Abstract
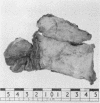
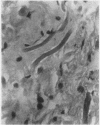
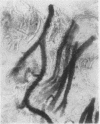
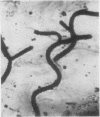
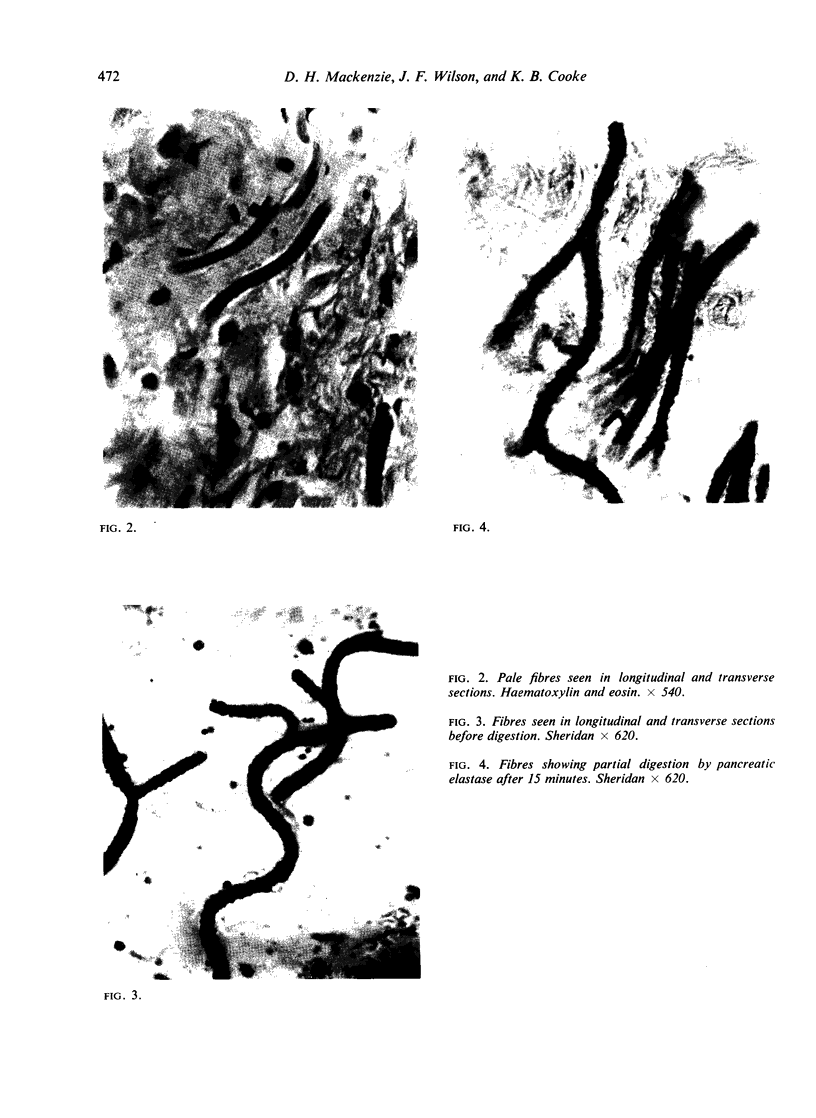
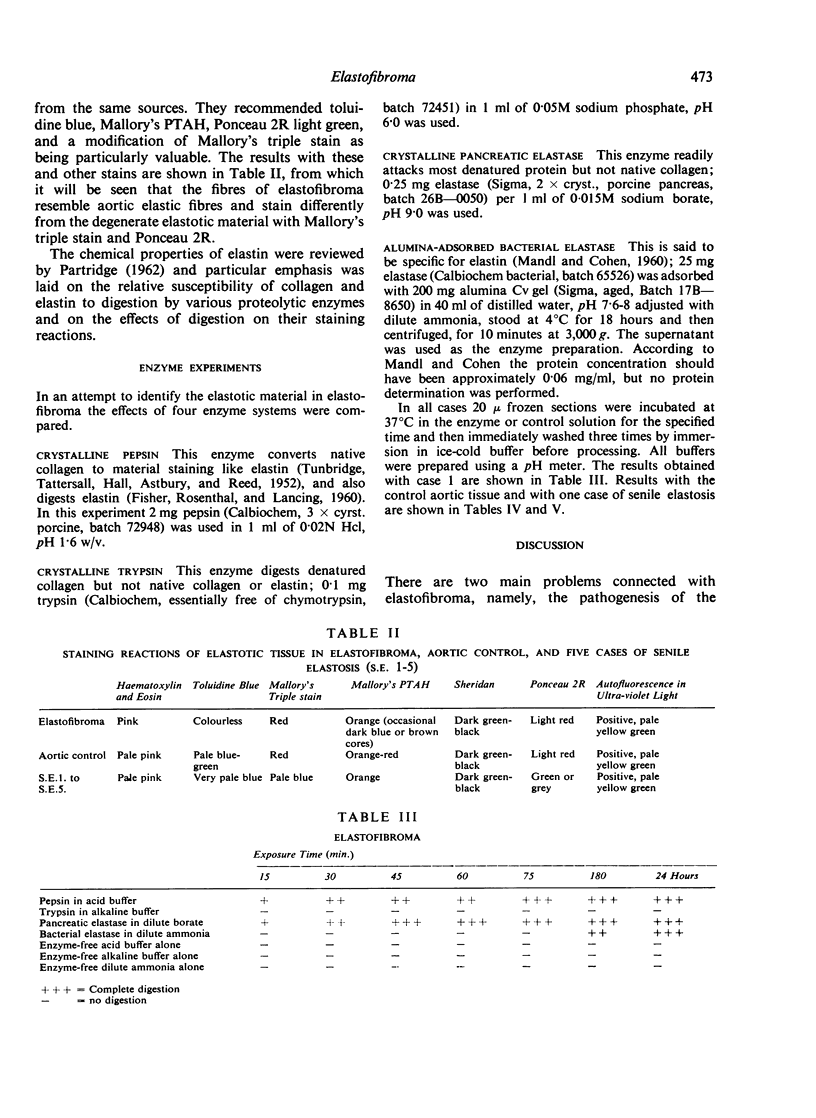
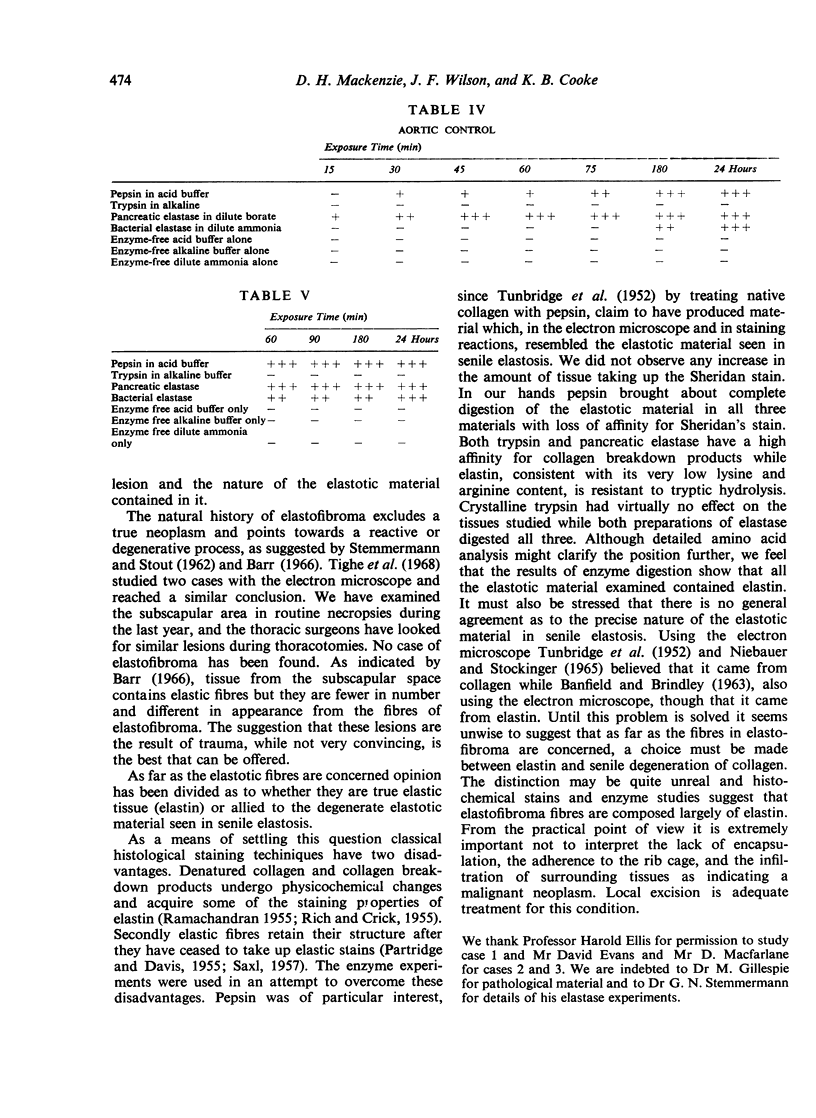
Three cases of elastofibroma are described and the literature is reviewed. It is suggested that they are non-neoplastic lesions resulting from trauma. Their staining reactions and the response of the elastic type fibres to enzyme digestion suggest that these fibres are either true elastin or very closely related to it.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANFIELD W. G., BRINDLEY D. C. PRELIMINARY OBSERVATIONS ON SENILE ELASTOSIS USING THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. J Invest Dermatol. 1963 Jul;41:9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr J. R. Elastofibroma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jun;45(6):679–683. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.6.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. K., Clearkin K. P., Nakachi K., Burdick C. O. Elastofibroma dorsi. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jul 21;275(3):154–155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196607212750307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELVAUX T. C., Jr, LESTER J. P. ELASTOFIBROMA DORSI. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jan;43:72–74. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/43.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E. R., ROSENTHAL T. B., LANSING A. I. Elastolytic effect of pepsin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1960 Mar;8:102–104. doi: 10.1177/8.2.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLMAN T., PENN J., BRONKS D., ROUX M. Abnormal elastic fibers; appearance in cutaneous carcinoma, irradiation injuries, and arterial and other degenerative connective tissue lesions in man. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Jun;59(6):733–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDL I., COHEN B. B. Bacterial elastase. I. Isolation, purification and properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Nov;91:47–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston A., Wilson Jones E. Elastofibroma dorsi. Br J Surg. 1965 Dec;52(12):980–981. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800521217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEBAUER G., STOCKINGER L. UBER DIE SENILE ELASTOSIS. HISTOCHEMISCHE UND ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1965;221:122–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F., ADAIR G. S. The chemistry of connective tissues. 2. Soluble proteins derived from partial hydrolysis of elastin. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):11–21. doi: 10.1042/bj0610011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCHTLER H., SWEAT F. HISTOCHEMICAL SPECIFITY OF STAINING METHODS FOR CONNECTIVE TISSUE FIBERS: RESORCIN-FUCHSIN AND VAN GIESON'S PICRO-FUCHSIN. Z Zellforch Microsk Anat Histochem. 1964;79:24–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00304175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN G. N. Structure of collagen. Nature. 1956 Apr 14;177(4511):710–711. doi: 10.1038/177710b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICH A., CRICK F. H. The structure of collagen. Nature. 1955 Nov 12;176(4489):915–916. doi: 10.1038/176915a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAXL H. The physiological significance of the reaction between elastin and elastomucase in relation to the production of clearing factor. Gerontologia. 1957;1(3):142–163. doi: 10.1159/000210694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUNBRIDGE R. E., TATTERSALL R. N., HALL D. A., ASTBURY W. T., REED R. The fibrous structure of normal and abnormal human skin. Clin Sci. 1952 Nov;11(4):315–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tighe J. R., Clark A. E., Turvey D. J. Elastofibroma dorsi. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jul;21(4):463–469. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]