Abstract
Background:
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are common in the general population, and frequent PVCs may result in the poor quality of life or even the damage of cardiac function. We examined the efficacy and safety of a traditional Chinese medicine Wenxin Keli for the treatment of frequent PVCs among a relatively large Chinese cohort.
Methods:
We performed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial. A total of 1200 eligible participants were randomly assigned in a ratio of 1:1 to receive Wenxin Keli or the placebo for 4 weeks. The primary and secondary endpoint was the change of PVC numbers and PVC-related symptoms after a 4-week treatment compared with baseline, respectively. In addition, vital signs, laboratory values, and electrocardiographic parameters were assessed in a safety analysis.
Results:
At the initial evaluation, no significant differences in the baseline characteristics were observed between the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group. A smaller number of PVCs was observed after the 4-week treatment than at baseline, in both the Wenxin Keli group (5686 ± 5940 vs. 15,138 ± 7597 beats/d, P < 0.001) and the placebo group (10,592 ± 8009 vs. 14,529 ± 5929 beats/d, P < 0.001); moreover, the Wenxin Keli group demonstrated a significantli greater reduction in the frequency of PVCs than the placebo group (P < 0.001). In a full analysis set, patients in the Wenxin Keli group exhibited significantly higher total effective responses in the reduction of PVCs compared to those in the placebo group (83.8% vs. 43.5%, P < 0.001). The per-protocol analysis yielded similar results (83.0% vs. 39.3%, P < 0.001). Treatment with Wenxin Keli also demonstrated superior performance compared to the placebo with respect to PVC-related symptoms. No severe adverse effects attributable to Wenxin Keli were reported.
Conclusions:
Wenxin Keli treatment effectively reduced the overall number of PVCs and alleviated PVC-related symptoms in patients without structural heart diseases and had no severe side effects.
Keywords: Wenxin Keli, Premature Ventricular Contractions, Efficacy, Safety, Clinical Trial
INTRODUCTION
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), also known as premature ventricular complexes, are early depolarization of the myocardium originating in the ventricle due to increased automaticity, triggered activity, or reentry. PVCs are relatively common with an estimated incidence of 1–4% in the general population, and they are generally age-dependent.[1] The prevalence of PVCs is 1% on surface 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) examination and between 40% and 75% on 24-h ambulatory ECG (AECG) monitoring.[2] As PVCs can occur not only in the healthy population but also in subjects with known heart diseases, patients with PVCs present with various manifestations that range from being asymptomatic to experiencing debilitating symptoms with impaired quality of life, developing PVC-induced cardiomyopathy, the onset of nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, or even heart failure.[3,4,5] In a community-wide cardiovascular epidemiology study, it was demonstrated that PVCs in subjects with structurally normal hearts began to exhibit adverse prognostic significance in patients older than 30 years.[6] More recent studies have also shown that symptomatic PVCs, and especially PVCs elicited during exercise, even in the absence of identifiable heart diseases, are correlated with an increased risk of total mortality.[3,7,8,9]
Evidence-based management of frequent PVCs usually includes pharmacological treatments and catheter ablation therapy for symptomatic patients who failed to medical therapy.[10] Although currently available conventional anti-arrhythmic drugs (AADs) such as beta blockers or Class I or III anti-arrhythmic agents are the first-line recommendation for patients with symptoms that can be attributed to frequent PVCs, these Western AADs may be suboptimal in the treatment of frequent PVCs either due to their significantly low efficacy or proarrhythmia effects.[11,12] On the contrary, many complementary and alternative medical (CAM) remedies have anti-arrhythmic properties similar to prescription of AADs and may have low toxicity and less adverse clinical events. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), one of the CAM therapies, has a long history of use in China to treat diseases related to cardiac arrhythmias. Wenxin Keli is a Chinese herb extract reported to be of benefit in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac inflammation, and heart failure.[13] Wenxin Keli is composed of five main herbal extracts: Nardostachys chinensis Batal extract (NcBe), Codonopsis, Notoginseng, amber, and Rhizoma Polygonati. In China, Wenxin Keli is the first Chinese-developed anti-arrhythmic medicine approved by the China Food and Drug Administration and possesses a licensable indication for frequent PVCs, which was included in the 2009 revision of the National Reimbursement Drug List. Recent animal model work and in vitro studies have supported the ability of Wenxin Keli to suppress and prevent cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, via unique anti-arrhythmic mechanisms.[9,13,14,15,16] However, the clinical efficacy and potential herb-drug related safety regarding Wenxin Keli used in humans has yet to be studied. Therefore, to further confirm the efficacy of Wenxin Keli observed in experimental results, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial was designed to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of Wenxin Keli in the treatment of patients with frequent PVCs.
METHODS
Patients
We enrolled 1200 patients with frequent PVCs from 60 hospitals around China. The enrollment criteria included patients aged 18–75 years with frequent PVCs (≥8640 beats/d or ≥360 beats/h as recorded by AECG) who were willing and able to provide written consent. All the eligible patients were required to discontinue other AADs for at least 5 half-lives prior to enrollment. Both men and women were included. We excluded patients who had severe valvular disease, congenital heart disease, pericardial disease, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, aneurysm, decompensated congestive heart failure (NYHA functional Class III or IV), cardiogenic shock and those who had cerebrovascular diseases, primary hematopoietic system disease, severe mental illness, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), or blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels >2 folds of the upper normal limit or creatinine levels higher than the upper normal limit. Other exclusion criteria were: (1) Drugs, electrolytes, acid-base balance disorders, emotional factors, and other reversible factors that induce frequent PVCs; (2) Bradycardia including sick sinus syndrome and second degree or higher atrial-ventricular blocks; (3) Having undergone or being likely to undergo a pacemaker procedure or percutaneous coronary intervention; (4) Women of childbearing potential who refused to use contraception, and pregnant or lactating women; (5) A suspicion of allergies to the study drugs; (6) Blood pressure <90/60 mmHg (1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa); (7) Suspected or known alcohol/drug abuse history; (8) Participation in other clinical trials within 3 months prior to enrollment; and (9) Other major concomitant diseases.
Study design
This study was designed as a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter study in patients with frequent PVCs. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of each participating center, and the study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Good Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided written informed consent. The study was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Register Center (ChiCTR-TRC-12002159).
The present study consisted of a run-in period prior to randomization and a treatment period of 4 weeks. All of the patients had undergone a medical history review, physical examinations, laboratory measurements (including serum glucose, electrolyte, ALT, AST, BUN, and creatinine), 12-lead ECG and AECG screening, and echocardiography examination before enrollment. The eligible patients were then randomly assigned, via the computer-generated block randomization prepared in advance, to receive either 9 g of Wenxin Keli (Shandong Buchang Pharmaceutical Co., China) orally 3 times (08:00, 13:00, and 19:00) per day for 4 weeks or matched placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Symptoms, physical examinations, vital signs, 12-lead ECG, AECG, echocardiography, and laboratory examinations were performed at baseline and at the final visit. The efficacy and safety of Wenxin Keli were assessed after 4 weeks of treatment. The flowchart of study enrollment and follow-up was presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
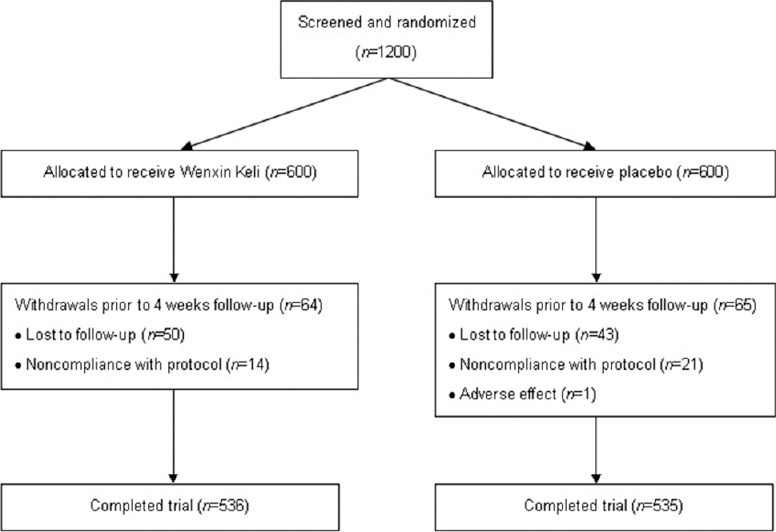
Flowchart detailing enrollment and follow-up.
Randomization and blinding
Stratified and blocked randomization was used according to different centers, and the 60 centers were divided into 60 strata. Patients in each center were further divided into Wenxin Keli and placebo groups using blocked randomization. Based on the results of the sample size estimated, a random number from 1 to 1200 was generated by SAS software (version 9.13, SAS Institute Inc., USA), and the subjects were randomly assigned by each center. The results of the randomized allocation were sent by the distribution systems of the responsible department to each research center. Each patient's random number and his/her drug number were same throughout the trial. The placebo were identical to the Wenxin Keli in appearance, size, weight, color, and taste and were packaged in identical boxes and given to patients by research nurses. The investigators, laboratory personnel, statistical processors, and patients enrolled in this trial were blinded to the study group allocation.
Outcome measures
The primary efficacy variable was evaluated as the relative percent reduction of the overall frequency of PVCs from baseline to 4 weeks after treatment and was defined as the formula: (The number of PVCs during baseline week − the number of PVCs during the last week)/(The number of PVCs during baseline week) × 100. The definitions of the therapeutic effects of Wenxin Keli on frequent PVCs were as follows: (1) Significantly effective response (SER) – The number of PVCs after treatment decreased by 75% or more compared with baseline; (2) Effective response (ER) – The number of PVCs after treatment decreased by 50–75% compared with baseline; and (3) No ER (NER) – The number of PVCs after treatment decreased by <50%, no change, or the number of PVCs increased compared with baseline. The total effective rate (TER) of Wenxin Keli on PVCs was calculated as the combined endpoints of the SER and ER.
The secondary efficacy variable included changes in PVC-related symptom scores from baseline to 4 weeks after treatment. The symptoms used for this assessment included palpitation, chest discomfort, insomnia, and fatigue. Specific doctors performed the follow-up and finished PVC-related symptoms score assessments each weekend. The frequency and intensity of the symptoms were rated as none, mild, moderate, or severe, which corresponded to symptom scores of 0, 1, 2, and 3 points, respectively. The definitions of the therapeutic effects of Wenxin Keli on the PVC-related symptom scores were as follows: (1) SER – The symptom scores after treatment decreased by ≥2 points compared with baseline; (2) ER – The symptom scores after treatment decreased by 1 point compared with baseline; and (3) NER – The symptom scores after treatment did not change, or the scores increased compared with baseline. The TER of the PVC-related symptom scores was calculated as the combined endpoints of the SER and ER.
Safety evaluation
The safety analysis included all randomized patients who received ≥1 dose of Wenxin Keli. All patients underwent weekly follow-up safety assessments during the study. Vital signs, routine blood tests, liver function and kidney function tests, electrolyte tests, and ECGs both at baseline and at the end of treatment were examined. Adverse events were monitored and determined by the investigator during follow-up using the criteria of definitely, probably, possibly, probably not, and definitely not attributable to Wenxin Keli. Premature termination of the trial was considered if the patient had a major adverse event or significant worsening of PVC-related symptoms.
Sample size
The sample size was calculated based on the following method. The TER after treatment with the placebo for the total number of PVCs was assumed to be 35%, and it is necessary that a TER following treatment with Wenxin Keli is at least 25% greater than the placebo with a Type I error rate of alpha = 0.05 and a power of 80% (Type II error rate of beta = 0.2), and thus, the required sample size for each group was 489, resulting in n = 2 × 489 = 978 patients. Accounting for a dropout rate of 20% of the patients after randomization, a total sample size of 1200 was required (600 in the Wenxin Keli group and 600 in the placebo group).
Statistical analysis
The baseline data from patients who underwent randomization were analyzed as the full analysis set (FAS). The per-protocol set (PPS) included all patients in the FAS who complied with the protocol and completed the study through the final visit. The analysis of the primary and second efficacy endpoints were performed in both FAS and PPS. Continuous data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), and dichotomous data were presented as numbers and percentages. Comparisons of the data between patient groups were performed using independent sample t-tests for continuous data. Paired sample t-tests were used to compare the pre- and post-treatment data from each group. The Fisher exact test or the Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare binary variables or ranked data. Ninety-five percent confidence interval (CI, two-sided) was presented as appropriate. All statistical analyses were performed with SAS software. A P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant, and all statistical tests were two-sided.
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
From June to December 2012, 1200 patients were enrolled in this study and were randomly assigned to receive Wenxin Keli or the placebo. The baseline characteristics of the study patients are shown in Table 1. The Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group were comparable with respect to demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations, AECG parameters, and medical treatments. Of the 1200 patients enrolled and randomized, 93 patients due to loss to follow-up, 35 patients due to noncompliance with the study protocol, and another patient due to a major adverse event were excluded. The dropout rate by trial arm was 64 cases in the Wenxin Keli group (dropout rate: 10.7%) and 65 cases in the placebo group (dropout rate: 10.8%). As a result, a total of 1071 (89.3%) patients (536 in the Wenxin Keli group and 535 in the placebo group) completed the 4-week follow-up and were included in further efficacy analyses.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study population
| Items | Wenxin Keli group (n = 600) | Placebo group (n = 600) | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 53.7 ± 12.2 | 53.9 ± 11.8 | −0.285 | 0.776 |
| Male | 281 (46.8) | 290 (48.3) | 0.603 | |
| Smoker | 104 (17.3) | 111 (18.5) | 0.442 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.8 ± 10.1 | 23.2 ± 3.4 | 1.285 | 0.199 |
| Race | ||||
| Han | 586 (97.7) | 586 (97.7) | 1.000 | |
| Other | 14 (2.3) | 14 (2.3) | 1.000 | |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg, 1 mmHg = 0.133 kPa | 121.0 ± 11.5 | 120.1 ± 9.6 | 1.386 | 0.166 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 77.8 ± 10.4 | 77.2 ± 9.7 | 1.026 | 0.305 |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Palpitation | 581 (96.8) | 570 (95.0) | 0.128 | |
| Chest discomfort | 532 (88.7) | 522 (87.0) | 0.819 | |
| Insomnia | 466 (77.3) | 448 (74.7) | 0.050 | |
| Fatigue | 471 (78.5) | 473 (78.8) | 0.386 | |
| Ambulatory monitoring parameters | ||||
| Overall monitoring duration, h | 23.6 ± 0.6 | 23.6 ± 0.6 | −1.076 | 0.282 |
| Overall heart rate, beats/d | 106,193 ± 12,787 | 106,281 ± 12,220 | −0.123 | 0.902 |
| PVCs, beats/d | 15,138 ± 7597 | 14,529 ± 5929 | 1.548 | 0.122 |
| PACs, beats/d | 105 ± 539 | 166 ± 759 | −1.564 | 0.118 |
Values are n (%) or mean±SD; BMI: Body mass index; PVCs: Premature ventricular contractions; PACs: Premature atrial contractions.
Efficacy analysis
There was no significant difference in the total number of PVCs at baseline between the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group (P = 0.122, Table 1). Whereas a smaller number of PVCs was observed after a 4-week treatment than at baseline, in both the Wenxin Keli group (5686 ± 5940 vs. 15,138 ± 7597 beats/d, P < 0.001) and the placebo group (10,592 ± 8009 vs. 14,529 ± 5929 beats/d, P < 0.001); in addition, compared to the placebo group, the Wenxin Keli group had a statistically significant change in the total PVC frequency after the 4-week treatment period (P < 0.001, Figure 2). In the FAS analysis [Table 2], in the comparison between the pretreatment and 4 weeks posttreatment data, the SER and ER were 41.8% and 42.0% in Wenxin Keli group, and 15.7% and 27.8% in placebo group, respectively; the proportion of patients with a TER reduction in the frequency of total PVCs for the Wenxin Keli and placebo groups were 83.8% and 43.5%, respectively (P < 0.001); the proportion of patients with a TER reduction in the frequency of PVCs was significantly greater in the Wenxin Keli group compared with the placebo group (37.4%, 95% CI: 30.0–45.5%, P < 0.001). The PPS analysis showed similar trends (40.2%, 95% CI: 31.9–49.4%, P < 0.001, Table 3).
Figure 2.
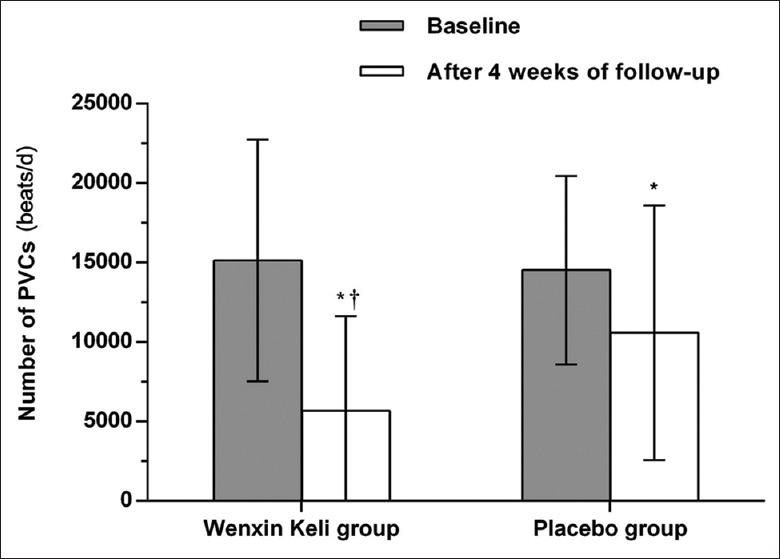
The total number of PVCs from baseline to 4 weeks after treatment in the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group. PVCs: Premature ventricular contractions. *P < 0.001 vs. baseline, †P < 0.001 vs. the placebo group.
Table 2.
Primary and secondary endpoint results after 4 weeks of follow-up in the FAS, n (%)
| Items | Wenxin Keli group (n = 600) | Placebo group (n = 600) | Rate difference, % (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary endpoints | ||||
| SER | 251 (41.8) | 94 (15.7) | ||
| ER | 252 (42.0) | 167 (27.8) | ||
| TER | 503 (83.8) | 261 (43.5) | 37.4 (30.0–45.5) | <0.001 |
| Secondary endpoints | ||||
| Palpitation | ||||
| SER | 133 (22.2) | 46 (7.7) | ||
| ER | 327 (54.5) | 180 (30.0) | ||
| TER | 460 (76.7) | 226 (37.7) | 25.1 (18.8–32.2) | <0.001 |
| Chest discomfort | ||||
| SER | 108 (18.0) | 54 (9.0) | ||
| ER | 322 (53.6) | 157 (26.1) | ||
| TER | 430 (71.6) | 211 (35.1) | 27.3 (20.4–35.0) | <0.001 |
| Insomnia | ||||
| SER | 81 (13.5) | 28 (4.7) | ||
| ER | 281 (46.9) | 125 (20.9) | ||
| TER | 362 (60.4) | 153 (25.6) | 27.0 (19.7–35.6) | <0.001 |
| Fatigue | ||||
| SER | 80 (13.3) | 30 (5.0) | ||
| ER | 297 (49.5) | 151 (25.2) | ||
| TER | 377 (62.8) | 181 (30.2) | 27.3 (19.7–36.0) | <0.001 |
FAS: Full analysis set; CI: Confidence interval; SER: Significantly effective response; ER: Effective response; TER: Total effective response; Rate difference: Rate of TER in Wenxin Keli group - Rate of TER in placebo group; P: Wenxin Keli group vs. Placebo group.
Table 3.
Primary and secondary endpoint results after 4 weeks of follow-up in the PPS, n (%)
| Items | Wenxin Keli group (n = 536) | Placebo group (n = 535) | Rate difference, % (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary endpoints | ||||
| SER | 200 (37.3) | 48 (9.0) | ||
| ER | 245 (45.7) | 162 (30.3) | ||
| TER | 445 (83.0) | 210 (39.3) | 40.2 (31.9–49.4) | <0.001 |
| Secondary endpoints | ||||
| Palpitation | ||||
| SER | 115 (21.5) | 43 (8.0) | ||
| ER | 297 (55.4) | 158 (29.5) | ||
| TER | 412 (76.9) | 201 (37.5) | 24.3 (17.9–31.4) | <0.001 |
| Chest discomfort | ||||
| SER | 95 (17.7) | 49 (9.2) | ||
| ER | 290 (54.1) | 140 (26.2) | ||
| TER | 385 (71.8) | 189 (35.3) | 26.6 (19.7–34.3) | <0.001 |
| Insomnia | ||||
| SER | 69 (12.9) | 26 (4.9) | ||
| ER | 254 (47.4) | 112 (20.9) | ||
| TER | 323 (60.3) | 138 (25.8) | 26.5 (19.1–35.0) | <0.001 |
| Fatigue | ||||
| SER | 72 (13.4) | 28 (5.2) | ||
| ER | 262 (48.9) | 135 (25.2) | ||
| TER | 334 (62.3) | 163 (30.4) | 26.4 (18.9–35.1) | <0.001 |
PPS: Per-protocol set; CI: Confidence interval; SER: Significantly effective response; ER: Effective response; TER: Total effective response; Rate difference: Rate of TER in Wenxin Keli group - Rate of TER in placebo group; P: Wenxin Keli group vs. Placebo group.
In terms of the secondary endpoints, there were no significant differences in the severity of PVC-related symptoms, including palpitation, chest discomfort, insomnia and fatigue, at baseline between the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group [Table 4]. Nevertheless, significant differences were observed in the respective PVC-related symptoms at the final visit between the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group [Table 4]. When analyzed by FAS and PPS, patients receiving the Wenxin Keli treatment experienced significantly greater SER, ER as well as TER of improvements in their PVC-related symptoms including palpitation, chest discomfort, insomnia, and fatigue compared to patients receiving the placebo treatment (all P < 0.001, Tables 2 and 3).
Table 4.
A comparison of PVC-related symptom severity between the Wenxin Keli group and the placebo group at baseline and 4 weeks after treatment, n (%)
| Items | Baseline | 4 weeks after treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wenxin Keli group (n = 600) | Placebo group (n = 600) | P | Wenxin Keli group (n = 550) | Placebo group (n = 556) | P | |
| Palpitation | ||||||
| None | 19 (3.2) | 30 (5.0) | 0.128 | 226 (41.1) | 105 (18.9) | <0.001 |
| Mild | 225 (37.5) | 230 (38.3) | 279 (50.7) | 251 (45.1) | ||
| Moderate | 295 (49.2) | 297 (49.5) | 42 (7.6) | 184 (33.1) | ||
| Severe | 61 (10.2) | 43 (7.2) | 3 (0.5) | 16 (2.9) | ||
| Chest discomfort | ||||||
| None | 68 (11.3) | 78 (13.0) | 0.819 | 302 (54.9) | 157 (28.2) | <0.001 |
| Mild | 269 (44.8) | 268 (44.7) | 203 (36.9) | 250 (45.0) | ||
| Moderate | 228 (38.0) | 218 (36.3) | 41 (7.5) | 137 (24.6) | ||
| Severe | 35 (5.8) | 36 (6.0) | 4 (0.7) | 12 (2.2) | ||
| Insomnia | ||||||
| None | 134 (22.3) | 152 (25.3) | 0.050 | 298 (54.2) | 210 (37.8) | <0.001 |
| Mild | 256 (42.7) | 280 (46.7) | 218 (39.6) | 216 (38.8) | ||
| Moderate | 188 (31.3) | 145 (24.2) | 33 (6.0) | 116 (20.9) | ||
| Severe | 22 (3.7) | 23 (3.8) | 1 (0.2) | 14 (2.5) | ||
| Fatigue | ||||||
| None | 129 (21.5) | 127 (21.2) | 0.386 | 359 (65.3) | 204 (36.7) | <0.001 |
| Mild | 310 (51.7) | 307 (51.2) | 167 (30.4) | 243 (43.7) | ||
| Moderate | 154 (25.7) | 151 (25.2) | 23 (4.2) | 105 (18.9) | ||
| Severe | 7 (1.2) | 15 (2.5) | 1 (0.2) | 4 (0.7) | ||
PVC: Premature ventricular contraction; P: Wenxin Keli group vs. Placebo group.
Safety analysis
The adverse events are presented in Table 5. A total of 1200 patients were included in the safety set analysis. Adverse events were reported in 7 patients, including 3 in the Wenxin Keli group and 4 in the placebo group (all P > 0.05 between the two groups). All reported adverse events were mild and were judged to be probably not attributable to Wenxin Keli. Only one patient in the placebo group was withdrawn from the protocol because of stomach pain. Neither death nor serious adverse events related to Wenxin Keli was reported during the study. Compared with the placebo group, the administration of Wenxin Keli had no significant impact on the liver, kidney functions as well as the ECG parameters [Table 6].
Table 5.
Adverse events reported during the study, n (%)
| Items | Wenxin Keli group (n = 600) | Placebo group (n = 600) |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal discomfort | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) |
| Headache | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Dizziness | 1 (0.2) | 0 |
| Palpitation | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Osphyalgia | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Total adverse events | 3 (0.5) | 4 (0.7) |
| Withdrew due to Wenxin Keli | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
Table 6.
Changes in the laboratory tests and ECG parameters between the two groups before and after treatment, medium (range)
| Variables | Wenxin Keli group | Placebo group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 4 weeks | 0 week | 4 weeks | |
| Laboratory tests | ||||
| ALT, IU/L | 20.0 (5.6–51.0) | 23.0 (6.6–56.0) | 20.0 (6.0–45.0) | 23.2 (7.8–58.0) |
| AST, IU/L | 22.0 (7.0–48.0) | 22.0 (8.0–43.0) | 21.0 (8.0–45.0) | 22.0 (8.0–45.0) |
| Scr, mmol/L | 69.8 (40.1–136.0) | 70.0 (41.0–131.7) | 71.0 (32.0–134.2) | 68.1 (25.0–129.2) |
| BUN, mmol/L | 4.9 (2.3–19.2) | 5.0 (2.0–19.4) | 4.8 (2.2–22.3) | 4.8 (2.1–21.4) |
| ECG parameters | ||||
| Width of P wave, ms | 73.0 (30.0–130.0) | 74.0 (30.0–136.0) | 73.0 (31.0–132.0) | 74.5 (30.0–133.0) |
| PR interval, ms | 154.0 (100.0–227.0) | 158.0 (98.0–236.0) | 154.0 (102.0–246.0) | 156.0 (96.0–234.0) |
| Width of QRS wave, ms | 94.0 (52.0–151.0) | 88.0 (52.0–134.0) | 92.5 (50.0–153.0) | 87.0 (56.0–142.0) |
| QT interval, ms | 388.0 (280.0–479.0) | 382.0 (306.0–458.0) | 386.0 (284.0–464.0) | 384.0 (300.0–450.0) |
| Mean HR, bpm | 73 (60–98) | 74 (60–94) | 74 (60–98) | 74 (60–96) |
| Maximum HR, bpm | 114 (73–157) | 114 (80–151) | 115 (78–156) | 115 (75–148) |
| Minimum HR, bpm | 54 (42–74) | 55 (39–75) | 54 (42–74) | 55 (37–76) |
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; Scr: Serum creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; HR: Heart rate; ECG: Electrocardiogram.
DISCUSSION
To the best of our knowledge, this report describes the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial regarding TCM treatment for frequent PVCs. Although conventional AADs are the first-line therapy for patients with incapacitating PVC-related symptoms, given the proarrhythmic effects and adverse side effect profiles of most AADs,[11,12] it is essential to explore novel safe and effective AADs for the treatment of frequent PVCs. In our study, Wenxin Keli improved the overall counts of PVCs and PVC-related symptoms in a pre- and post-treatment analysis, and its efficacy was significantly superior to that of the placebo. In addition, the results of the present study also demonstrated that Wenxin Keli was tolerated and safe in patients with frequent PVCs after short-term treatment. Our study indicates that Wenxin Keli is a relatively safe drug that may be widely used in clinical practice.
Wenxin Keli is a formally approved TCM, which has been widely used as an alternative approach for cardiac arrhythmias in China,[17,18,19,20] and several recent experimental studies have demonstrated that it is a significantly effective treatment for cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac inflammation, and chronic heart failure. Liu et al.[16] investigated the effects of NcBe, one of the main components of Wenxin Keli, on the activation kinetics of normal rat cardiac sodium channels and transient outward potassium channels, and found that NcBe was able to significantly block the INa and Ito of normal rat ventricular myocytes, which may account for some of its anti-arrhythmic effects. Also, Xing et al.[9] have found that Wenxin Keli may inhibit cardiac arrhythmias by down-regulating the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II signal transduction pathway, similar to amiodarone in rat models of myocardial infarction. Chen et al.[14] further explored the mechanism of the anti-arrhythmic effect of Wenxin Keli in hypertrophied ventricular myocytes and found that Wenxin Keli affects cardiac arrhythmias via significantly shortening the prolongation of the action potential duration and reducing the L-type calcium current (ICa-L) by accelerating the inactivation of the channels and delaying the recovery time from inactivation. In addition, Xue et al.[15] have found that, in the rabbit models, Wenxin Keli suppressed early afterdepolarizations, delayed afterdepolarizations, and triggered ventricular arrhythmias via selective inhibition of the late INa that is proved to contribute to arrhythmogenesis.[21] The other possible mechanisms underlying the ventricular anti-arrhythmic effect of Wenxin Keli observed in this study included abolishing rate-dependent change in repolarization and indirectly alleviating intracellular Ca2+ overloads via reducing the sodium influx. In particular, consistent with the results of a previous study,[13] Wenxin Keli decreased ventricular fast INa only mildly and had weaker effects on the ventricular effective refractory period without significant use-dependence, which may confirm its clinical cardiac safety profile in terms of stabilizing the width of the QRS wave and decreasing the incidence of systolic heart failure and mortality.[22,23]
We acknowledge that there are some limitations in our study. Firstly, the follow-up period of our study was short (only for 4 weeks) and this period may not be sufficient to evaluate the medium- to long-term effects of Wenxin Keli for the treatment of frequent PVCs, as well as the adverse events associated with long-term therapy. Long-range clinical trials are needed to further verify our study results and assess the long-term efficacy and safety of Wenxin Keli in the treatment of frequent PVCs. In addition, all patients enrolled in the current study did not have structural heart diseases, and patients in the presence of organic heart diseases, such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, primary cardiomyopathy, or heart failure, should be included and analyzed in future clinical trials. Finally, an active-controlled group was not set in this study, and whether Wenxin Keli is superior or noninferior to conventional AADs needs to be elucidated in the future.
In conclusion, our data suggest that Wenxin Keli can be safely and effectively used to treat frequent PVCs in symptomatic patients without severe structural heart diseases for 4 weeks. Further studies investigating the efficacy and safety of Wenxin Keli in frequent PVC patients with underlying structural heart diseases are warranted.
Financial support and sponsorship
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2013ZX09104004) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the Medical Statistical Center of the Chinese National Cardiovascular Center and colleagues from the 60 hospitals around China for their dedication, support, and hard work, these hospitals are as following (in alphabetical order): Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University; Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical College; Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical College; Anhui Provincial Hospital; Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital; Shanghai Changning District Center Hospital; Chongqing Three Gorges Central Hospital; Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University; Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine; First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin University; First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University; First Affiliated Hospital of Lanzhou University; Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University; Fujian Provincial Hospital; General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University; Guang’anmen Hospital, CACMS; Guangdong Provincial Central Hospital; Hainan General Hospital; Henan Provincial People's Hospital; Hubei General Hospital (Renming Hospital of Wuhan University); Hunan Provincial People's Hospital; National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, China and Fuwai Hospital, CAMS and PUMC; Ningbo First Hospital; Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital, Clinical Medical School, Yangzhou University; Shanghai Putuo District Center Hospital; Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital; Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University; Shandong Shengli Hospital; Shanghai First People's Hospital; Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University; Shanghai Yangpu District Central Hospital; Shanxi Provincial People's Hospital; Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital; The Affiliated Hospital of Luzhou Medical College; The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou Medical Univershity; The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University; The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University (The First Hospital of Zhejiang Province); The First Teaching Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University; The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University; The General Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army (301 hospital); The People's Hospital of Liaoning Province; The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University; The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University; The Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University; The Second Hospital of Jilin University; The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University; The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University; Tianjin Chest Hospital; West China Hospital, Sichuan University; Xiamen Heart Center; Xiyuan Hospital, CACMS; Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University; Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University; Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University.
Footnotes
Edited by: Xiu-Yuan Hao and Qiang Shi
REFERENCES
- 1.Kennedy HL, Whitlock JA, Sprague MK, Kennedy LJ, Buckingham TA, Goldberg RJ. Long-term follow-up of asymptomatic healthy subjects with frequent and complex ventricular ectopy. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:193–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501243120401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ng GA. Treating patients with ventricular ectopic beats. Heart. 2006;92:1707–12. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.067843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jouven X, Zureik M, Desnos M, Courbon D, Ducimetière P. Long-term outcome in asymptomatic men with exercise-induced premature ventricular depolarizations. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:826–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200009213431201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sheldon SH, Gard JJ, Asirvatham SJ. Premature ventricular contractions and non-sustained ventricular tachycardia: Association with sudden cardiac death, risk stratification, and management strategies. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2010;10:357–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee GK, Klarich KW, Grogan M, Cha YM. Premature ventricular contraction-induced cardiomyopathy: A treatable condition. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5:229–36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.111.963348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chiang BN, Perlman LV, Ostrander LD, Jr, Epstein FH. Relationship of premature systoles to coronary heart disease and sudden death in the Tecumseh epidemiologic study. Ann Intern Med. 1969;70:1159–66. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-6-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bikkina M, Larson MG, Levy D. Prognostic implications of asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias: The Framingham Heart Study. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:990–6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-12-990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frolkis JP, Pothier CE, Blackstone EH, Lauer MS. Frequent ventricular ectopy after exercise as a predictor of death. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:781–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xing Y, Gao Y, Chen J, Zhu H, Wu A, Yang Q, et al. Wenxin-keli regulates the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II signal transduction pathway and inhibits cardiac arrhythmia in rats with myocardial infarction. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013. 2013 doi: 10.1155/2013/464508. 464508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Adams JC, Srivathsan K, Shen WK. Advances in management of premature ventricular contractions. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2012;35:137–49. doi: 10.1007/s10840-012-9698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kowey PR, Yan GX. Proarrhythmias and antiarrhythmias: Two sides of the same coin. Heart Rhythm. 2005;2:957–9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2005.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zipes DP, Camm AJ, Borggrefe M, Buxton AE, Chaitman B, Fromer M, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:e247–346. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Burashnikov A, Petroski A, Hu D, Barajas-Martinez H, Antzelevitch C. Atrial-selective inhibition of sodium-channel current by Wenxin Keli is effective in suppressing atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9:125–31. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.08.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Y, Li Y, Guo L, Chen W, Zhao M, Gao Y, et al. Effects of wenxin keli on the action potential and L-type calcium current in rats with transverse aortic constriction-induced heart failure. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013. 2013 doi: 10.1155/2013/572078. 572078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xue X, Guo D, Sun H, Wang D, Li J, Liu T, et al. Wenxin Keli suppresses ventricular triggered arrhythmias via selective inhibition of late sodium current. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36:732–40. doi: 10.1111/pace.12109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu YW, Guo JH, Zhang P, Li JW, Li C. The effects of Nardostachys chinensis batal extract on the sodium current and transient outward potassium current of rat ventricular myocytes (in Chinese) Chin J Card Pacing Electrophysiol. 2009;23:533–5. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Du ZD, Lin Y, Liu LY, Wang Y, Wang LP. The efficacy of Chinese herbal compound ‘Wen Xin’ on premature contraction in children: A randomized control trial (in Chinese) Chin J Evid Based Pediatr. 2006;1:40–5. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lei CB. Effect of Wenxin Keli on cardiac arrhythmias (in Chinese) J Mod Clin Med. 2006;32:89–90. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhao DM, Dai MB, Zhi ZJ. Observation of effect and safety of Wenxin granule on the treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy with ventricular arrhythmias (in Chinese) Hebei J Tradit Chin Med. 2010;32:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sun LP. Clinical observation of Wenxin Granule on treatment of premature ventricular contractions in patients with chronic heart failure (in Chinese) Liaolin J Chin Tradit Med. 2010;37:100–1. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Noble D, Noble PJ. Late sodium current in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease: Consequences of sodium-calcium overload. Heart. 2006;92(Suppl 4):iv1–iv5. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.078782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.de Paola AA, Horowitz LN, Morganroth J, Senior S, Spielman SR, Greenspan AM, et al. Influence of left ventricular dysfunction on flecainide therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987;9:163–8. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Preliminary report: Effect of encainide and flecainide on mortality in a randomized trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction. The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:406–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908103210629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


