Abstract
Serum lactic dehydrogenase, alpha-hydroxy-butyrate dehydrogenase, iso-citric dehydrogenase, and glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase activities were measured daily for two weeks postoperatively in the serum of 22 patients undergoing cardiac surgery with extracorporeal circulation.
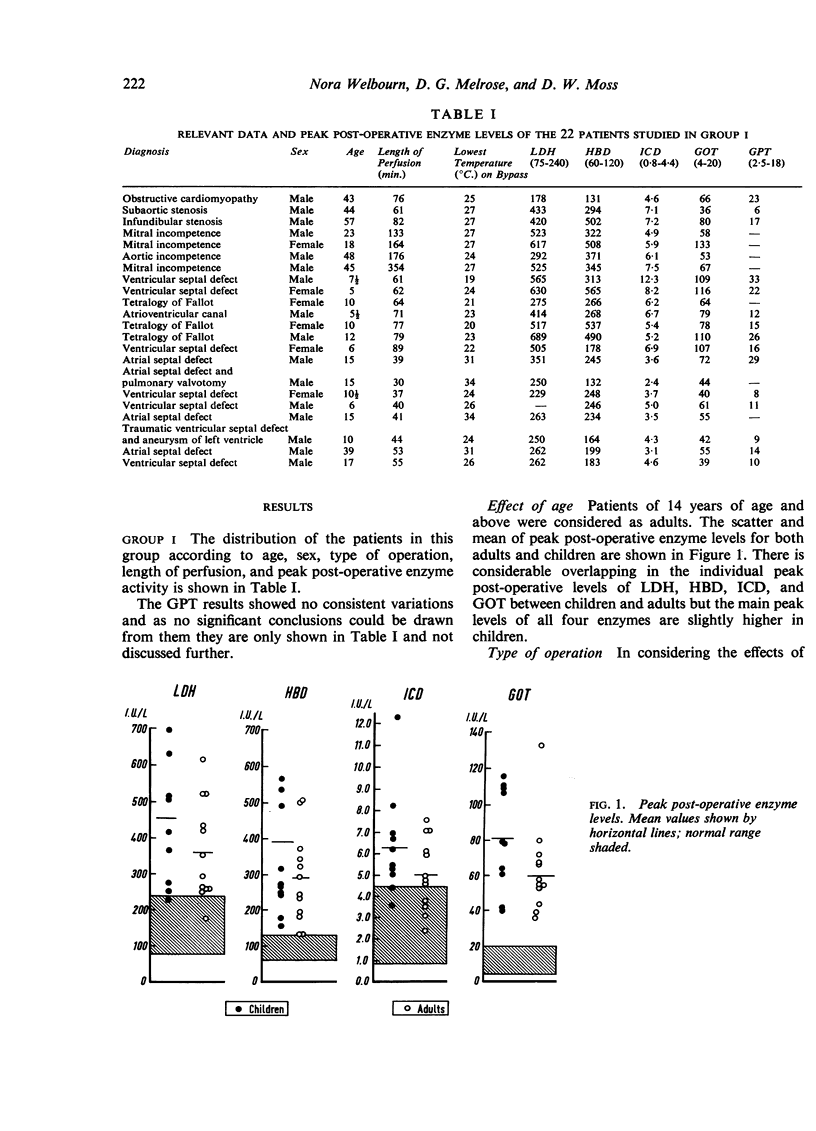
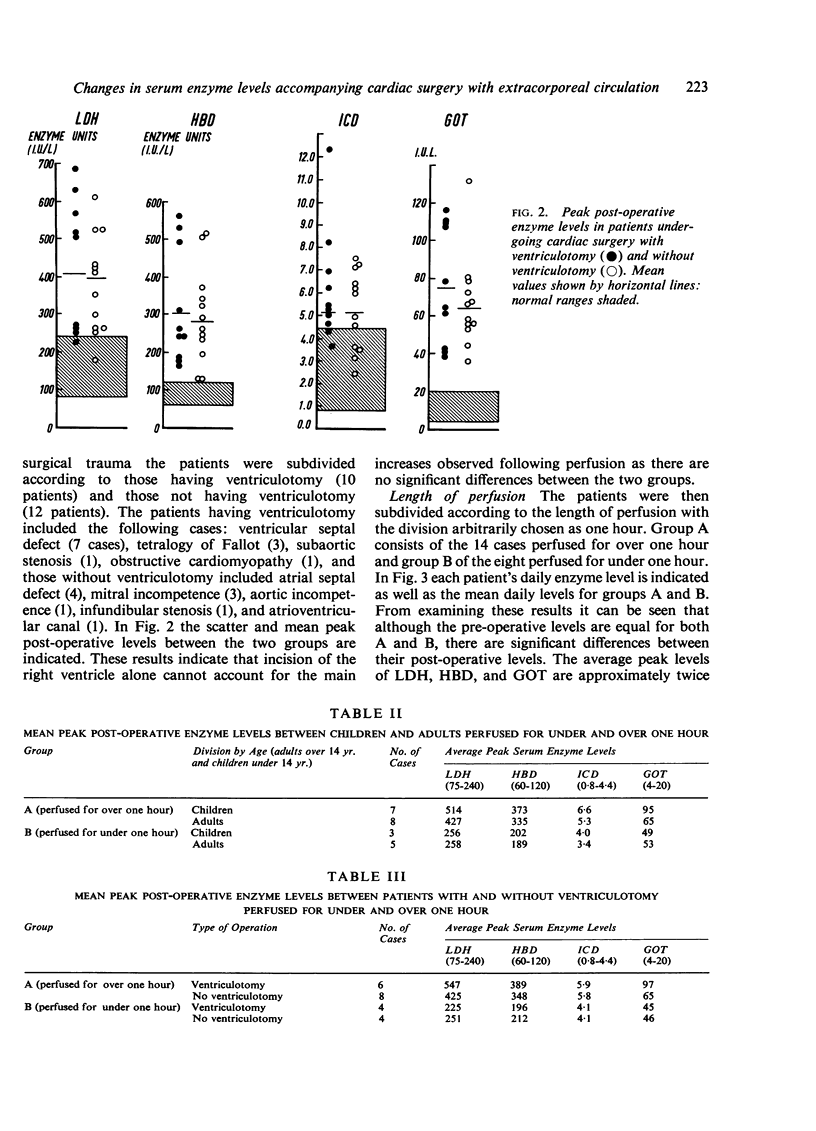
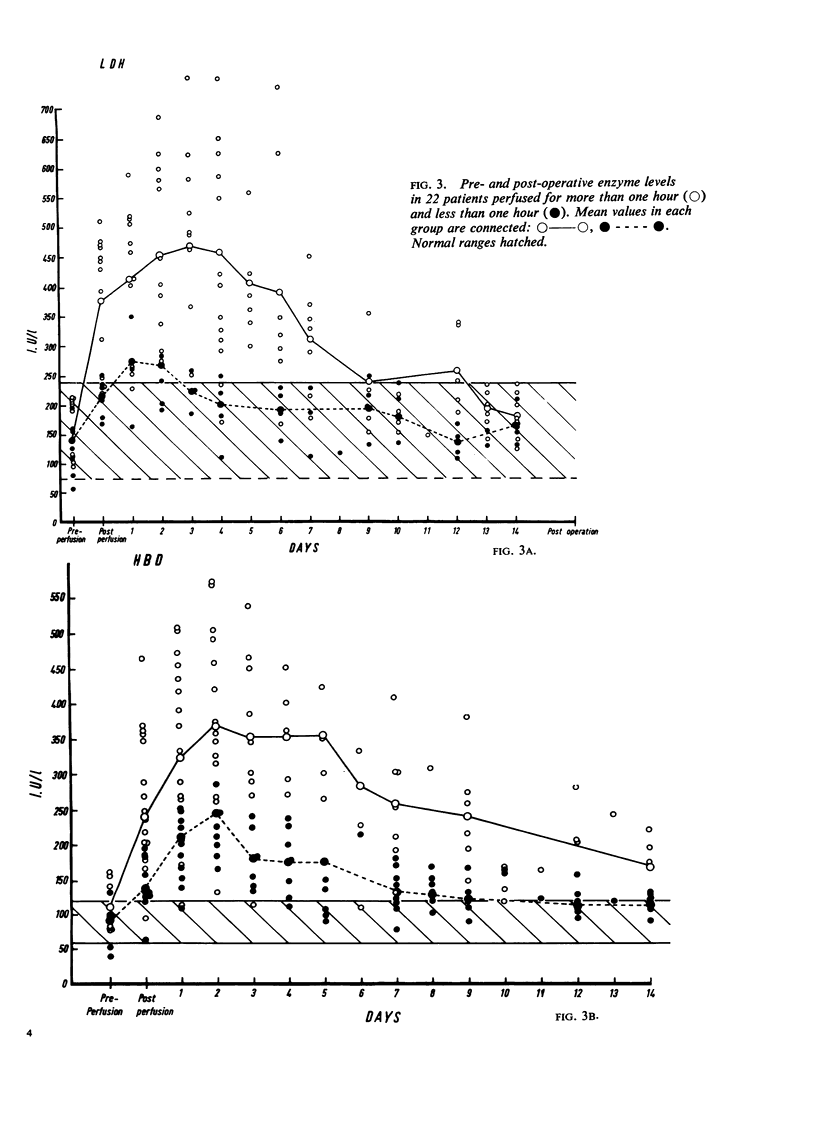
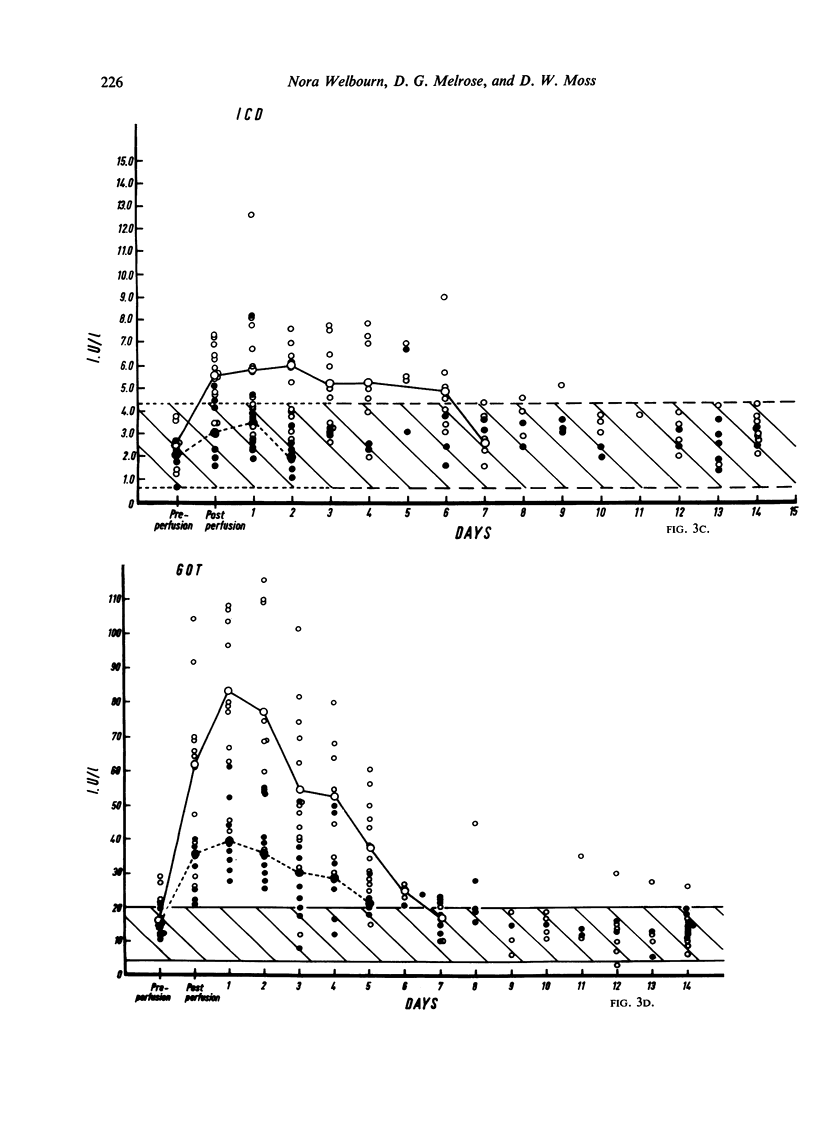
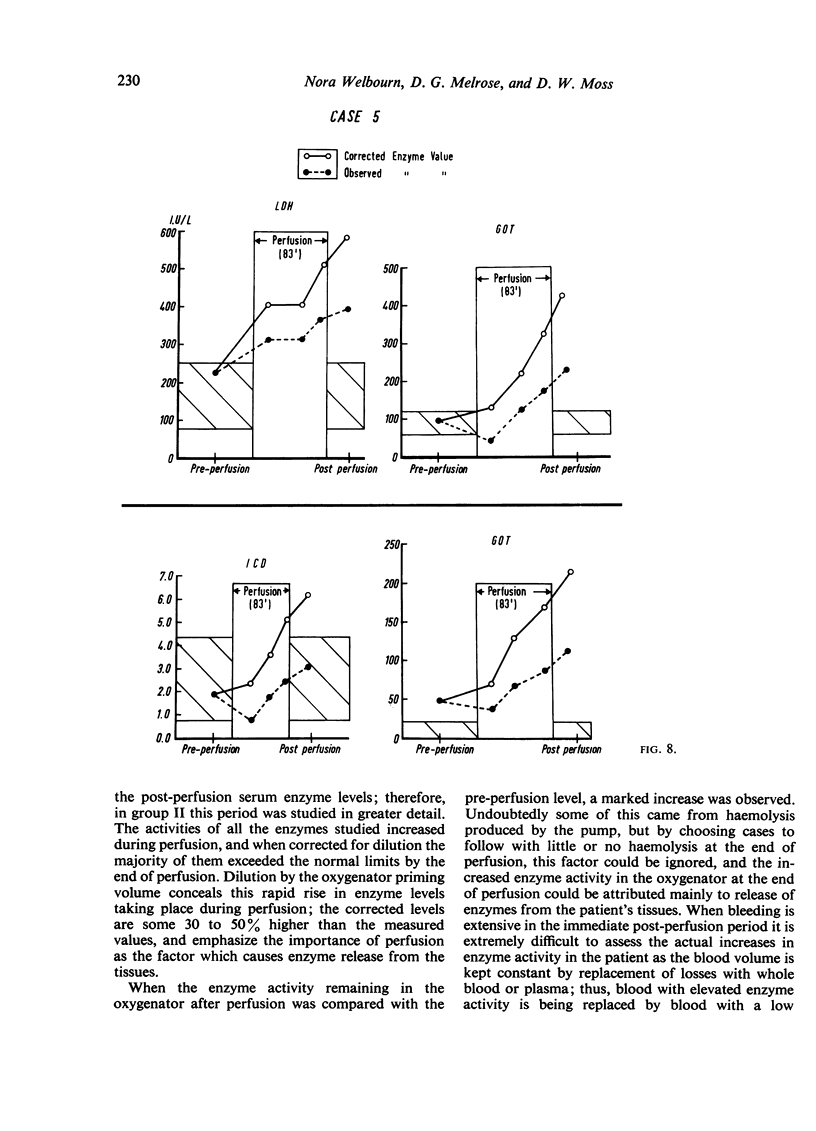
The length of perfusion was found to be a major factor affecting the extent of increased post-operative enzyme activities. Significantly higher levels were demonstrated in patients perfused for over one hour compared with those perfused for under one hour. Hepatocellular damage, age, and type of operation were not considered to be major factors in determining the extent of this increased activity.
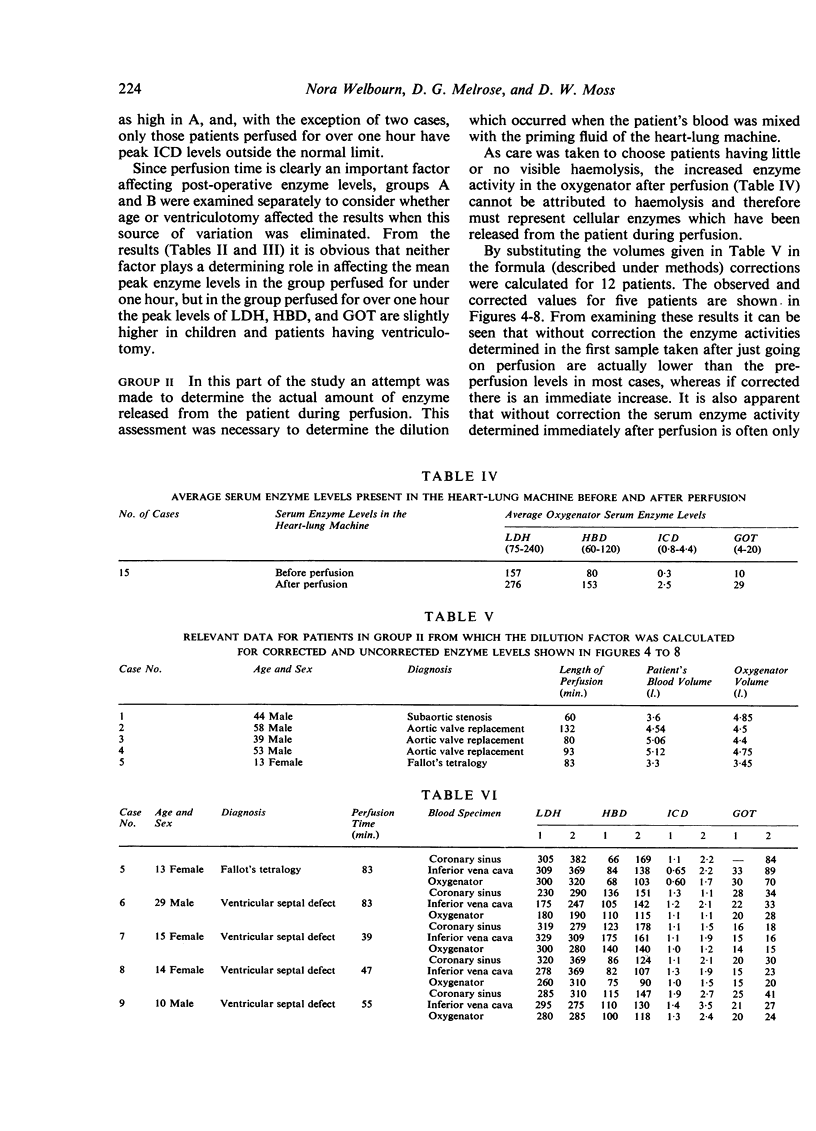
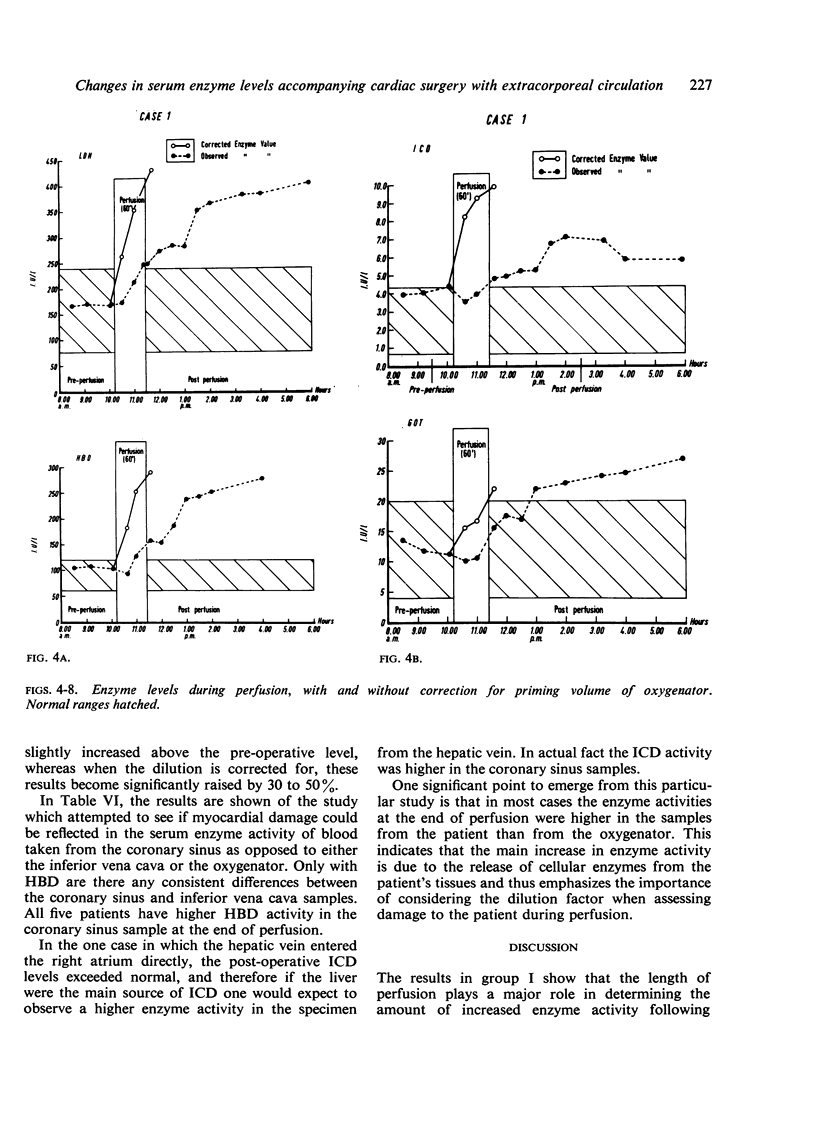
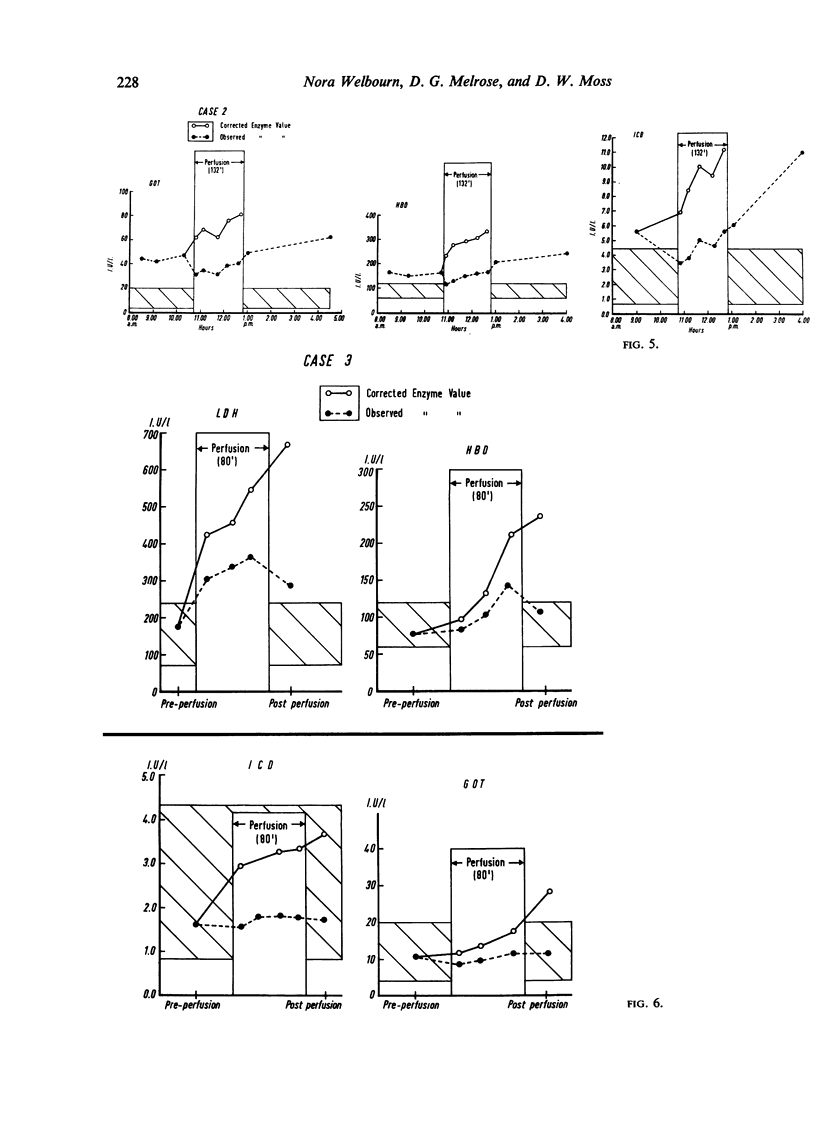
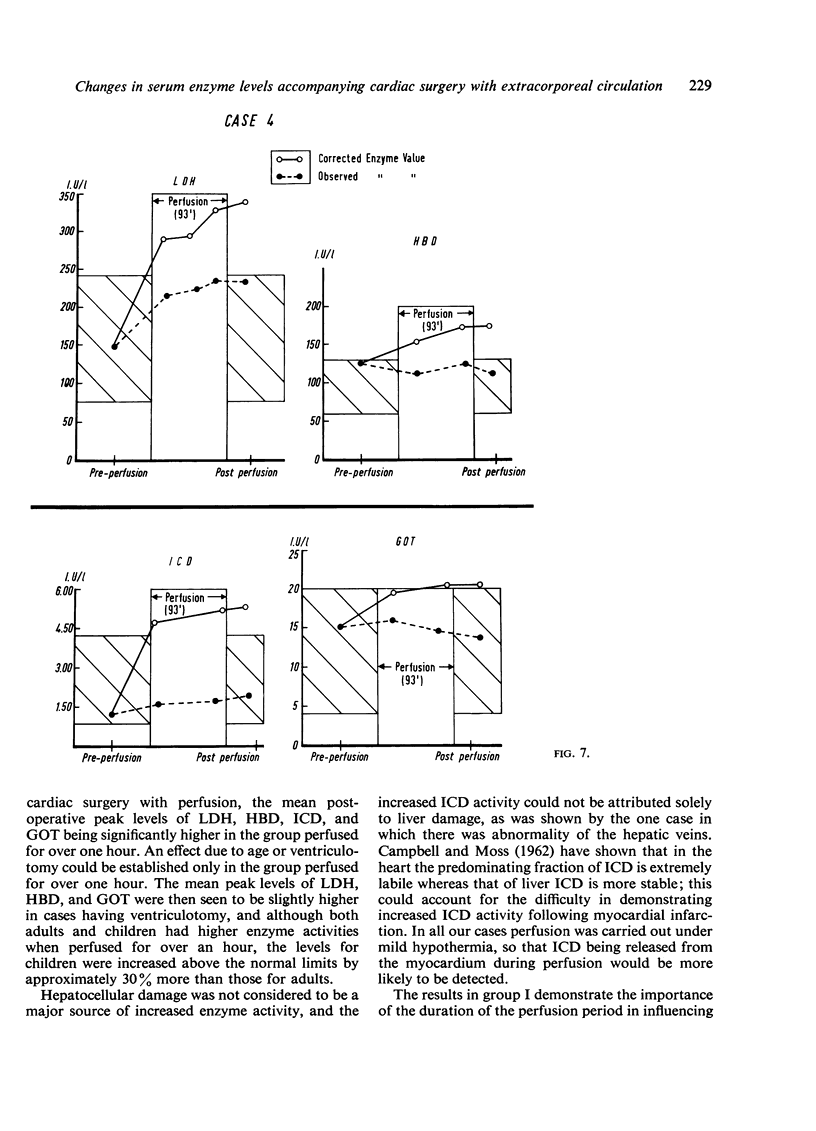
A considerable increase in enzyme activity was found to occur during perfusion when the dilution introduced by mixing the patient's circulation with the priming fluid of the heart-lung machine was taken into account. This dilution, when accounted for, increased the observed enzyme activity by 30 to 50%.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAER H., BLOUNT S. G., Jr The response of the serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase to open-heart operation. Am Heart J. 1960 Dec;60:867–878. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(60)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANG N. U., IVERSEN K., JAGT T., TOBIASSEN G. Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase activity as an index of centrilobular liver cell necrosis in cardiac and circulatory failure. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Aug 15;164:385–393. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1959.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANDURA F., MINARDI C. Sul comportamento della transaminasi glutammicoossalacetica sierica in pazienti sottoposti a interventi chirurgici e in soggetti traumatizzati. Minerva Chir. 1957 Sep 30;12(18):1077–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAFOORD C., NORBERG B., SENNING A. Clinical studies in extracorporeal circulation with a heart-lung machine. Acta Chir Scand. 1957 Mar 28;112(3-4):220–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVER W. L., JOHNSON G., Jr, BEAL J. M. Alterations in serum glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase activity following operations. Surg Forum. 1957;8:77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI CARLO G., PARISI A. Modificazioni dell'attività transaminasica nel decorso post-operatorio e suo significato. Riforma Med. 1957 Nov 9;71(45):1275–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT B. A., WILKINSON J. H. Serum "alpha-hydroxybutyric dehydrogenase" in myocardial infarction and in liver disease. Lancet. 1961 Apr 1;1(7179):698–699. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91724-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER R. S., ROSSALL R. E., BLACK W., DVORKIN J. Serum transaminase response to cardiac surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1962 Jun;43:810–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSS W. H., GERLACH U., SCHUR-MEYER E. Uber die Pathogenese und die klinische Bedeutung der Hyperfermentämie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1958 Aug 1;83(31):1310–1315. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1113777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONTZ J., BOUNOUS G., HEIMBURGER I., SU C. S., TERAMOTO S., SHUMACKER H. B., Jr, ONNIS M. Renal and portal blood flow under normothermic and hypothermic conditions during extracorporeal circulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1960;39:781–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. J., CAMPBELL D. M. International enzyme units. An attempt at international agreement. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 May;6:301–306. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONTTINEN A. alpha-Hydroxybutyric dehydrogenase in the detection of myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1961 Sep 2;2(7201):556–556. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92994-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE S. H., SCHULKINS T. Serum transaminase levels following prolonged surgical anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1956 Jul-Aug;17(4):531–535. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195607000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONG D. M., Jr, SANCHEZ L., VARCO R. L., LILLEHEI C. W. The use of low molecular weight dextran and serum albumin as plasma expanders in extracorporeal circulation. Surgery. 1961 Jul;50:12–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELROSE D. G. Types of heart-lung machines used in extra-corporeal circulation. Postgrad Med J. 1961 Nov;37:639–645. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.37.433.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKELL W. K., ALLBRITTEN F. F., Jr Serum transaminase content related to tissue injury. Surgery. 1957 Jul;42(1):240–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORBERG B., SENNING A. A study of serum enzymes during and after open heart surgery with the Crafoord-Senning heart-lung machine. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1959;Suppl 245:275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERSON D. A., JUDGE R. D. Effect of operation on serum transaminase levels. AMA Arch Surg. 1958 Dec;77(6):892–897. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1958.01290050062012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PYOERAELAE K., GORDIN R., KONTTINEN A., TELIVUO L. SERUM ENZYMES AFTER CARDIAC SURGERY. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Sep;174:361–374. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb07935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUINN J. W., SIRAK H. D., SHABANAH E. H., FRAJOLA W. J. Transaminase values following open-heart surgery. Ann Surg. 1960 Jul;152:45–50. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196007000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSALKI S. B., WILKINSON J. H. Reduction of alpha-ketobutyrate by human serum. Nature. 1960 Dec 24;188:1110–1111. doi: 10.1038/1881110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMPSON J. J. Serum transaminase and other enzymes in acute myocardial infarction. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1958 Oct;1(2):187–205. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(59)80058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER D. D., BARNARD C. N., VARCO R. L., LILLEHEI C. W. Serum transaminase patterns following intracardiac surgery. Surgery. 1958 Dec;44(6):1083–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERKEL R. L., SPENCER J. A., WOLFSON S. K., Jr, WILLIAMS-ASHMAN H. G. Serum isocitric dehydrogenase activity with particular reference to liver disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Aug;52(2):176–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANDJORD P. E., THOMAS K. E., WHITE L. P. Studies on isocitric and lactic dehydrogenases in experimental myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2111–2118. doi: 10.1172/JCI103989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER W. F., MORGAN H. G. PLASMA-TRANSAMINASE LEVELS IN CARDIAC SURGERY WITH EXTRACORPOREAL CIRCULATION. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):683–686. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., TRAUTSCHOLD I., GORRIZ A., ZILL R. [On the behavior of serum glutamate-oxalacetate transaminase, glutamate-pyruvate transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase activity after surgical heart interventions]. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Jan;6:99–108. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. P. Some enigmas in the comparison of multiple serum enzyme levels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):349–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


