Abstract
In chronic renal failure and after acute renal failure, fibrinogen levels are raised and there is diminished fibrinolysis as the result of renal damage. A similar situation is found in nephrosis, possibly due to fibrinolytic inhibitors.
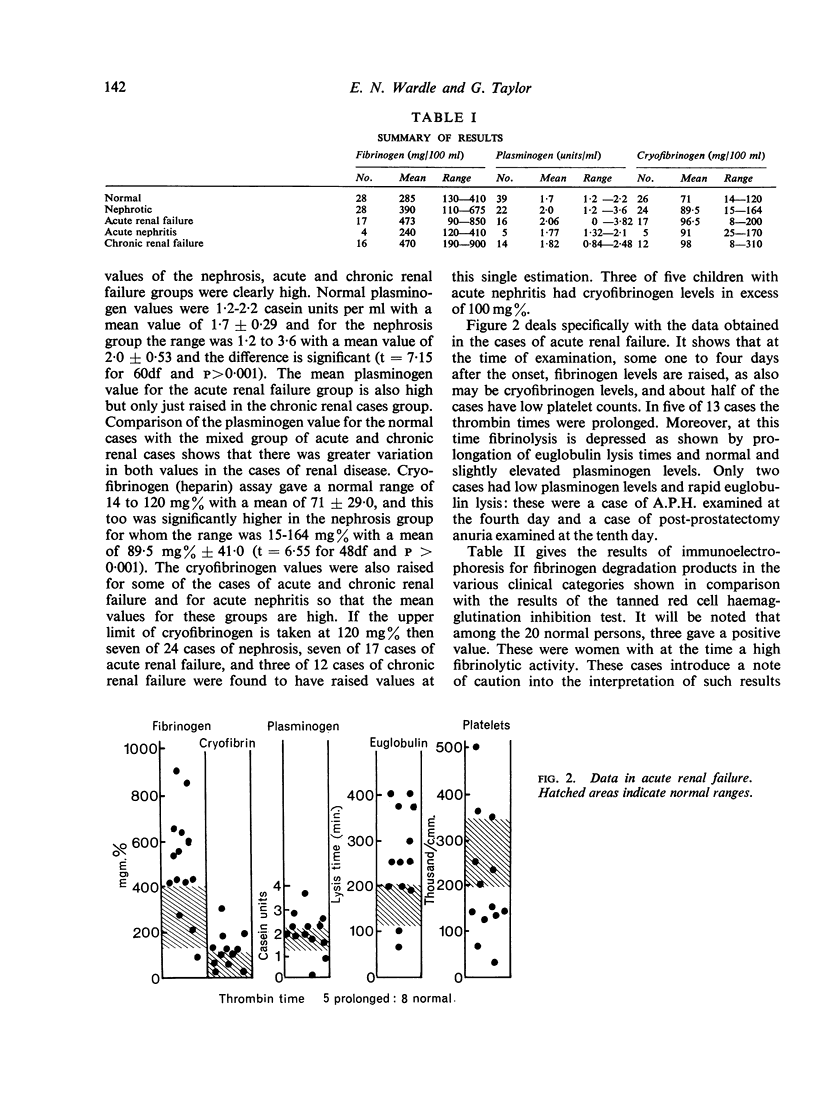
Increased levels of cryofibrinogen were found in one quarter of cases of acute nephritis, nephrosis, and acute and chronic renal failure. In addition, after acute renal failure low platelet counts, prolonged thrombin times, and high levels of fibrin degradation products, yet with diminished fibrinolysis, indicate that intravascular coagulation has occurred. A positive result for fibrin degradation products was found in 17 of 20 cases of acute renal failure but in none of 10 cases of chronic uraemia.
Intravascular coagulation is a process in which fibrin is deposited in the glomerular filters and may account for anuria, and, in the renal vasculature, where it may cause ischaemic tubular necrosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKELL M. The effect of citrate on euglobulin methods of estimating fibrinolytic activity. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):403–405. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaldi P. A., Rozenberg M. C., Stewart J. H. The bleeding disorder of uraemia. A qualitative platelet defect. Lancet. 1966 Jul 9;2(7454):66–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91802-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD N., YOUNG D. P., MACLEOD M. FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN PLASMA AND URINE IN CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:365–368. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERREIRA H. C., MURAT L. G. An immunological method for demonstrating fibrin degradation products in serum and its use in the diagnosis of fibrinolytic states. Br J Haematol. 1963 Jul;9:299–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb06554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLUECK H. I., HERRMANN L. G. COLD-PRECIPITABLE FIBRINOGEN, "CRYOFIBRINOGEN". Arch Intern Med. 1964 May;113:748–757. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.00280110128024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABER I. G., SEVITT S. Renal function in burned patients and its relationship to morphological changes. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;12(1):25–44. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Januszko T., Furman M., Buluk K. The kidneys and the liver as the organs regulating the fibrinolytic system of the circulating blood. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrieu M. J., Marder V. J., Inceman S. Effects of fibrinogen degradation products on platelets and coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;20:215–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P., BARAKAT A. A., DOUGLAS A. S. PLASMA FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN RENAL DISEASE. Scott Med J. 1965 May;10:189–194. doi: 10.1177/003693306501000502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE COAGULATION PROCESS AND GLOMERULAR DISEASE. Am J Med. 1965 Aug;39:179–183. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MORRIS R. H., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE PATHOGENIC ROLE OF FIBRIN DEPOSITION IN THE GLOMERULAR LESIONS OF TOXEMIA OF PREGNANCY. J Exp Med. 1963 Sep 1;118:467–478. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



