Abstract
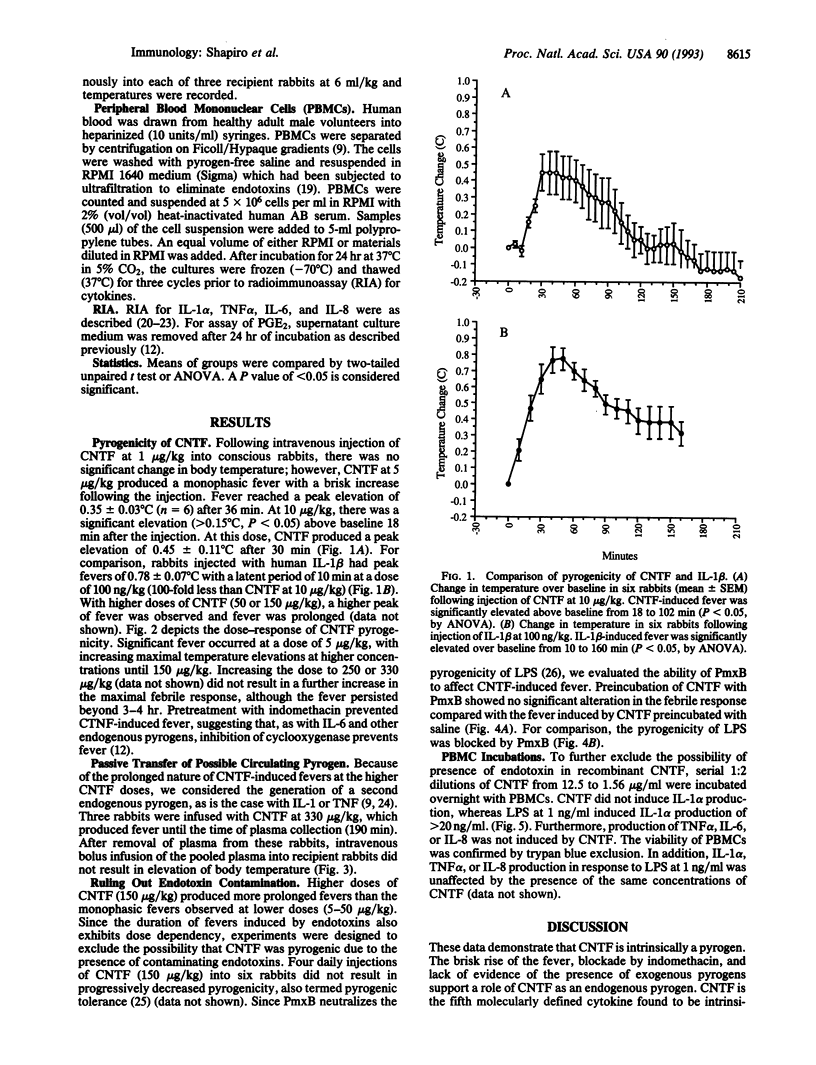
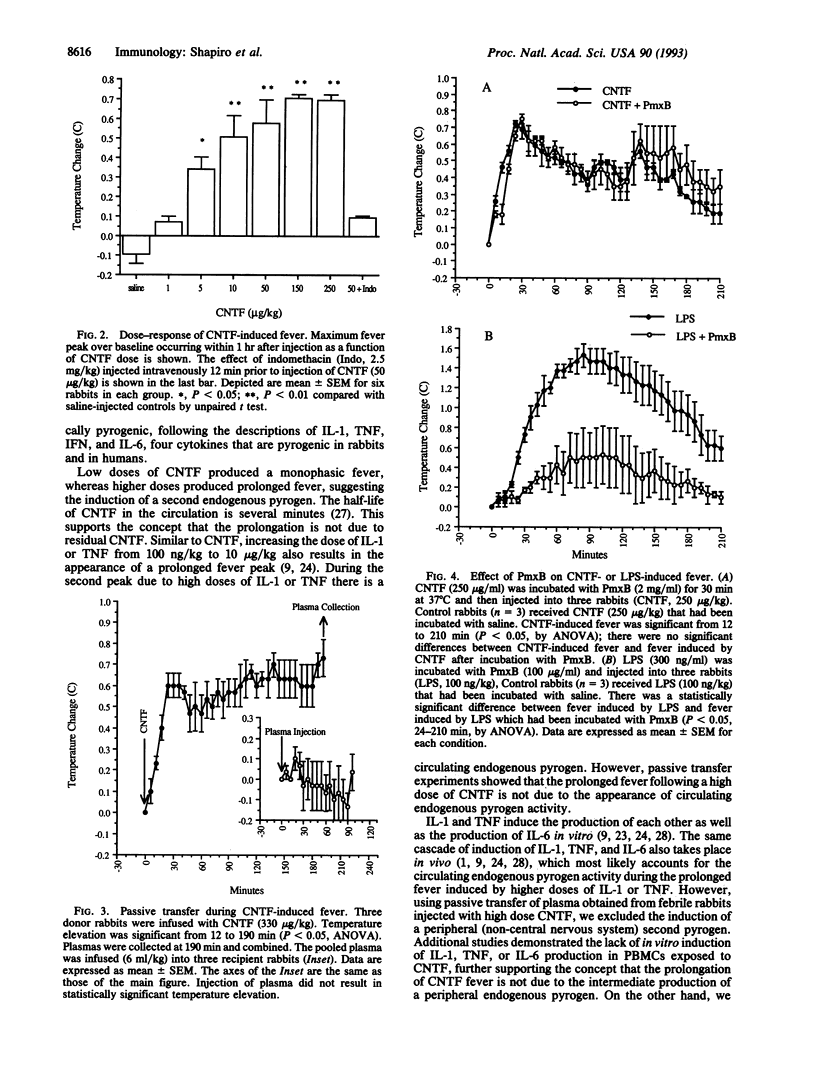
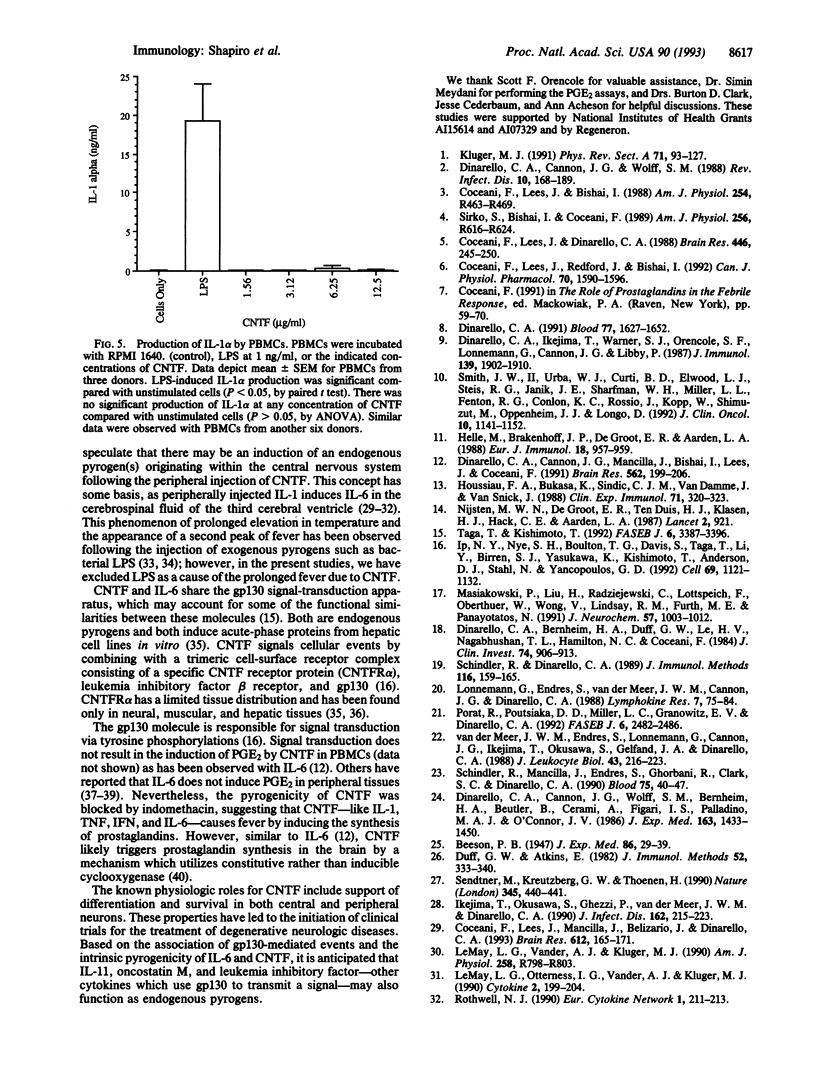
Fever is initiated by the action of polypeptide cytokines called endogenous pyrogens, which are produced by the host during inflammation, trauma, or infection and which elevate the thermoregulatory set point in the hypothalamus. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) supports the differentiation and survival of central and peripheral neurons. We describe the activity of CNTF as intrinsically pyrogenic in the rabbit. CNTF induced a monophasic fever which rose rapidly (within the first 12 min) following intravenous injection; CNTF fever was blocked by pretreatment with indomethacin. The fever induced by CNTF was not due to contaminating endotoxins. Increasing doses of CNTF resulted in prolongation of the fever, suggesting the subsequent induction of additional endogenous pyrogenic activity. After passive transfer of plasma obtained during CNTF-induced fever, endogenous pyrogen activity was not present in the circulation; CNTF also did not induce the endogenous pyrogens interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, or interleukin 6 in vitro. Nevertheless, a second endogenous pyrogen may originate within the central nervous system following the systemic injection of CNTF. Of the four endogenous pyrogens described to date (interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, interferon, and interleukin 6), CNTF, like interleukin 6, utilizes the cell-surface gp 130 signal-transduction apparatus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E. Pathogenesis of fever. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:580–646. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Bishai I. Further evidence implicating prostaglandin E2 in the genesis of pyrogen fever. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):R463–R469. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.254.3.R463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Dinarello C. A. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious cat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90883-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Mancilla J., Belizario J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor in cerebrospinal fluid: changes during pyrogen fever. Brain Res. 1993 May 28;612(1-2):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91657-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Redford J., Bishai I. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: effectiveness against interleukin-1 fever. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;70(12):1590–1596. doi: 10.1139/y92-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bernheim H. A., Duff G. W., Le H. V., Nagabhushan T. L., Hamilton N. C., Coceani F. Mechanisms of fever induced by recombinant human interferon. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):906–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI111508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Mancilla J., Bishai I., Lees J., Coceani F. Interleukin-6 as an endogenous pyrogen: induction of prostaglandin E2 in brain but not in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 25;562(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90622-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M. New concepts on the pathogenesis of fever. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):168–189. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Ikejima T., Warner S. J., Orencole S. F., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin 1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1902–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Brakenhoff J. P., De Groot E. R., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 is involved in interleukin 1-induced activities. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):957–959. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Bukasa K., Sindic C. J., Van Damme J., Van Snick J. Elevated levels of the 26K human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin 6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the central nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):320–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Okusawa S., Ghezzi P., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 induces tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro and a circulating TNF-like activity in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):215–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluger M. J. Fever: role of pyrogens and cryogens. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):93–127. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMay L. G., Otterness I. G., Vander A. J., Kluger M. J. In vivo evidence that the rise in plasma IL 6 following injection of a fever-inducing dose of LPS is mediated by IL 1 beta. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90016-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMay L. G., Vander A. J., Kluger M. J. Role of interleukin 6 in fever in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):R798–R803. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.3.R798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonnemann G., Endres S., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Dinarello C. A. A radioimmunoassay for human interleukin-1 alpha: measurement of IL-1 alpha produced in vitro by human blood mononuclear cells stimulated with endotoxin. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Summer;7(2):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo J. A., Sousa S. L., Alander C., Raisz L. G., Dinarello C. A. Comparison of the bone-resorbing activity in the supernatants from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with that of cytokines through the use of an antiserum to interleukin 1. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Liu H. X., Radziejewski C., Lottspeich F., Oberthuer W., Wong V., Lindsay R. M., Furth M. E., Panayotatos N. Recombinant human and rat ciliary neurotrophic factors. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijsten M. W., de Groot E. R., ten Duis H. J., Klasen H. J., Hack C. E., Aarden L. A. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and acute phase responses. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):921–921. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podor T. J., Jirik F. R., Loskutoff D. J., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Human endothelial cells produce IL-6. Lack of responses to exogenous IL-6. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:374–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Poutsiaka D. D., Miller L. C., Granowitz E. V., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor blockade reduces endotoxin and Borrelia burgdorferi-stimulated IL-8 synthesis in human mononuclear cells. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2482–2486. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.7.1532945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Wyche A., Siegel N., Needleman P. Regulation of fibroblast cyclooxygenase synthesis by interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3022–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J. Mechanisms of the pyrogenic actions of cytokines. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1990 Oct-Nov;1(4):211–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Dinarello C. A. A method for removing interleukin-1- and tumor necrosis factor-inducing substances from bacterial cultures by ultrafiltration with polysulfone. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Mancilla J., Endres S., Ghorbani R., Clark S. C., Dinarello C. A. Correlations and interactions in the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human blood mononuclear cells: IL-6 suppresses IL-1 and TNF. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooltink H., Stoyan T., Roeb E., Heinrich P. C., Rose-John S. Ciliary neurotrophic factor induces acute-phase protein expression in hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81489-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Yaron I., Meyer F. A., Yaron M., Dayer J. M. Modulation of the effects of interleukin-1 on glycosaminoglycan synthesis by the urine-derived interleukin-1 inhibitor, but not by interleukin-6. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1807–1814. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Kreutzberg G. W., Thoenen H. Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents the degeneration of motor neurons after axotomy. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):440–441. doi: 10.1038/345440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirko S., Bishai I., Coceani F. Prostaglandin formation in the hypothalamus in vivo: effect of pyrogens. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):R616–R624. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.3.R616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., 2nd, Urba W. J., Curti B. D., Elwood L. J., Steis R. G., Janik J. E., Sharfman W. H., Miller L. L., Fenton R. G., Conlon K. C. The toxic and hematologic effects of interleukin-1 alpha administered in a phase I trial to patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Jul;10(7):1141–1152. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.7.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Kishimoto T. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3387–3396. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1334470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF S. M., MULHOLLAND J. H., WARD S. B. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF THE PYROGENIC RESPONSE OF RABBITS TO ENDOTOXIN. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:268–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Ikejima T., Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Dinarello C. A. Concentrations of immunoreactive human tumor necrosis factor alpha produced by human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Mar;43(3):216–223. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



