Abstract
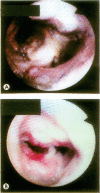
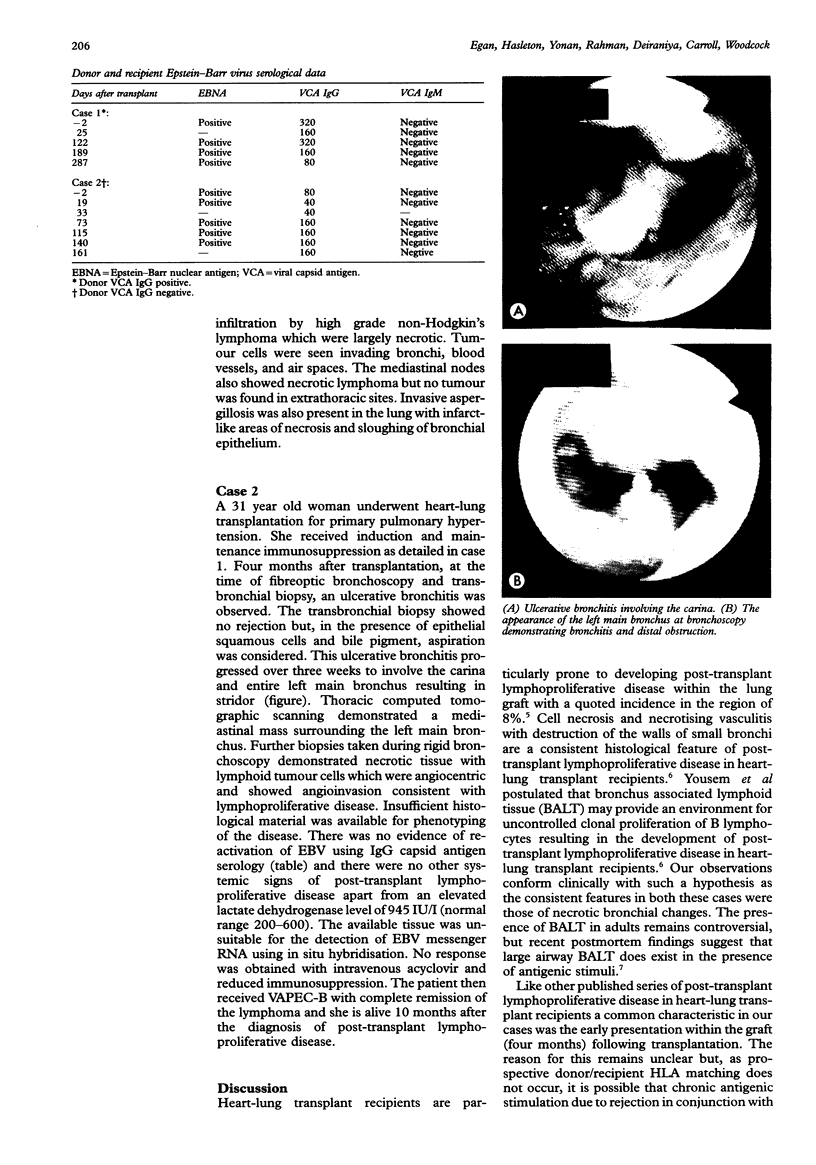
Following heart-lung transplantation two of 21 patients who survived more than 100 days developed post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Both presented with localised ulcerative bronchitis documented at flexible bronchoscopy four months after transplantation. Histological examination showed necrosis with acute inflammation and ulceration. Case 2 demonstrated lymphoproliferative disease from biopsies subsequently taken at rigid bronchoscopy. Case 1 later developed lung nodules and a monoclonal high grade B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma was confirmed by an open lung biopsy. The bronchoscopic features described should alert clinicians to post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease as an underlying diagnosis and suggest that bronchus associated lymphoid tissue is the initial site for clonal proliferation in the disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage J. M., Kormos R. L., Stuart R. S., Fricker F. J., Griffith B. P., Nalesnik M., Hardesty R. L., Dummer J. S. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in thoracic organ transplant patients: ten years of cyclosporine-based immunosuppression. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1991 Nov-Dec;10(6):877–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. R., Rymo L. Characterization of the major Epstein-Barr virus-specific RNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.376-389.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle T. J., Tamburini M., Berend K. R., Kizilbash A. M., Borowitz M. J., Lyerly H. K. Human B-cell lymphoma in severe combined immunodeficient mice after active infection with Epstein-Barr virus. Surgery. 1992 Aug;112(2):378–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. J., Hasleton P. S., Yonan N., Rahman A. N., Deiraniya A. K., Carroll K. B., Woodcock A. A. Necrotic, ulcerative bronchitis, the presenting feature of lymphoproliferative disease following heart-lung transplantation. Thorax. 1995 Feb;50(2):205–207. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagington J., Gray J. Cyclosporin A immunosuppression, Epstein-Barr antibody, and lymphoma. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):536–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A., Jaffe R., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Porter K., Burnham J. A., Makowka L., Ho M., Locker J. The pathology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):173–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond I., Pritchard G. E., Ashcroft T., Avery A., Corris P. A., Walters E. H. Bronchus associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) in human lung: its distribution in smokers and non-smokers. Thorax. 1993 Nov;48(11):1130–1134. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.11.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Crawford D. H. B-cell lymphoma in organ transplant recipients. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1990 Jul;2(3):221–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Randhawa P., Locker J., Paradis I. L., Dauber J. A., Griffith B. P., Nalesnik M. A. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in heart-lung transplant recipients: primary presentation in the allograft. Hum Pathol. 1989 Apr;20(4):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]