Abstract
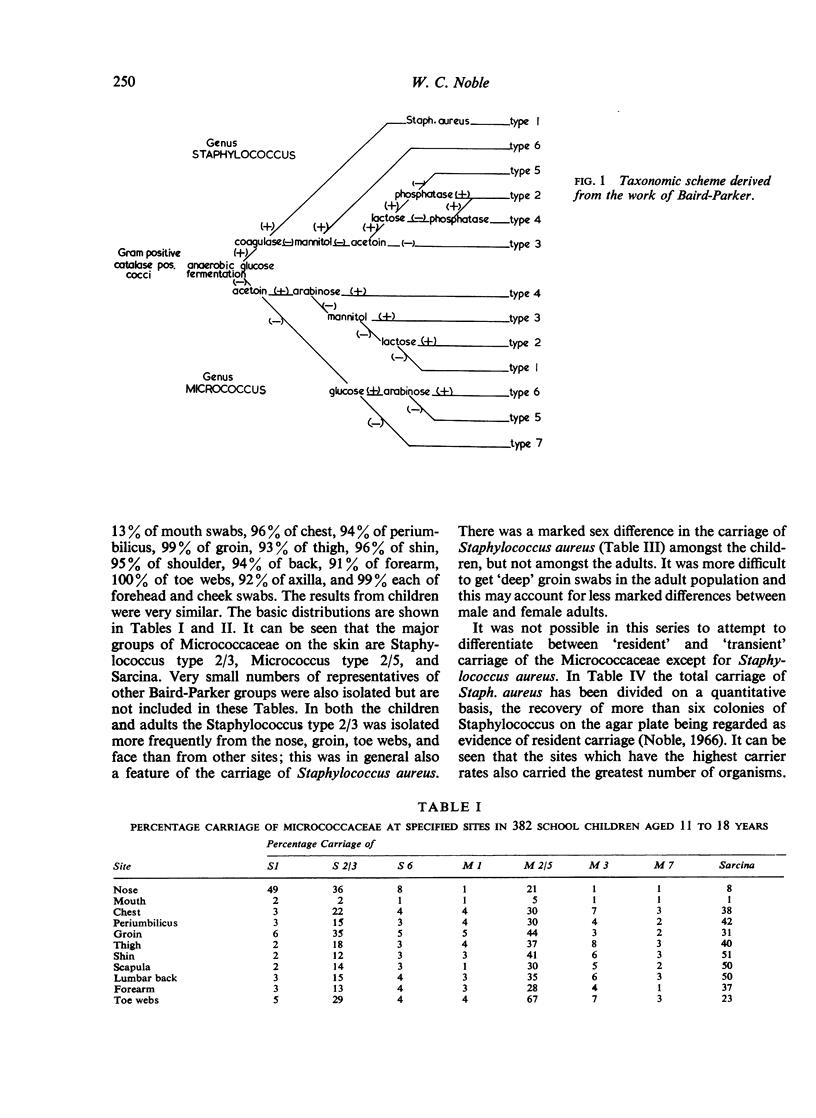
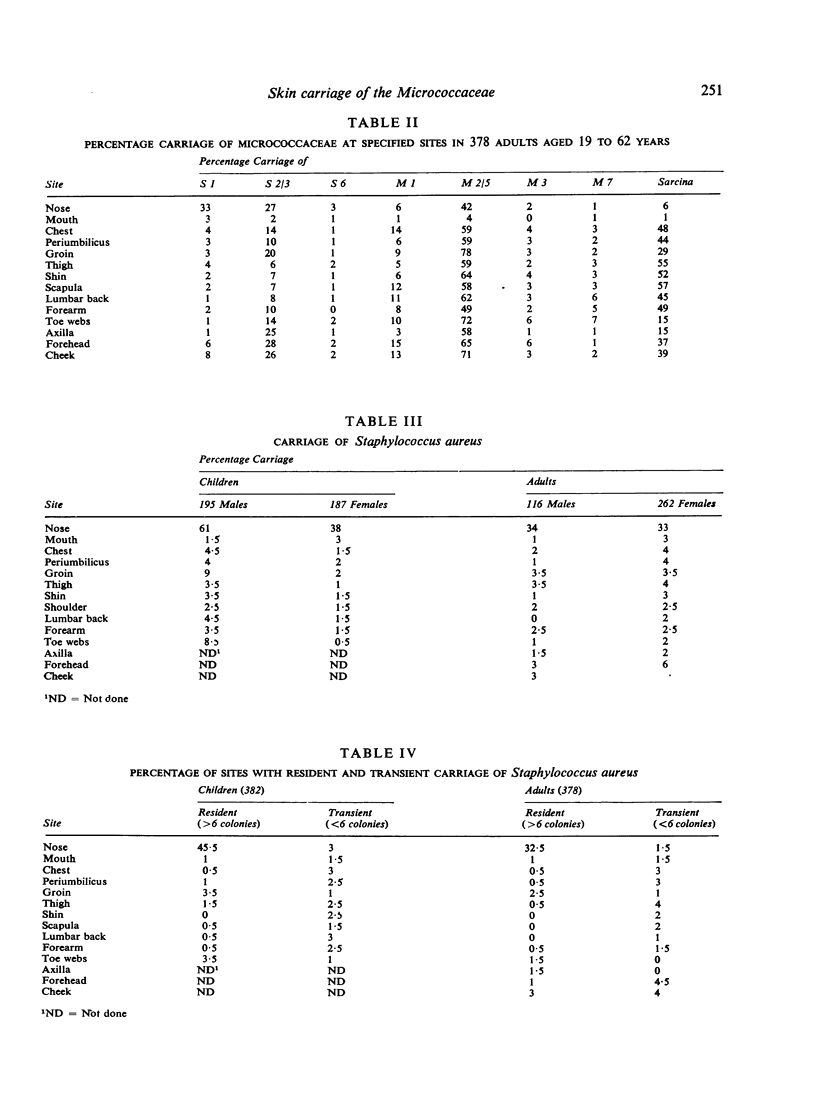
The micrococcal flora of the skin of 382 children and 378 adults have been investigated using a scheme derived from the work of Baird-Parker (1963). The predominant groups are Staphylococcus type 2 and Micrococcus type 2. Some differences in the carriage at different sites have been found: in general the nose, axillae, groin, and toe webs have a similar flora but this differs a little from other, glabrous skin sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., KUPER S. W. A. Identification of Staphylococcus pyogenes by the phosphatase reaction. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;63(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETHUNE D. W., BLOWERS R., PARKER M., PASK E. A. DISPERSAL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY PATIENTS AND SURGICAL STAFF. Lancet. 1965 Feb 27;1(7383):480–483. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLAGHAN R. P., COHEN S. J., STEWART G. T. Septicaemia due to colonization of Spitz-Holter valves by staphylococci. Five cases treated with methicillin. Br Med J. 1961 Mar 25;1(5229):860–863. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5229.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN S. T., STEEL K. L. COMPARISON OF DIFFERENTIATING CRITERIA FOR STAPHYLOCOCCI AND MICROCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:804–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.804-805.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M. J., McArtor R. E. Staphylococcal septicemia. A study of one hundred cases. Ohio State Med J. 1967 Oct;63(10):1325–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL R. G. STAPHYLOCOCCI AND URINARY INFECTION. Br Med J. 1965 Apr 24;1(5442):1127–1127. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5442.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble W. C. Staphylococcus aureus on the hair. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Nov;19(6):570–572. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakoff S., Richards I. D., Parker M. T., Lidwell O. M. Nasal and skin carriage of Staphylococcus aureus by patients undergoing surgical operation. J Hyg (Lond) 1967 Dec;65(4):559–566. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RESNEKOV L. Staphylococcal endocarditis following mitral valvotomy with special reference to coagulase-negative Staphylococcus albus. Lancet. 1959 Oct 17;2(7103):597–600. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91697-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. P. Micrococcaceae from the uinary tract in pregnancy. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jul;20(4):631–632. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.4.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. M., BEALS P. D., KINGSBURY K. R., HASENCLEVER H. F. Observations on Staphylococcus albus septicemia in mice and men. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Sep;102(3):375–388. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00030010375005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink M. S., Strong S. The pathogenic variety of Staphylococcus albus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):295–299. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



