Abstract
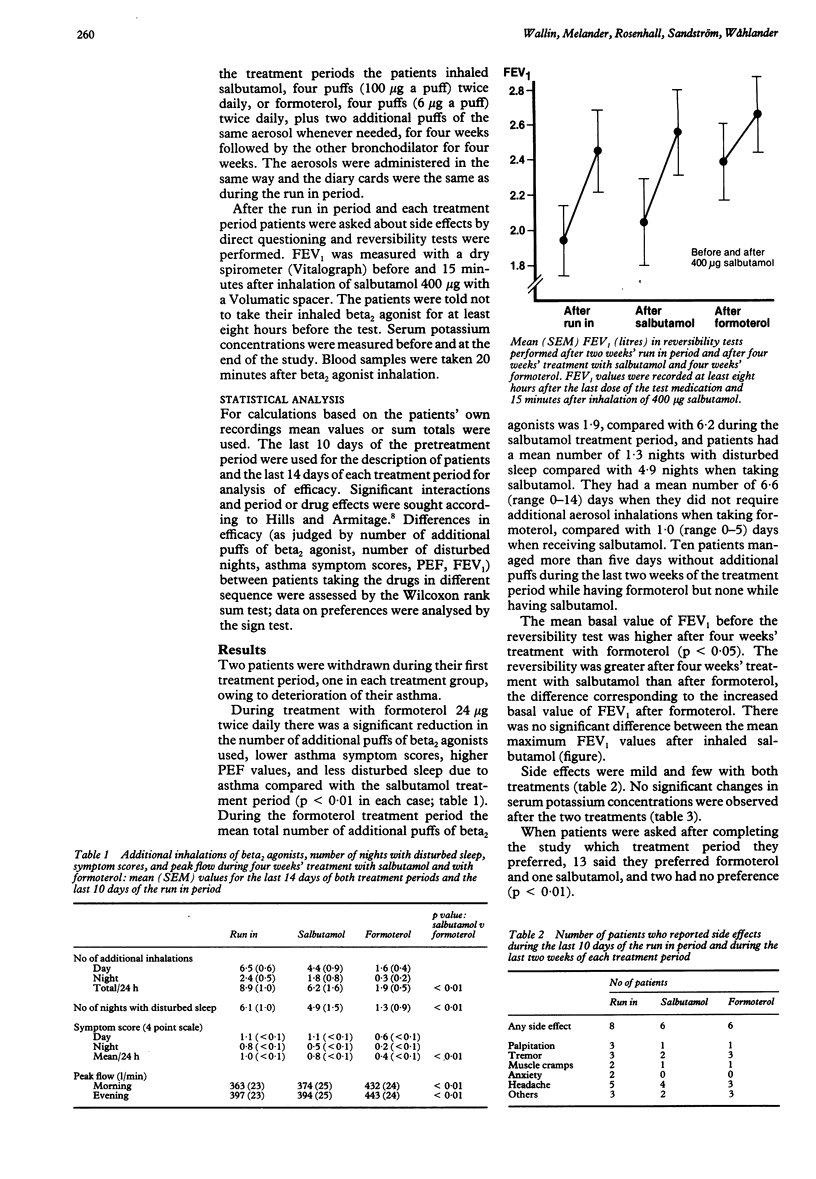
Sixteen patients with stable chronic asthma participated in a double blind crossover study comparing the new inhaled long acting beta 2 agonist formoterol with salbutamol. Inhaled (n = 15) and oral steroid (n = 1) treatment were maintained at the same daily dose throughout the study. For four weeks the patients received either formoterol 24 micrograms twice daily or salbutamol 400 micrograms twice daily, plus additional puffs (with the same drug) when needed. Asthma symptoms, additional puffs of beta 2 agonist, peak expiratory flow (PEF), and side effects were recorded daily. During treatment with formoterol the patients used fewer additional puffs of beta 2 agonist, had better symptom scores, less disturbed sleep, more days without additional aerosol, and higher PEF both morning and evening than during salbutamol treatment. Thus formoterol 24 micrograms twice daily gave long lasting bronchodilatation and asthma symptoms were well controlled with regular twice daily administration.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J., Greening A. P., Neville L., Timmers J., Poole G. W. Single-dose slow-release aminophylline at night prevents nocturnal asthma. Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):299–301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker N., Quennedey M. C., Rouot B., Schwartz J., Velly J. Effects of N-aralkyl substitution of beta-agonists on alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor subtypes: pharmacological studies and binding assays. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;34(2):107–112. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb04195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax A. J., McNabb W. R., Davies H. J., Spiro S. G. Slow-release oral salbutamol and aminophylline in nocturnal asthma: relation of overnight changes in lung function and plasma drug levels. Thorax. 1980 Jul;35(7):526–530. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.7.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel M. R. The pulmonary clock. Thorax. 1981 Jul;36(7):481–486. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.7.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M., Armitage P. The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida H. Cardiorespiratory activitirs of 3-formylamino-4-hydroxy-alpha-(n-1-methyl-2-p-methoxyphenethylaminomethyl)-benzylalcohol-hemifumarate(BD 40A) and some other beta-adrenoceptor stimulants in conscious guinea pigs. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(7):1337–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida H. Comparison of the action of BD 40 A and some other beta-adrenoceptor stimulants on the isolated trachea and atria of the guinea pig. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(5):839–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl C. G., Svedmyr N. Formoterol fumarate, a new beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Acute studies of selectivity and duration of effect after inhaled and oral administration. Allergy. 1989 May;44(4):264–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1989.tb01068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma D. S., Koëter G. H., Keyzer J. J., Meurs H. Influence of slow-release terbutaline on the circadian variation of catecholamines, histamine, and lung function in nonallergic patients with partly reversible airflow obstruction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;77(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma D. S., Koëter G. H., vd Mark T. W., Reig R. P., Sluiter H. J. The effects of oral slow-release terbutaline on the circadian variation in spirometry and arterial blood gas levels in patients with chronic airflow obstruction. Chest. 1985 May;87(5):653–657. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.5.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior J. G., Nowell R. V., Cochrane G. M. High-dose inhaled terbutaline in the management of chronic severe asthma: comparison of wet nebulisation and tube-spacer delivery. Thorax. 1982 Apr;37(4):300–303. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.4.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolensky M. H., Reinberg A., Queng J. T. The chronobiology and chronopharmacology of allergy. Ann Allergy. 1981 Oct;47(4):234–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



