Abstract
Background
While DNA barcoding is an important technology for the authentication of the botanical origins of Chinese medicines, the suitable markers for DNA barcoding of the genus Uncaria have not been reported yet. This study aims to determine suitable markers for DNA barcoding of the genus Uncaria (Gouteng).
Methods
Genomic DNA was extracted from the freshly dried leaves of Uncaria plants by a Bioteke’s Plant Genomic DNA Extraction Kit. Five candidate DNA barcode sites (ITS2, rbcL, psbA–trnH, ITS, and matK) were amplified by PCR with established primers. The purified PCR products were bidirectionally sequenced with appropriate amplification primers in an ABI-PRISM3730 instrument. The candidate DNA barcodes of 257 accessions of Uncaria in GenBank were aligned by ClustalW. Sequence assembly and consensus sequence generation were performed with CodonCode Aligner 3.7.1. The identification efficiency of the candidate DNA barcodes was evaluated with BLAST and nearest distance methods. The interspecific divergence and intraspecific variation were assessed by the Kimura 2-Parameter model. Genetic distances were computed with Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis 6.0.
Results
The accessions of the five candidate DNA barcodes from 11 of 12 species of Uncaria in China and four species from other countries were included in the analysis, while 54 of total accessions were submitted to GenBank. In a comparison of the interspecific genetic distances of the five candidate barcodes, psbA–trnH exhibited the highest interspecific divergence based on interspecific distance, theta prime, and minimum interspecific distance, followed by ITS2. The distribution of the interspecific distance of ITS2 and psbA–trnH was higher than the corresponding intraspecific distance. Additionally, psbA–trnH showed 95.9 % identification efficiency by both the BLAST and nearest distance methods regardless of species or genus level. ITS2 exhibited 92.2 % identification efficiency by the nearest distance method, but 87 % by the BLAST method.
Conclusion
While psbA–trnH and ITS2 (used alone) were applicable barcodes for species authentication of Uncaria, psbA–trnH was a more suitable barcode for authentication of Uncaria macrophylla.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13020-015-0072-7) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Background
Uncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Jacks is used to treat convulsion, hypertension, epilepsy, eclampsia, migraine, and cerebral diseases [1–3]. Rhynchophylline, isorhynchophylline, corynoxeine, and isocorynoxeine are the major components of U.rhynchophylla [4]. Oleanane and ursane-type triterpenes, (including uncarinic acids, ursolic acid, 3-hydroxyurs-12-en-27,28-dioic acid, hyperin, and catechin) were found in Uncaria [1, 5]. Uncaria comprises 34 species [6], 10 of which are found in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Among the 10 species of Uncaria in Guangxi, U. rhynchophylla and Uncaria macrophylla are the most widely and abundantly distributed [7]. Stems with hooks from several species of Uncaria, including U. rhynchophylla, U. macrophylla, Uncaria hirsuta, Uncaria sinensis, and Uncaria sessilifructus, have been used in Chinese medicine (CM) preparations, Gouteng in Chinese. Only the above five species plants of the genus Uncaria can serve as the botanical origins of Gouteng according to the Chinese Pharmacopeia (10th edition) [8]. Adulterants of Gouteng include Uncaria laevigata, Uncaria lancifolia, Uncaria scandens, Uncaria rhynchophylloides, and Uncaria homomalla [7, 9], due to similar organoleptic characteristics to those of U. rhynchophylla. But their chemical constituents and therapeutic effects are distinct from those of U. rhynchophylla [2, 10, 11].
DNA barcoding can accurately identify species on the basis of short standardized genes or DNA regions [12, 13], without confounding factors such as environmental influence, growth phase, and morphological diversity within species [14–16]. The mitochondrial gene encoding cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (co1) is a potential DNA barcode in most animal species as well as some fungal species. However, the co1 gene and other mitochondrial genes from plants have limited use in identifying plant species across a wide range of taxa, due to their low genetic variations and variable mitochondrial genomes [17]. Several DNA regions, such as ITS2, psbA–trnH, matK, rbcL, ITS, ycf5, and rpoC1 [14, 18–21] have been evaluated as potential DNA barcodes in medicinal plants. Among these candidate barcoding loci, the ITS2 locus not only had the highest identification efficiency among all tested regions, but also discriminated a wide range of plant taxa [14, 22]. By contrast, ITS1 was a useful barcode for identifying Salvia species [23]. The psbA–trnH intergenic region was a suitable DNA marker for identification of flowering plants [17, 18], pteridophytes [24], Lonicera japonica Thunb from Caprifoliaceae [21], and aquatic plant species [25].
The authentication of the botanical origins of Gouteng is based on the morphological characteristics, microscopic structures, or chemical components of specimens [26]. The accuracy is often affected by environmental and subjective factors, especially for dry medicinal materials from different origins [26]. Chemical analysis methods, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and HPLC coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry, have also been studied [27]. Multiple genetic molecular markers have been used to screen Uncaria, such as random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and rDNAs (including 5.8S rDNA, ITS1, and ITS2) [28].
This study aims to determine suitable markers for DNA barcoding of the genus Uncaria. In this study, five candidate loci (ITS2, rbcL, psbA–trnH, ITS, and matK) were tested for their potential as DNA barcodes for Uncaria.
Methods
Plant materials
Fifty-four sequences from our laboratory (all submitted to GenBank), among which 12 samples of six species of Uncaria (U. rhynchophylla, U. macrophylla, U. sessilifructus, U. hirsuta, U. lancifolia and U. homomalla) are used as Gouteng in CM markets, were collected from areas in Guangxi Province, including Rongshui, Sanjiang, Shanglin, Ningming, and Jinxi county, Nanning Sitang town, and Guangxi Medicinal Botanical Garden, in 2009 and 2010 by Professor Ruisong Huang. The plant species were identified by Shouyang Liu, Yiling Zhu, and Kejian Yan through morphological characteristics and analysis of microscopic structures [7, 10]. All of the voucher specimens (all the voucher numbers can be seen in Table 1) were deposited in the Key Laboratory of Biological Molecular Medicine Research of Guangxi Higher Education, Guangxi Medical University.
Table 1.
Uncaria information used in this study
| Voucher no | Species | Habitat site (county, province, country) | GenBank accession no. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | rbcL | psbA–trnH | ITS | matK | |||
| PS1001MT01 | U. rhynchophylla_01 | Rongshui, Guangxi, China | KM057008 | KM057019 | KM057031 | KM057043 | KM057054 |
| PS1001MT02 | U. rhynchophylla_02 | Sanjiang, Guangxi, China | KM057009 | KM057020 | KM057032 | KM057044 | |
| – | U. rhynchophylla_03 | Chinaa | AJ346900 | AJ346900 | |||
| PS1040MT01 | U. rhynchophylla_04 | Chinaa | JF421552 | ||||
| URH-1 | U. rhynchophylla_05 | Chinaa | KF881222 | KF881177 | KF881265 | ||
| URH-2 | U. rhynchophylla_06 | Chinaa | KF881223 | KF881178 | |||
| PS1002MT01 | U. macrophylla_01 | Nanning, Guangxi, China | KM057010 | KM057021 | KM057033 | KM057045 | KM057055 |
| PS1002MT02 | U. macrophylla_02 | Nanning, Guangxi, China | KM057011 | KM057022 | KM057034 | KM057046 | KM057056 |
| PS1002MT03 | U. macrophylla_03 | Ningming, Guangxi, China | KM057012 | KM057023 | KM057035 | KM057047 | KM057057 |
| PS1038MT03 | U. macrophylla_04 | Chinaa | GQ434637 | GQ436558 | GQ435234 | ||
| PS1038MT04 | U. macrophylla_05 | Chinaa | GQ434638 | GQ436559 | GQ435235 | ||
| PS1038MT01 | U. macrophylla_06 | Chinaa | GQ434636 | ||||
| UMA-1 | U. macrophylla_07 | Chinaa | KF881209 | KF881134 | KF881170 | ||
| UMA-2 | U. macrophylla_08 | Chinaa | KF881210 | KF881135 | KF881171 | ||
| UMA-3 | U. macrophylla_09 | Chinaa | KF881211 | KF881136 | KF881172 | KF881257 | |
| UMA-4 | U. macrophylla_10 | Chinaa | KF881212 | KF881137 | KF881173 | KF881258 | |
| UMA-5 | U. macrophylla_11 | Chinaa | KF881213 | KF881259 | |||
| UMA-6 | U. macrophylla_12 | Chinaa | KF881214 | KF881138 | KF881174 | ||
| UMA-7 | U. macrophylla_13 | Chinaa | KF881215 | ||||
| UMA-8 | U. macrophylla_14 | Chinaa | KF881216 | KF881139 | KF881175 | KF881260 | |
| UMA-9 | U. macrophylla_15 | Chinaa | KF881261 | ||||
| PS1003MT01 | U. sessilifructus_01 | Nanning, Guangxi, China | KM057013 | KM057024 | KM057036 | KM057048 | KM057058 |
| PS1003MT02 | U. sessilifructus_02 | Shangsi, Guangxi, China | KM057037 | ||||
| – | U. sessilifructus_03 | Chinaa | GU937111 | GU937111 | |||
| PS1041MT02 | U. sessilifructus_04 | Chinaa | GQ434640 | ||||
| USE-1 | U. sessilifructus_05 | Chinaa | KF881195 | KF881122 | |||
| USE-2 | U. sessilifructus_06 | Chinaa | KF881196 | KF881123 | KF881160 | ||
| USE-3 | U. sessilifructus_07 | Chinaa | KF881197 | KF881124 | KF881161 | ||
| USE-4 | U. sessilifructus_08 | Chinaa | KF881198 | KF881125 | KF881162 | ||
| USE-5 | U. sessilifructus_09 | Chinaa | KF881199 | KF881126 | |||
| USE-6 | U. sessilifructus_10 | Chinaa | KF881200 | KF881127 | |||
| USE-7 | U. sessilifructus_11 | Chinaa | KF881201 | KF881128 | KF881249 | ||
| PS1004MT01 | U. hirsuta_01 | Nanning, Guangxi, China | KM057014 | KM057026 | KM057038 | KM057049 | KM057059 |
| PS1004MT02 | U. hirsuta_02 | Nanning, Guangxi, China | KM057015 | KM057027 | KM057039 | KM057050 | KM057060 |
| PS1004MT03 | U. hirsuta_03 | Rongshui, Guangxi, China | KM057016 | KM057028 | KM057040 | KM057051 | |
| – | U. hirsuta_04 | Chinaa | GU937110 | GU937110 | |||
| UHI-1 | U. hirsuta_05 | Chinaa | KF881235 | ||||
| PS1005MT01 | U. lancifolia_01 | Jingxi, Guangxi, China | KM057017 | KM057029 | KM057041 | KM057052 | KM057061 |
| Razafimandimbison et al. 713 (S) | U. lancifolia_02 | Unknowna | KC737634 | KC737740 | KC737634 | ||
| ULA-1 | U. lancifolia_03 | Chinaa | KF881218 | KF881140 | KF881176 | KF881262 | |
| ULA-2 | U. lancifolia_04 | Chinaa | KF881219 | KF881263 | |||
| ULA-3 | U. lancifolia_05 | Chinaa | KF881220 | KF881264 | |||
| ULA-4 | U. lancifolia_06 | Chinaa | KF881221 | ||||
| PS1006MT01 | U. homomalla_01 | Shanglin, Guangxi, China | KM057018 | KM057030 | KM057042 | KM057053 | KM057062 |
| Munzinger 177 | U. homomalla_02 | Unkowna | KC737633 | KC737739 | KC737633 | ||
| UHO-1 | U. homomalla_03 | Chinaa | KF881202 | KF881129 | KF881163 | KF881250 | |
| UHO-2 | U. homomalla_04 | Chinaa | KF881203 | KF881130 | KF881164 | KF881251 | |
| UHO-3 | U. homomalla_05 | Chinaa | KF881204 | KF881131 | KF881165 | KF881252 | |
| UHO-4 | U. homomalla_06 | Chinaa | KF881205 | KF881132 | KF881166 | KF881253 | |
| UHO-5 | U. homomalla_07 | Chinaa | KF881206 | KF881167 | KF881254 | ||
| UHO-6 | U. homomalla_08 | Chinaa | KF881207 | KF881168 | KF881255 | ||
| UHO-7 | U. homomalla_09 | Chinaa | KF881208 | KF881133 | KF881169 | KF881256 | |
| PS1039MT01 | U. sinensis_01 | Chinaa | FJ980386 | GQ436560 | GQ435236 | FJ980386 | |
| USI-1 | U. sinensis_02 | Chinaa | KF881146 | ||||
| USI-2 | U. sinensis_03 | Chinaa | KF881147 | KF881183 | KF881271 | ||
| USI-3 | U. sinensis_04 | Chinaa | KF881272 | ||||
| USI-4 | U. sinensis_05 | Chinaa | KF881234 | KF881148 | KF881184 | KF881273 | |
| Razafimandimbison 304 (LBR, MO, P, TAN) | U. africana_01 | Gabona | AJ414545 | AJ347006 | AJ414545 | ||
| Taylor, Chanderbali, and Bourne 12075 (MO) | U. guianensis_01 | Guyanaa | AJ414546 | AJ347007 | AJ414546 | ||
| Andersson et al. 2031 (GB) | U. tomentosa_01 | Unknowna | GQ852159 | GQ852159 | |||
| Andersson et al. 2038 (GB) | U. tomentosa_02 | Unknowna | GQ852363 | ||||
| BioBot06438 | U. tomentosa_03 | Area de Conservacion Guanacaste, Rincon Rainforest, Sendero Venado, Costa Ricaa | JQ593902 | ||||
| BioBot06439 | U. tomentosa_04 | Area de Conservacion Guanacaste, Rincon Rainforest, Sendero Venado, Costa Ricaa | JQ593903 | ||||
| Razafimandimbison et al. 766 (S) | U. lanosa_01 | Unkowna | KC737635 | KC737741 | KC737635 | ||
| UYU-1 | U. yunnanensis_01 | Chinaa | KF881243 | KF881156 | KF881191 | KF881281 | |
| UYU-2 | U. yunnanensis_02 | Chinaa | KF881244 | ||||
| UYU-3 | U. yunnanensis_03 | Chinaa | KF881245 | KF881157 | KF881282 | ||
| UYU-4 | U. yunnanensis_04 | Chinaa | KF881246 | KF881158 | KF881193 | KF881283 | |
| UYU-5 | U. yunnanensis_05 | Chinaa | KF881247 | KF881194 | |||
| UYU-6 | U. yunnanensis_06 | Chinaa | KF881248 | KF881159 | KF881284 | ||
| WP2E0309 | U. appendiculata_01 | Papua New Guineaa | JF738785 | ||||
| WP1D0176 | U. appendiculata_02 | Papua New Guineaa | JF738676 | ||||
| WP5E1207 | U. appendiculata_03 | Papua New Guineaa | JF739007 | ||||
| Razafimandimbison et al. 768 (S) | U. scandens_01 | Unknowna | KC737636 | KC737742 | KC737636 | ||
| USC-1 | U. scandens_02 | Chinaa | KF881236 | KF881149 | KF881185 | KF881274 | |
| USC-2 | U. scandens_03 | Chinaa | KF881237 | KF881150 | KF881186 | KF881275 | |
| USC-3 | U. scandens_04 | Chinaa | KF881238 | KF881151 | KF881187 | KF881276 | |
| USC-4 | U. scandens_05 | Chinaa | KF881239 | KF881152 | KF881188 | KF881277 | |
| USC-5 | U. scandens_06 | Chinaa | KF881240 | KF881153 | KF881278 | ||
| USC-6 | U. scandens_07 | Chinaa | KF881241 | KF881154 | KF881189 | KF881279 | |
| USC-7 | U. scandens_08 | Chinaa | KF881242 | KF881155 | KF881190 | KF881280 | |
| HITBC:Liana Mengsong 107_7_4 | U. laevigata_01 | Mengsong, Yunnan, Chinaa | KF181471 | HG004898 | |||
| ULAE-1 | U. laevigata_02 | Chinaa | KF881224 | KF881142 | KF881179 | KF881266 | |
| ULAE-2 | U. laevigata_03 | Chinaa | KF881225 | KF881267 | |||
| ULAE-3 | U. laevigata_04 | Chinaa | KF881226 | KF881143 | KF881268 | ||
| ULAE-4 | U. laevigata_05 | Chinaa | KF881227 | KF881144 | KF881180 | KF881269 | |
| ULAE-5 | U. laevigata_06 | Chinaa | KF881228 | KF881181 | |||
| ULAE-6 | U. laevigata_07 | Chinaa | KF881229 | KF881270 | |||
| ULAE-7 | U. laevigata_08 | Chinaa | KF881230 | KF881182 | |||
| Total no. of sequences | 257 | 77 | 63 | 49 | 58 | 10 | |
aFrom GenBank
In total, 257 accessions related to the five candidate DNA barcoding sites (ITS2, rbcL, psbA–trnH, ITS, and matK) from 89 samples belonging to 15 species of Uncaria were analyzed in this study. All accession data were downloaded from GenBank, except for the above 54 sequences, which were amplified and sequenced in our laboratory. All datasets of Uncaria species used in the study contained more than two samples, except for Uncaria africana, Uncaria guianensis, and Uncaria lanosa. Some accessions in which the sequences contained undetermined bases or were from sp. species (taxa of species unclear or unnamed) were not selected. In this study, the correctness of the accessions downloaded from GenBank was tested through blasting against those of congener plants. Only the sequences with both a similarity ratio and query cover ratio higher than 90 % in the same species were suitable for selection. However, some accessions containing inversion sequences were collected in this dataset because they could influence the sequence divergence and supply some important genetic characters [29]. The total data and sample information used in this study are shown in Table 1.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification, and sequencing
In this study, genomic DNA was extracted from the freshly dried leaves of Uncaria plants by the improved protocol of a new rapid Plant Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (centrifugal column type, DP3112; Bioteke Corporation, Beijing, China). The Uncaria leaves were ground in liquid nitrogen, and the cell nuclear separation solution (3 ml for 0.5 g sample) was immediately added to the samples to remove impurities from the cytoplasm before the cell nuclei were lysed [30]. PCR amplification of the five candidate DNA barcode sites was performed in a Tprofessional Gradient 96 Type (Biometra, Göttingen, Germany) with approximately 30 ng of genomic DNA as a template in a 25-µL reaction mixture. Each reaction contained 1 × PCR buffer (2.0 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM each dNTP, 0.1 µM each primer; synthesized by Sangon Biotech, Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and 1.0 U Taq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China). The primers and reaction conditions used were the same as those used by Chen et al. [14]. The PCR products were electrophoresed in a 1.5 % agarose gel in 1 × TAE buffer, then purified with a TIANGel Midi Purification Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co. Ltd, Beijing, China). The purified PCR products were bidirectionally sequenced with appropriate amplification primers (Additional file 1) in an ABI-PRISM3730 instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA) by Sangon Biotech, Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
Sequence alignment and data analysis
Sequence assembly and consensus sequence generation were performed by CodonCode Aligner 3.7.1 (CodonCode Co., MA, USA) by trimming the low quality sequence and primer areas. The matK and rbcL regions were delimited by alignment with known sequences in databases by CodonCode Aligner. After removal of the psbA and trnH genes at the ends of psbA–trnH, the boundary of the psbA–trnH intergenic spacer was determined according to the annotations of similar sequences in GenBank. The five candidate DNA barcodes were aligned by ClustalW (EMBL-EBI, Heidelberg, German). Kimura 2-Parameter (K2P) genetic distances were computed with Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis 6.0 (The Biodesign Institute, AZ, USA) [31]. All interspecific and intraspecific distances, including theta prime, minimum interspecific distance, theta, and coalescent depth for all accessions of each locus, were calculated and compared to evaluate the interspecific divergence and intraspecific variation by the K2P model. Meanwhile, statistical analysis of the distribution divergency of the genetic distance between different sequences was performed through the Wilcoxon signed-rank test to assess the barcoding gap for different candidate loci with SPSS software (SPSS 16.0: International Business Machines Corporation Statistical Product and Service Solutions, Armonk, New York, USA), which the test statistical W+ and W− were calculated for two side test, as described previously [14, 22]. The BLAST1 and nearest distance methods were used to evaluate the species identification efficiency [32, 33].
Results
PCR amplification and base composition of the five loci of Uncaria
The sequence length and GC content of the five candidate loci (ITS2, rbcL, psbA–trnH, ITS, and matK) were obtained from the CodonCode Aligner and Clustal W alignment results (Table 2). The GC content of psbA–trnH was the lowest, while that of ITS2 was the highest. The variability of the length range of the psbA–trnH intergenic spacer was greater than that of the other candidates. The psbA–trnH region of U. macrophylla was more divergent than that of the other Uncaria plants.
Table 2.
Analysis of the five candidate barcode loci of Uncaria
| Items | ITS2 | rbcL | psbA–trnH | ITS | matK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species numbers | 14 | 15 | 10 | 14 | 7 |
| Accession no. | 77 | 63 | 49 | 58 | 10 |
| Length range (average) (bp) | 210–221 (220) | 512–656 (608) | 235–315 (287) | 607–621 (616) | 757–814 (808) |
| Average of GC content (%) | 66.3 | 43.0 | 24.8 | 62.8 | 33.1 |
| No. of variable sites in all taxa | 41 | 16 | 173 | 86 | 13 |
| No. of indels in all taxa | 2 | 0 | 39 | 14 | 0 |
| BLAST method (identification efficiency [%]) | 87.0 | 42.9 | 95.9 | 91.4 | 80 |
| Nearest distance method (identification efficiency [%]) | 92.2 | 76.2 | 95.9 | 84.5 | 80 |
Genetic interspecific divergence and intraspecific variation
Six parameters (Table 3) represented the genetic divergences of species in Uncaria. In a comparison of the intraspecific distances of the five candidate barcodes among Uncaria species, the intraspecific distance of psbA–trnH was higher than that of the other loci at the species level. Meanwhile, the interspecific genetic distance of the psbA–trnH intergenic spacer exhibited the highest divergence according to the interspecific distance, theta prime, and minimum interspecific distance. The interspecific distance of ITS2 was the second highest after psbA–trnH. All interspecific divergences of ITS2, psbA–trnH, and ITS were greatly higher than the corresponding intraspecific divergences. Furthermore, the overall mean distance of psbA–trnH was the highest among the five loci (Fig. 1).
Table 3.
Calculation of interspecific and intraspecific divergences for Uncaria
| Parameters | ITS2 | rbcL | psbA–trnH | ITS | matK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraspecific divergence theta | 0.0044 ± 0.0063 | 0.0010 ± 0.0013 | 0.0674 ± 0.0508 | 0.0080 ± 0.0089 | 0.0010 ± 0.0003 |
| Coalescent depth | 0.0171 ± 0.0292 | 0.0022 ± 0.0025 | 0.1060 ± 0.0705 | 0.0153 ± 0.0151 | 0.0012 ± 0.0000 |
| All intraspecific distance | 0.0059 ± 0.0128 | 0.0010 ± 0.0021 | 0.0480 ± 0.0401 | 0.0047 ± 0.0079 | 0.0009 ± 0.0006 |
| Theta prime | 0.0340 ± 0.0089 | 0.0040 ± 0.0021 | 0.0986 ± 0.0299 | 0.0253 ± 0.0050 | 0.0060 ± 0.0024 |
| Minimum interspecific distance | 0.0151 ± 0.0141 | 0.0009 ± 0.0017 | 0.0192 ± 0.0232 | 0.0104 ± 0.0092 | 0.0030 ± 0.0028 |
| All interspecific distance | 0.0348 ± 0.0166 | 0.0042 ± 0.0033 | 0.1068 ± 0.0468 | 0.0239 ± 0.0102 | 0.0057 ± 0.0027 |
Fig. 1.
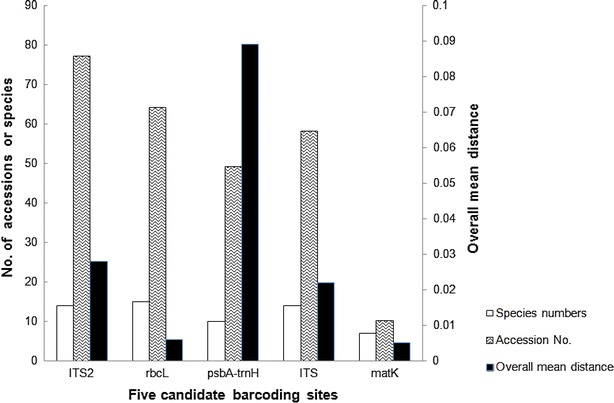
Distribution of overall mean distance for all sequence pairs among five loci. The number at right y axis is the estimates of average evolutionary divergence over all sequence pairs for each locus, which is the base substitutions per site from averaging over all sequence pairs. Analyses were conducted by the maximum composite likelihood method in MEGA6 [31]
The psbA–trnH intergenic spacer had the highest interspecific divergence among all the loci based on the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The second highest interspecific divergence was shown by ITS2. The scale of the interspecific divergence of psbA–trnH was higher than ITS2, ITS, matK and rbcL, respectively (all P < 0.001), that of ITS2 was higher than ITS, matK and rbcL, respectively (all P < 0.001, Table 4). Furthermore, the intraspecific divergences between ITS and matK, rbcL and matK, ITS2 and matK, psbA–trnH and matK, and ITS and rbcL did not exhibit any significant differences (P > 0.05, Table 5).
Table 4.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test for interspecific divergences
| W+ | W− | Inter relative rank | n | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | rbcL | W+ = 1.00, W− = 639.50 | 1282 | 2.25 × 10−210 | ITS2 > rbcL |
| ITS2 | psbA–trnH | W+ = 506.72, W− = 98.66 | 957 | 1.42 × 10−149 | ITS2 < psbA–trnH |
| ITS2 | ITS | W+ = 365.08, W− = 744.61 | 1358 | 8.42 × 10−143 | ITS2 > ITS |
| ITS2 | matK | W+ = 0.00, W− = 16.50 | 32 | 7.93 × 10−7 | ITS2 > matK |
| rbcL | psbA–trnH | W+ = 360.00, W− = 0.00 | 719 | 2.27 × 10−119 | rbcL < psbA–trnH |
| rbcL | ITS | W+ = 442.81, W− = 20.38 | 862 | 8.05 × 10−141 | rbcL < ITS |
| rbcL | matK | W+ = 22.63, W− = 17.86 | 41 | 0.0193 | rbcL < matK |
| psbA-trnH | ITS | W+ = 27.27, W− = 287.47 | 560 | 1.80 × 10−92 | psbA-trnH > ITS |
| psbA-trnH | matK | W+ = 0.00, W− = 16.50 | 32 | 7.93 × 10−7 | psbA-trnH > matK |
| ITS | matK | W+ = 0.00, W− = 16.50 | 32 | 7.93 × 10−7 | ITS > matK |
Table 5.
Wilcoxon signed-rank test for intraspecific divergences
| W+ | W− | Intra relative rank | n | P value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 | rbcL | W+ = 23.12, W− = 45.44 | 149 | 7.54 × 10−6 | ITS2 > rbcL |
| ITS2 | psbA–trnH | W+ = 60.70, W− = 11.00 | 124 | 1.90 × 10−20 | ITS2 < psbA–trnH |
| ITS2 | ITS | W+ = 49.59, W− = 37.93 | 127 | 0.0166 | ITS2 > ITS |
| ITS2 | matK | W+ = 2.00, W− = 0.00 | 4 | 0.1025 | ITS2 = matK |
| rbcL | psbA–trnH | W+ = 46.00, W− = 0.00 | 101 | 1.19 × 10−16 | rbcL < psbA–trnH |
| rbcL | ITS | W+ = 29.17, W− = 26.60 | 84 | 0.3788 | rbcL = ITS |
| rbcL | matK | W+ = 2.00, W− = 0.00 | 4 | 0.1025 | rbcL = matK |
| psbA–trnH | ITS | W+ = 10.50, W− = 34.22 | 70 | 4.23 × 10−12 | psbA–trnH > ITS |
| psbA–trnH | matK | W+ = 1.00, W− = 2.50 | 4 | 0.2763 | psbA–trnH = matK |
| ITS | matK | W+ = 2.00, W− = 0.00 | 4 | 0.1025 | ITS = matK |
Analysis of barcoding gaps
As a barcode for identifying botanical species, the divergence between species should be higher than the variation within species [34]. Although the histogram of the K2P genetic distance analysis revealed a partial overlap “barcoding gap” between the intraspecific and interspecific divergence of ITS2 or psbA–trnH (Fig. 2), the intraspecific variation of psbA–trnH and ITS2 was considerably lower than the distribution of their interspecific divergence. The genetic divergence distribution of ITS was similar to that of ITS2. No clear “barcoding gap” corresponding to the rbcL or matK loci was observed, wherein the genetic distance distribution of more than 90 % of accessions was less than 0.020. However, the distribution of the interspecific divergence of ITS2 and psbA–trnH provided a better resolution than that of rbcL and matK.
Fig. 2.
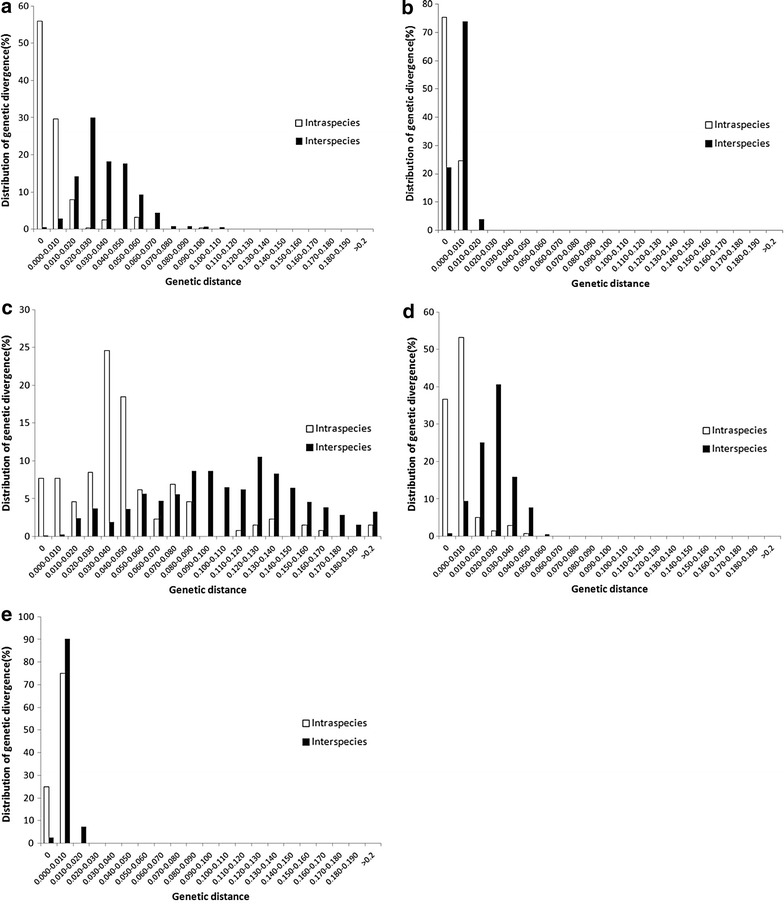
Distribution of divergence between interspecific and intraspecific genetic distance for five candidate barcoding loci among 257 accessions. a ITS2; b rbcL; c psbA–trnH; d ITS; e, matK. x axis, genetic distance; y axis, distribution of genetic divergence
Identification efficiency and characteristics of Clustal W alignment
The BLAST and nearest distance methods were employed to test the applicability of the five loci for species identification of Uncaria. psbA–trnH presented 95.9 % identification efficiency with both the BLAST and nearest distance methods at the species or genus level. ITS2 exhibited 92.2 % identification efficiency by the nearest distance method, but 87 % by the BLAST method, whereas rbcL showed only 76.2 % by the nearest distance method and 42.9 % by the BLAST method (Table 2). Meanwhile, psbA–trnH of U. macrophylla exhibited more obvious characteristics than U. rhynchophylla and the other species tested (Figs. 3, 4, 5). Two insertion fragments existed in the psbA–trnH sequence of U. macrophylla, including a serial seven A fragment at 171–177 bp, and another double repeat “ATTAAA” at 234–247 bp. The psbA–trnH intergenic spacer can be used as a barcode for the identification of Uncaria plants. The phylogeny of Uncaria ITS2 (computed model: Maximum Composite Likelihood) [31] showed that only four accessions (4/77 accessions) were in the incorrect taxonomic category (Fig. 6), which was less than the other loci tested. Thus, ITS2 could be another suitable DNA barcode for Uncaria.
Fig. 3.

ClustalW results of psbA–trnH of Uncaria plants. Identical positions are shown as dot; indels as dash; the red box site show a seven A repeat inserted at 171–177 bp, the differences of U. macrophylla from U. rhychophylla and other Uncaria species
Fig. 4.

ClustalW results of psbA–trnH of Uncaria plants. Identical positions are shown as dot; indels as dash; the red box site show a cis-repeats of ATTAAA insertion at 234–239 bp, the differences of U. macrophylla from U. rhychophylla and other Uncaria species
Fig. 5.
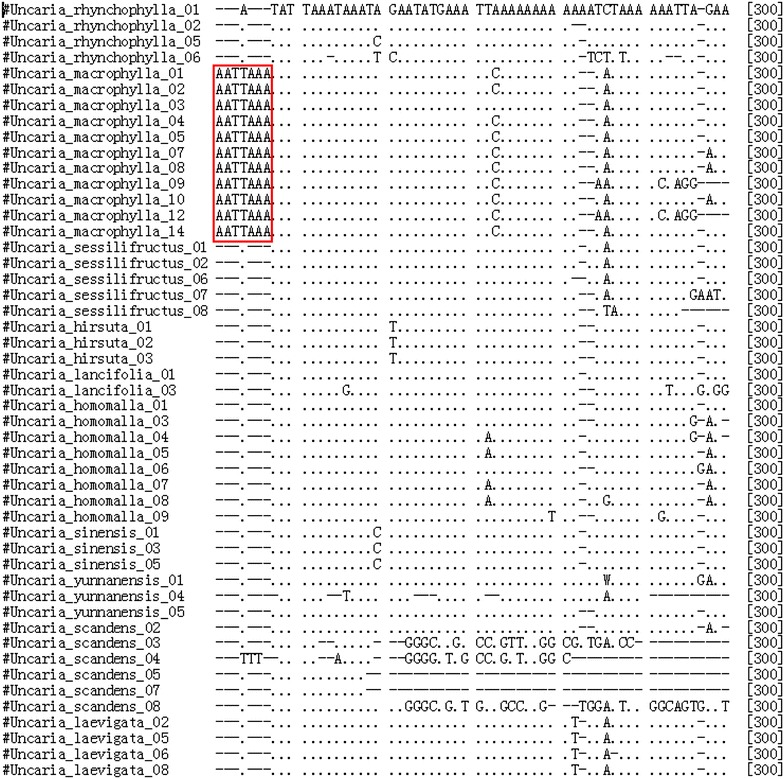
ClustalW results of psbA–trnH of Uncaria plants. Identical positions are shown as dot; indels as dash; the red box site show a cis-repeats of ATTAAA insertion at 241-247 bp, the differences of U. macrophylla from U. rhychophylla and other Uncaria species
Fig. 6.
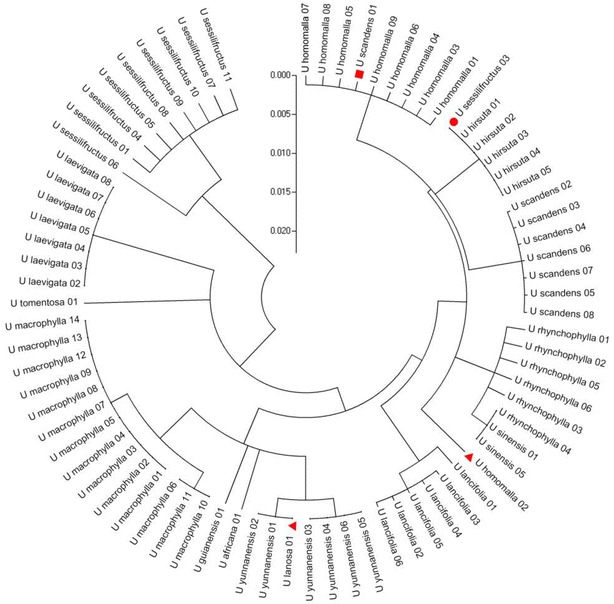
Phylogeny tree of Uncaria ITS2. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method, the evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood model. Only four accessions labeled by triangular, square or circular symbol were incorrectly taxonomic category
Discussion
Significance of authentication of Uncaria by DNA barcoding
Gouteng is commonly exploited as the major ingredient herb of CM prescriptions for hypertension or migraine treatment [2, 35]. The amount of stems with hooks of U. rhynchophylla (Gouteng) required in traditional clinic and pharmaceutical production, has been increased; while the natural growth of U. rhynchophylla, U. hirsuta and U. macrophylla which could serve as the botanical origins of Gouteng was limited with the rising of collection. Some other species of the genus Uncaria are often collected to adulterate Guoteng, such as U. laevigata, U. lancifolia, U. scandens [7]. Therefore, the correct genotypic identification of Uncaria plant material is essential in order to protect public health and for industrial production.
Although some methods have been developed to distinguish Uncaria plants based on morphotype, microcharacter, or physical and chemical reactions [8, 9], these are dependent on taxonomy experts. Currently, the genetic molecular markers for the genus Uncaria were related to RAPD, rDNA, and ITS, while DNA barcoding assays have not yet been reported. This study included 11 of 12 species of Uncaria in China, with U. rhynchophylloides missing in the screen for suitable DNA barcodes for Uncaria.
In the present study, psbA–trnH presented 95.9 % identification efficiency for Uncaria accessions tested with both BLAST and nearest distance methods at the species or genus level. ITS2 also exhibited high identification efficiency at 92.2 or 87 % with the nearest distance or BLAST method, respectively.
Quality and amplification efficiency of DNA from Uncaria
The DNA of Uncaria was not extracted efficiently, due to the large amounts of polysaccharides, polyphenols, and alkaloids present in the samples. A cell nuclear separation solution was used to remove the impurities from genomic DNA [30]. The quality of the DNA extracted from the Uncaria plants satisfied the requirements for PCR amplification and sequencing. The efficiency of both PCR amplification and sequencing for psbA–trnH was the highest among the five candidate loci. Specifically, PCR amplification showed 96.7 % efficiency, while sequencing showed 100 % efficiency. Because the average GC content of ITS2 was 66.3 %, which was higher than that of the other loci, the resulting DNA extract was slightly difficult to amplify.
Selection of candidate DNA barcodes
In this study, the length of psbA–trnH of Uncaria ranged from 235 to 315 bp (mean 287 bp), which was longer than that of ITS2, but shorter than that of rbcL, ITS, and matK. Additionally, psbA–trnH of Uncaria exhibited the highest interspecific divergence among the five loci tested, based on the results of six parameters of the K2P model or Wilcoxon signed-rank test of interspecific divergence. The interspecies divergence of psbA–trnH was higher than the relevant intraspecies variation. Furthermore, psbA–trnH of U. macrophylla was significantly distinct from that of U. rhynchophylla and the other species because of two insertion fragments: one was a seven A repeat inserted at 171–177 bp and the other was two cis-repeats of ATTAAA at 233–247 bp (Figs. 3, 4, 5). Although one TAAAAAA repeat was observed at 171–177 bp in psbA–trnH from Uncariayunnanensis, no double cis-repeats of ATTAAA were observed at 233–247 bp. Meanwhile, one inversion sequence of length 73–74 bp with identity ratios of more than 98 % in psbA–trnH of Uncaria was found in this study (Additional file 2). The intragenic variation of the genus Uncaria was large because of this inversion phenomenon existing in psbA–trnH. This situation was also observed in psbA–trnH of Aconitum L. [29]. The characteristics of the insertion sequences in psbA–trnH could effectively authenticate Uncaria species.
ITS2 was another suitable locus for distinguishing different species of Uncaria. The length range of ITS2 was 210–221 bp (mean 219.9 bp), which was the shortest among the five loci. Consequently, 95.8 % efficiency could be reached by PCR amplification. In a comparison of the interspecific genetic distances of the five candidate barcodes among Uncaria species, the mean interspecific distance of ITS2 was higher than its mean intraspecific divergence, and the values were second only to those of psbA–trnH (Table 3). Based on the phylogenetic analysis of ITS2 by the neighbor-joining method and the evolutionary distances computed by the Maximum Composite Likelihood model, more than 93 % of Uncaria at the species level in this study were divided into monophyla as recognized species. Among 77 accessions of ITS2, comprising 14 species of Uncaria, only four accessions were in an incorrect taxonomic category, according to the construction of a phylogenetic tree for ITS2 (Fig. 6). Uncaria manifested complex morphological features and genetic backgrounds, and even some specimens with obvious differences in appearance possessed similar ITS sequences [28]. This could explain the existence of some accessions that appeared in different monophyla from their original morphological taxa. Some species submitted to GenBank may have been wrongly categorized. Sequences with lengths of less than 100 bp, those with ambiguous bases containing more than one “N”, or those belonging to unnamed species (such as those with spp. and aff. in the species name) were excluded [20] from this study to guarantee the reliability of the selected sequences.
A better “barcoding gap” was observed between the interspecific divergence and intraspecific variation of ITS2 compared with the other loci. ITS, which contained three fragments (ITS1, 5.8S rDNA, ITS2), exhibited a similar identification efficiency to that of ITS2. Both rbcL and matK were unsuitable genetic loci for authentication of the botanical origins of Gouteng, because of the absence of a clear barcoding gap between the interspecific divergence and intraspecific variation by the K2P model. The overall mean distance of rbcL was only 0.002 and that for matK was 0.005, as computed by the Maximum Composite Likelihood model (Fig. 1). Moreover, we found that the combination of psbA–trnH with ITS2 would provide a better result for the authentication of Uncaria plants, and could even distinguish between incorrect and correct taxa or identify some cryptic species. Currently, a preliminary system for DNA barcoding of herbal materials has been established based on a two-locus combination of ITS2 and psbA–trnH barcodes [36]. Recently, ITS2 was successfully exploited in a survey involving commercial Rhodiola products, including decoction pieces [37].
psbA–trnH and ITS2 also exhibited high authentication power for different species of Uncaria. Both psbA–trnH and ITS2 revealed the distinct divergence of U. macrophylla from U. rhynchophylla and the other species at the species level.
Conclusion
While psbA–trnH and ITS2 (used alone) were applicable barcodes for species authentication of Uncaria, psbA–trnH was a more suitable barcode for authentication of U. macrophylla.
Authors’ contributions
YSW conceived and designed the study. YLT, RSH, PX, KZL extracted DNA and performed PCR; YLT, DZC and YLuo checked the quality of PCR products and analyzed the sequencing results; YLT, NXC and YLiu analyzed the data; YSW wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Shou-yang Liu and Mr. Yi-ling Zhu, Mr. Ke-jian Yan for their help with the collection and identification of the Uncaria specimens. We appreciate the essential comments provided by Dr. Hui Yao and all others that much improved the manuscript. We thank the Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, P.R.China, for providing the calculation and analysis platform. The work was supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2010GXNSFA013145); Scientific Research Project Foundation for Higher Education School from Guangxi Provincial Department of Education (201203YB038); National Natural Scientific Foundation of P.R. China (No.31260069).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
- ITS
internal transcribed spacer
- psbA–trnH
gene spacer between psbA and trnH in chloroplast DNA
- K2P
Kimura 2-Parameter
- CM
Chinese medicine
- HPLC
high-performance liquid chromatography
- RAPD
random amplified polymorphic DNA
Additional files
10.1186/s13020-015-0072-7 The univeral primers for candidate barcodes PCR amplication and sequening in the study.
10.1186/s13020-015-0072-7 The accessions containing inversion sequence in psbA-trnH of Uncaria.
Contributor Information
Yin-lin Tang, Email: tangyinlin2008@163.com.
Yao-sheng Wu, Email: wuyaosheng03@sina.com, Email: wuyaosheng2012@gxmu.edu.cn.
Rui-song Huang, Email: hrs.3130064@163.com.
Nai-xia Chao, Email: hurry211625@163.com.
Yong Liu, Email: 12229281@qq.com.
Peng Xu, Email: xupeng2009@163.com.
Ke-zhi Li, Email: scottssdssd@126.com.
Dan-zhao Cai, Email: danzhaoc@sohu.com.
Yu Luo, Email: luoyu2005@126.com.
References
- 1.Zhang YB, Yang WZ, Yao CL, Feng RH, Yang M, Guo DA, Wu WY. New triterpenic acids from Uncaria rhynchophylla: chemistry, NO-inhibitory activity, and tandem mass spectrometric analysis. Fitoterapia. 2014;96:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2014.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ndagijimana A, Wang X, Pan G, Zhang F, Feng H, Olaleye O. A review on indole alkaloids isolated from Uncaria rhynchophylla and their pharmacological studies. Fitoterapia. 2013;86:35–47. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Xian YF, Lin ZX, Mao QQ, Hu Z, Zhao M, Che CT, Ip SP. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Neuroprotective Compounds from Uncaria rhynchophylla against Beta-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:802625. doi: 10.1155/2012/802625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qu J, Gong T, Ma B, Zhang L, Kano Y, Yuan D. Comparative study of fourteen alkaloids from Uncaria rhynchophylla hooks and leaves using HPLC-diode array detection-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization/MS method. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(1):23–30. doi: 10.1248/cpb.60.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shimada Y, Goto H, Kogure T, Shibahara N, Sakakibara I, Sasaki H, Terasawa K. Protective effect of phenolic compounds isolated from the hooks and stems of Uncaria sinensis on glutamate-induced neuronal death. Am J Chin Med. 2001;29(1):173–180. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X01000198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Flora of China (Rubiaceae) [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=3&taxon_id=134135].
- 7.Huang RS, Zhu YL, Yan KJ. Investigation on Plant Resources of Uncaria Schreb in Guangxi and Folk Application in Zhuang and Yao. Guangxi YiKe DaXue XueBao. 2012;29(2):306–308. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Commission CP. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. 10. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2010. p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- 9.He Q, Zeng X. The authentication about the appearance characters of Gouteng and its adulterants. ShiYong ZhongYiYao ZaZhi. 2011;29(4):279. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Huang RS, Zhang P, Zhu YL, Yan KJ, Qin DJ. The analysis of Rhynchophylline contents in part of Uncaria Schreb plant breeds. ZhongGuo ShiYan FangJiXue ZaZhi. 2012;18(8):125–128. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gattuso M, Di Sapio O, Gattuso S, Pereyra EL. Morphoanatomical studies of Uncaria tomentosa and Uncaria guianensis bark and leaves. Phytomedicine. 2004;11(2–3):213–223. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hebert PD, Gregory TR. The promise of DNA barcoding for taxonomy. Syst Biol. 2005;54(5):852–859. doi: 10.1080/10635150500354886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schindel DE, Miller SE. DNA barcoding a useful tool for taxonomists. Nature. 2005;435(7038):17. doi: 10.1038/435017b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen S, Yao H, Han J, Liu C, Song J, Shi L, Zhu Y, Ma X, Gao T, Pang X, et al. Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS One. 2010;5(1):e8613. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pang X, Song J, Zhu Y, Xie C, Chen S. Using DNA Barcoding to Identify Species within Euphorbiaceae. Planta Med. 2010;76(15):1784–1786. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1249806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Techen N, Parveen I, Pan Z, Khan IA. DNA barcoding of medicinal plant material for identification. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2014;25C:103–110. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer EA, Weigt LA, Janzen DH. Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(23):8369–8374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503123102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kress WJ, Erickson DL. A two-locus global DNA barcode for land plants: the coding rbcL gene complements the non-coding trnH–psbA spacer region. PLoS One. 2007;2(6):e508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Newmaster SG, Fazekas AJ, Steeves RA, Janovec J. Testing candidate plant barcode regions in the Myristicaceae. Mol Ecol Resour. 2008;8(3):480–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.02002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yao H, Song J, Liu C, Luo K, Han J, Li Y, Pang X, Xu H, Zhu Y, Xiao P, et al. Use of ITS2 region as the universal DNA barcode for plants and animals. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sun Z, Gao T, Yao H, Shi L, Zhu Y, Chen S. Identification of Lonicera japonica and its Related Species Using the DNA Barcoding Method. Planta Med. 2011;77:301–306. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1250324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gao T, Yao H, Song J, Liu C, Zhu Y, Ma X, Pang X, Xu H, Chen S. Identification of medicinal plants in the family Fabaceae using a potential DNA barcode ITS2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;130(1):116–121. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang M, Zhao HX, Wang L, Wang T, Yang RW, Wang XL, Zhou YH, Ding CB, Zhang L. Potential use of DNA barcoding for the identification of Salvia based on cpDNA and nrDNA sequences. Gene. 2013;528(2):206–215. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ma XY, Xie CX, Liu C, Song JY, Yao H, Luo K, Zhu YJ, Gao T, Pang XH, Qian J, et al. Species identification of medicinal pteridophytes by a DNA barcode marker, the chloroplast psbA–trnH intergenic region. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(11):1919–1924. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ghahramanzadeh R, Esselink G, Kodde LP, Duistermaat H, van Valkenburg JL, Marashi SH, Smulders MJ, van de Wiel CC. Efficient distinction of invasive aquatic plant species from non-invasive related species using DNA barcoding. Mol Ecol Resour. 2013;13(1):21–31. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhu S, Zhou L, Pang H, Huang H, Gao X, Zeng C. Molecular identification of one Uncaria plant. Zhongguo ZhongYao ZaZhi. 2011;36(5):535–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xie S, Shi Y, Wang Y, Wu C, Liu W, Feng F, Xie N. Systematic identification and quantification of tetracyclic monoterpenoid oxindole alkaloids in Uncaria rhynchophylla and their fragmentations in Q-TOF-MS spectra. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013;81–82:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gang T, Liu T, Zhu Y, Liu ZY. Molecular identification of medicinal plant genus Uncaria in Guizhou. Zhong Yao Cai. 2008;31(6):825–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.He J, Wong KL, Shaw PC, Wang H, Li DZ. Identification of the medicinal plants in Aconitum L. by DNA barcoding technique. Planta Med. 2010;76(14):1622–1628. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1240967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xu P, Wu YS, Huang RS, Zhou J, Luo Y, Li KZ, Tang YL, Liu Y. Polymorphism of Three Kinds of Medicinal Plants Uncaria from Guangxi by RAPD. ShiZhen GuoYi GuoYao. 2012;23(3):3. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1596–1599. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meyer CP, Paulay G. DNA barcoding: error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biol. 2005;3(12):e422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lahaye R, van der Bank M, Bogarin D, Warner J, Pupulin F, Gigot G, Maurin O, Duthoit S, Barraclough TG, Savolainen V. DNA barcoding the floras of biodiversity hotspots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(8):2923–2928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709936105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hebert PD, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR. Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc Biol Sci. 2003;270(Suppl 1):S96–S99. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chang YY, Tsai YT, Lai JN, Yeh CH, Lin SK. The traditional Chinese medicine prescription patterns for migraine patients in Taiwan: a population-based study. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(3):1209–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen S, Pang X, Song J, Shi L, Yao H, Han J, Leon C. A renaissance in herbal medicine identification: from morphology to DNA. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(7):1237–1244. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xin T, Li X, Yao H, Lin Y, Ma X, Cheng R, Song J, Ni L, Fan C, Chen S. Survey of commercial Rhodiola products revealed species diversity and potential safety issues. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8337. doi: 10.1038/srep08337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


