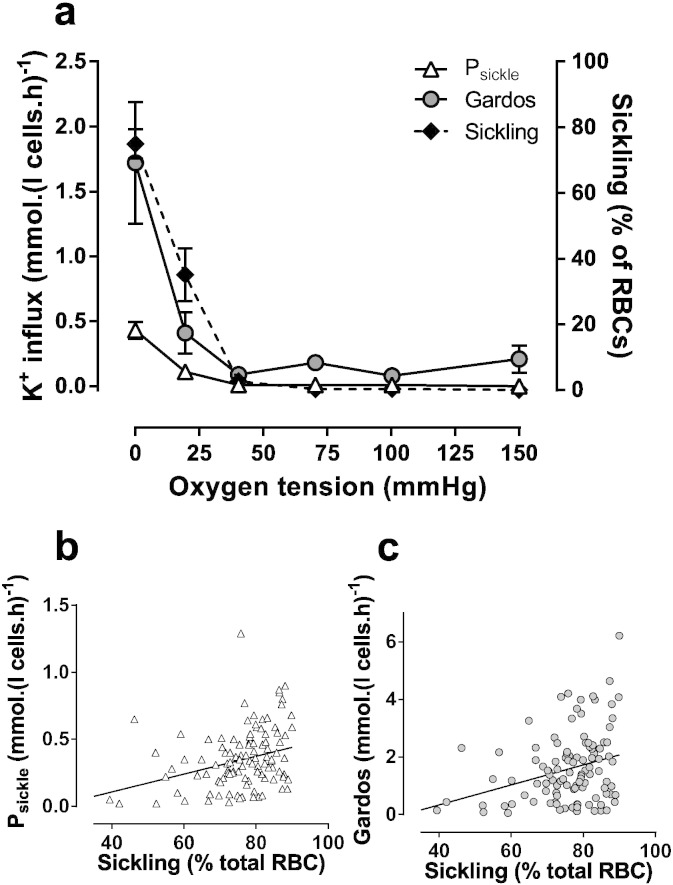
Fig. 2.
Conductive K+ pathways and sickling in red cells from HbSC patients. Red cells (20% haematocrit, Hct) were equilibrated in Eschweiler tonometers at the indicated oxygen tension for 20 min. Red cell aliquots were then fixed in 0.3% glutaraldehyde and percentage sickling assessed by light microscopy. Further aliquots were diluted ten-fold into test tubes for measurement of K+ influx (given as mmol K+.(l cells.h)− 1). Psickle activity is defined as the deoxygenation-induced K+ influx in Cl− free saline in the presence of ouabain (100 μM), bumetanide (10 μM) and clotrimazole (CLT; 5 μM), and the Gardos channel activity as the CLT-sensitive K+ influx in the presence of ouabain and bumetanide. (a) Oxygen dependence of sickling, Psickle and Gardos channel. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M., n = 4–8. (b, c) Pearson correlation of Psickle and Gardos channel activities with % sickling. Correlations were r = 0.302 (p < 0.01) for Psickle and r = 0.305 (p < 0.01) for the Gardos channel.