Abstract
The levels of γG, γA, and γM globulins were estimated in a group of patients with Down's anomaly and in groups of mentally retarded children and normal children, matched for age and sex, using an immunological method.
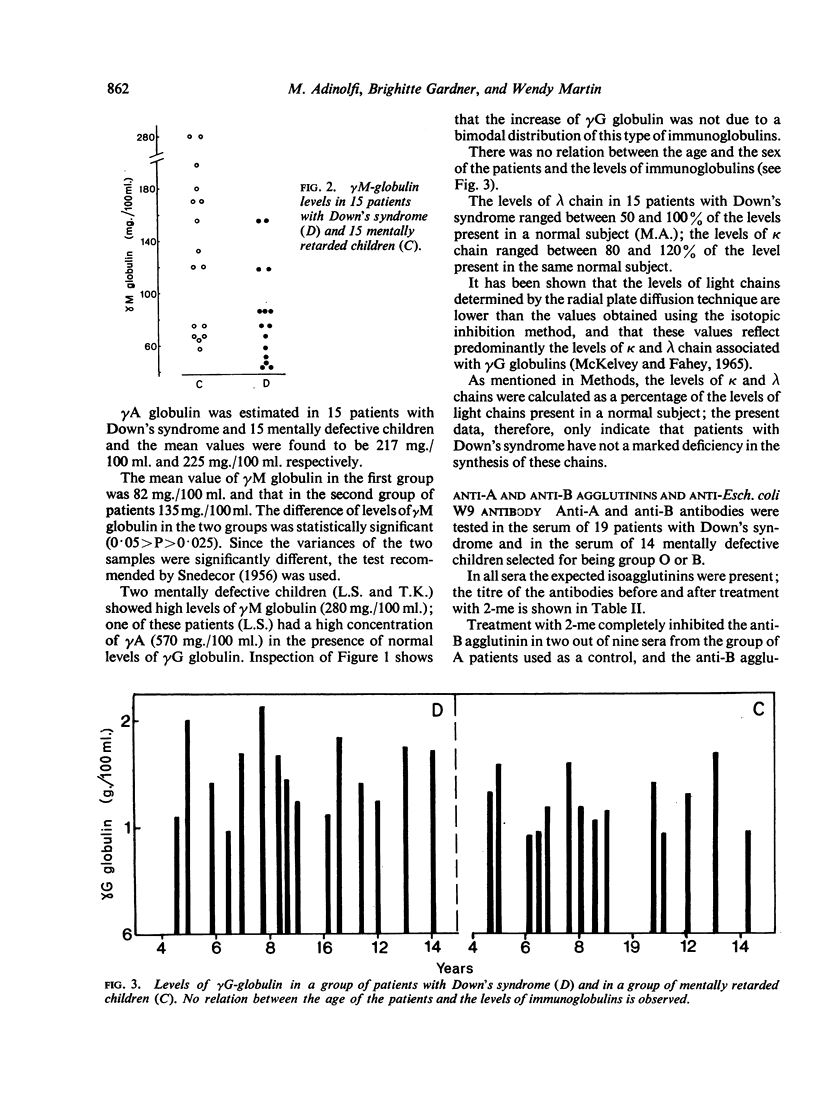
Higher levels of γG globulin were observed in patients with Down's syndrome, in association with a small but significant lower concentration of γM globulin.
The titres of anti-A and anti-B agglutinins and antibodies to Escherichia coli, estimated before and after treatment of serum with 2-mercaptoethanol, were found to be within normal levels.
These data seem to suggest that patients with Down's syndrome do not produce `faulty' immunoglobulins as has been previously postulated. It is suggested that the abnormal levels of immunoglobulins found in Down's anomaly are not peculiar to patients with Down's syndrome but occur in other disorders in which the reticuloendothelial system or the lymphocytes are involved.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPLETON M. D., PRITHAM G. H. Biochemical studies in mongolism. II: The influence of age and sex on the plasma proteins. Am J Ment Defic. 1963 Jan;67:521–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adinolfi M., Glynn A. A., Lindsay M., Milne C. M. Serological properties of gamma-A antibodies to Escherichia coli present in human colostrum. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):517–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGHLAN M. K., EVANS P. R. INFANTILE ECZEMA, ASTHMA AND HAY FEVER IN MONGOLISM. Guys Hosp Rep. 1964;113:223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLUCK E. R., PRITHAM G. H. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES IN MONGOLISM. III. STRUCTURES OF GAMMA-GLOBULINS FROM MONGOLOID BLOOD. Am J Ment Defic. 1964 Jul;69:31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKelvey E. M., Fahey J. L. Immunoglobulin changes in disease: quantitation on the basis of heavy polypeptide chains, IgG (gammaG), IgA (gammaA), and IgM (gammaM), and of light polypeptide chains, type K (I) and type L (II). J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1778–1787. doi: 10.1172/JCI105285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRITHAM G. H., APPLETON M. D., FLUCK E. R. Biochemical studies in mongolism. I: The influence of environment on the concentrations and mobilities of plasma proteins. Am J Ment Defic. 1963 Jan;67:517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBEL A. E., STRAZZULLA M., SHERMAN B. S., ELKAN B., MORGENSTERN S. W., MARIUS N., MEISEL A. Vitamin A absorption and other blood composition studies in mongolism. Am J Ment Defic. 1958 Jan;62(4):642–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


