Abstract
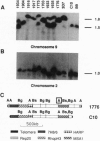
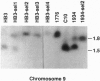
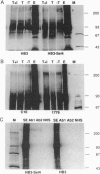
Virulence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum is believed to relate to adhesion of parasitized erythrocytes to postcapillary venular endothelium (asexual cytoadherence). Transmission of malaria to the mosquito vector involves a switch from asexual to sexual development (gametocytogenesis). Continuous in vitro culture of P. falciparum frequently results in irreversible loss of asexual cytoadherence and gametocytogenesis. Field isolates and cloned lines differing in expression of these phenotypes were karyotyped by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. This analysis showed that expression of both phenotypes mapped to a 0.3-Mb subtelomeric deletion of chromosome 9. This deletion frequently occurs during adaptation of parasite isolates to in vitro culture. Parasites with this deletion did not express the variant surface agglutination phenotype and the putative asexual cytoadherence ligand designated P. falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1, which has recently been shown to undergo antigenic variation. The syntenic relationship between asexual cytoadherence and gametocytogenesis suggests that expression of these phenotypes is genetically linked. One explanation for this linkage is that both developmental pathways share a common cytoadherence mechanism. This proposed biological and genetic linkage between a virulence factor (asexual cytoadherence) and transmissibility (gametocytogenesis) would help explain why a high degree of virulence has evolved and been maintained in falciparum malaria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alano P., Carter R. Sexual differentiation in malaria parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:429–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. M., May R. M. Coevolution of hosts and parasites. Parasitology. 1982 Oct;85(Pt 2):411–426. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000055360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt A. R., Simmons D. L., Tansey J., Newbold C. I., Marsh K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):57–59. doi: 10.1038/341057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Anders R. F., Dillon H. E., Davern K. M., Martin M., Petersen C., Brown G. V. Adherence of infected erythrocytes to venular endothelium selects for antigenic variants of Plasmodium falciparum. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Culvenor J. G., Ng J. S., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Plasmodium falciparum: cytoadherence of a knobless clone. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Goozé L., Wycherley K., Wilkinson D., Boyd A. W., Forsyth K. P., Edelman L., Brown G. V., Leech J. H. Knob-independent cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum to the leukocyte differentiation antigen CD36. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1883–1892. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Goozé L., Wycherley K., Wollish W., Southwell B., Leech J. H., Brown G. V. Antigenic variation in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9171–9174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Subtelomeric chromosome deletions in field isolates of Plasmodium falciparum and their relationship to loss of cytoadherence in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2428–2432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Cross G. A. Molecular basis for trypanosome antigenic variation. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Forsyth K. P., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J. Chromosome size polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions and are frequent in natural parasite populations. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall I., Collins W. E., Gysin J., Sherman I. W. Synthetic peptides based on motifs present in human band 3 protein inhibit cytoadherence/sequestration of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4703–4707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth K. P., Philip G., Smith T., Kum E., Southwell B., Brown G. V. Diversity of antigens expressed on the surface of erythrocytes infected with mature Plasmodium falciparum parasites in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J. Malarial proteins at the membrane of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes and their involvement in cytoadherence to endothelial cells. Prog Allergy. 1988;41:98–147. doi: 10.1159/000415221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Corcoran L. M. Molecular karyotype of Plasmodium falciparum: conserved linkage groups and expendable histidine-rich protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7672–7676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Peterson E. Pathogenicity, stability, and immunogenicity of a knobless clone of Plasmodium falciparum in Colombian owl monkeys. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):760–766. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.760-766.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. R., Svanborg Edén C. Selection and evolution of virulence in bacteria: an ecumenical excursion and modest suggestion. Parasitology. 1990;100 (Suppl):S103–S115. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000073054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh K., Howard R. J. Antigens induced on erythrocytes by P. falciparum: expression of diverse and conserved determinants. Science. 1986 Jan 10;231(4734):150–153. doi: 10.1126/science.2417315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Ho M., Tandon N. N., Van Seventer G. A., Shaw S., White N. J., Jamieson G. A., Chulay J. D., Webster H. K. Molecular basis of sequestration in severe and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: differential adhesion of infected erythrocytes to CD36 and ICAM-1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):163–169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Tandon N. N., Magowan C., Jamieson G. A., Chulay J. D. Identification of a platelet membrane glycoprotein as a falciparum malaria sequestration receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1469–1471. doi: 10.1126/science.2467377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oquendo P., Hundt E., Lawler J., Seed B. CD36 directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarapotikul J., Langsley G. Chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions of the subtelomeric pPFrep20 sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4331–4340. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. A chromosomal rearrangement in a P. falciparum histidine-rich protein gene is associated with the knobless phenotype. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):474–477. doi: 10.1038/322474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V. Chromosomal polymorphisms and gene expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jan;68(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Sherwood J. A., Spitalnik S. L., Panton L. J., Howard R. J., Dixit V. M., Frazier W. A., Miller L. H., Ginsburg V. Thrombospondin binds falciparum malaria parasitized erythrocytes and may mediate cytoadherence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):64–66. doi: 10.1038/318064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. J., Craig A. G., Berendt A. R., Pinches R., Nash G., Marsh K., Newbold C. I. Rapid switching to multiple antigenic and adhesive phenotypes in malaria. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):689–692. doi: 10.1038/357689a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley M. W., Biggs B. A., Forsyth K. P., Brown H. J., Thompson J. K., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J. Chromosome 9 from independent clones and isolates of Plasmodium falciparum undergoes subtelomeric deletions with similar breakpoints in vitro. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Apr;40(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeinya I. J., Graves P. M., Carter R., Aikawa M., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum: effect of time in continuous culture on binding to human endothelial cells and amelanotic melanoma cells. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Oct;56(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udomsangpetch R., Aikawa M., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Perlmann P. Cytoadherence of knobless Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes and its inhibition by a human monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):763–765. doi: 10.1038/338763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., Higgins D. G., McCutchan T. F. Plasmodium falciparum appears to have arisen as a result of lateral transfer between avian and human hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3140–3144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]