Abstract
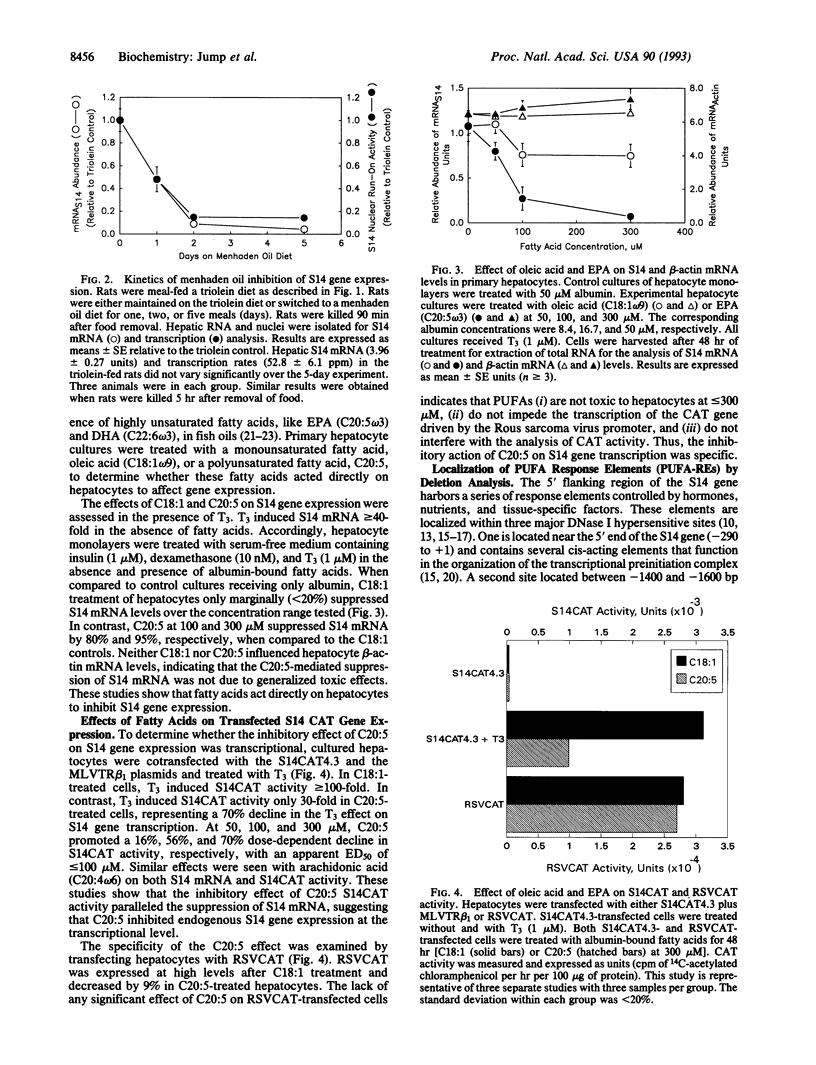
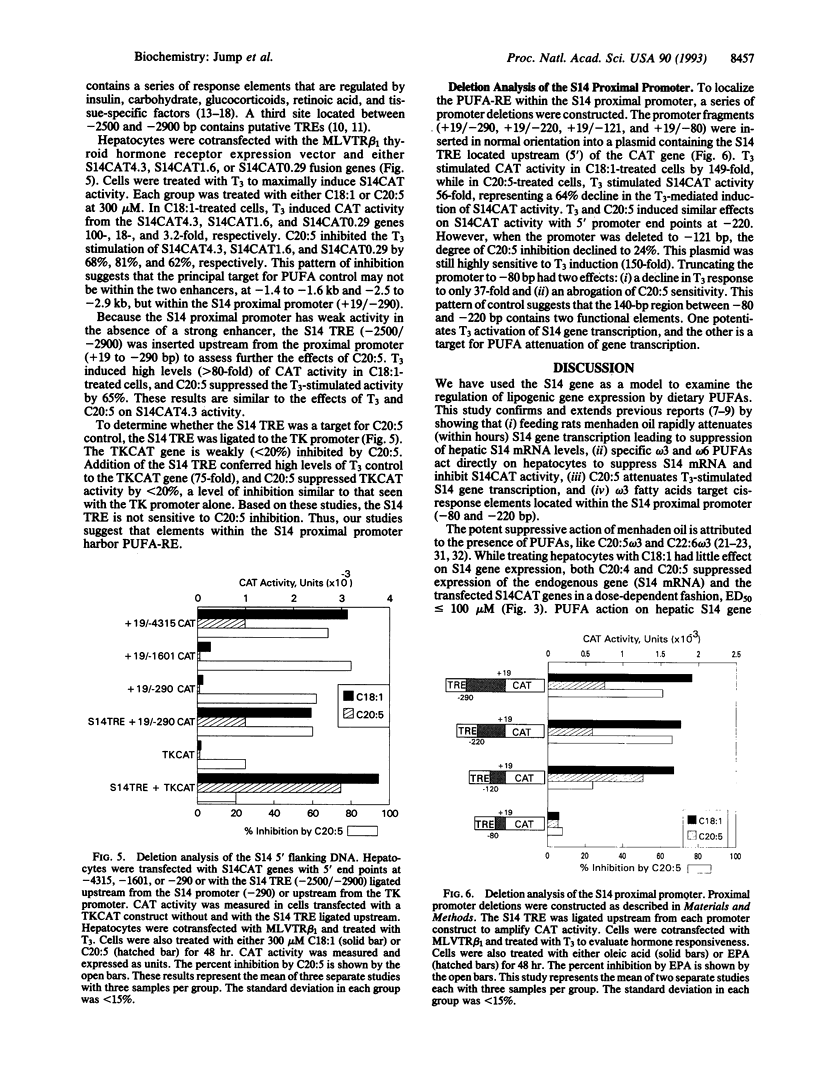
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have been shown to have significant effects on hepatic lipogenic gene expression. The S14 gene has been used as a model to examine the effects of PUFAs on hepatic lipogenic gene expression. In vivo studies showed that feeding rats a high carbohydrate diet containing menhaden oil rapidly (within hours) and significantly (> or = 50%) attenuates hepatic S14 gene transcription and S14 mRNA abundance. The suppressive effect of menhaden oil was both gene and tissue specific. The effect of PUFAs on expression of the S14 mRNA and a transfected S14 fusion gene (i.e., S14CAT4.3) was examined in cultured hepatocytes in the presence of triiodothyronine (T3), insulin, dexamethasone, and albumin under serum-free conditions. Whereas T3 stimulated both S14 mRNA (> 40-fold) and S14CAT4.3 (> 100-fold), eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5 omega 3) significantly attenuated (> or = 80%) both S14 mRNA and S14CAT activity in a dose-dependent fashion. The effects of C20:5 on hepatocyte gene expression were both gene and fatty acid specific. Deletion analysis of transfected S14CAT fusion genes indicated that the S14 thyroid hormone response element (at -2.5 to -2.9 kb) was not sensitive to C20:5 control. The cis-linked PUFA response elements were localized to a region within the S14 proximal promoter (at -80 to -220 bp). This region also contains cis-acting elements that potentiate T3 activation of S14 gene transcription. These studies suggest that C20:5 (or its metabolites) regulates factors within the S14 proximal promoter region that are important for T3 activation of S14 gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong M. K., Blake W. L., Clarke S. D. Arachidonic acid suppression of fatty acid synthase gene expression in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90645-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake W. L., Clarke S. D. Suppression of rat hepatic fatty acid synthase and S14 gene transcription by dietary polyunsaturated fat. J Nutr. 1990 Dec;120(12):1727–1729. doi: 10.1093/jn/120.12.1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. D., Armstrong M. K., Jump D. B. Dietary polyunsaturated fats uniquely suppress rat liver fatty acid synthase and S14 mRNA content. J Nutr. 1990 Feb;120(2):225–231. doi: 10.1093/jn/120.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. D., Armstrong M. K., Jump D. B. Nutritional control of rat liver fatty acid synthase and S14 mRNA abundance. J Nutr. 1990 Feb;120(2):218–224. doi: 10.1093/jn/120.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. C., McGill H. C., Jr, Carey K. D., Getz G. S. In vivo regulation of hepatic LDL receptor mRNA in the baboon. Differential effects of saturated and unsaturated fat. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7014–7020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda H., Katsurada A., Iritani N. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of mRNA levels of lipogenic enzymes in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Biochem. 1992 Jan;111(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnight S. H., Jr, Harris W. S., Connor W. E., Illingworth D. R. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, hyperlipidemia, and thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Mar-Apr;2(2):87–113. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher M., Widmark E., Li Q., Gustafsson J. A. Fatty acids activate a chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby D. B., Zilz N. D., Towle H. C. Sequences within the 5'-flanking region of the S14 gene confer responsiveness to glucose in primary hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17623–17626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Bell A., Lepar G., Hu D. Insulin rapidly induces rat liver S14 gene transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1655–1660. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Bell A., Santiago V. Thyroid hormone and dietary carbohydrate interact to regulate rat liver S14 gene transcription and chromatin structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3474–3478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Oppenheimer J. H. High basal expression and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine regulation of messenger ribonucleic acid S14 in lipogenic tissues. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2259–2266. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B. Rapid induction of rat liver S14 gene transcription by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4698–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromhout D., Bosschieter E. B., de Lezenne Coulander C. The inverse relation between fish consumption and 20-year mortality from coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1205–1209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepar G. J., Jump D. B. Hormonal regulation of the S14 gene in 3T3-F442A cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1207–1214. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepar G. J., Jump D. B. Retinoic acid and dexamethasone interact to regulate S14 gene transcription in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;84(1-2):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90072-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Clarke S. D., Jump D. B. Tissue specificity of S14 and fatty acid synthase in vitro transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):631–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91779-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Jump D. B. Identification of functional cis-acting elements within the rat liver S14 promoter. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):761–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2800761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Jump D. B. Localization of an adipocyte-specific retinoic acid response domain controlling S14 gene transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):470–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92408-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Connor W. E., Reardon M. F., Connor S., Wong S., Boston R. Suppression by diets rich in fish oil of very low density lipoprotein production in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):82–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI111422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntambi J. M. Dietary regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gene expression in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10925–10930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Endo N., Rutledge S. J., Vogel R., Shinar D., Rodan G. A. Identification of a new member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily that is activated by a peroxisome proliferator and fatty acids. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1634–1641. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1333051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Abraham S. Effect of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids on the activity and content of fatty acid synthetase in mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 13;711(2):316–326. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih H. M., Towle H. C. Definition of the carbohydrate response element of the rat S14 gene. Evidence for a common factor required for carbohydrate regulation of hepatic genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13222–13228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum-Odin R., Adkins-Finke B., Blake W. L., Phinney S. D., Clarke S. D. Modification of fatty acid composition of membrane phospholipid in hepatocyte monolayer with n-3, n-6 and n-9 fatty acids and its relationship to triacylglycerol production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 25;921(2):378–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. E., Nakayama R., Holten D. Repression of pentose phosphate pathway dehydrogenase synthesis and mRNA by dietary fat in rats. J Nutr. 1988 Mar;118(3):408–415. doi: 10.1093/jn/118.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussant M. J., Wilson M. D., Clarke S. D. Coordinate suppression of liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthetase by polyunsaturated fat. J Nutr. 1981 Jan;111(1):146–153. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.1.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Grant S. G., Reue K., Carrasquillo B., Lusis A. J., Kinniburgh A. J. cis-acting determinants of basal and lipid-regulated apolipoprotein A-IV expression in mice. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19009–19016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilz N. D., Murray M. B., Towle H. C. Identification of multiple thyroid hormone response elements located far upstream from the rat S14 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8136–8143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



