Highlight
Under darkness, JAZ7 was up-regulated and the mutant showed a severe leaf senescence phenotype. Genetics and transcriptomic analysis revealed JAZ7 as an important regulator of dark-induced leaf senescence.
Key words: Arabidopsis, AtJAZ7, COI1, MYC2, dark-induced leaf senescence, transcriptomics.
Abstract
JASMONATE ZIM-domain (JAZ) proteins play important roles in plant defence and growth by regulating jasmonate signalling. Through data mining, we discovered that the JAZ7 gene was up-regulated in darkness. In the dark, the jaz7 mutant displayed more severe leaf yellowing, quicker chlorophyll degradation, and higher hydrogen peroxide accumulation compared with wild-type (WT) plants. The mutant phenotype of dark-induced leaf senescence could be rescued in the JAZ7-complemented and -overexpression lines. Moreover, the double mutants of jaz7 myc2 and jaz7 coi1 exhibited delayed leaf senescence. We further employed GeneChip analysis to study the molecular mechanism. Some key genes down-regulated in the triple mutant myc2 myc3 myc4 were up-regulated in the jaz7 mutant under darkness. The Gene Ontology terms ‘leaf senescence’ and ‘cell death’ were significantly enriched in the differentially expressed genes. Combining the genetic and transcriptomic analyses together, we proposed a model whereby darkness can induce JAZ7, which might further block MYC2 to suppress dark-induced leaf senescence. In darkness, the mutation of JAZ7 might partially liberate MYC2/MYC3/MYC4 from suppression, leading the MYC proteins to bind to the G-box/G-box-like motifs in the promoters, resulting in the up-regulation of the downstream genes related to indole-glucosinolate biosynthesis, sulphate metabolism, callose deposition, and JA-mediated signalling pathways. In summary, our genetic and transcriptomic studies established the JAZ7 protein as an important regulator in dark-induced leaf senescence.
Introduction
Leaf senescence is a programmed cell death process essential for plant growth and survival. Leaf senescence can be induced by many developmental and environmental factors, such as aging, darkness, hormones, drought, high salinity, extreme temperature, and pathogen attacks (Lim et al., 2007). Dark-induced senescence has frequently been used as a model system to study natural senescence and to promote some typical senescence symptoms such as chlorophyll degradation and protein catabolism (Weaver et al., 1998; Guo and Gan, 2005). Previous studies have revealed many regulators of dark-induced leaf senescence, such as WRKY22 (Zhou et al., 2011). Nitric oxide (NO) is a very important molecule regulating dark-induced leaf senescence, where Nitric Oxide Synthase1 reduces the levels of reactive oxygen species to protect against dark-induced senescence (Guo and Crawford, 2005). NO can regulate dark-induced leaf senescence through EIN2 (ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 2) in Arabidopsis (Niu and Guo, 2012).
High-throughput technology has greatly facilitated the study of aging- and darkness-related leaf senescence genes. Bhalerao et al. (2003) reported differentially expressed genes in autumn leaves by sequencing expressed sequence tags of a cDNA library in aspen (Populus tremula). A DNA microarray was used to study the leaf transcriptome of naturally senesced aspen leaves (Andersson et al., 2004). A high-resolution time-course profile of gene expression during development of a single leaf over a 3-week period up to senescence was obtained by microarray analysis (Breeze et al., 2011). Lin and Wu (2004) used the Arabidopsis ATH1 Genome Array to examine global gene expression in dark-induced leaf senescence. More than 800 genes were identified as senescence-associated genes, including large transcription factor families such as NAC, WRKY, C2H2-type zinc finger, AP2/EREBP, and MYB proteins (Gepstein et al., 2003). These senescence-associated genes are closely involved in different plant hormone biosynthesis and signal transduction pathways (Lim et al., 2007). Phytohormones, such as cytokinin, ethylene, abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, and auxin, normally act as internal factors to cause leaf senescence through a regulatory network (Aharoni and Lieberman, 1979; Gan and Amasino, 1995; Jing et al., 2005; Lim et al., 2007; Dong et al., 2008; Ghanem et al., 2008).
Jasmonic acid (JA) plays an important role in regulating dark-induced leaf senescence. The bioactive JA–isoleucine (JA–Ile) perception is dependent on the inositol phosphate-potentiated COI1–JAZ co-receptor (Sheard et al., 2010). COI1-dependent JA repression of rubisco activase was suggested to be an essential mechanism for JA-induced leaf senescence (Shan et al., 2010). JASMONATE ZIM-domain (JAZ) proteins were discovered as repressors of JA signalling through the SCFCOI1-dependent 26S proteasome pathway for protein degradation (Chini et al., 2007; Thines et al., 2007). There are 13 JAZ genes in Arabidopsis (Thireault et al., 2015). Both JAZ4 and JAZ8 were found to interact physically with WRKY57 for negative regulation of JA-induced leaf senescence (Jiang et al., 2014). WRKY57 functions as a node of convergence for JA- and auxin-mediated signalling in JA-induced leaf senescence. Generally, the JAZ proteins play important roles in plant defence and growth by regulating JA signalling (Chini et al., 2007; Thines et al., 2007; Yan et al., 2007; Chung et al., 2008; Grunewald et al., 2009; Demianski et al., 2011); however, the function of JAZ proteins in serving as an upstream regulator for leaf senescence has yet to be established.
The majority of the 13 JAZ proteins form homodimers and heterodimers, but interestingly, there is no evidence that any of the JAZ proteins interact with JAZ7 (Chini et al., 2009; Chung and Howe, 2009). Some JAZ proteins (possibly JAZ7) interact directly with TOPLESS (TPL) rather than using NINJA (Novel Interactor of JAZ) (Shyu et al., 2012). Meanwhile, JAZ proteins interact with other transcription regulators. A select set of JAZ proteins (i.e. JAZ1, JAZ3, and JAZ9) can bind EIN3 and EIL1, which are involved in ethylene signalling (Zhu et al., 2011). Overexpression of JAZ1 can disturb the bHLH–MYB interaction between PAP1–TT8 and GL1–GL3 (Qi et al., 2011). Some JAZ proteins such as JAZ1, JAZ8, and JAZ11 interact directly with MYB21 and MYB24 (Song et al., 2011). Direct interaction between JAZ1 and HDA6 has recently been confirmed (Zhu et al., 2011). In addition, JAZ proteins recruit TPL and TPL-related proteins through NINJA for transcription repression (Pauwels et al., 2010). Furthermore, JA signalling is reported to be involved in cambium formation, and COI1, MYC2, JAZ7, and especially JAZ10 are cambium regulators (Sehr et al., 2010). Overall, JAZ proteins regulate plant defence, growth, development, and in particular JA signalling, by interacting with both COI1 and various transcriptional factors. Despite the importance of the JAZ gene family, the function of JAZ7 is still largely unknown.
In addition to JAZ proteins, MYC2 has emerged as a master regulator of most aspects of the JA signalling pathway in Arabidopsis (Kazan and Manners, 2013). MYC3 and MYC4 are the closest homologues of MYC2, and were recently identified as targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in regulating the JA-dependent transcriptional response (Fernandez-Calvo et al., 2011; Niu et al., 2011). Most JAZ proteins—including JAZ7—interact with MYC2, MYC3, and/or MYC4 (Fernandez-Calvo et al., 2011; Schweizer et al., 2013). Furthermore, the MYC transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 regulate glucosinolate (GS) biosynthesis, insect performance, and feeding behaviour. MYC2 interacts with the G-box and related sequences, and controls genes activated by JA. A previous study showed that MYC2 binds directly to the promoter of several GS biosynthesis genes in vivo (Schweizer et al., 2013). Recent studies have indicated that MYC transcription factors (MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4) are short-lived proteins degraded by the proteasome in darkness (including shade conditions) and stabilized by light and JA. MYC2 protein stability is regulated by phosphorylation-coupled proteolysis through the proteosome (Zhai et al., 2013; Chico et al., 2014). In addition, MYCs are required for JA-mediated defences against the necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea and for the shade-triggered increased susceptibility (Chico et al., 2014). In contrast to MYCs, simulated shade conditions stabilize seven of the ten JAZ repressors and reduce their degradation by JA. Despite the progress, it is still unclear how JAZ proteins interact with MYCs to signal leaf senescence or other processes.
In this study, we integrated a systems biology approach with a classic genetics study to identify JAZ7 involvement in dark-induced leaf senescence. The JAZ7 gene was significantly up-regulated during darkness. Further analysis of mutant phenotypes for the JAZ family genes revealed that a knockout mutant of JAZ7 resulted in severe leaf senescence under dark treatment. Unlike other JAZ genes, very limited information is available for the functions of JAZ7. Genetic analysis showed that JAZ7 is very important for dark-induced leaf senescence. The dark-induced leaf senescence phenotype could be rescued in the JAZ7-complemented and -overexpression lines. Further genetic analysis showed that JAZ7 interacted with COI1 and/or MYC2 to regulate dark-induced leaf senescence. We further conducted transcriptomic analysis to dissect the molecular and systems mechanisms underlying the JAZ7-mediated dark-induced leaf senescence.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0, jaz7 mutant line, JAZ7-complemented line 35S::JAZ7/jaz7, and JAZ7-overexpression line 35S::JAZ7/WT, as well as other mutant lines) seeds were surface sterilized and sown on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 0.8% agar in Petri plates. The seeds were stratified for 3 d at 4 °C and then transferred to a conditioning chamber with a circadian cycle of 16h of light (22 °C) and 8h of darkness (19 °C). The Arabidopsis seedlings were transferred to soil 10 d after germination.
Identification of the jaz7 T-DNA insertion mutant
The jaz7 mutant (WiscDsLox7H11) contained a T-DNA insertion in the second exon (see Fig. 2A). Homozygous T-DNA insertion mutant plants were confirmed by PCR using a combination of a T-DNA border primer (LB: 5'-GCGTGGACCGCTTGCTGCAACT-3') and gene-specific primers (LP: 5'-CATCATCAAAAACTGCGACAAGCC-3', and RP: 5'-GGTAACGGTGGTAAGGGGAAGT-3').
Construction of transgenic Arabidopsis line JAZ7-complemented line 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 and JAZ7-overexpression line 35S::JAZ7/WT
In order to generate the genetic complemented line 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 and overexpression line 35S::JAZ7/WT, the ORF for the JAZ7 gene was isolated by PCR using the forward primer 5'-GCTCTAGAATGATCATCATCATCAAAAACTGC-3' and reverse primer 5'-GGGGTACC CTATCGGTAACGGTGGTAAG-3'. The ORF (447bp) of JAZ7 was inserted into the super-1300 vector in the XbaI and KpnI sites under the control of a constitutive cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. The construct was verified by sequencing and introduced into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 strain. The Arabidopsis plants were transformed using the floral infiltration method (Clough and Bent, 1998). Transgenic plants were selected by hygromycin resistance and confirmed by PCR. The homozygous T2 seeds of transgenic plants were used for further analysis.
Double-mutant construction
The Arabidopsis double-mutant plants jaz7 coi1 and jaz7 myc2 were constructed by the manual cross-pollination method (Li et al., 1994). Those homozygous for the single mutation jaz7 (WiscDsLox7H11), coi1 (SALK_045434), and myc2 (SALK_017005C) were used. After self-pollinate of F1 plants, the homozygous double mutants were identified from the F2 generation by PCR using a combination of the T-DNA border primer LB and gene-specific primers LP/RP. The homozygous F3 seeds were used for further analysis.
Dark treatment for leaf senescence, 3,3'-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining, and chlorophyll content measurement
Arabidopsis plants were grown in soil for 4 weeks, and the fifth or sixth rosette leaf was detached for dark treatment. The detached leaves were incubated in Petri dishes wrapped in aluminium foil and containing two layers of filter paper soaked in 15ml of distilled water.
The hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) staining agent DAB (Sigma-Aldrich) was dissolved in water and adjusted to pH 3.8 with KOH. The staining process was as described in Bowling et al. (1997). Quantitative measurement of H2O2 production was performed using an Amples Red H2O2/peroxidase assay kit (Molecular Probes) and the whole procedure followed the manufacturer’s instructions. An ANOVA test of pair-wise comparisons between all genotypes under the treatments was performed using the Excel packages (Brady et al., 2015).
Chlorophyll relative content was measured using a SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter. More than 30 leaves were tested to make a distribution analysis. Each treated leaf was measured three to four times on different areas. The SPAD readings were used directly to quantify chlorophyll content (Uddling et al., 2007; Ling et al., 2011; Ishimaru et al., 2012; Omondi and Kniss, 2014).
Sample treatment and RNA extraction
Three-week-old Arabidopsis plants grown in soil were used for dark treatment. The control plants were kept under regular growth conditions as described previously, with a diurnal cycle of 16h of light (22 °C) and 8h of darkness (19 °C). The plants for dark treatment were transferred to a continuously dark room for 3 d. After treatment, at 10 am (2h after lights on), dark-treated and control plants were harvested and quickly placed in liquid nitrogen for total RNA extraction.
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). About 200mg of plant material was grounded in liquid nitrogen and mixed with 1ml of TRIzol. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 5min, and then 0.2ml of chloroform was added and the mixture incubated at room temperature for 10min. The resultant mixture was centrifuged at 12 000g at 4 °C for 10min. The supernatant was transferred to a 1.5ml Eppendorf tube and an equal volume of isopropyl alcohol was added, followed by centrifugation. The RNA was washed with 75% ethanol and dissolved in 100 μl of RNase-free water. All RNA samples were then purified using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration of RNA was measured with an Eppendorf Biophotometer based on A 260/A 280 and A 260/A 230 ratios.
Real-time RT-PCR
For real-time reverse transcription (RT-PCR analysis, 2 µg of total RNA was used to synthesize cDNA with an M-MLV Reverse Transcription Reagents Kit (Invitrogen). The cDNA samples were diluted to 2ng μl–1 for real-time RT-PCR. Triplicate quantitative assays were performed on 8ng of cDNA using the SYBR Green Master mix with an ABI 7900 sequence detection system according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Applied Biosystems). Primers were designed by Primer3 (http://frodo.wi.mit.edu/) and are listed in Supplementary Table S5 at JXB online. The relative quantitation method (ΔΔC T) was used to evaluate quantitative variation among replicates. Two reference genes, 18S rRNA and actin7 (At5g09810), were applied as internal controls to normalize all data for the real-time RT-PCR experiments. The primers of the two reference genes are listed in Supplementary Table S5.
Affymetrix GeneChip experiment
For Affymetrix GeneChip analysis, 8 μg of total RNA for each sample was used to prepare biotin-labelled cRNA targets. All the procedures for cDNA and cRNA synthesis, cRNA fragmentation, hybridization, washing and staining, and scanning were conducted according to the GeneChip Standard Protocol (Eukaryotic Target Preparation). In this experiment, a Poly-A RNA Control kit and a One-Cycle cDNA Synthesis kit were applied. The Affymetrix ATH1 GeneChip was used for this experiment. Affymetrix GCOS software was used for data normalization and comparative analysis. The overall intensities of all probe sets of each array were scaled to 500 to guarantee that hybridization intensity of all arrays was equivalent. A one-way ANOVA test was applied to identify the differentially expressed probe sets through Partek Genomics Suite 6.3. The annotation of each probe set in the Affymetrix ATH1 GeneChip was provided by BLAST from Arabidopsis TAIR10 (http://www.arabidopsis.org)
Promoter and gene function analysis
The 2kb promoter sequence of each gene was obtained from TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org). The Arabidopsis Promoter Element Discovery Tools (http://stan.cropsci.uiuc.edu/tools.php) and PLACE database (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/) were used for common motif searching.
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was performed using the agriGO website (Du et al., 2010) and gene set enrichment analysis using plantGSEA (Yi et al., 2013).
Results and discussion
Darkness induces JAZ gene expression
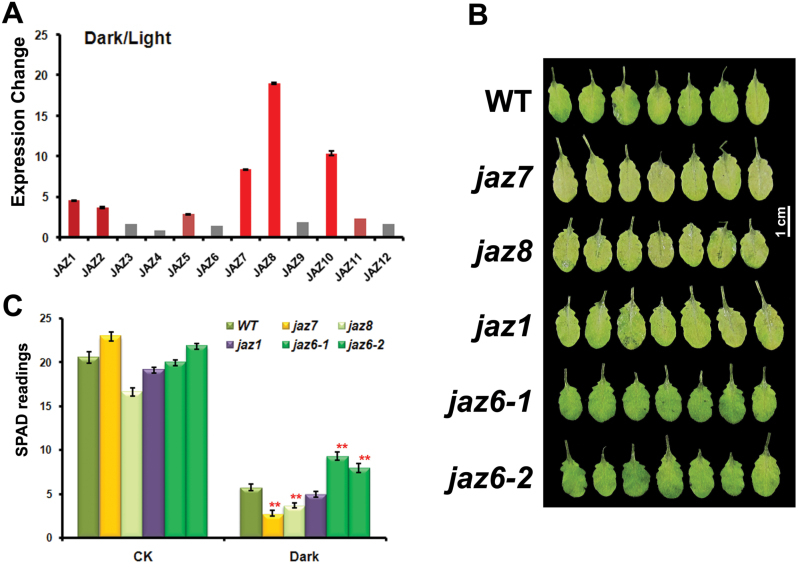
We first discovered the potential role of JAZ proteins in dark-induced leaf senescence through data mining of previously published transcriptomics data for dark-induced leaf senescence (Lin and Wu, 2004). JAZ genes were found to be significantly induced under dark treatment, and nine out of 12 JAZ genes showed more than 2-fold up-regulation for either 1 or 5 d of dark treatments (Supplementary Table S1 at JXB online). The expression patterns of Arabidopsis JAZ family genes under dark treatment were further investigated using real-time RT-PCR analysis (Fig. 1A and Supplementary Table S1). Seven JAZ genes were significantly up-regulated by dark treatment. In addition, Parlitz et al. (2011) showed that JAZ7 and JAZ10 were significantly induced after 2, 4, and 6 d of dark treatment (Supplementary Table S1). The real-time RT-PCR data and data mining of transcriptomics results both revealed that JAZ genes were induced in the dark and might be involved in dark-induced leaf senescence.
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the response of JAZ family genes to dark-induced leaf senescence. (A) Real-time RT-PCR detection of the expression changes of JAZ genes under dark treatment. Total RNA was obtained from leaves of 4-week-old WT plants grown under dark or normal conditions for 3 d. The results show the fold expression change in the dark relative to growth in the light. (B) Rosette leaves of several JAZ mutants under dark treatment. The fifth and sixth leaves were detached from the different mutant plants, incubated with wetted filter paper in dark conditions for 118h, and photographed. (C) The chlorophyll content (SPAD readings) of leaves from JAZ mutants under dark treatment and control conditions for 118h. jaz7, WiscDsLox7H11; jaz8, WiscDsLox255G12; jaz1, SALK_011957; jaz6-1, SALK_136462; jaz6-2, SALK_038013. SPAD readings were determined using a SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter. **P<0.01 (significant difference between mutants and WT according to Student’s t-test). The error bars in (A) and (C) represent the standard error of replicates.
Genetic analysis reveals JAZ7 as an important regulator of dark-induced leaf senescence
Genetic analysis of dark-induced leaf senescence phenotypes for jaz1, jaz6, jaz7, and jaz8 was further carried out using T-DNA insertion mutant lines (Fig. 1B, C). After 5 d of dark treatment, the detached leaves of jaz7 mutant lines showed a significantly more severe leaf senescence phenotype, with yellow leaves and less chlorophyll content compared with WT (Col-0). Mutant lines of jaz1 and jaz8 also showed less chlorophyll content than WT, while mutants of the two jaz6 alleles showed resistance to senescence. Among all mutant lines, the jaz7 mutant showed the most statistically significant decrease in chlorophyll content compared with WT. This result highlighted the important role of JAZ7 as a potential negative regulator in dark-induced leaf senescence.
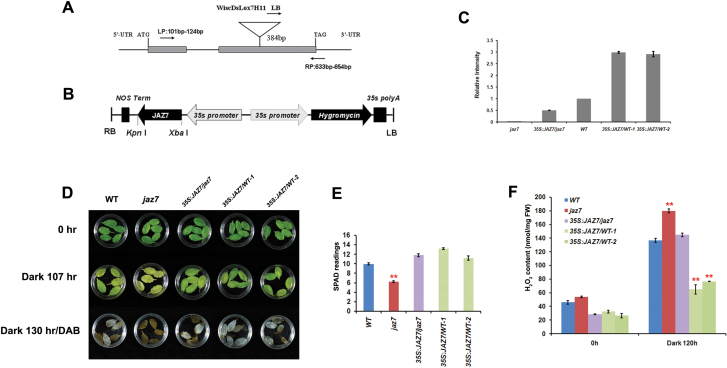
Genetic complementation of the jaz7 mutant phenotype was carried out with two types of transgenic strategies: 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 to complement the JAZ7 mutation in the jaz7 mutant, and 35S::JAZ7/WT to overexpress the JAZ7 gene in WT. Both types of transformants were validated by real-time RT-PCR (Fig. 2A–C). The 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 successfully rescued leaf senescence by showing a similar phenotype to WT (Fig. 2D, 2E). In addition, 35S::JAZ7/WT displayed a significantly delayed leaf senescence in darkness, further confirming the role of JAZ7 as a negative regulator of dark-induced leaf senescence (Fig. 2D). Among all genetic lines, the jaz7 mutant had the lowest chlorophyll level in leaves, and overexpression lines had the highest (Fig. 2E). Overall, the genetic complementation experiments and overexpression studies verified the role of JAZ7 in negative regulation of dark-induced leaf senescence.
Fig. 2.
Phenotype analysis of jaz7 mutant, JAZ7-complemented (35S::JAZ7/jaz7), WT, and JAZ7-overexpression (35S::JAZ7/WT) plants under dark treatment. (A) T-DNA insertion position of the jaz7 mutant line at 384bp from the 5'-untranslated region (UTR). Boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. (B) Constructs used for transformation of the 35S::JAZ7/jaz7-complemented line and JAZ7-overexpression lines. (C) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of JAZ7 gene expression in the jaz7 mutant line, WT, complemented line 35S::JAZ7/jaz7, and overexpression line 35S::JAZ7/WT. (D) Fifth or sixth detached rosette leaves from the jaz7 mutant, 35S::JAZ7/jaz7, WT, and 35S::JAZ7/WT lines under dark treatment for 4–5 d in water, and DAB staining of the treated leaves. (E) Chlorophyll content (SPAD readings) of leaves after dark treatment for 107h. Error bars represent the standard error of >50 leaves at the same stage. (F) H2O2 content of leaves from the jaz7 mutant, 35S::JAZ7/jaz7, WT, and 35S::JAZ7/WT lines before and after dark treatment. The SPAD reading was determined using a SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter. FW, fresh weight of leaf tissues. **P<0.01 (significant difference between mutants and WT according to Student’s t-test). The error bars in (C) and (F) represent the standard error of replicates.
H2O2 is involved in JAZ7-mediated dark-induced leaf senescence
The signalling pathway of JAZ7-mediated dark-induced leaf senescence was further studied from several aspects. First, the role of H2O2 in JAZ7 signalling for dark-induced leaf senescence was studied. H2O2 has been established to be important in signalling during stress responses and can be involved in senescence (Orozco-Cardenas et al., 2001; Ali et al., 2007; Aftab et al., 2011). DAB staining was used to detect H2O2 accumulation under dark treatment, and most jaz7 mutant leaves stained dark brown, while WT and 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 leaves were lighter in colour, and the 35S::JAZ7/WT lines showed the least staining (Fig. 2D). The quantitative assay suggested that the jaz7 mutant produced more H2O2 than WT and 35S::JAZ7/jaz7. The JAZ7 overexpression lines had the lowest H2O2 levels after 120h of dark treatment (Fig. 2F). Using a pair-wise ANOVA test, the genotypic variation (mutation and overexpression of JAZ7 gene) was found to significantly alter the H2O2 level under darkness (Supplementary Table S2 at JXB online). The H2O2 measurement results indicated that the JAZ7 protein might suppress leaf senescence by reducing H2O2 levels.
COI1 genetically interacts with JAZ7 to regulate dark-induced leaf senescence
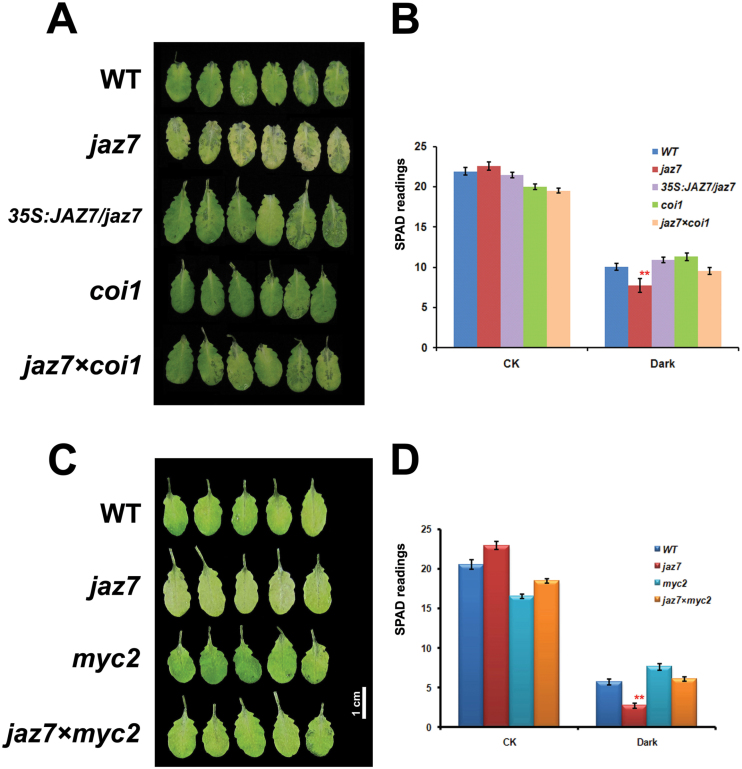
Considering that JAZ proteins are repressors of JA signalling through the SCFCOI1-dependent 26S proteasome pathway (Chini et al., 2007; Thines et al., 2007), we further studied how JAZ7 interacted genetically with COI1 during dark-induced leaf senescence. The jaz7 coi1 double mutant was generated to investigate whether the JAZ7-mediated dark-induced leaf senescence was COI1 dependent or not (Supplementary Fig. S1A, B at JXB online). The leaf senescence phenotype for the jaz7 mutant was partially rescued by mutation of COI1 (Fig. 3A). Basically, after 5 d of darkness treatment, the jaz7 coi1 double mutant had a similar phenotype to WT plants under darkness, while the coi1 mutant plants remained green. The chlorophyll level was significantly reduced after dark treatment in all lines (Fig. 3B). The rate of chlorophyll degradation in the jaz7 mutant was much faster than in the jaz7 coi1 double-mutant, WT, overexpression line, and coi1 mutant plants. The results suggested that in the jaz7 coi1 double mutant, JAZ7 is knocked down but that the other JAZ proteins might be stabilized by the coi1 mutant, thus repressing MYCs and overcoming the lack of JAZ7.
Fig. 3.
Phenotype analysis of the jaz7 and double-mutant (jaz7 coi1 and jaz7 myc2) plants under dark treatment. (A) Leaves of WT, jaz7 mutant, 35S::JAZ7/jaz7 mutant, coi1 mutant, and jaz7 coi1 double-mutant lines under dark treatment. The rosette leaves were detached from different mutant plants and photographed after incubation in darkness for 118h. (B) Chlorophyll content (SPAD readings) of the leaves of jaz7 and coi1 mutants after dark treatment for 118h. (C) Leaves of WT, jaz7 mutant, myc2 mutant, and jaz7 myc2 double mutants after dark treatment for 118h. (D) Chlorophyll content (SPAD readings) of leaves of jaz7 and myc2 mutants after dark treatment for 118h. **P<0.01 (significant difference between mutants and WT according to Student’s t-test). The error bars in (B) and (D) represent the standard error of replicates.
MYC2 might be a downstream target of JAZ7
We further studied the downstream target for JAZ7 and explored the genetic interaction of JAZ7 with MYC genes. MYC2 serves as a transcriptional activator of JA responses and JAZ7 physically interacts with MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 (Fernandez-Calvo et al., 2011; Schweizer et al., 2013). Darkness/shade conditions can stabilize JAZ7 and destabilize MYC proteins (Chico et al., 2014). The rosette leaves detached from WT, jaz7 mutant, myc2 mutant, and jaz7 myc2 double-mutant plants, were treated in darkness to evaluate dark-induced leaf senescence (Fig. 3C, D and Supplementary Fig. S1C, D). The jaz7 mutant displayed a strong yellowing phenotype at 5 d, while the myc2 mutant and jaz7×myc2 double mutant showed comparatively delayed leaf senescence and chlorophyll degradation as compared with jaz7 mutant. The result indicated that the mutation of MYC2 could partially rescue the dark-induced chlorophyll degradation in the jaz7 mutant, and further suggested that MYC2 might be the target of JAZ7 in the signalling of dark-induced leaf senescence.
Transcriptome analysis of jaz7 mutant and WT plants under darkness
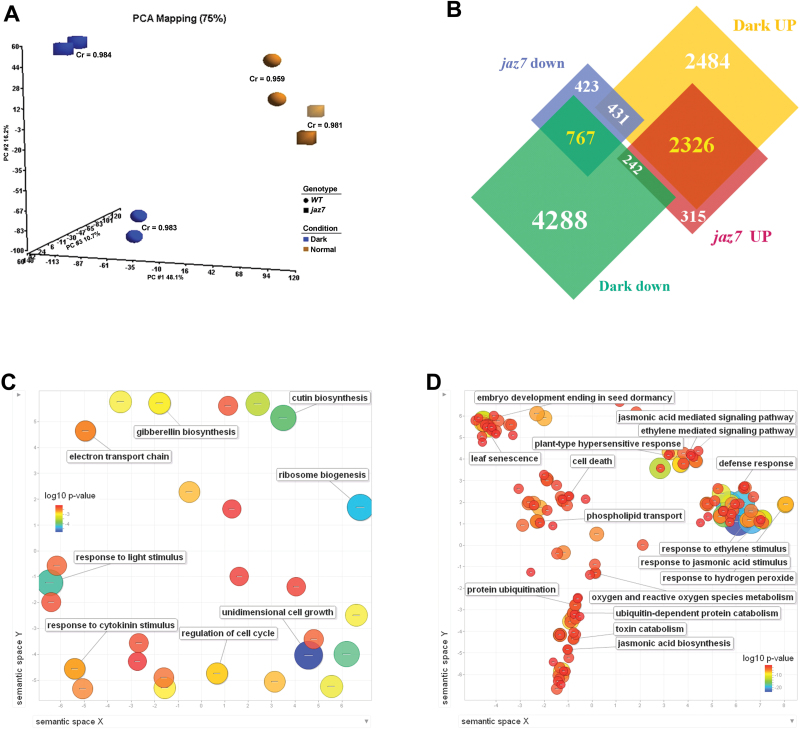
Transcriptomics was used to further explore the downstream network regulated by JAZ7 for dark-induced leaf senescence. We used the Arabidopsis ATH1 GeneChip to investigate the genome-wide gene expression differences in dark-induced senescence between WT and jaz7. Rosette leaves of Arabidopsis WT and jaz7, after 3 d of dark treatment and control conditions, were harvested for GeneChip hybridization, with two independent biological replicates for each sample (Supplementary Table S3 at JXB online). Principal component analysis (PCA) showed that the replicate chips of each sample were similar to each other, and the correlation coefficients of the expression profiling for replicate chips were >0.95 (Fig. 4A). The PCA results also showed that the difference between WT and jaz7 was much higher in darkness than in control conditions (Fig. 4A). Next, we applied ANOVA to identify the differentially expressed probe sets with the cut-off values of ≥1.6 in fold change and of P≤0.05. We first checked the differential expression pattern of DIN (dark-inducible) genes (Fujiki et al., 2001). The eight DIN genes were all significantly induced under dark treatment both in WT and jaz7; DIN9 and DIN11 were up-regulated in jaz7 samples compared with WT in darkness (Supplementary Table S4 at JXB online). We divided the differentially expressed genes into two categories: dark- and genotype-influenced genes (Fig. 4B). Genes differentially expressed between genotypes fell into two categories: 2883 up-regulated and 1621 down-regulated genes in jaz7 samples compared with WT. The dark-influenced genes were also divided into two categories: 5241 up-regulated and 5297 down-regulated genes (Fig. 4B). The Venn diagram shows the intersection of the four categories: of the 1621 down-regulated genes in jaz7, 767 (>45%) were down-regulated and 431 (about 25%) were up-regulated after dark treatment, while of the 2883 up-regulated genes in jaz7, 2326 (>80%) were up-regulated and 242 (<10%) were down-regulated by dark treatment (Fig. 4B). We proposed that two groups of genes were the key factors causing the difference between WT and the jaz7 mutant: 767 genes that were down-regulated by darkness and had lower expression in the jaz7 mutant (defined as group I), and 2326 genes that were highly expressed in the jaz7 mutant and up-regulated by darkness (group II). Therefore, further GO enrichment analyses based on these two groups were carried out. The result for group I (767 genes, Fig. 4C and Supplementary Table S3) showed such enriched GO terms as ‘response to light stimulus’ [GO: 0009416, false discovery rate (FDR) P value=7.77E–5], ‘electron transport chain’ (GO:0022900, FDR P value=2.59E–3), ‘ribosome biogenesis’ (GO: 0042254, FDR P value=5.28E–5), and ‘cutin biosynthetic process’ (GO:0010143, FDR P value=1.05E–4). The enriched GO terms for group II (2326 genes, Fig. 4D and Supplementary Table S3) are also shown and included ‘leaf senescence’ (GO:0010150, FDR P value=2.48E–7), ‘response to hydrogen peroxide’ (GO: 0042542, FDR P value=2.28E–8), ‘cell death’ (GO: 0008219, FDR P value=2.42E–3), ‘defence response’ (GO:0006952, FDR P value=1.47E–6), and ‘protein ubiquitination’ (GO:0016567, FDR P value=1.15E–4).
Fig. 4.
Summary of the differential expression probe sets between WT and jaz7 under normal and dark treatments. (A) PCA for the samples based on the raw data of the expression profiling. (B) Venn diagrams illustrate the differential expression probe sets under normal and dark treatments in WT and jaz7 plants. (C) GO enrichment analysis of the 767 probe sets up-regulated in WT and light conditions. (D) GO enrichment analysis of the 2326 probe sets up-regulated in jaz7 and dark conditions.
Based on the enriched GO terms and important superfamilies in differentially expressed genes between the jaz7 mutant and WT following dark treatment, we selected some genes that were possibly related to senescence/aging to confirm our GeneChip result, including JAZ family genes, cytochrome P450s, and UDP-glucoronosyl/UDP-glucosyl transferase family genes. For the real-time RT-PCR validation, additional biological samples were collected under the same conditions as for the GeneChip analysis. Both 18S rRNA and the housekeeping gene actin7 (At5g09810) were used as reference genes to calculate the relative expression levels. The result of real-time RT-PCR for the majority of the tested genes confirmed the microarray results (Supplementary Fig. S2 at JXB online). The fold change of genes analysed by real-time RT-PCR were not exactly the same as those obtained in the GeneChip data, but the change trends were similar.
Relevance of JAZ- and MYC-regulated pathways
To elucidate the relevance of the regulations by JAZ7 and MYC transcription factors, the previously published down-regulated transcripts in the triple mutant myc2 myc3 myc4 (Schweizer et al., 2013) were compared with differentially expressed genes in the jaz7 mutant versus WT. The 28 genes down-regulated in the triple mutant were significantly up-regulated in the jaz7 mutant in darkness but not under light conditions (Table 1). These genes included those involved in indole-GS, sulphur metabolism, and JA-related pathways. About half of the genes were relevant to indole-GS and sulphur metabolism, including ASA1, ASB1, CYP79B2, UGT74B1, GGP1, SOT16/17, APR1, APK2, and APS1. These genes are essential for glutathione biosynthesis, which is important for Arabidopsis defence, hypersensitive reactions, and programmed cell death. Schweizer et al. (2013) reported that MYC2/MYC3/MYC4 are necessary for direct transcriptional activation of GS biosynthesis genes and play crucial roles in the regulation of defence secondary metabolite production. In the triple mutant myc2 myc3 myc4, both aliphatic- and indole-GS biosynthesis genes were significantly down-regulated, as well as those related to the sulphate assimilation pathway. Our ATH1 GeneChip data indicated that the mutation of JAZ7 elevated only the expression levels of genes related to indole-GS biosynthesis and sulphate metabolism under dark treatment (Table 1). This may be because JA can trigger indole-GS accumulation in Arabidopsis, and the induction of tryptophan and indole-GS transcripts are mainly JA dependent (Brader et al., 2001). Thus, JAZ7 might bind to MYC2/MYC3/MYC4 to prevent the activation of indole-GS biosynthesis and sulphur metabolism genes during dark-induced leaf senescence. Furthermore, the genes related to JA pathways were also enriched (Table 1), including OPR3, ST2A, NATA1, and MYB21, as well as oxidation–reduction pathway genes such as 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, which suggested a potential role of JA signalling and interference of JAZ7 with its regulation of MYC-dependent cell death and senescence. Further motif analysis revealed that MYC2-binding motifs [G-box (CACGTG) and G-box-like motif (CACATG)] were over-represented in the 2kb promoter regions of these overlapping genes. The predicted MYC2-binding motif and the MYC2-binding information for these GS genes are given in Table 1.
Table 1.
MYC2-, MYC3-, and MYC4-regulated genes affected by mutation of JAZ7 in darkness
| Locus ID | MYCs motif (CACNTG) | Col-0/myc234 a | WT dark/jaz7 dark | WT light/jaz7 light | Gene name | Gene included in functional category of: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold change | P value | Fold change | P value | Fold change | P value | Indole derivative metabolism | Glucosinolate metabolism | Sulphur metabolism | Response to JA stimulus | Oxidation– reduction | |||
| At5g05730 | ✓ | 2.27 | 1.47E–04 | –4.28 | 7.75E–06 | –1.05 | 9.22E–01 | ASA1 | ✓ | ||||
| At1g25220 | ✓ | 2.25 | 2.95E–02 | –1.83 | 1.17E–02 | –1.33 | 5.93E–01 | ASB1 | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At4g27070 | ✓ | 2.03 | 7.95E–03 | –2.37 | 1.39E–02 | 1.05 | 9.50E–01 | TSB2 | ✓ | ||||
| At4g39950b | ✓ | 11.42 | 6.17E–06 | –4.06 | 5.95E–04 | –1.08 | 9.52E–01 | CYP79B2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At1g24100b | ✓ | 3.93 | 5.27E–06 | –2.21 | 9.39E–03 | 1.05 | 8.49E–01 | UGT74B1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At4g30530 | ✓ | 3.22 | 1.90E–05 | –1.81 | 2.43E–02 | –1.38 | 3.09E–01 | GGP1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At1g74100b | ✓ | 4.12 | 4.52E–06 | –2.28 | 2.64E–02 | –1.76 | 5.14E–01 | SOT16 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| At1g18590 | ✓ | 15.50 | 1.18E–07 | –1.97 | 2.52E–02 | –2.06 | 1.80E–02 | SOT17 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At4g39940b | ✓ | 35.27 | 5.54E–08 | –2.17 | 5.19E–03 | –1.33 | 1.04E–01 | APK2,AKN2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At4g04610b | ✓ | 4.21 | 1.18E–04 | –8.31 | 4.35E–05 | –1.37 | 4.46E–01 | APR1, PAPS reductase | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| At3g22890 | ✓ | 1.99 | 1.14E–03 | –2.32 | 6.40E–03 | 1.26 | 3.45E–01 | APS1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| At1g51760 | ✓ | 1.85 | 6.39E–04 | –2.22 | 6.61E–03 | –2.66 | 6.22E–02 | IAR3, JR3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At5g01500 | 2.93 | 3.21E–05 | –3.61 | 1.52E–02 | 1.61 | 5.60E–01 | TAAC/PAPST1 | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| At4g29700 | ✓ | 3.59 | 5.24E–05 | –2.06 | 2.05E–02 | –1.38 | 1.98E–01 | Alkaline- phosphatase-like protein | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At5g07010 | ✓ | 2.34 | 2.62E–04 | –2.98 | 1.18E–04 | 1.27 | 9.44E–01 | ST2A | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At2g06050 | ✓ | 3.36 | 1.55E–05 | –2.61 | 2.51E–02 | –1.19 | 5.47E–01 | OPR3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At2g39030 | ✓ | 7.74 | 3.10E–05 | –2.96 | 1.32E–03 | –1.46 | 3.73E–01 | NATA1 | ✓ | ||||
| At3g27810 | ✓ | 1.89 | 2.43E–03 | –3.19 | 2.92E–03 | –3.36 | 4.21E–01 | ATMYB21, ATMYB3, MYB21 | ✓ | ||||
| At1g61120 | ✓ | 5.22 | 2.65E–05 | –4.81 | 1.99E–04 | –1.55 | 4.58E–01 | TPS04 | ✓ | ||||
| At3g51450 | ✓ | 1.91 | 2.00E–03 | –2.37 | 3.03E–02 | –1.39 | 2.13E–01 | Calcium-dependent phosphotriesterase | ✓ | ||||
| At1g06620 | ✓ | 2.53 | 5.47E–05 | –2.31 | 3.75E–03 | –1.35 | 6.23E–01 | 2-Oxoglutarate- dependent dioxygenase | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| At2g38240 | ✓ | 4.47 | 6.37E–05 | –2.70 | 2.68E–04 | –1.43 | 8.94E–01 | Oxoglutarate/ iron-dependent oxygenase | ✓ | ||||
| At4g20860 | ✓ | 2.29 | 1.74E–03 | –3.35 | 2.97E–03 | –1.77 | 8.03E–01 | FAD-binding Berberine protein | |||||
| At1g74010 | 2.39 | 9.69E–03 | –2.17 | 1.29E–02 | –1.12 | 9.35E–01 | Calcium-dependent phosphotriesterase | ||||||
| At4g24350 | ✓ | 1.92 | 3.88E–04 | –2.69 | 2.99E–02 | –1.49 | 3.01E–02 | Phosphorylase | |||||
| At3g03240 | ✓ | 1.94 | 1.52E–03 | –1.95 | 4.18E–02 | 1.20 | 8.70E–01 | α/β-Hydrolases | |||||
| At2g25730 | ✓ | 1.86 | 1.27E–02 | –1.87 | 1.23E–02 | –1.29 | 6.89E–01 | Unknown protein | |||||
| At5g40210 | ✓ | 2.43 | 4.17E–04 | –2.48 | 1.85E–03 | 1.39 | 3.06E–02 | Nodulin MtN21 /EamA-like transporter | |||||
Bold values represent statistically significant changes (fold change ≥1.8 and P≤0.05).
a Data from Schweizer et al. (2013).
b The genes were reported with MYC2 bound in the promoter region by ChIP-seq (Schweizer et al., 2013).
In addition, indole-GS biosynthesis is required for the Flg22-induced callose response and Arabidopsis innate immune response (Clay et al., 2009; Schlaeppi et al., 2010). Transcriptome analysis of WT and jaz7 mutant plants under dark treatment showed that a large number of callose deposition genes were also up-regulated in the jaz7 mutant. Most of these callose-response genes were related to the indole-GS pathway, such as TSA1/TRP3, CYP79B2, UGT74B1, CYP81F2, and PEN3. All of the results suggested that the JAZ7-mediated MYC-regulated indole-GS genes were involved in callose deposition, essential for plant innate immunity response, programmed cell death, and leaf senescence.
Towards a model for JAZ7-mediated dark-induced leaf senescence
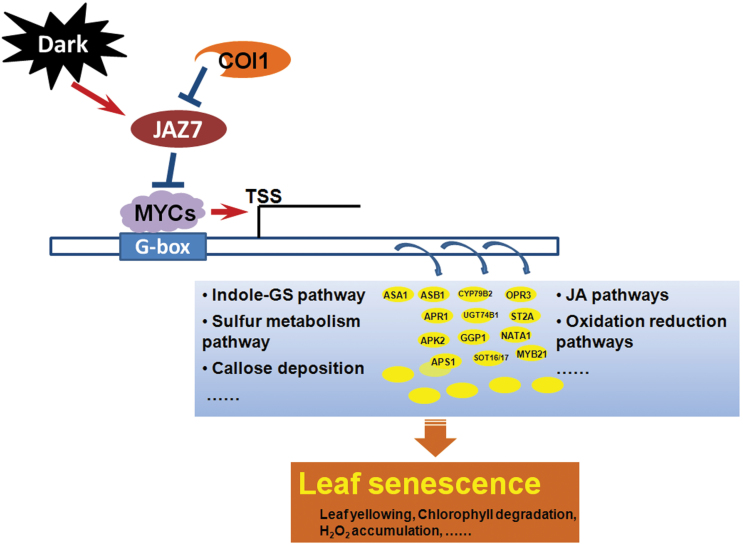
Together, the genetic and transcriptomic analyses suggested a model (Fig. 5) whereby darkness can induce JAZ7, which might further block MYC2 to suppress dark-induced leaf senescence. The function of JAZ7 may also depend on COI1. In darkness, the mutation of JAZ7 might partially liberate MYC2/MYC3/MYC4 from suppression, leading the MYC proteins to bind to the G-box/G-box-like motifs in the promoters, resulting in up-regulation of the downstream genes related to indole-GS biosynthesis, sulphate metabolism, callose deposition, and JA-mediated signalling pathways. Overall, the genetic and systems biology analyses suggest that JAZ7 plays an essential role in regulating the dark-induced leaf senescence relevant to many physiological processes.
Fig. 5.
Working model of the role of JAZ7 in dark-induced leaf senescence.
Under darkness, expression of the JAZ7 gene is significantly induced, and the jaz7 mutant had enhanced dark-induced leaf senescence. JAZ7-mediated dark-induced senescence might be COI1 dependent and antagonistic to regulation by MYCs. During darkness, the mutation of JAZ7 might partially liberate MYCs from suppression, leading the MYCs to bind to the G-box/G-box-like motifs in the promoters and resulting in the up-regulation of the downstream genes related to indole-GS biosynthesis, sulphate metabolism, callose deposition, and JA-mediated signalling pathways.
Supplementary data
Supplementary data are available at JXB online.
Supplementary Fig. S1. Real-time RT-PCR for target genes in jaz7, coi1, and myc2 mutants and double mutants jaz7 coi1, jaz7 myc2.
Supplementary Fig. S2. Real-time RT-PCR for selected probe sets.
Supplementary Table S1. Expression pattern of JAZ family genes under dark treatment.
Supplementary Table S2. ANOVA tables for pair-wise comparisons in Fig. 2F.
Supplementary Table S3. GeneChip raw data for WT and jaz7 samples under normal and dark treatments.
Supplementary Table S4. Expression pattern of DIN genes for WT and jaz7 under normal and dark treatments.
Supplementary Table S5. List of primers used for real-time RT-PCR.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Shu-Hsing Wu for providing the raw ATH1 datasets of dark-treated Arabidopsis. We thank Dr Yuannian Jiao for help with data mining, and we also thank Xue Zheng, Zhonghui Li, and Lan Liu for their technical support. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant nos 31171276 and 90817006) and the Ministry of Education of China (grant no. NCET-09-0735).
References
- Aftab T, Khan MM, Idrees M, Naeem M, Moinuddin, Hashmi N. 2011. Methyl jasmonate counteracts boron toxicity by preventing oxidative stress and regulating antioxidant enzyme activities and artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Protoplasma 248, 601–612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni N, Lieberman M. 1979. Ethylene as a regulator of senescence in tobacco leaf discs. Plant Physiology 64, 801–804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali MB, Hahn EJ, Paek KY. 2007. Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid induced oxidative stress and accumulation of phenolics in Panax ginseng bioreactor root suspension cultures. Molecules 12, 607–621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A, Keskitalo J, Sjodin A, et al. 2004. A transcriptional timetable of autumn senescence. Genome Biology 5, R24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalerao R, Keskitalo J, Sterky F, et al. 2003. Gene expression in autumn leaves. Plant Physiology 131, 430–442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling SA, Clarke JD, Liu Y, Klessig DF, Dong X. 1997. The cpr5 mutant of Arabidopsis expresses both NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent resistance. The Plant Cell 9, 1573–1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brader G, Tas E, Palva ET. 2001. Jasmonate-dependent induction of indole glucosinolates in Arabidopsis by culture filtrates of the nonspecific pathogen Erwinia carotovora . Plant Physiology 126, 849–860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady SM, Burow M, Busch W, et al. 2015. Reassess the t test: interact with all your data via ANOVA. The Plant Cell 27, 2088–2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeze E, Harrison E, McHattie S, et al. 2011. High-resolution temporal profiling of transcripts during Arabidopsis leaf senescence reveals a distinct chronology of processes and regulation. The Plant Cell 23, 873–894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chico JM, Fernandez-Barbero G, Chini A, Fernandez-Calvo P, Diez-Diaz M, Solano R. 2014. Repression of jasmonate-dependent defenses by shade involves differential regulation of protein stability of MYC transcription factors and their JAZ repressors in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 26, 1967–1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chini A, Fonseca S, Chico JM, Fernandez-Calvo P, Solano R. 2009. The ZIM domain mediates homo- and heteromeric interactions between Arabidopsis JAZ proteins. The Plant Journal 59, 77–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chini A, Fonseca S, Fernandez G, et al. 2007. The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature 448, 666–671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung HS, Howe GA. 2009. A critical role for the TIFY motif in repression of jasmonate signaling by a stabilized splice variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 21, 131–145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung HS, Koo AJ, Gao X, Jayanty S, Thines B, Jones AD, Howe GA. 2008. Regulation and function of Arabidopsis JASMONATE ZIM-domain genes in response to wounding and herbivory. Plant Physiology 146, 952–964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay NK, Adio AM, Denoux C, Jander G, Ausubel FM. 2009. Glucosinolate metabolites required for an Arabidopsis innate immune response. Science 323, 95–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. 1998. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana . The Plant Journal 16, 735–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demianski AJ, Chung KM, Kunkel BN. 2011. Analysis of Arabidopsis JAZ gene expression during Pseudomonas syringae pathogenesis. Molecular Plant Pathology 13, 46–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong H, Niu Y, Li W, Zhang D. 2008. Effects of cotton rootstock on endogenous cytokinins and abscisic acid in xylem sap and leaves in relation to leaf senescence. Journal of Experimental Botany 59, 1295–304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Z, Zhou X, Ling Y, Zhang Z, Su Z. 2010. agriGO: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community. Nucleic Acids Research 38, W64–W70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Calvo P, Chini A, Fernandez-Barbero G, et al. 2011. The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. The Plant Cell 23, 701–715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y, Yoshikawa Y, Sato T, Inada N, Ito M, Nishida I, Watanabe A. 2001. Dark-inducible genes from Arabidopsis thaliana are associated with leaf senescence and repressed by sugars. Physiologia Plantarum 111, 345–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan S, Amasino RM. 1995. Inhibition of leaf senescence by autoregulated production of cytokinin. Science 270, 1986–1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepstein S, Sabehi G, Carp MJ, Hajouj T, Nesher MF, Yariv I, Dor C, Bassani M. 2003. Large-scale identification of leaf senescence-associated genes. The Plant Journal 36, 629–642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem ME, Albacete A, Martinez-Andujar C, Acosta M, Romero-Aranda R, Dodd IC, Lutts S, Perez-Alfocea F. 2008. Hormonal changes during salinity-induced leaf senescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Journal of Experimental Botany 59, 3039–3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunewald W, Vanholme B, Pauwels L, Plovie E, Inze D, Gheysen G, Goossens A. 2009. Expression of the Arabidopsis jasmonate signalling repressor JAZ1/TIFY10A is stimulated by auxin. EMBO Reports 10, 923–928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo FQ, Crawford NM. 2005. Arabidopsis nitric oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. The Plant Cell 17, 3436–3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Y, Gan S. 2005. Leaf senescence: signals, execution, and regulation. Current Topics in Developmental Biology 71, 83–112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, et al. 2012. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport. Scientific Reports 2, 286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y, Liang G, Yang S, Yu D. 2014. Arabidopsis WRKY57 functions as a node of convergence for jasmonic acid- and auxin-mediated signaling in jasmonic acid-induced leaf senescence. The Plant Cell 26, 230–245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing HC, Schippers JH, Hille J, Dijkwel PP. 2005. Ethylene-induced leaf senescence depends on age-related changes and OLD genes in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany 56, 2915–2923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazan K, Manners JM. 2013. MYC2: the master in action. Molecular Plant 6, 686–703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li HM, Altschmied L, Chory J. 1994. Arabidopsis mutants define downstream branches in the phototransduction pathway. Genes & Development 8, 339–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim PO, Kim HJ, Nam HG. 2007. Leaf senescence. Annual Review of Plant Biology 58, 115–136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin JF, Wu SH. 2004. Molecular events in senescing Arabidopsis leaves. The Plant Journal 39, 612–628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling Q, Huang W, Jarvis P. 2011. Use of a SPAD-502 meter to measure leaf chlorophyll concentration in Arabidopsis thaliana . Photosynthesis Research 107, 209–214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu Y, Figueroa P, Browse J. 2011. Characterization of JAZ-interacting bHLH transcription factors that regulate jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany 62, 2143–2154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu YH, Guo FQ. 2012. Nitric oxide regulates dark-induced leaf senescence through EIN2 in Arabidopsis. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 54, 516–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omondi EC, Kniss AR. 2014. Interplanting annual ryegrass, wheat, oat, and corn to mitigate iron deficiency in dry beans. PLoS One 9, e115673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco-Cardenas ML, Narvaez-Vasquez J, Ryan CA. 2001. Hydrogen peroxide acts as a second messenger for the induction of defense genes in tomato plants in response to wounding, systemin, and methyl jasmonate. The Plant Cell 13, 179–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parlitz S, Kunze R, Mueller-Roeber B, Balazadeh S. 2011. Regulation of photosynthesis and transcription factor expression by leaf shading and re-illumination in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Journal of Plant Physiology 168, 1311–1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels L, Barbero GF, Geerinck J, et al. 2010. NINJA connects the co-repressor TOPLESS to jasmonate signalling. Nature 464, 788–791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi T, Song S, Ren Q, Wu D, Huang H, Chen Y, Fan M, Peng W, Ren C, Xie D. 2011. The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-Repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana . The Plant Cell 23, 1795–1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeppi K, Abou-Mansour E, Buchala A, Mauch F. 2010. Disease resistance of Arabidopsis to Phytophthora brassicae is established by the sequential action of indole glucosinolates and camalexin. The Plant Journal 62, 840–851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer F, Fernandez-Calvo P, Zander M, Diez-Diaz M, Fonseca S, Glauser G, Lewsey MG, Ecker JR, Solano R, Reymond P. 2013. Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 regulate glucosinolate biosynthesis, insect performance, and feeding behavior. The Plant Cell 25, 3117–3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehr EM, Agusti J, Lehner R, Farmer EE, Schwarz M, Greb T. 2010. Analysis of secondary growth in the Arabidopsis shoot reveals a positive role of jasmonate signalling in cambium formation. The Plant Journal 63, 811–822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan X, Wang J, Chua L, Jiang D, Peng W, Xie D. 2010. The role of Arabidopsis Rubisco activase in jasmonate-induced leaf senescence. Plant Physiology 155, 751–764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard LB, Tan X, Mao H, et al. 2010. Jasmonate perception by inositol-phosphate-potentiated COI1-JAZ co-receptor. Nature 468, 400–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu C, Figueroa P, Depew CL, Cooke TF, Sheard LB, Moreno JE, Katsir L, Zheng N, Browse J, Howe GA. 2012. JAZ8 lacks a canonical degron and has an EAR motif that mediates transcriptional repression of jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 24, 536–550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song S, Qi T, Huang H, Ren Q, Wu D, Chang C, Peng W, Liu Y, Peng J, Xie D. 2011. The jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 23, 1000–1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thines B, Katsir L, Melotto M, Niu Y, Mandaokar A, Liu G, Nomura K, He SY, Howe GA, Browse J. 2007. JAZ repressor proteins are targets of the SCFCOI1 complex during jasmonate signalling. Nature 448, 661–665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireault C, Shyu C, Yoshida Y, St Aubin B, Campos ML, Howe GA. 2015. Repression of jasmonate signaling by a non-TIFY JAZ protein in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal 82, 669–679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddling J, Gelang-Alfredsson J, Piikki K, Pleijel H. 2007. Evaluating the relationship between leaf chlorophyll concentration and SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter readings. Photosynthesis Research 91, 37–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver LM, Gan S, Quirino B, Amasino RM. 1998. A comparison of the expression patterns of several senescence-associated genes in response to stress and hormone treatment. Plant Molecular Biology 37, 455–469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Y, Stolz S, Chetelat A, Reymond P, Pagni M, Dubugnon L, Farmer EE. 2007. A downstream mediator in the growth repression limb of the jasmonate pathway. The Plant Cell 19, 2470–2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi X, Du Z, Su Z. 2013. PlantGSEA: a gene set enrichment analysis toolkit for plant community. Nucleic Acids Research 41, W98–W103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Q, Yan L, Tan D, Chen R, Sun J, Gao L, Dong MQ, Wang Y, Li C. 2013. Phosphorylation-coupled proteolysis of the transcription factor MYC2 is important for jasmonate-signaled plant immunity. PLoS Genetics 9, e1003422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X, Jiang Y, Yu D. 2011. WRKY22 transcription factor mediates dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Molecules and Cells 31, 303–313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, An F, Feng Y, et al. 2011. Derepression of ethylene-stabilized transcription factors (EIN3/EIL1) mediates jasmonate and ethylene signaling synergy in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 108, 12539–12544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.