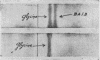
Abstract
The quantity of beta-aminoisobutyric acid (BAIB) excreted in the urine of patients with an intact spleen suffering from thalassaemia major appears to be proportional to the number of the circulating normoblasts and inversely proportional to the haemoglobin level.
After splenectomy only minute amounts of BAIB are excreted. Transfusion constantly, but temporarily, reduces urinary excretion of beta-aminoisobutyric acid. Other anaemic but non-thalassaemic patients may excrete low levels.
Full text
PDF
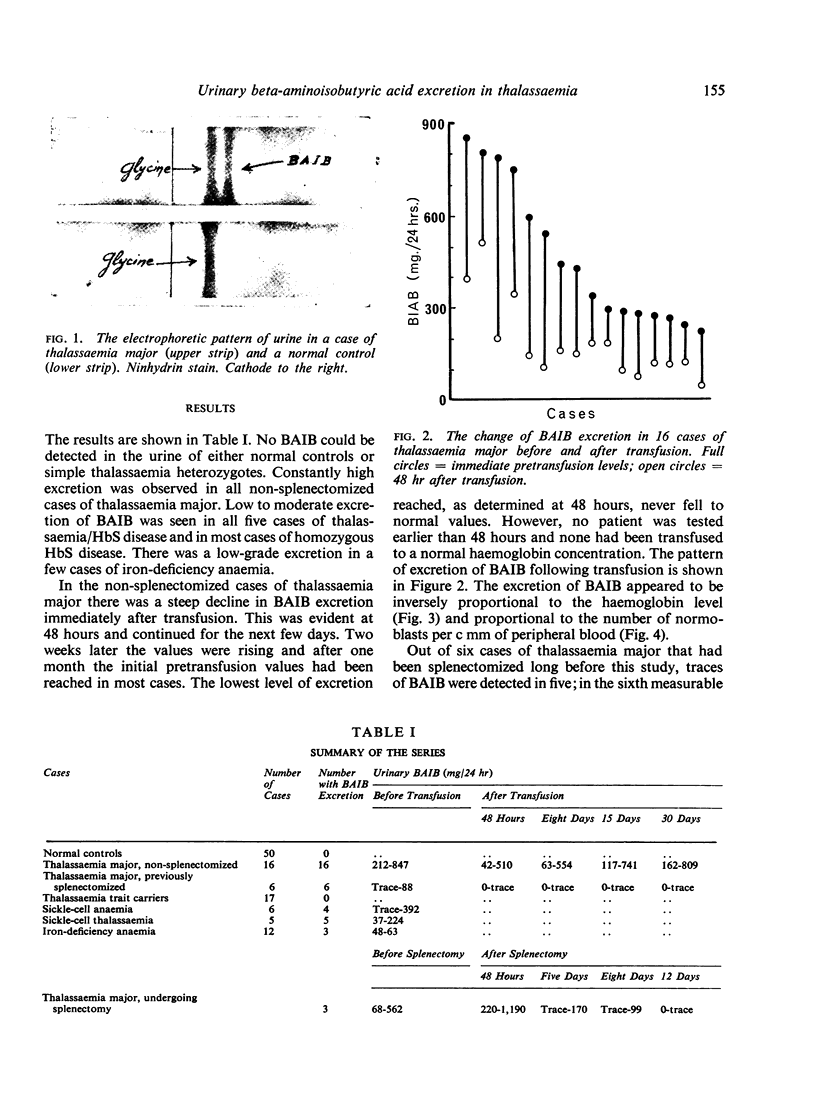
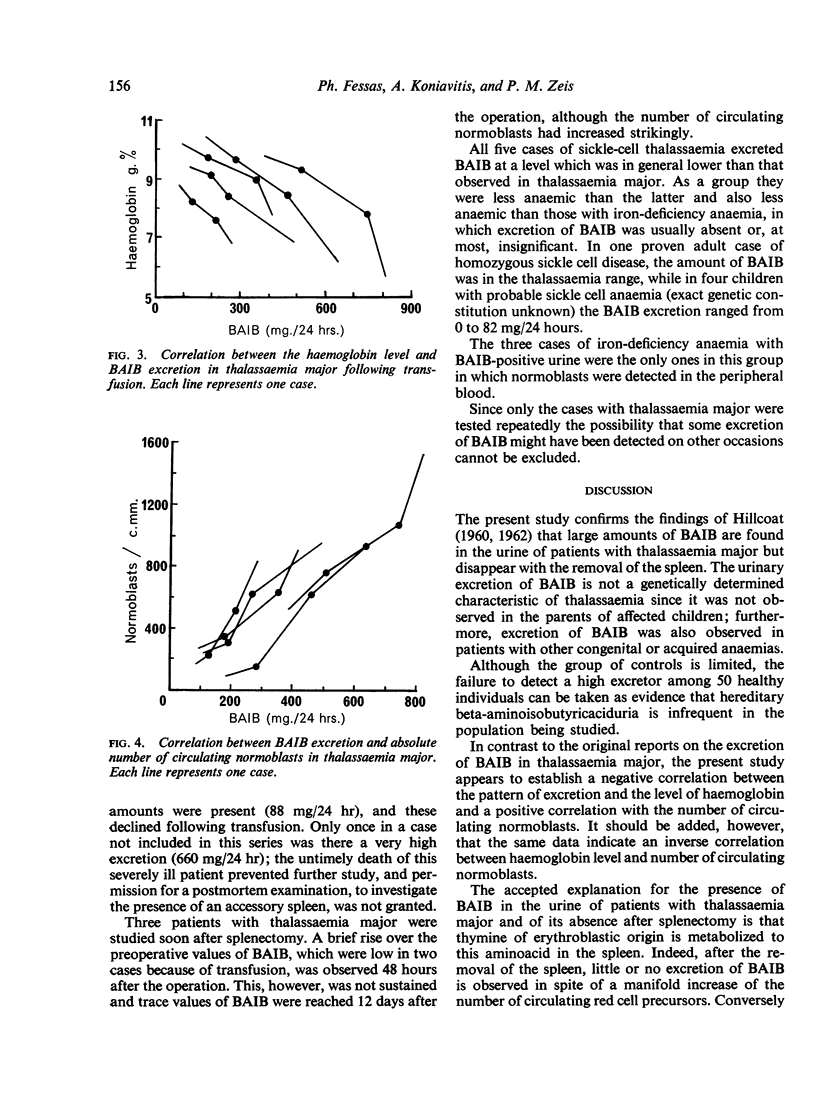

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HILLCOAT B. L. The occurrence of beta-amino-isobutyric acid in the urine of patients with thalassemia major. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Oct;38:441–445. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]