Abstract
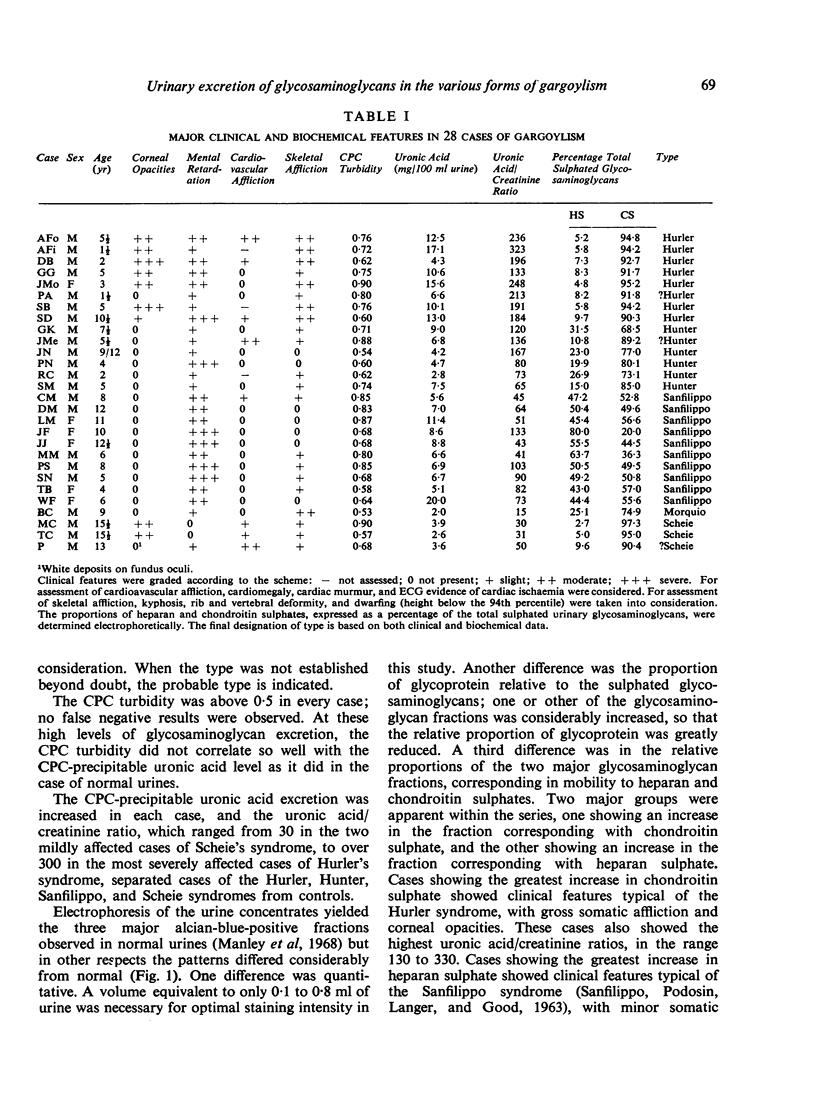
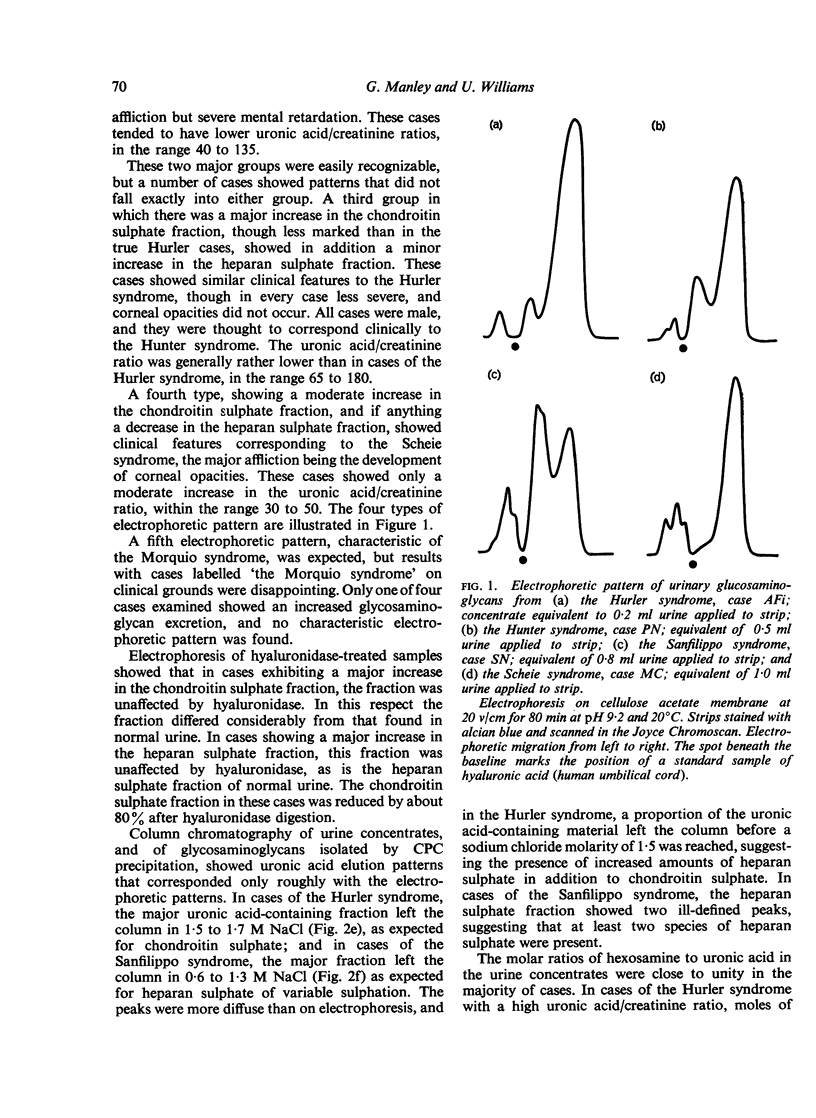
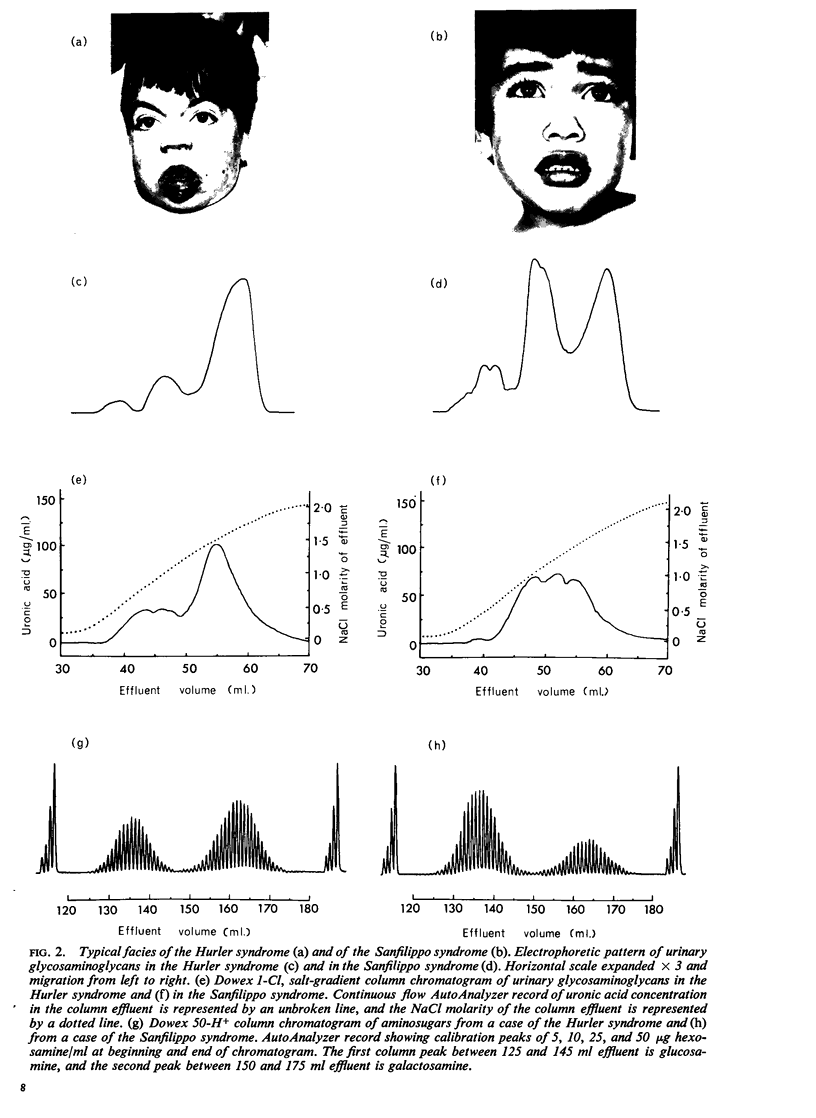
The urinary excretion of glycosaminoglycans in 28 cases of gargoylism, embracing the Hurler, Hunter, Sanfilippo, Morquio, and Scheie syndromes (McKusick, 1966), has been examined using the cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) turbidity test, the uronic acid/creatinine ratio, and the electrophoretic pattern of urine concentrates, as routine procedures. Ion-exchange column chromatographic techniques were also employed for the fractionation of glycosaminoglycans and aminosugars. Molecular weights were investigated by gel filtration and ultracentrifugation.
The CPC turbidity test was positive in every case. The uronic acid/creatinine ratio provided a sensitive index of increased glycosaminoglycan excretion. Cases of the Hurler syndrome showed the highest, and cases of the Morquio and Scheie syndromes the lowest, ratios. A correlation was observed between the uronic acid/creatinine ratio and the clinical severity of the disease. Cellulose acetate electrophoresis differentiated clearly between the two major forms of gargoylism, the Hurler and Sanfilippo syndromes, but differentiation between the Hurler, Hunter, and Scheie syndromes was more difficult on electrophoretic data alone. Results obtained with cases diagnosed as the Morquio syndrome were disappointing. The existence of formes frustes of the Sanfilippo syndrome among the mentally subnormal is predicted. Errors caused by bacterial contamination of urine samples are emphasized. The atypical behaviour of urinary glycosaminoglycans in analytical procedures is discussed. Molecular weight studies suggested heterogeneity. The nature of the basic defect in gargoylism is discussed.
Full text
PDF



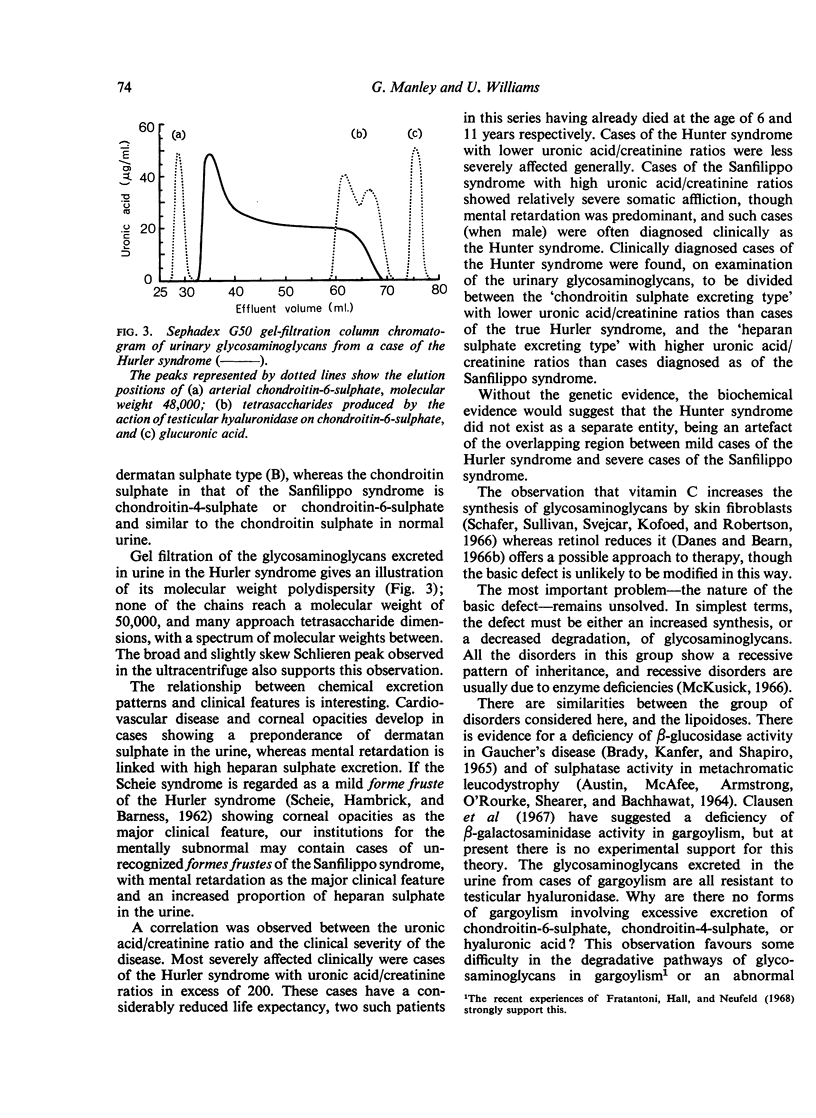

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERRY H. K., SPINANGER J. A paper spot test useful in study of Hurler's syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jan;55:136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOAS N. F. Method for the determination of hexosamines in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):553–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORFMAN A. METABOLISM OF ACID MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES. Biophys J. 1964 Jan;4:SUPPL155–SUPPL165. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86935-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S., Bearn A. G. Hurler's syndrome. A genetic study in cell culture. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratantoni J. C., Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. The defect in Hurler's and Hunter's syndromes: faulty degradation of mucopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):699–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANLOZ R. W. The nomenclature of mucopolysaccharides. Arthritis Rheum. 1960 Jun;3:233–237. doi: 10.1002/art.1780030306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht J., Dorfman A. Structure of heparitin sulfate in tissues of the Hurler syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Dec 9;21(5):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90413-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrini U., Fraccaro M., Tiepolo L., Scappaticci S., Lenzi L., Perona G. P. Mucopolysaccharidoses; autoradiographic study of sulphate-35S uptake by cultured fibroblasts. Ann Hum Genet. 1968 Jan;31(3):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1968.tb00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley G., Hawksworth J. Diagnosis of Hurler's syndrome in the hospital laboratory and the determination of its genetic type. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Feb;41(215):91–96. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.215.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley G., Severn M., Hawksworth J. Excretion patterns of glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins in normal human urine. J Clin Pathol. 1968 May;21(3):339–345. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. Hurler's syndrome: biosynthesis of acid mucopolysaccharides in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1310–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINS M. M., STEVENS H. F., LINKER A. Morquio's disease: An abnormality of mucopolysaccharide metabolism. J Pediatr. 1963 Jun;62:881–889. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIE H. G., HAMBRICK G. W., Jr, BARNESS L. A. A newly recognized forme fruste of Hurler's disease (gargoylism). Am J Ophthalmol. 1962 May;53:753–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGNI G., ROMANO C., TORTOROLO G. DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR GARGOYLISM. Lancet. 1964 Aug 22;2(7356):420–420. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90442-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer I. A., Sullivan J. C., Svejcar J., Kofoed J., Robertson W. van B. Vitamin C-induced increase of dermatan sulfate in cultured Hurler's fibroblasts. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):1008–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teller W. M. Urinary excretion patterns of individual acid mucopolysaccharides. Nature. 1967 Mar 18;213(5081):1132–1133. doi: 10.1038/2131132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELLWEGER H., PONSETI I. V., PEDRINI V., STAMLER F. S., von NOORDEN G. Morquio-Ullrich's disease. Report of 2 cases. J Pediatr. 1961 Oct;59:549–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(61)80239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]