Abstract
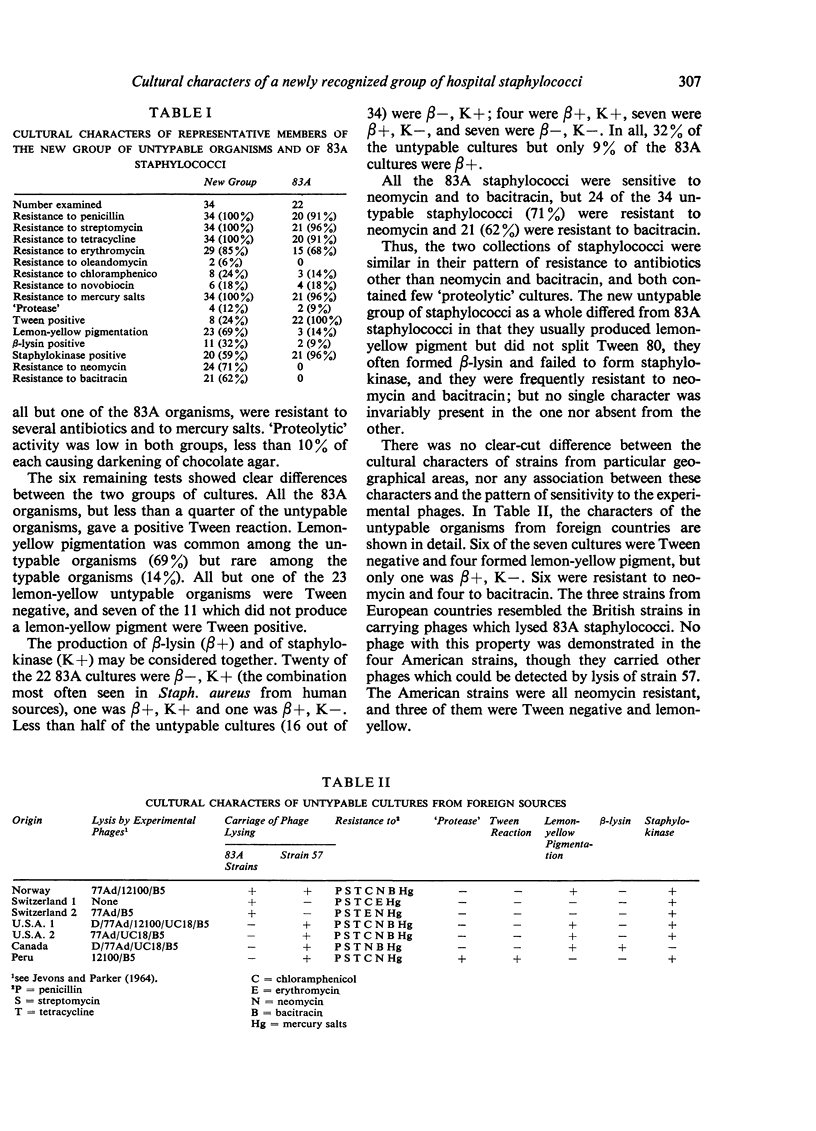
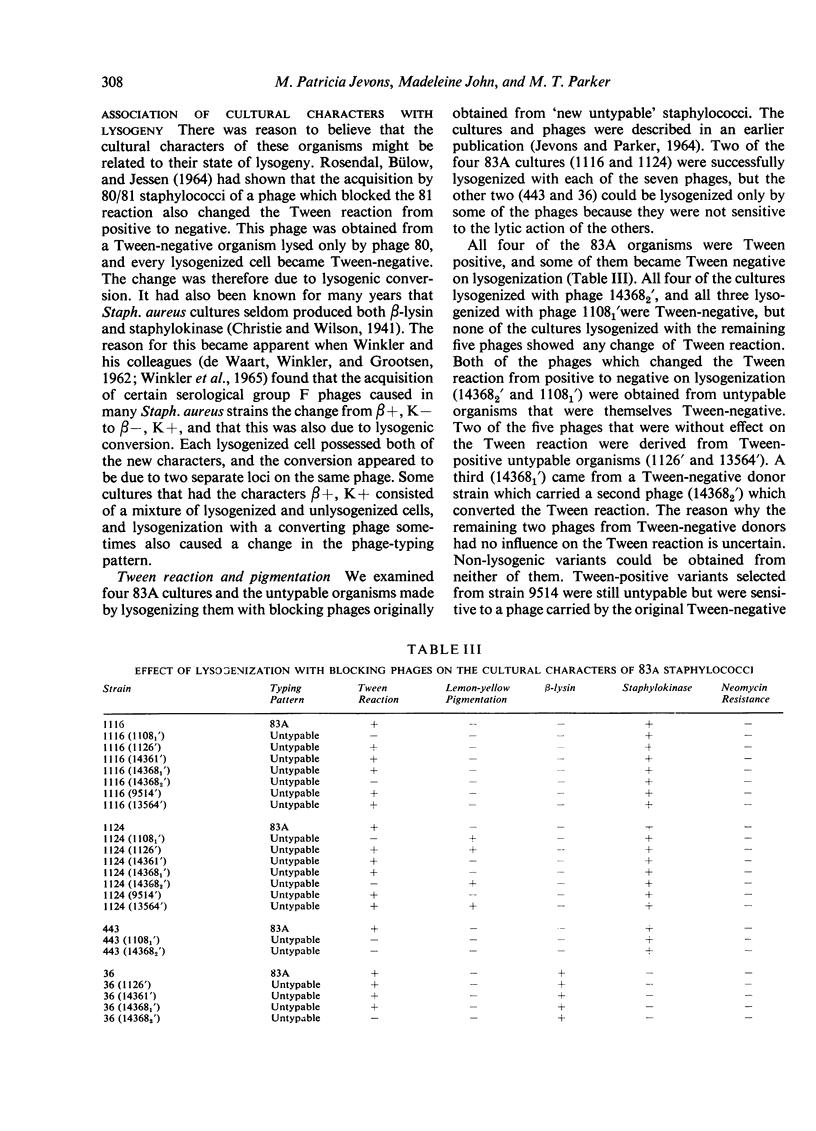
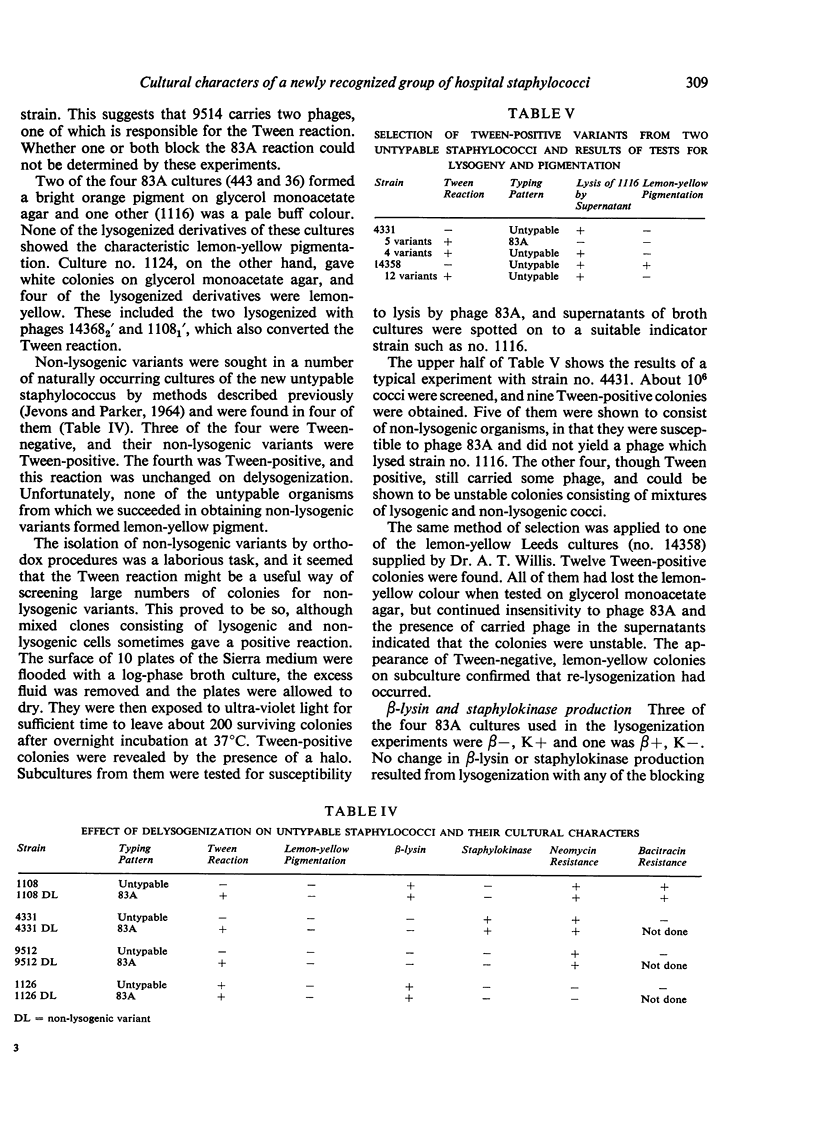
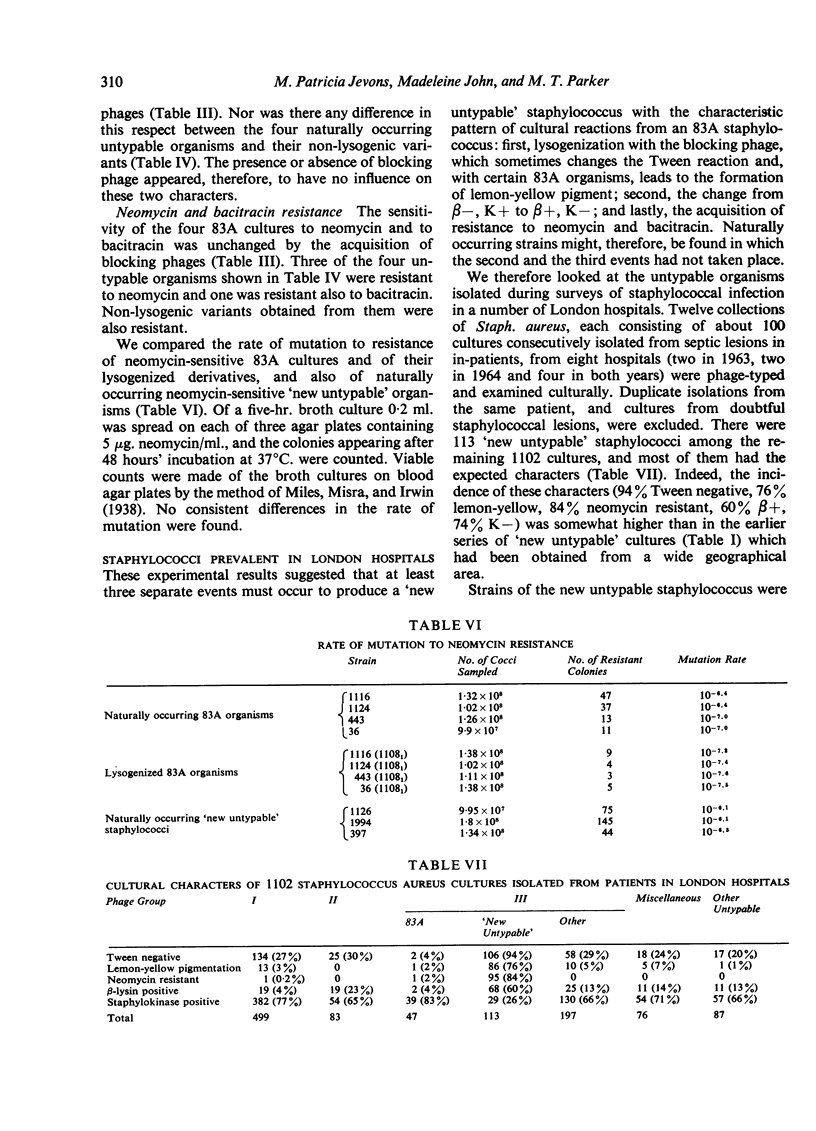
Members of a newly recognized group of hospital staphylococci, which are believed to have arisen from 83A staphylococci by lysogenization, differ from them in several cultural characters. Some but not all of these characters appear to be determined by the carriage of phage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN L. S., FEKETY F. R., CLUFF L. E. Studies of the epidemiology of staphylococcal infection. IV. The changing ecology of hospital staphylococci. N Engl J Med. 1962 Feb 22;266:367–372. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196202222660801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMTOIS R. D., BYNOE E. T. REPORT ON A PARTICULAR PHAGE-TYPE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS ISOLATED IN SOME HOSPITALS IN CANADA. Can J Public Health. 1963 Aug;54:357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMTOIS R. D. UNTYPABLE STAPHYLOCOCCI-LYSIS BY EXPERIMENTAL PHAGES AND OTHER CHARACTERISTICS. Can J Public Health. 1965 May;56:199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEGOLD S. M., GAYLOR D. W. Enterocolitis due to phage type 54 staphylococci resistant to kanamycin, neomycin, paromomycin and chloramphenicol. N Engl J Med. 1960 Dec 1;263:1110–1116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196012012632204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN S. M. Mercury sensitivity of staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1962 May;15:249–251. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH L. J., OSTRANDER W. E., SMITH Z. F., BESWICK D. E. Appearance of kanamycin resistance in a single phage type of Staphylococcus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:157–159. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.157-159.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS S. I., WILLIS A. T., GOODBURN G. M. PIGMENT PRODUCTION AND ENZYMATIC ACTIVITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCI: THE DIFFERENTIATION OF PATHOGENS FROM COMMENSALS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:151–156. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS S. I., WILLIS A. T. NEOMYCIN RESISTANCE IN NEWLY RECOGNISED STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Lancet. 1963 Aug 31;2(7305):459–460. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS S. I., WILLLIS A. T., LUDLAM G. B., GOODBURN G. M. Studies on newly recognised strains of Staphylococcus aureus associated with hospital infection. Lancet. 1963 May 4;1(7288):972–973. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEVONS M. P., PARKER M. T. THE EVOLUTION OF NEW HOSPITAL STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:243–250. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., BABB J. R., BROWN V. L., COLLINS B. J. NEOMYCIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN A BURNS UNIT. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Jun;62:221–228. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL A. A. NEW EPIDEMIC STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. EMERGENCE AND SPREAD IN A GENERAL HOSPITAL. Lancet. 1964 Apr 18;1(7338):859–862. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUIE P. G., COLLIN M., CARDLE J. B. Neomycin-resistant staphylococci. Lancet. 1960 Jul 16;2(7142):124–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. J. NEOMYCIN RESISTANCE IN A NEWLY RECOGNIZED STAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Lancet. 1963 Aug 17;2(7303):333–334. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92996-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENDAL K., BUELOW P., JESSEN O. LYOGENIC CONVERSION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, TO A CHANGE IN THE PRODUCTION OF EXTRACELLULAR "TWEEN"-SPLITTING ENZYME. Nature. 1964 Dec 19;204:1222–1223. doi: 10.1038/2041222b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUNTREE P. M., BEARD M. A. THE SPREAD OF NEOMYCIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI IN A HOSPITAL. Med J Aust. 1965 Apr 3;1(14):498–502. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1965.tb71863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Willis A. T., O'Connor J. J. New epidemic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1965 Oct 16;2(7416):772–773. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMPLE N. E., BLACKBURN E. A. A newly recognised strain of Staphylococcus aureus associated with epidemics in six hospitals. Lancet. 1963 Mar 16;1(7281):581–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92690-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS D. C., HILL E. O., CULBERTSON W. R., ALTEMEIER W. A. Development of new bacteriophages for staphylococcal typing. Surg Forum. 1960;10:334–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISDALE W. A., FENSTER L. F., KLATSKIN G. Acute staphylococcal enterocolitis complicating oral neomycin therapy in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1960 Nov 17;263:1014–1016. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196011172632009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER G. C. Newly recognised strains of Staphylococcus aureus associated with hospital staphylococci. Lancet. 1963 May 25;1(7291):1156–1156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91824-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIS A. T., JACOBS S. I., GOODBURN G. M. Observations on multiple-antibiotic-resistant epidemic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1963 Jul 13;2(7298):67–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K. C., de Waart J., Grootsen C. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococci to loss of beta-toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jun;39(3):321–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



