Abstract
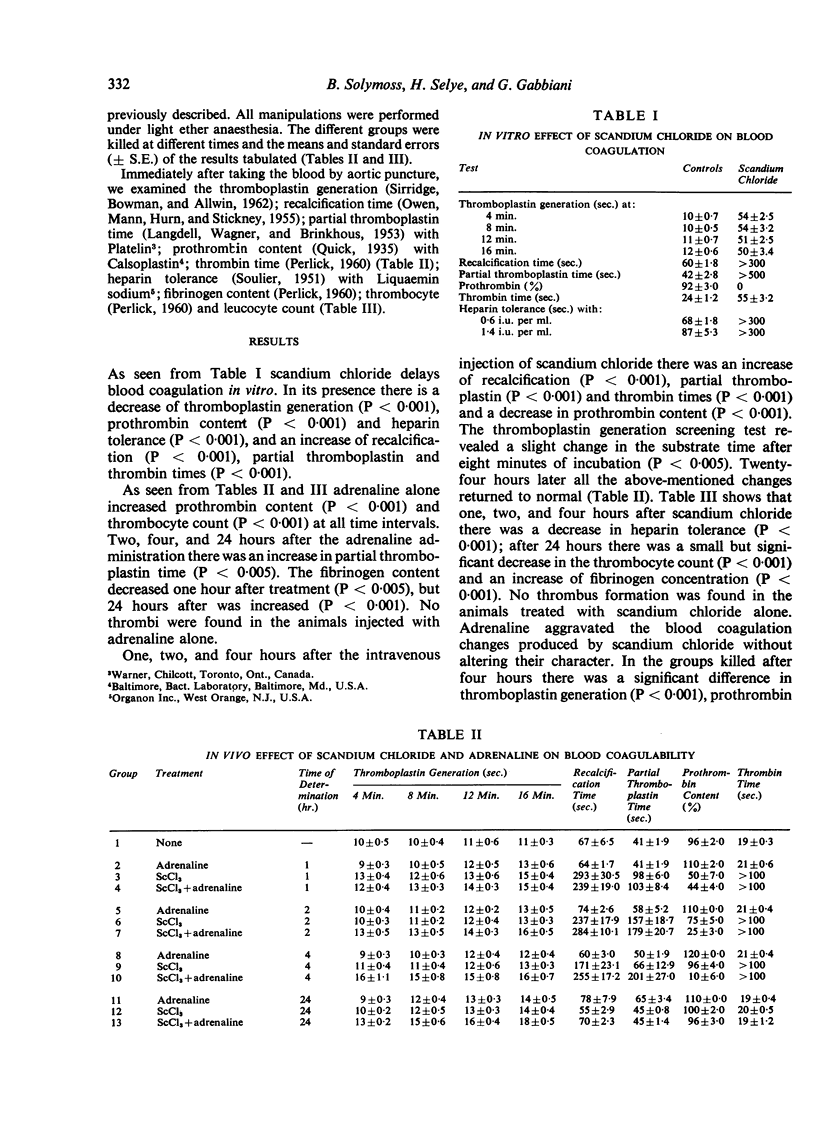
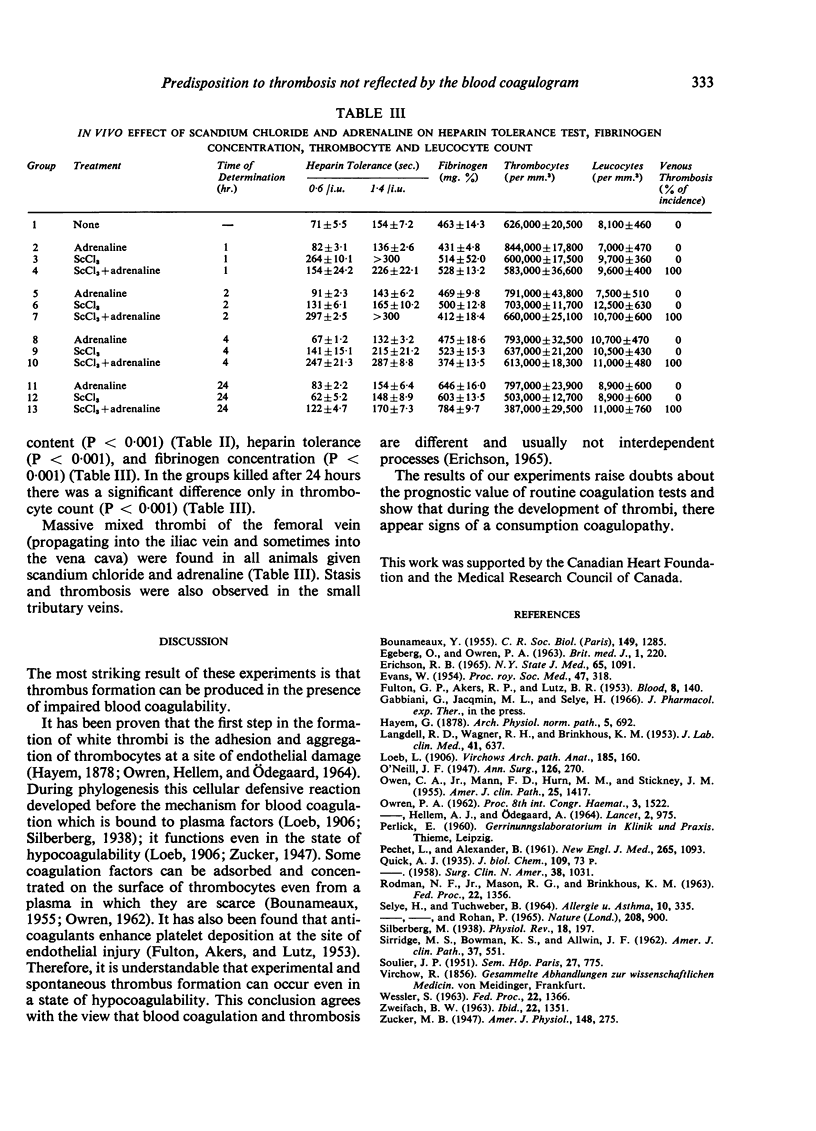
Experiments on rats indicate that thrombosis of large veins can develop while blood coagulability is decreased. Hence, coagulation tests have only a limited value in predicting a thrombotic tendency, although they do show characteristic changes during the formation of thrombi.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOUNAMEAUX Y. Action de la thromboplastine sur l'adhésivité des plaquettes in vitro. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1955 Jun;149(11-12):1285–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICHSON R. B. THE HYPERCOAGULABLE STATE. N Y State J Med. 1965 May 1;65:1091–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. Anticoagulant therapy in coronary occlusion. Proc R Soc Med. 1954 May;47(5):318–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON G. P., AKERS R. P., LUTZ B. R. White thrombo-embolism and vascular fragility in the hamster cheek pouch after anticoagulants. Blood. 1953 Feb;8(2):140–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'nejll J. F. The Effects on Venous Endothelium of Alterations in Blood Flow Through the Vessels in Vein Walls, and the Possible Relation to Thrombosis. Ann Surg. 1947 Sep;126(3):270–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN C. A., Jr, MANN F. D., HURN M. M., STICKNEY J. M. Evaluation of disorders of blood coagulation in the clinical laboratory. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Dec;25(12):1417–1426. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.12_ts.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWREN P. A., HELLEM A. J., ODEGAARD A. LINOLENIC ACID FOR THE PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS AND MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION. Lancet. 1964 Nov 7;2(7367):975–978. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90928-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHET L., ALEXANDER B. Increased clotting factors in pregnacy. N Engl J Med. 1961 Nov 30;265:1093–1097. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196111302652205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, MASON R. G., BRINKHOUS K. M. SOME PATHOGENETIC MECHANISMS OF WHITE THROMBUS FORMATION: AGGLUTINATION AND SELF-DESTRUCTION OF THE PLATELET. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1356–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELYE H., TUCHWEBER B. EIN DURCH VERSCHIEDENE AGENZIEN ERZEUGBARES THROMBOHAEMORRHAGISCHES PHAENOMEN. Allerg Asthma (Leipz) 1964;10:335–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOULIER J. P. Modifications apportées à la technique du test de tolérance à l'héparine in vitro. Sem Hop. 1951 Mar 6;27(18):775–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selye H., Tuchweber B., Rohan P. Thromboses in large veins and pulmonary embolisms induced by catecholamines or serotonin. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):900–901. doi: 10.1038/208900a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSLER S. STASIS, HYPERCOAGULABILITY, AND THROMBOSIS. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1366–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZWEIFACH B. W. PERIPHERAL VASCULAR FACTORS IN THE GENESIS OF STASIS AND THROMBOSIS. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1351–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


