when compared to sham groups (VH: 2254 ± 137, Dvl: 2314 ± 157 a.u.); nevertheless, the augmentation in DHE fluorescence was partially attenuated in IR Dvl rats (2759 ± 58 a.u., p<0.05).
Figure 4.
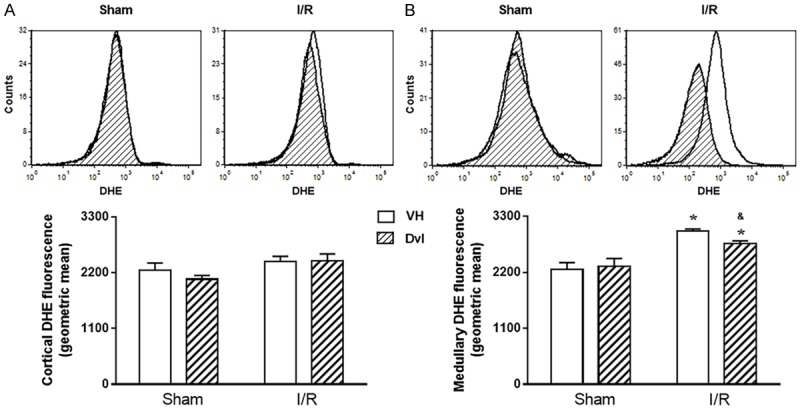
Production of superoxide anions. Representative histograms from flow cytometric analysis (top panel) using dihydroethidium (DHE) in all studied groups in the renal cortex (A) and medulla (B); the X axis illustrates the fluorescence intensity for the number of counted cells. No changes were observed in quantification of cortical superoxide anion production (A, bottom panel); however, a remarkable increase in DHE fluorescence was observed in medullary IR vehicle-treated animals, which was partially attenuated by Dvl treatment (B, bottom panel). N=5-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs.sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
Figure 5 displays the results of hydrogen peroxide production using DCF flow cytometry. Typical histograms are demonstrated in the top panel and quantification of DCF fluorescence in the bottom panel, in both renal cortex (A) and medulla (B). Based on DCF fluorescence, neither IR (Sham VH: 2164 ± 75, IR VH: 2463 ± 85 a.u.) nor Dvl treatment (Sham Dvl: 2407 ± 175, IR Dvl: 2576 ± 138 a.u.) affected hydrogen peroxide production in the renal cortex. Once again, IR resulted in increased medullary DCF fluorescence (Sham VH: 2205 ± 63 vs. IR VH: 2723 ± 73 a.u., p<0.05). Dvl administered by intravenous injection did not modify hydrogen peroxide production in sham animals (2210 ± 67 a.u.); however, it did prevent IR-induced increase in DCF fluorescence (2417 ± 53 a.u., p<0.05).
Figure 5.
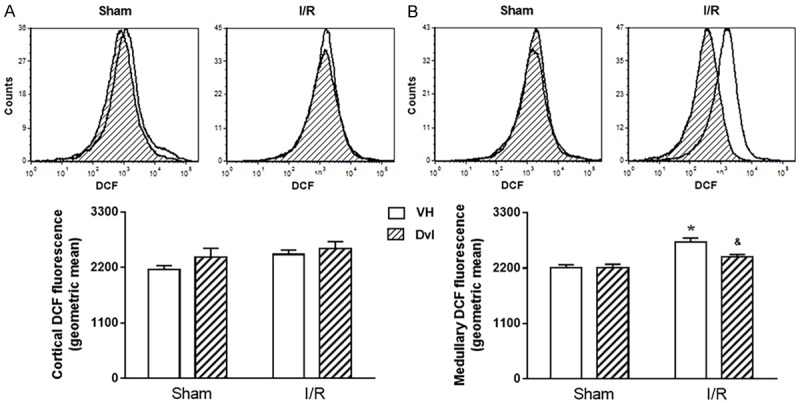
Hydrogen peroxide quantification. Representative histograms from flow cytometric analysis (top panel) using 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF) in all studied groups in the renal cortex (A) and medulla (B); the X axis illustrates the fluorescence intensity for the number of counted cells. No changes were observed in the quantification of cortical hydrogen peroxide (A, bottom panel); however, a remarkable increase in DCF fluorescence was observed in medullary IR vehicle-treated animals, which was partially attenuated by Dvl treatment (B, bottom panel). N=5-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
In Figure 6, we can observe typical DAF flow cytometry histograms (top) and the quantification of nitric oxide production (bottom) in renal cortex (A) and medulla (B). Dvl treatment did not change DAF fluorescence in sham animals in the cortical (VH: 1992 ± 47 vs. Dvl: 2069 ± 98 a.u.) or medullary (VH: 2038 ± 61 a.u. vs. Dvl: 2205 ± 162 a.u.) kidney. However, IR-vehicle-treated animals presented higher nitric oxide production (cortex: 2466 ± 107, medulla: 3081 ± 274 a.u., p<0.05), and Dvl treatment prior to IR resulted in similar levels of DAF fluorescence (cortex: 2123 ± 43, medulla: 2164 ± 154 a.u.) in the IR-Dvl animals when compared to sham group.
Figure 6.
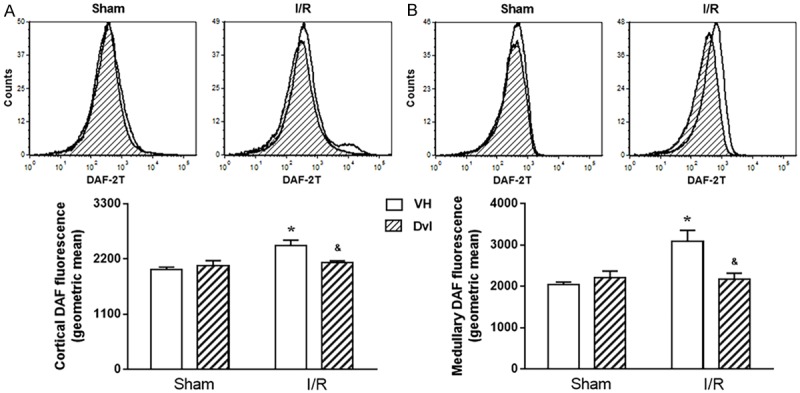
Effects of Dvl on renal production of nitric oxide. Renal cortical (A) and medullary (B) production of nitric oxide. The top panel demonstrates representative histograms from flow cytometric analysis using 4,5-diaminofluorescein-2/diacetate (DAF), and the bottom panel shows the quantification of intracellular nitric oxide production in sham and IR animals treated with vehicle or Dvl in all studied groups. In both renal cortex and medulla, IR VH animals presented an increase in DAF fluorescence, and Dvl intravenous injection prior to IR resulted in a reduction of nitric oxide production. N=5-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. I/R VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
We also evaluated peroxynitrite and hydroxyl production (HPF fluorescence) in renal cortex (Figure 7A) and medulla (Figure 7B). Typical histograms (top) and quantification of HPF fluorescence (bottom) demonstrate that Dvl treatment had no effect on peroxynitrite and hydroxyl production in renal cortex (VH: 1722 ± 48 vs. Dvl: 1749 ± 31 a.u) or medulla (VH: 1740 ± 65 vs. Dvl: 1866 ± 134 a.u.) in sham animals. However, IR increased cortical (2228 ± 121 a.u., p<0.05) and medullary (2641 ± 215 a.u., p<0.05) HPF fluorescence, and Dvl treatment in these animals did result in a reduction of peroxynitrite and hydroxyl production in the kidney (cortex: 1854 ± 47, medulla: 1792 ± 88 a.u., p<0.05).
Figure 7.
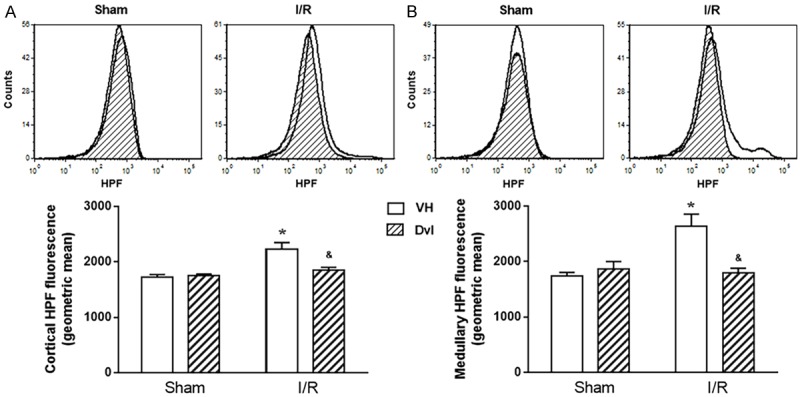
Participation of hydroxyl radical and peroxynitrite. Renal cortical (A) and medullary (B) production of hydroxyl radical and peroxynitrite. The top panel demonstrates representative histograms from flow cytometric analysis using 2-[6-(4’-hydroxy) phenoxy-3H-xanthen-3-on-9-yl] benzoic acid (HPF), and the bottom panel shows the quantification of hydroxyl radical and peroxynitrite production in sham and IR animals treated with vehicle or Dvl in all studied groups. In both renal cortex and medulla, IR VH animals presented an increase in HPF fluorescence, and Dvl intravenous injection prior to IR resulted in a reduction of nitric oxide production. N=5-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
The results of apoptosis in the kidney are displayed in Figure 8. During early phases of apoptosis, phosphatidylserine, usually located in the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane, translocates to the outer layer, becoming available for Annexin V binding. PI is an acid-nucleic acid-specific marker that is excluded from live cells; however, it stains DNA and RNA once the plasma membrane is disrupted. Therefore, flow cytometry using Annexin V and PI could distinguish live and healthy cells (Q3: Annexin V-/PI-) from early apoptotic cells (Q4: Annexin V+/PI-) and late apoptotic or necrotic cells (Q2: Annexin V+/PI+). Representative dotplots (A) and quantification of apoptosis (B) demonstrate that IR significantly increased the percentage of apoptotic cells (6.2 ± 0.5%, p<0.05) when compared to sham animals (VH: 2.5 ± 0.5, Dvl: 2.9 ± 0.6%). Dvl administration exerted a beneficial effect on the IR Dvl group (2.5 ± 0.5%), resulting in apoptosis values similar to those observed in the sham group.
Figure 8.
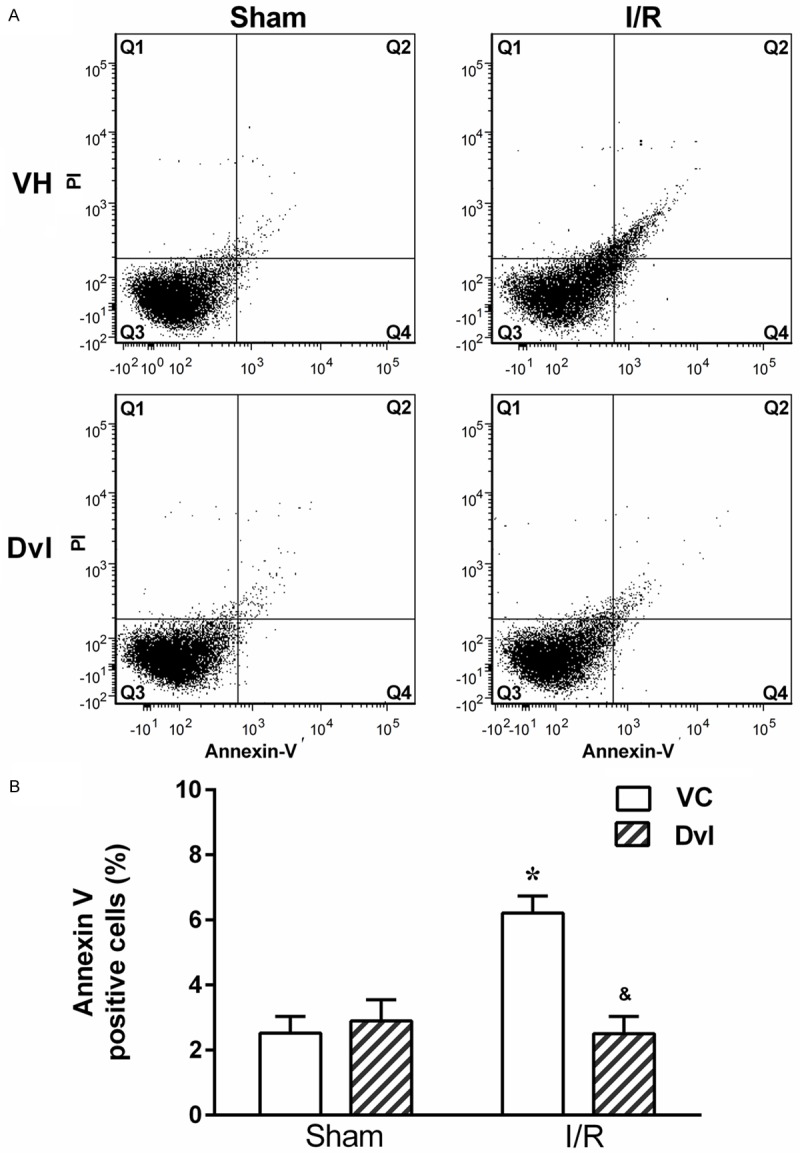
Flow cytometry detection of apoptosis. A. Representative dot plot of Annexin-V and PI flow cytometry for kidney cells. Top left quadrant (Q1) shows damaged cells (Annexin V-/PI+); top right quadrant (Q2) contains cells in late apoptosis or already dead (Annexin V+/PI+); bottom left quadrant (Q3) shows viable cells (Annexin V-/PI-); bottom right quadrant (Q4) represents cells that are in early apoptosis (Annexin V+/PI-). Note an increase in the apoptotic cell number in vehicle-treated IR animals, which is significantly reduced in the Dvl-treated IR group. B. Bar graphs showing the average percentage of renal apoptotic cells (Q2+Q4) in vehicle- (white bars) and Dvl- (cross-hatched bars) treated sham and IR animals. N=4-6. Values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs. sham group; &p<0.05 vs. IR VH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
Discussion
In the present study, we evaluated the effects of Dioclea violacea lectin administered prior to ischemia-reperfusion (IR)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). Our data demonstrate that Dvl administration in IR animals increases glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma and blood flow, while, at the same time, it diminishes renal vascular resistance. Dvl also decreased IR-induced hyperuremia, apoptosis, and myeloperoxidase activity, and preserved tissue morphology. Furthermore, analyses of oxidative stress revealed that the generation of reactive oxygen species was also reduced by Dvl administration in the IR group. Taken together, these data indicate that Dvl lectin administration may have a powerful effect on improving IR-renal dysfunction. This beneficial out comemay be associated with reduced oxidative stress and inflammation, a sobserved in the experimental animals.
Ischemia-reperfusion injury of native and transplant kidneys is a major cause of acute kidney injury and an important determinant of long-term kidney dysfunction [33]. The pathophysiological process of AKI following IR leads to functional and structural changes that are centered around the proximal tubule cells and endothelium [34]. Several pathological events are involved, including disruption of the actin cytoskeleton, generation of reactive oxygen molecules, inflammatory responses and apoptosis [35]. A widely used experimental model to simulate AKI is renal ischemia/reperfusion (IR). Ischemia from renal artery for 45 min followed by 24-hour reperfusion, as used in our study, is the most appropriate animal model to mimic the hemodynamic changes that happen in renal function in humans with AKI [1]. In accordance with our results, others have demonstrated that this model displays a decrease in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate, increase in apoptosis and reactive oxygen species, neutrophil infiltration in kidney, and the presence of histological changes characteristic of AKI [20,25,36].
It has been reported that lectins from the Diocleinae subtribe promote an increase in glomerular filtration rate, perfusion pressure, and renal vascular resistance in isolated kidney [37,38]. Our work showed that Dvl did not interfere with renal function in the sham group, but rather, it rescued glomerular filtration rate, renal vascular resistance and renal blood flow in ischemic animals to normal levels. Furthermore, Dvl reduced the level of urea in the plasma of IR animals. Corresponding to the amelioration of functional markers, we observed reduced histomorphological damage in kidneys from animals pretreated with Dvl.
In renal IR injury, cellular damage is mediated by inflammation [25,39,40], and in our model of IR, we observed an increase in renal inflammation, evaluated through MPO activity. MPO is an enzyme abundant in neutrophils, and it is well established that MPO activity reflects the quantity of neutrophils migrating to tissue during inflammation [24,25]. Our study showed that renal myeloperoxidase activity was significantly increased after IR, but that it was reduced by prior administration of Dvl. These results suggest that the renoprotective action of Dvl involves the inhibition of neutrophil infiltration. In support of our findings, other studies have shown that Dvl reduced neutrophil migration induced by fMLP or carrageenan into rat peritoneal cavities, as well as into of mice with hemorrhagic cystitis [16,17]. Lectins from the Diocleinae subtribe show high homology in amino acid sequence, but they can differ in their biological activities [17,41]. However, other lectins from the Diocleinae subtribe, like Canavalia grandiflora, Dioclea guianensis, Dioclea virgata, and Cratylia floribunda, presented similar results in inhibiting neutrophil infiltration [15,17]. To explain the mechanism of action, it is suggested that lectins operate against the adhesive activities of selectins, competing with these glycoproteins by carbohydrate ligands on endothelial or leukocyte cell membranes [17]. It is well known that selectins play an important role in neutrophil infiltration in kidney IR [42,43], and while we have not tested the influence of Dvl on selectins, it is supposed that the mechanism is the same. In addition to its anti-inflammatory effect, other studies have shown that Dvl also exerts proinflammatory actions, depending on the route of administration [41,44].
Several studies have shown that neutrophil infiltration into the post-ischemic kidney is causative of renal failure. Neutrophils can release various mediators, including proteases, cytokines, and ROS [25,45,46]. Although neutrophils are considered an important source of ROS, hypoxia-reoxygenation is sufficient to cause injury to various cell types, even in the absence of activated neutrophils. Endothelial cells themselves release superoxide anions when subjected to ischemia-reperfusion [47]. In our study, we observed an increase in ROS in renal medulla of the IR group, as assessed by superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, peroxynitrite and hydroxyl levels, and this increase was reversed by Dvl.
Superoxide anion is formed when oxygen accepts one electron (O2 + e-=•O2 -), and it plays a role in AKI [48,49]. Although •O2 - is a weak oxidant, it acts as a precursor of stronger ROS, like hydrogen peroxide, peroxynitrite, hypochlorite and chloramines [48,50]. Hydrogen peroxide is formed when oxygen accepts two electrons or by dismutation of two superoxide anions (O2 + 2e- + 2H+=H2O2 or •O2 - + •O2 - + 2H+=H2O2). H2O2 has a longer half-life than superoxide and is freely diffusible across cell membranes. This molecule can induce cell injury by itself, and it is the precursor of additional ROS, including-hypochlorous acid and hydroxyl radical, an extremely powerful oxidant [48]. Peroxynitrite anion is produced by the reaction between superoxide anion and nitric oxide (NO) and is a potent oxidant [47,51]. In kidney ischemia-reperfusion, these molecules react with proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and cell membrane lipids, resulting in organic radical formation, enzyme inactivation, lipid peroxidation and renal cell destruction [50].
Since the increased oxidative stress contributes to the induction of renal injury in ischemia-reperfusion, treatment with several antioxidant substances has shown promise [45,52,53]. Our work demonstrates, for the first time, the antioxidant effect of Dvl. However, we did not study the pathways leading to the production of ROS. It is possible that Dvl acts directly on the antioxidant defense system, increasing the activity of enzymes like glutathione peroxidase (GPX1), catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), which reduce oxidation rates in an organism and, hence, halt the progression of injury in acute kidney disease [53-55]. It is well known that kidney IR also leads to an increase in oxidant enzyme activity, such as NADPH oxidase and xanthine oxidase, which generate ROS and matrix metalloproteinase induction [56,57]. Dvl might also affect these pathways, but more studies are required to confirm these hypotheses.
Dvl might also increase the production of nitric oxide (NO), a potent antioxidant that can protect from ROS damage [58]. NO generated by the constitutive enzyme endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is beneficial,and mechanisms that increase eNOS activity protect against renal I/R injury [59]. Previous studies observed that Dvl increases the action of NO in vitro by promoting vasorelaxation, as well as other lectins from the Diocleinae subtribe, such as Dioclea rostrata, Dioclea grandiflora, Canavalia gladiata and Canavalia brasiliensis [13,60,61]. However, in our model of renal ischemia-reperfusion, NO increased in renal medulla of the ischemic group, possibly by the increase of (iNOS) protein expression, as already observed in other studies [62,63]. It is hypothesized that excessive NO produced in response to an increase in iNOS is deleterious to renal function because excess NO reacts with O2 to form ONOO- [58,62]. On the other hand, the expression of eNOS is decreased in acute kidney injury, contributing to renal impairment from renal vasoconstriction [20]. In our work, Dvl did not increase the levels of NO, as seen before, but rather, normalized the levels of NO in renal medulla of IR rats, indicating that Dvl may have an effect on eNOS/iNOS imbalance during AKI.
As determined from flow cytometry, the kidney of IR rats presented apoptotic cells, corroborating other studies using the same AKI rat [39], as well as mouse [64], models, a phenomenon which is consistent with the histopathology of acute kidney disease in human [65]. Our study is the first to evaluate the effects of Dvl in apoptosis in vivo when applied intravenously, and we observe that Dvl treatment was able to reduce both early and late apoptosis in AKI rats to sham levels. When applied via the subcutaneous route, Dvl had the opposite effect in that it induced apoptosis in mouse lymph nodes and necrosis of high endothelial venules [44]. In vitro, other lectins from the Diocleinae subtribe, such as Canavalia brasiliensis and Canavalia ensiformis, also induced increased apoptosis in culture of splenocyte [12] and human leukemia cell lines [66]. These results are consistent with the findings that Dvl has anti-inflammatory effect by intravenous injection and proinflammatory effect by local administration. The improvement in apoptosis in the IR group could be associated with amelioration of ROS, since it is well established that ROS production is able to initiate cell death programs in the form of apoptosis or necrosis [47].
Therefore, this article demonstrates, for the first time, that Dvl promotes beneficial effects, both functionally and histomorphologically, in AKI induced by IR in rat kidney. This improvement of renal outcome is linked to a reduction in neutrophil infiltration and apoptotic markers, as well as suppression of oxidative stress. These unique findings suggest that Dioclea violacea lectin is not toxic for the kidney and could be used as a promising approach in the management of AKI, including that generated by IR.
Acknowledgements
National Council for the Development of Science and Technology-CNPq; State Agency for the Development of Science and Technology; Multiuser Laboratory of Biomolecular Analysis and Multiuser Laboratory of Histology and Immunohistochemistry of the Health Sciences Center of the Federal University of Espirito Santo.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Singh AP, Junemann A, Muthuraman A, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Grover K, Dhawan R. Animal models of acute renal failure. Pharmacol Rep. 2012;64:31–44. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tögel F, Westenfelder C. Recent advances in the understanding of acute kidney injury. Prime Reports. 2014;6:83. doi: 10.12703/P6-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moore EM, Bellomo R, Nichol AD. The meaning of acute kidney injury and its relevance to intensive care and anaesthesia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2012;40:929–948. doi: 10.1177/0310057X1204000604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Klenzac J, Himmelfarb J. Sepsis and the kidney. Crit Care Clin. 2005;21:211–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2005.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Coca SG, Bauling P, Schifftner T, Howard CS, Teitelbaum I, Parikh CR. Contribution of acute kidney injury toward morbidity and mortality in burns: a contemporary analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:517–523. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.12.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kuitunen A, Vento A, Suojaranta-Ylinen R, Pettilä V. Acute renal failure after cardiac surgery: evaluation of the RIFLE classification. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81:542–546. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.07.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rudnick MR, Goldfarb S, Tumlin J. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Is the picture any clearer? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:261–262. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04951107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gettings LG, Reynolds HN, Scalea T. Outcome in post-traumatic acute renal failure when continuous renal replacement therapy is applied early vs. late. Intensive Care Med. 1999;25:805–813. doi: 10.1007/s001340050956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sands JM, Neylan JF, Olson RA, O’Brien DP, Whelchel JD, Mitch WE. Atrial natriuretic factor does not improve the outcome of cadaveric renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991;1:1081–1086. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V191081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bon D, Chatauret N, Giraud S, Thuillier R, Favreau F, Hauet T. New strategies to optimize kidney recovery and preservation in transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:339–347. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Furuichi K, Shintani H, Sakai Y, Ochiya T, Matsushima K, Kaneko S, Wada T. Effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal cells on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16:679–689. doi: 10.1007/s10157-012-0614-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Oliveira Silva F, das Neves Santos P, de Melo CM, Teixeira EH, de Sousa Cavada B, Arruda FV, Cajazeiras JB, Almeida AC, Pereira VA, Porto AL. Immunostimulatory activity of ConBr: a focus on splenocyte proliferation and proliferative cytokine secretion. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;346:237–44. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Assreuy AM, Fontenele SR, Pires Ade F, Fernandes DC, Rodrigues NV, Bezerra EH, Moura TR, do Nascimento KS, Cavada BS. Vasodilator effects of Diocleinae lectins from the Canavalia genus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009;380:509–21. doi: 10.1007/s00210-009-0465-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Warren JR. Polymyxin B suppresses the endotoxin inhibition of concanavalin A-mediated erythrocyte agglutination. Infect Immun. 1982;35:594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.594-599.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nunes BS, Rensonnet NS, Dal-Secco D, Vieira SM, Cavada BS, Teixeira EH, Moura TR, Teixeira CS, Clemente-Napimoga JT, Cunha FQ, Napimoga MH. Lectin extracted from Canavalia grandiflora seeds presents potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009;379:609–616. doi: 10.1007/s00210-009-0397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Assreuy AMS, Martins GJ, Moreira MEF, Brito GAC, Cavada BS, Ribeiro RA, Flores CA. Prevention of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis by glucose-manose binding plant lectins. J Urol. 1999;161:1988–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Assreuy AM, Shibuya MD, Martins GJ, De Souza ML, Cavada BS, Moreira RA, Oliveira JT, Ribeiro RA, Flores CA. Anti-inflammatory effect of glucose-mannose binding lectins isolated from Brazilian beans. Mediators Inflamm. 1997;6:201–210. doi: 10.1080/09629359791695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Teixeira EH, Napimoga MH, Carneiro VA, de Oliveira TM, Cunha RMS, Havt A, Martins JL, Pinto VPT, Gonçalves RB, Cavada BS. In vitro inhibition of Streptococci binding to enamel acquired pellicle by plant lectins. J Appl Microbiol. 2006;101:111–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sivarajah A, Chatterjee PK, Patel NS, Todorovic Z, Hattori Y, Brown PA, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Cuzzocrea S, Thiemermann C. Agonists of Peroxisome-Proliferator Activated Receptor-Gamma Reduce Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Am J Nephrol. 2003;23:267–276. doi: 10.1159/000072088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Betz B, Schneider R, Kress T, Schick MA, Wanner C, Sauvant C. Rosiglitazone affects nitric oxide synthases and improves renal outcome in a rat model of severe ischemia/reperfusion injury. PPAR Res. 2012;2012:219319. doi: 10.1155/2012/219319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rocco L, Gil FZ, da Fonseca Pletiskaitz TM, de Fátima Cavanal M, Gomes GN. Effect of sodium overload on renal function of offspring from diabetic mothers. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008;23:2053–2060. doi: 10.1007/s00467-008-0884-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Magalhães JCG, da Silveira AB, Mota DL, Paixão AD. Renal function in juvenile rats subjected to prenatal malnutrition and chronic salt overload. Exp Physiol. 2006;91:611–619. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2005.032995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pundir M, Arora S, Kaur T, Singh R, Singh AP. Effect of modulating the allosteric sites of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury. J Surg Res. 2013;183:668–677. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G, Bradley PP. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation-estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:206–209. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hagar HH, Abd El Tawab R. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonism alleviates renal injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. J Surg Res. 2012;178:e25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Folkmann JK, Loft S, Møller P. Oxidatively damaged DNA in aging dyslipidemic ApoE-/- and wild-type mice. Mutagenesis. 2007;22:105–110. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gel059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dias AT, Rodrigues BP, Porto ML, Gava AL, Balarini CM, Freitas FP, Palomino Z, Casarini DE, Campagnaro BP, Pereira TM, Meyrelles SS, Vasquez EC. Sildenafil ameliorates oxidative stress and DNA damage in the stenotic kidneys in mice with renovascular hypertension. J Transl Med. 2014;12:35. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schachnik NC, Peruhype-Magalhães V, Paula GM, Lucas F, Freitas VM, Martins-Filho OA, Dusse LMS. Intracellular nitric oxide assessment in whole blood leukocytes by flow cytometry: optimization and applicability to monitor patients with chronic graft nephropathy. J Immunol Methods. 2009;343:103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Campagnaro BP, Tonini CL, Nogueira BV, Casarini DE, Vasquez EC, Meyrelles SS. DNA damage and augmented oxidative stress in bone marrow mononuclear cells from angiotensin-dependent hypertensive mice. Int J Hypertens. 2013;2013:305302. doi: 10.1155/2013/305202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tonini CL, Campagnaro BP, Louro LP, Pereira TMC, Vasquez EC, Meyrelles SS. Effects of aging and hypercholesterolemia on oxidative stress and DNA damage in bone marrow mononuclear cells in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:3325–3342. doi: 10.3390/ijms14023325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Setsukinai K, Urano Y, Kakinuma K, Majima HJ, Nagano T. Development of novel fluorescence probes that can reliably detect reactive oxygen species and distinguish specific species. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:3170–3175. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209264200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Monga J, Pandit S, Chauhan RS, Chauhan CS, Chauhan SS, Sharma M. Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction by (+)-cyanidan-3-ol in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kennedy SE, Erlich JH. Murine renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Nephrology. 2008;13:390–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2008.00979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Semedo P, Palasio CG, Oliveira CD, Feitoza CQ, Gonçalves GM, Cenedeze MA, Wang PM, Teixeira VPA, Reis MA, Pacheco-Silva A, Câmara NO. Early modulation of inflammation by mesenchymal stem cell after acute kidney injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9:677–682. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bagul A, Frost JH, Drage M. Stem cells and their role in renal ischaemia reperfusion injury. Am J Nephrol. 2013;37:16–29. doi: 10.1159/000345731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ferreyra C, Vargas F, Rodríguez-Gómez I, Pérez-Abud R, O’Valle F, Osuna A. Preconditioning with triiodothyronine improves the clinical signs and acute tubular necrosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion in rats. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Havt A, Barbosa PS, Sousa TM, Martins AM, Nobre AC, Nascimento KS, Teixeira EH, Pinto VP, Sampaio AH, Fonteles MC, Cavada BS, Monteiro HSA. Renal alterations promoted by the lectins from Canavalia ensiformis (ConA) and Dioclea guianensis (DguiL) seeds. Protein Pept Lett. 2003;10:191–107. doi: 10.2174/0929866033479130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Teixeira EH, Havt A, Barbosa PSF, Meneses DB, Fonteles MC, Monteiro HS, Sampaio AH, Cavada BS. Renal effects of the lectin from Canavalia brasiliensis seeds. Protein Pept Lett. 2001;8:477–484. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Si Y, Bao H, Xu L, Wang X, Shen Y, Wang J, Yang X. Dexmedetomidine protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidney. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Feitoza CQ, Gonçalves GM, Semedo P, Cenedeze MA, Pinheiro HS, Beraldo FC, dos Santos OF, Teixeira Vde P, dos Reis MA, Mazzali M, Pacheco-Silva A, Câmara NO. Inhibition of COX 1 and 2 prior to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury decreases the development of fibrosis. Mol Med. 2008;14:724–730. doi: 10.2119/2008-00064.Feitoza. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.de Alencar NM, Mota MR, Rodrigues NV, Martins JL, do Nascimento KS, Assreuy AM, Cavada BS. Neutrophil-infiltrated paw edema induced by mannose-binding Dioclea violacea lectin. Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65:220–5. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)70982-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Herter JM, Rossaint J, Block H, Welch H, Zarbock A. Integrin activation by P-Rex1 is requirid for selectin-mediated slow leukocyte rolling and intravascular crawling. Blood. 2013;121:2301–2310. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-457085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Singbartl K, Ley K. Protection from ischemia-reperfusion induced severe acute renal failure by blocking E-selectin. Crit Care Med. 2000;28:2507–2514. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200007000-00053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Barbosa T, Arruda S, Cavada B, Barbosa T, Freitas LA, Barral-netto M. In vivo lymphocyte activation and apoptosis by lectins of the Diocleinae subtribe. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2001;96:673–678. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762001000500016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Zacharowski K, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Thiemermann C. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Kidney Int. 2000;58:658–673. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Singbartl K, Forlow SB, Ley K. Platelet, but not endothelial, P-selectin is critical for neutrophil-mediated acute postischemic renal failure. FASEB J. 2001;15:2337–2344. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0199com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li C, Jackson RM. Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282:C227–C241. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00112.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Andreoli SP. Reactive oxygen molecules, oxidant injury and renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991;5:733–742. doi: 10.1007/BF00857888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sehajpal J, Kaur T, Bhatti R, Singh AP. Role of progesterone in melatonin-mediated protection against acute kidney injury. J Surg Res. 2014;191:441–447. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Masztalerz M, Włodarczyk Z, Czuczejko J, Słupski M, Kedziora J. Superoxide anion as a marker of ischemia-reperfusion injury of the transplanted kidney. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:46–8. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.12.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Noiri E, Nakao A, Uchida K, Tsukahara H, Ohno M, Fujita T, Brodsky S, Goligorsky MS. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;281:F948–F957. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2001.281.5.F948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Miloradović Z, Mihailović-Stanojević N, Milanović JG, Ivanov M, Kuburović G, Marković-Lipkovski J, Jovović D. Comparative effects of L-arginine and vitamin C pretreatment in SHR with induced postischemic acute renal failure. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2009;28:105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zou C, Hu H, Xi X, Shi Z, Wang G, Huang X. Pioglitazone protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by enhancing antioxidant capacity. J Surg Res. 2013;184:1092–1095. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Abraham P, Rabi S. Protective effect of aminoguanidine against cyclophosphamide-induce oxidative stress and renal damage in rats. Redox Rep. 2011;16:8–14. doi: 10.1179/174329211X12968219310837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mammadov E, Aridogan IA, Izol V, Acikalin A, Abat D, Tuli A, Bayazit Y. Protective effects of phosphodiesterase-4-specific inhibitor rolipram on acute ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat kidney. Urology. 2012;80:1390, e1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2012.07.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wu HH, Hsiao TY, Chien CT, Lai MK. Ischemic conditioning by short periods of reperfusion attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis and autophagy in the rat. J Biomed Sci. 2009;16:19. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tsuda H, Kawada N, Kaimori JY, Kitamura H, Moriyama T, Rakugi H, Takahara S, Isaka Y. Febuxostat suppressed renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via reduced oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;427:266–272. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mangge H, Becker K, Fuchs D, Gostner JM. Antioxidants, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. World J Cardiol. 2014;6:462–477. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chiazza F, Chegaev K, Rogazzo M, Cutrin JC, Benetti E, Lazzarato L, Fruttero R, Collino M. A nitric oxide-donor furoxan moiety improves the efficacy of edaravone against early renal dysfunction and injury evoked by ischemia/reperfusion. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:804659. doi: 10.1155/2015/804659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bezerra MJ, Rodrigues NV, Pires Ade F, Bezerra GA, Nobre CB, Alencar KL, Soares PM, do Nascimento KS, Nagano CS, Martins JL, Gruber K, Sampaio AH, Delatorre P, Rocha BA, Assreuy AM, Cavada BS. Crystal structure of Dioclea violacea lectin and a comparative study of vasorelaxant properties with Dioclea rostrata lectin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:807–815. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Andrade JL, Arruda S, Barbosa T, Paim L, Ramos MV, Cavada BS, Barral-Netto M. Lectin-induced nitric oxide production. Cell Immunol. 1999;194:98–102. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1999.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Korkmaz A, Kolankaya D. Inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase with rutin reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Can J Surg. 2013;56:6–14. doi: 10.1503/cjs.004811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chatterjee PK, Patel NS, Kvale EO, Dugo L, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Britti D, Yagoob M, Thiemermann C. GW274150, a potent and highly selective inhibitor of iNOS, reduces experimental renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2003;63:853–865. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kumar S, Allen DA, Kieswich JE, Patel NS, Harwood S, Mazzon E, Cuzzocrea S, Raftery MJ, Thiemermann C, Yaqoob MM. Dexamethasone ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN. 2009;20:2412–2425. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008080868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lerolle N, Nochy D, Guerot E, Bruneval P, Fagon JY, Diehl JL, Hill G. Histopathology of septic shock induced acute kidney injury: apoptosis and leukocytic infiltration. Intensive Care Med. 2009;36:471–478. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Faheina-Martins GV, Silveira AL, Cavalcanti BC, Ramos MV, Moraes MO, Pessoa C, Araújo DA. Antiproliferative effects of lectins from Canavalia ensiformis and Canavalia brasiliensis in human leukemia cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 2012;26:1161–1169. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2012.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


