Abstract
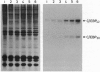
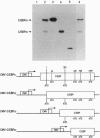
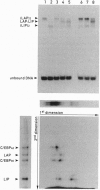
The CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) alpha is a leucine zipper protein that is preferentially expressed in certain cell types, such as adipocytes and hepatocytes. Here we show that C/EBP alpha mRNA is translated into two major proteins, C/EBP-42 and C/EBP-30, that differ in their content of N-terminal amino acid sequences. These results are best explained by a ribosome-scanning mechanism in which a fraction of ribosomes ignore the first two AUGs and initiate translation at an AUG located 351 nt downstream of the first one. Because C/EBP-30, the translation product initiated at the third AUG, is devoid of the potent transcription-activation domain contained in C/EBP-42, the former protein stimulates transcription from the mouse albumin promoter much less efficiently than the latter. The gene encoding the liver-enriched transcriptional-activator protein LAP (C/EBP-beta) has also been shown to issue two proteins, LAP and the liver-enriched transcriptional-inhibitory protein LIP, with different transcription-activation potentials. The production of multiple proteins from a single mRNA is not only shared between different C/EBP family members but also appears to be conserved in vertebrate evolution.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calkhoven C. F., Ab G., Wijnholds J. c/CEPB, a chicken transcription factor of the leucine-zipper C/EBP family [corrected]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4093–4093. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. More is better: activators and repressors from the same gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90178-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. Identification of two polypeptide segments of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein required for transcriptional activation of the serum albumin gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1416–1426. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. A rapid method for the isolation of DNA-binding proteins from purified nuclei of tissues and cells in culture. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3555–3559. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Severne Y., Georgiev O., Galli I., Wieland S. A novel expression assay to study transcriptional activators. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90008-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Tata J. R. Characterization and developmental expression of Xenopus C/EBP gene. Mech Dev. 1992 Jul;38(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90039-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]