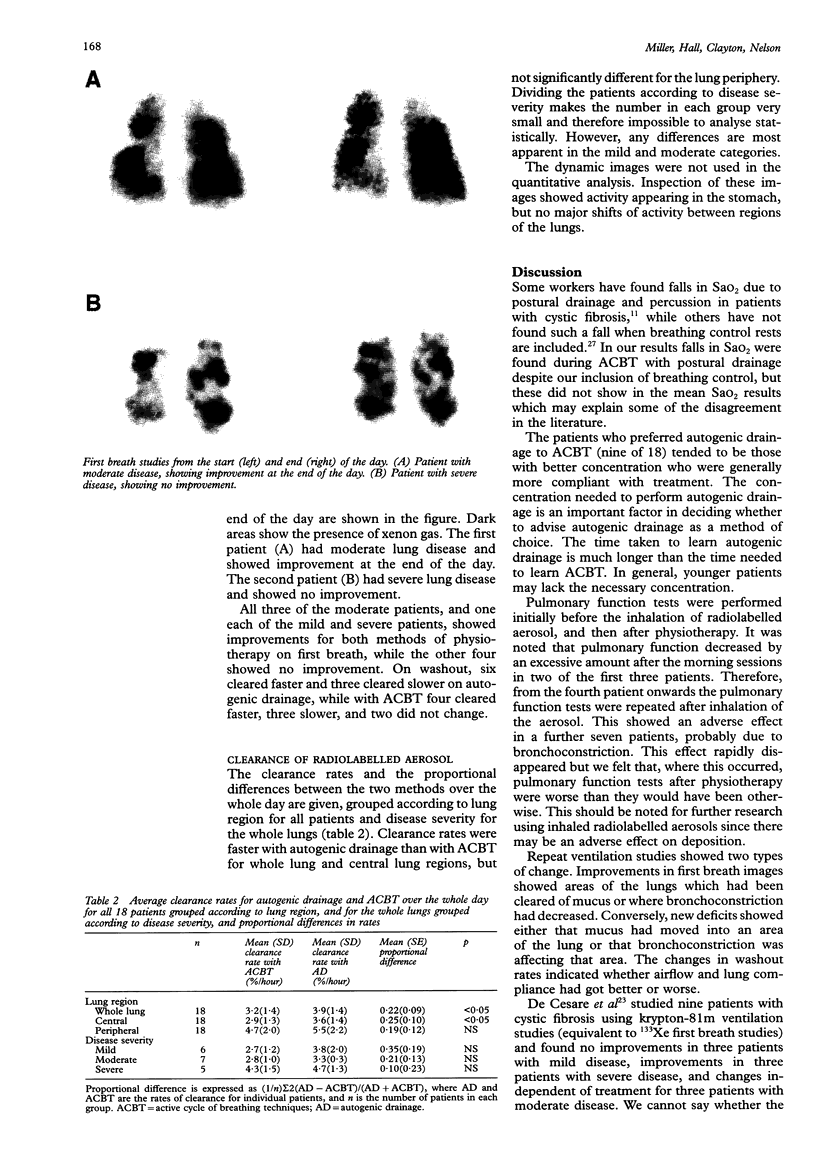
Abstract
BACKGROUND--Autogenic drainage has been suggested as an alternative method of chest physiotherapy in patients with cystic fibrosis. In this study autogenic drainage was compared with the active cycle of breathing techniques (ACBT) together with postural drainage. METHODS--Eighteen patients with cystic fibrosis took part in a randomised two-day crossover trial. There were two sessions of one method of physiotherapy on each day, either autogenic drainage or ACBT. The study days were one week apart. On each day the patients were monitored for six hours. Mucus movement was quantified by a radioaerosol technique. Airway clearance was studied qualitatively using xenon-133 scintigraphic studies at the start and end of each day. Expectorated sputum was collected during and for one hour after each session of physiotherapy. Pulmonary functions tests were performed before and after each session. Oxygen saturation (SaO2) and heart rate were measured before, during, and after each session. RESULTS--Autogenic drainage cleared mucus from the lungs faster than ACBT over the whole day. Both methods improved ventilation, as assessed by the xenon-133 ventilation studies. No overall differences were found in the pulmonary function test results, but more patients had an improved forced expiratory flow from 25% to 75% with autogenic drainage, while more showed an improved forced vital capacity with ACBT. No differences were found in sputum weight and heart rate, nor in mean SaO2 over the series, but four patients desaturated during ACBT. CONCLUSIONS--Autogenic drainage was found to be as good as ACBT at clearing mucus in patients with cystic fibrosis and is therefore an effective method of home physiotherapy. Patients with cystic fibrosis should be assessed as to which method suits them best.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrispin A. R., Norman A. P. The systematic evaluation of the chest radiograph in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol. 1974;2(2):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01314939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane G. M., Webber B. A., Clarke S. W. Effects of sputum on pulmonary function. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 5;2(6096):1181–1183. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6096.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCesare J. A., Babchyck B. M., Colten H. R., Treves S. Radionuclide assessment of the effects of chest physical therapy on ventilation in cystic fibrosis. Phys Ther. 1982 Jun;62(6):820–827. doi: 10.1093/ptj/62.6.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M., Kelstrup M., Andersen J. B., Kinoshita T., Falk P., Støvring S., Gøthgen I. Improving the ketchup bottle method with positive expiratory pressure, PEP, in cystic fibrosis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;65(6):423–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J., Traver G. A., Taussig L. M. Maximal expiratory flows after postural drainage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2):239–245. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M., Armitage P. The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isawa T., Teshima T., Hirano T., Ebina A., Motomiya M., Konno K. Lung clearance mechanisms in obstructive airways disease. J Nucl Med. 1984 Apr;25(4):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorin M. I., Denning C. R. Evaluation of postural drainage by measurement of sputum volume and consistency. Am J Phys Med. 1971 Oct;50(5):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell M., Redmond A. Comparative trial of manual and mechanical percussion technique with gravity-assisted bronchial drainage in patients with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jul;54(7):542–544. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.7.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Turner J. M., Macklem P. T., Little J. B. Significance of the relationship between lung recoil and maximum expiratory flow. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):95–108. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen J., Falk M., Groth S., Jensen C. The effects of postural drainage and positive expiratory pressure physiotherapy on tracheobronchial clearance in cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1991 Nov;100(5):1350–1357. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.5.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty M. J., Miller R. F. Aerosols for therapy and diagnosis. Eur J Nucl Med. 1993 Dec;20(12):1201–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF00171019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberwaldner B., Evans J. C., Zach M. S. Forced expirations against a variable resistance: a new chest physiotherapy method in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1986 Nov-Dec;2(6):358–367. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950020608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleger A., Theissl B., Oberwaldner B., Zach M. S. Self-administered chest physiotherapy in cystic fibrosis: a comparative study of high-pressure PEP and autogenic drainage. Lung. 1992;170(6):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00177578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad S. A. Current concepts in physiotherapy. J R Soc Med. 1993;86 (Suppl 20):23–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor J. A., Webber B. A. An evaluation of the forced expiration technique as an adjunct to postural drainage. Physiotherapy. 1979 Oct;65(10):304–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor J. A., Webber B. A., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. Evaluation of the forced expiration technique as an adjunct to postural drainage in treatment of cystic fibrosis. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 18;2(6187):417–418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6187.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor J. A., Webber B. A., Hodson M. E. Effect of chest physiotherapy on oxygen saturation in patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 1990 Jan;45(1):77–77. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman C. M., Waldes R., Sampson D., Newhouse M. T. Effect of chest physiotherapy on the removal of mucus in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):131–135. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHWACHMAN H., KULCZYCKI L. L. Long-term study of one hundred five patients with cystic fibrosis; studies made over a five- to fourteen-year period. AMA J Dis Child. 1958 Jul;96(1):6–15. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1958.02060060008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöni M. H. Autogenic drainage: a modern approach to physiotherapy in cystic fibrosis. J R Soc Med. 1989;82 (Suppl 16):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]