Abstract
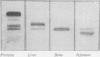
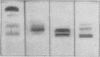
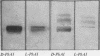
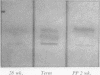
A very rapid method of agar gel electrophoresis on glass slides, together with a superior visualization technique employing simultaneous coupling of a hydrolysed naphthol substrate, have been developed for the identification of the tissues of origin of serum alkaline phosphatase. Combined with L-phenylalanine inhibition, specific for the intestinal enzyme, and heat inactivation, specific for the placental enzyme, the heterogeneity of serum alkaline phosphatase has been demonstrated. Normal adult serum contains predominantly liver-type alkaline phosphatase with a small but variable quantity of intestinal enzyme, and little or no bone enzyme.
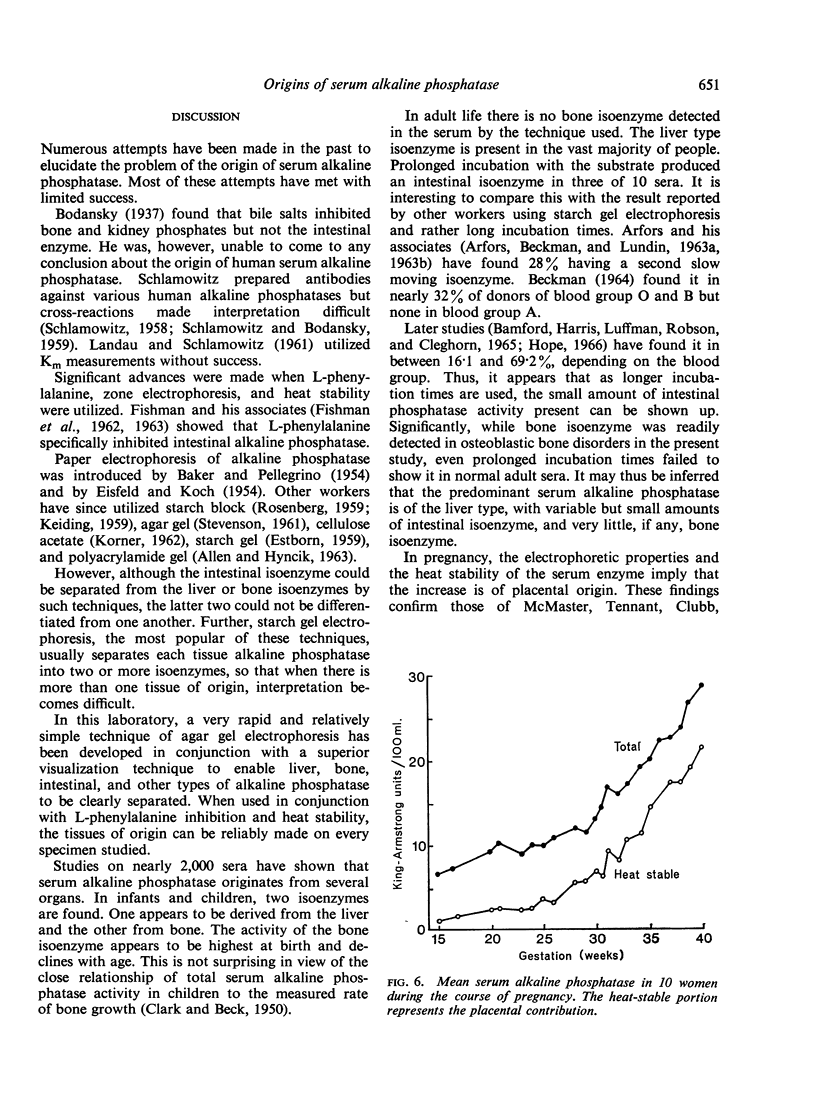
In childhood and in infancy there is in addition a bone isoenzyme present, the amount gradually falling to adult levels with age. In pregnancy, the rise in serum alkaline phosphatase is due to the placental enzyme.
A study of nearly 2,000 sera has been undertaken and it is found that the bone enzyme is increased in osteoblastic bone diseases while in hepato-biliary disorders there is an increase in liver type enzyme. The main theories explaining the rise in serum alkaline phosphatase are examined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARFORS K. E., BECKMAN L., LUNDIN L. G. GENETIC VARIATIONS OF HUMAN SERUM PHOSPHATASES. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1963;13:89–94. doi: 10.1159/000151789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong A. R., Banting F. G. The Site of Formation of the Phosphatase of Serum. Can Med Assoc J. 1935 Sep;33(3):243–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong A. R., King E. J., Harris R. I. PHOSPHATASE IN OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE. Can Med Assoc J. 1934 Jul;31(1):14–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER R. W., PELLEGRINO C. The separation and detection of serum enzymes by paper electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1954;6(2):94–101. doi: 10.3109/00365515409134847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAMFORD K. F., HARRIS H., LUFFMAN J. E., ROBSON E. B., CLEGHORN T. E. SERUM-ALKALINE-PHOSPHATASE AND THE ABO BLOOD-GROUPS. Lancet. 1965 Mar 6;1(7384):530–531. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKMAN L. ASSOCIATIONS BETWEEN HUMAN SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASES AND BLOOD GROUPS. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1964;14:286–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYER S. H. Human organ alkaline phosphatases: discrimination by several means including starch gel electrophoresis of antienzyme-enzyme supernatant fluids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 8;103:938–951. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE J. O. Serum alkaline phosphatase in liver disease: A concept of its significance. Gastroenterology. 1950 Dec;16(4):660–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK L. C., Jr, BECK E. Plasma alkaline phosphatase activity; normative data for growing children. J Pediatr. 1950 Mar;36(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(50)80103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clubb J. S., Neale F. C., Posen S. The behavior of infused human placental alkaline phosphatase in human subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Sep;66(3):493–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALGAARD J. B. Serum phosphatase after transfusion of phosphatase-rich blood to normal dogs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1951 Apr 25;22(2-3):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1951.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISFELD G., KOCH E. Das Verhalten der alkalischen und sauren Serumphosphatase des Menschen bei der Papierelektrophorese. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1954 May 15;9(10):514–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTBORN B. Visualization of acid and alkaline phosphatase after starch-gel electrophoresis of seminal plasma, serum and bile. Nature. 1959 Nov 21;184(Suppl 21):1636–1637. doi: 10.1038/1841636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN W. H., GREEN S., INGLIS N. I. Organ-specific behavior exhibited by rat intestine and liver alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 13;62:363–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell H. B., Robison R. The growth, development and phosphatase activity of embryonic avian femora and limb-buds cultivated in vitro. Biochem J. 1929;23(4):767–784.5. doi: 10.1042/bj0230767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTMAN A. B. Serum alkaline phosphatase activity in diseases of the skeletal and hepatobiliary systems. A consideration of the current status. Am J Med. 1959 Dec;27:875–901. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A. B., Olson K. B., Gutman E. B., Flood C. A. EFFECT OF DISEASE OF THE LIVER AND BILIARY TRACT UPON THE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF THE SERUM. J Clin Invest. 1940 Jan;19(1):129–152. doi: 10.1172/JCI101107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY A. M., IBER F. L., ROSS R. S. The serum alkaline phosphatase in chronic infiltrative disease of the liver. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):850–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope R. M. Human serum alkaline phosphatase variants and their association with the ABO blood groups in an Australian sample. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):323–326. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEIDING N. R. Differentiation into three fractions of the serum alkaline phosphatase and the behavior of the fractions in diseases of bone and liver. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1959;11:106–112. doi: 10.3109/00365515909060415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER N. H. Distribution of alkaline phosphatase in serum protein fractions. J Clin Pathol. 1962 May;15:195–199. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU W., SCHLAMOWITZ M. Studies of factors related to the differentiation of alkaline phosphatases derived from several tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:474–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMASTER Y., TENNANT R., CLUBB J. S., NEALE F. C. THE MECHANISM OF THE ELEVATION OF SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE IN PREGNANCY. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1964 Oct;71:735–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1964.tb04349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON G. R., KARL I. E., SCHWARTZ R., SHANK R. E. THE QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NORMAL HUMAN LIVER LOBULE. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. The purification of aklaline phosphatases of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj0570595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSS D. W., CAMPBELL D. M., ANAGNOSTOU-KAKARAS E., KING E. J. Characterization of tissue alkaline phosphatases and their partial purification by starch-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:441–447. doi: 10.1042/bj0810441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martland M., Robison R. The Possible Significance of Hexosephosphoric Esters in Ossification: Part V. The Enzyme in the Early Stages of Bone Development. Biochem J. 1924;18(6):1354–1357. doi: 10.1042/bj0181354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEALE F. C., CLUBB J. S., HOTCHKIS D., POSEN S. HEAT STABILITY OF HUMAN PLACENTAL ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:359–363. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACOCK A. C., REED R. A., HIGHSMITH E. M. ETHANOL FRACTIONATION OF HUMAN SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 Nov;8:914–917. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLIN S. G., SPELLBERG M. A., TEITELMAN L., OKUMURA M. The origin of elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase in hepatic disease. An experimental study. Gastroenterology. 1962 Apr;42:431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. E., 2nd, Cooperband S. R. Protein characteristics of serum and bile alkaline phosphatase. Gastroenterology. 1966 May;50(5):631–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. C., PIERCE J. E. DIFFERENTIAL ACTION OF NEURAMINIDASE ON HUMAN SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASES. Nature. 1964 Oct 31;204:472–473. doi: 10.1038/204472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG I. N. Zone electrophoretic studies of serum alkaline phosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1959 Apr;38(4):630–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI103841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R., Macleod M., Rosenheim A. H. The possible significance of hexosephosphoric esters in ossification: Calcification in vitro. Biochem J. 1930;24(6):1927–1941. doi: 10.1042/bj0241927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R., Rosenheim A. H. Calcification of hypertrophic cartilage in vitro. Biochem J. 1934;28(2):684–698.1. doi: 10.1042/bj0280684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R., Soames K. M. The Possible Significance of Hexosephosphoric Esters in Ossification: Part II. The Phosphoric Esterase of Ossifying Cartilage. Biochem J. 1924;18(3-4):740–754. doi: 10.1042/bj0180740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SADOVSKY E., ZUCKERMAN H. AN ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE SPECIFIC TO NORMAL PREGNANCY. Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Aug;26:211–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLAMOWITZ M., BODANSKY O. Tissue sources of human serum alkaline phosphatase, as determined by immunochemical procedures. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1433–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLAMOWITZ M. Immunochemical studies on alkaline phosphatase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):373–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBESTA D. G., BRADSHAW F. J., PROCKOP D. J. SOURCE OF THE ELEVATED SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION: STUDIES UTILIZING ISOLATED LIVER PERFUSION. Gastroenterology. 1964 Aug;47:166–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEME R. J. An improved technique of agar-gel electrophoresis on microscope slides. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKERMAN H., SADOVSKY E. THERMOSTABLE ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE IN PREGNANCY. Isr J Med Sci. 1965 Mar;1:230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]