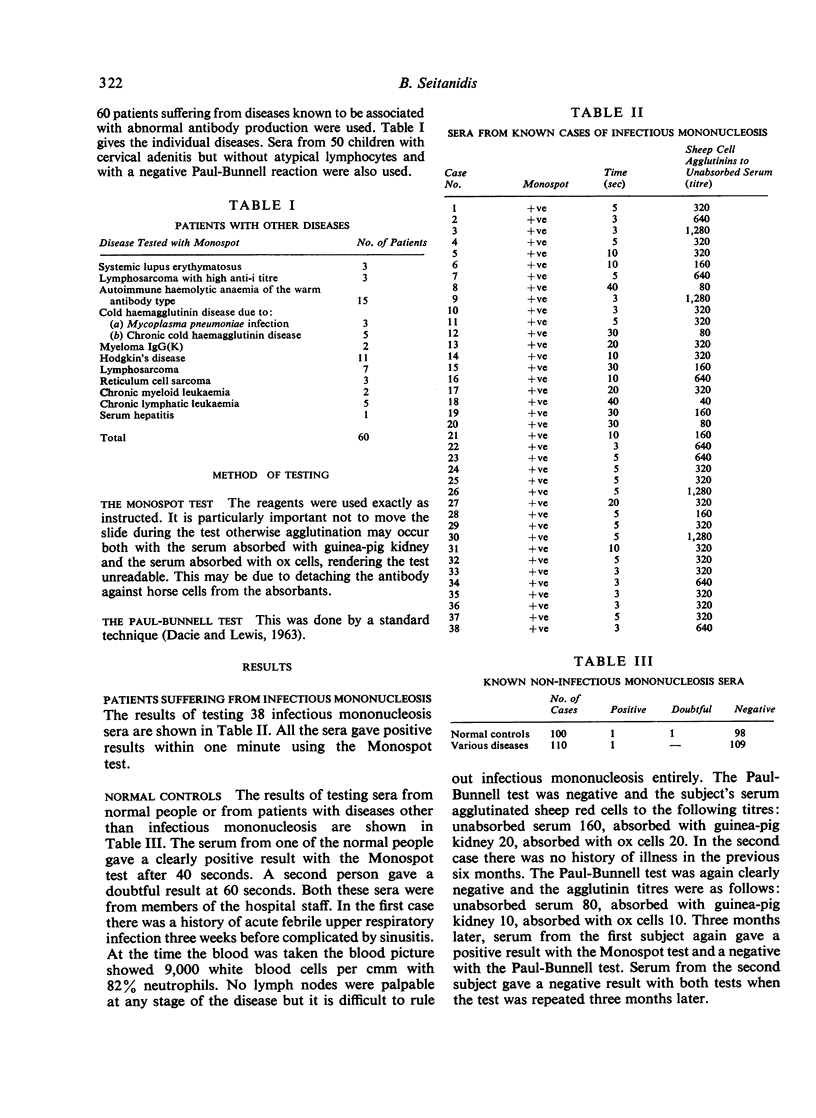
Abstract
The Monospot is a spot test designed for the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis and its efficacy has been compared with that of the standard Paul-Bunnell test. Three out of 210 (1·4%) sera from normal persons and persons suffering from diseases other than infectious mononucleosis gave `false' positive results when compared with the Paul-Bunnell test. Using 38 sera from patients with strong clinical and haematological evidence of infectious mononucleosis no false negative results were found with the Monospot test. The sera of 37 patients gave positive results with the Paul-Bunnell test: the one negative result was positive using serum taken a few days later.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beer P. THE HETEROPHILE ANTIBODIES IN INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS AND AFTER THE INJECTION OF SERUM. J Clin Invest. 1936 Nov;15(6):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI100811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Slaby R. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON P. C., CARMICHAEL D. S. IMMUNOCHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND SEROLOGIC BEHAVIOR OF ANTIBODIES AGAINST RED CELLS IN INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:529–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



