Abstract
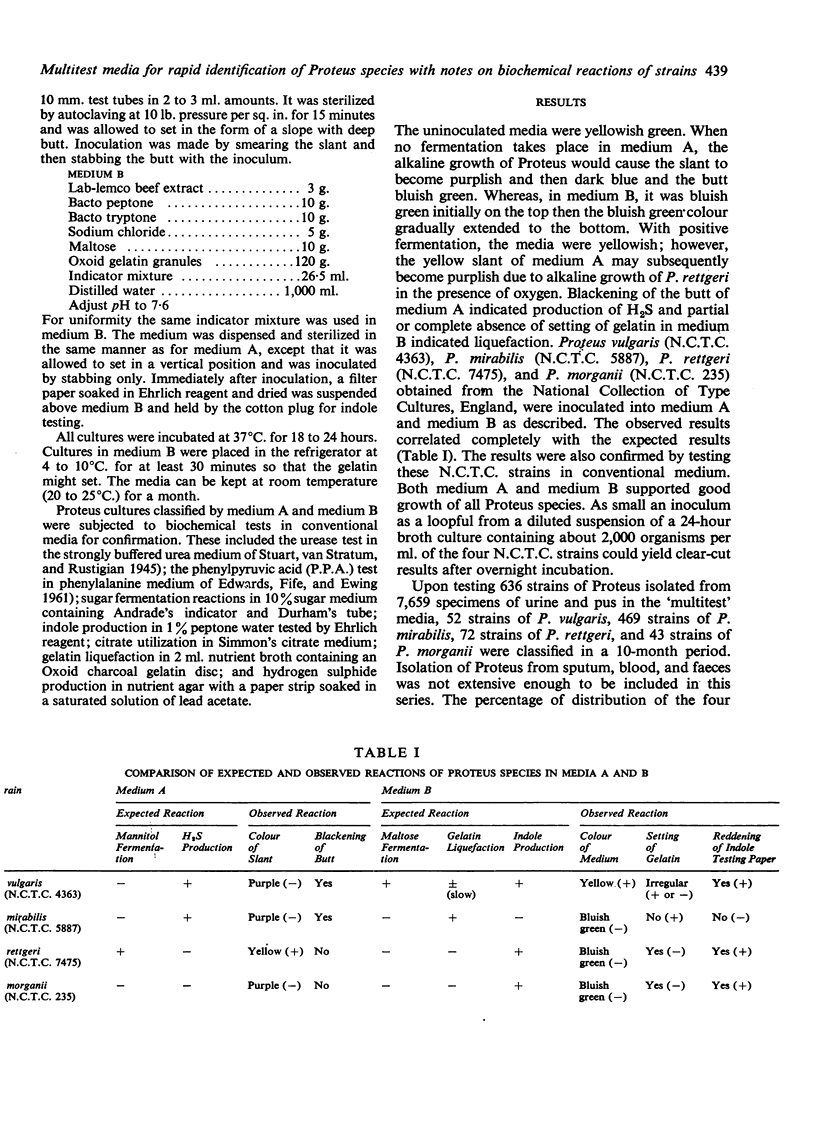
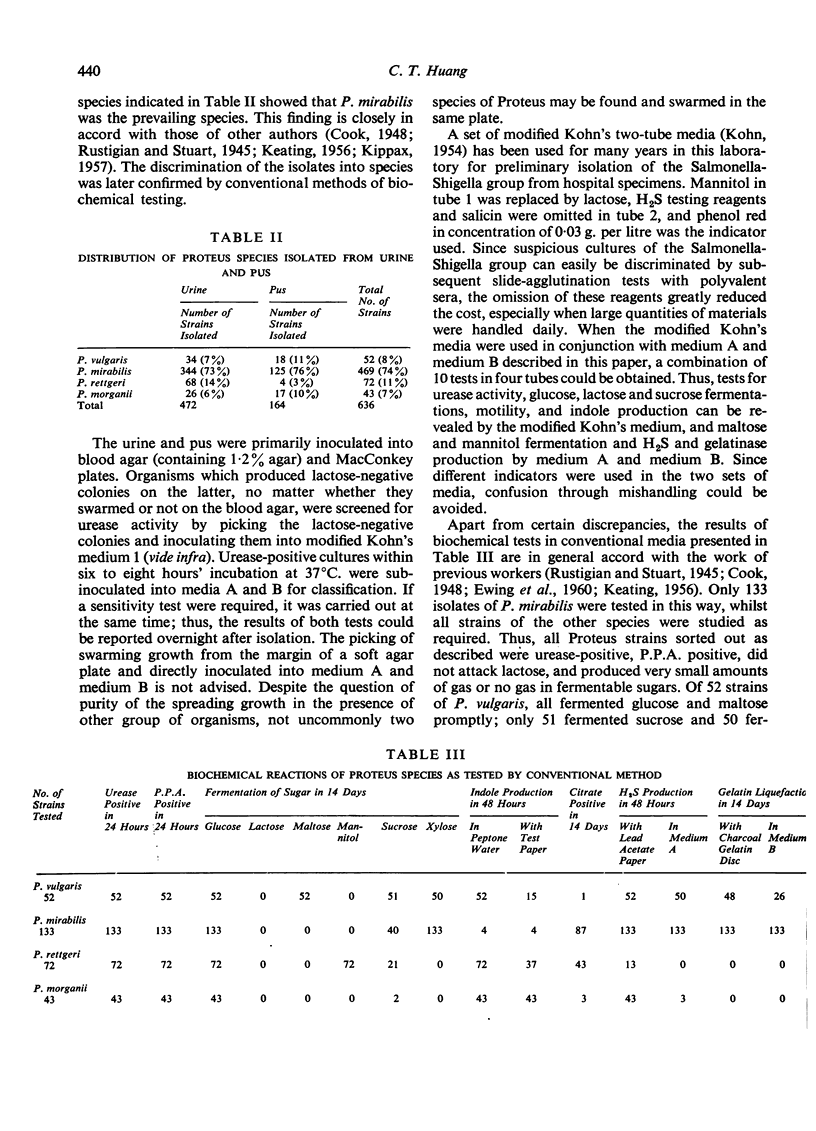
Two `multitest'1 media for biochemical classification of the genus Proteus into species were developed. The species so determined were checked with conventional methods. Results show that these media were useful for rapid identification of species. The biochemical reactions of four Proteus species isolated from clinical specimens as tested by conventional methods are reviewed and the occurrence of some atypical strains is described.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GREENE R. A., LARKS G. G. A quick method for the detection of gelatin liquefying bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1955 Feb;69(2):224–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.2.224-224.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEATING S. V. A biochemical and serological study of the genus Proteus. Med J Aust. 1956 Aug 4;43(5):168–172. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1956.tb56560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPPAZ P. W. A study of Proteus infections in a male urological ward. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Aug;10(3):211–214. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUTROP H. A modified Kohn's test for the demonstration of bacterial gelatin liquefaction. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(5):357–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1956.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSS K., VOROS S. The biochemical and serological properties of Proteus morganii. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1959;6:233–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER J. Culture of Enterobacteriaceae; I. A practical medium containing urea, tryptone, lactose and indicators. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Sep;20(9):880–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


