Abstract
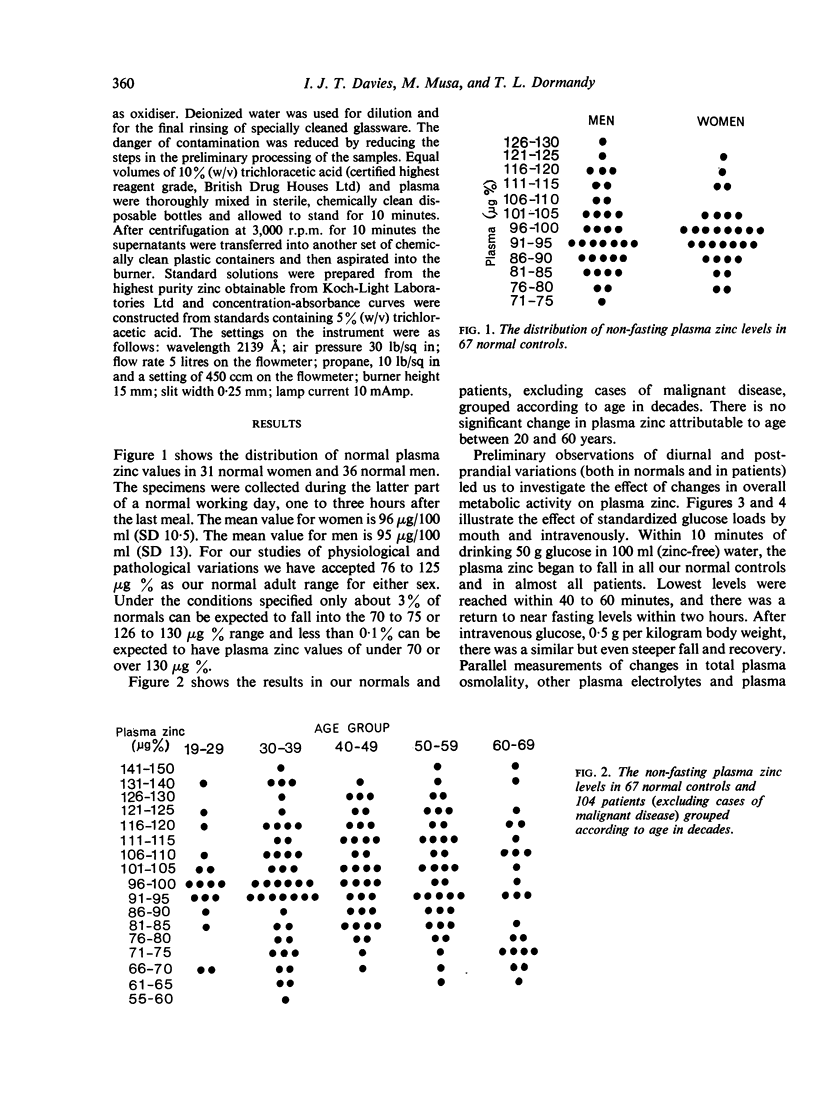
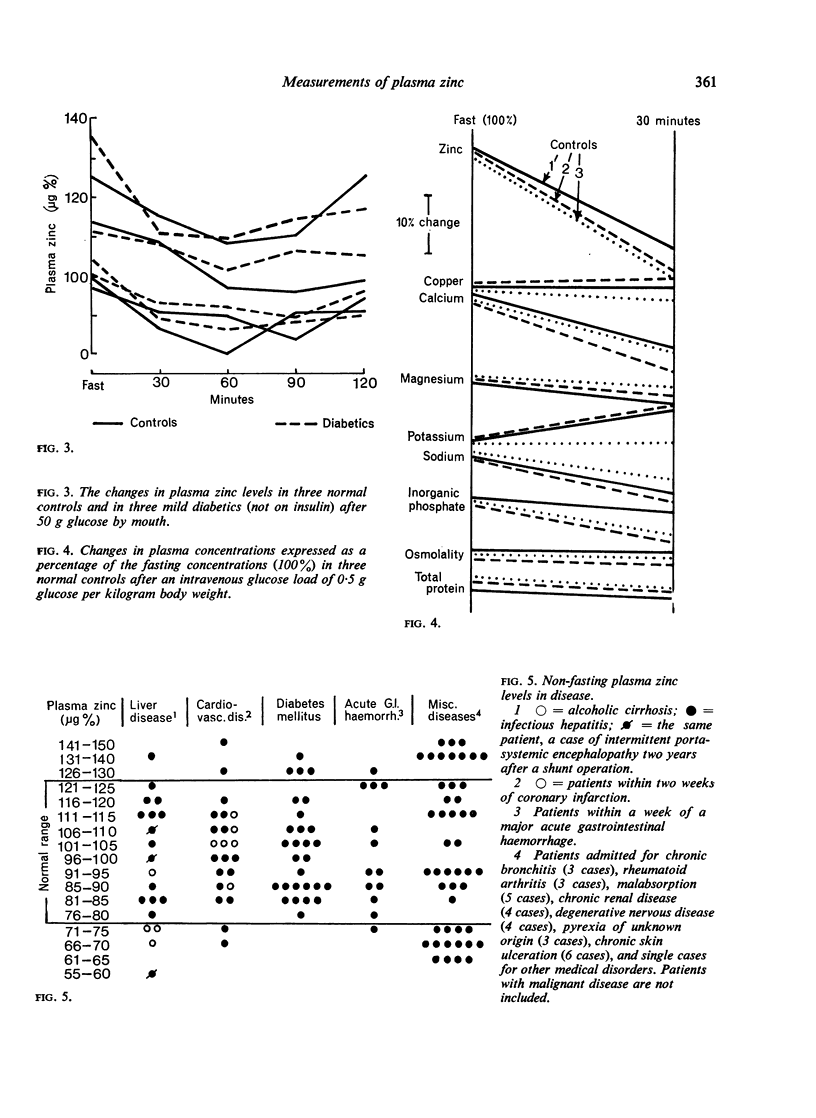
Zinc is an essential trace element. Previous methods of measuring zinc in clinical material have been difficult and reported findings must be treated with caution. Using atomic absorption spectroscopy it has been established that plasma zinc is one of the most uniform biochemical characteristics of normal adult blood. Sex and age differences in adult life are insignificant. Increased metabolic activity, on the other hand, induces a marked, immediate fall in plasma zinc level. The possible implications of this are discussed. Zinc levels in patients with diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and anaemia due to acute blood loss have been within normal limits. Plasma zinc is low in certain types of liver disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTHOLOMAY A. F., ROBIN E. D., VALLEE R. L., WACKER W. E. Zinc metabolism in hepatic dysfunction. I. Serum zinc concentrations in Laënnec's cirrhosis and their validation by sequential analysis. N Engl J Med. 1956 Aug 30;255(9):403–408. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195608302550901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilin D., Mann T. Carbonic anhydrase. Purification and nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1163–1176. doi: 10.1042/bj0341163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHIES J. C. Preparation and properties of highly purified alkaline phosphatase from swine kidneys. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1121–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRASAD A. S., MIALE A., Jr, FARID Z., SANDSTEAD H. H., SCHULERT A. R. Zinc metabolism in patients with the syndrome of iron deficiency anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, dwarfism, and hypognadism. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Apr;61:537–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pories W. J., Henzel J. H., Rob C. G., Strain W. H. Acceleration of wound healing in man with zinc sulphate given by mouth. Lancet. 1967 Jan 21;1(7482):121–124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDSTEAD H. H., SHUKRY A. S., PRASAD A. S., GABR M. K., HIFNEY A. E., MOKHTAR N., DARBY W. J. KWASHIORKOR IN EGYPT. I. CLINICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO PLASMA ZINC AND SERUM LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE. Am J Clin Nutr. 1965 Jul;17:15–26. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/17.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVLOV E. D., STRAIN W. H., HUEGIN F. Radiozinc studies in experimental wound healing. J Surg Res. 1962 May;2:209–212. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(62)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUCKER H. F., SALMON W. D. Parakeratosis or zinc deficiency disease in the pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Apr;88(4):613–616. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E., BARTHOLOMAY A. F., HOCH F. L. Zinc metabolism in hepatic dysfunction. II. Correlation of metabolic patterns with biochemical findings. N Engl J Med. 1957 Nov 28;257(22):1055–1065. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195711282572201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIKBLADH I. Studies on zinc in blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1950;2(2):143–148. doi: 10.3109/00365515009051850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDER F., DENNENY J. M. Effect of iron and zinc on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Nature. 1959 Aug 29;184(Suppl 10):742–743. doi: 10.1038/184742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



