Abstract
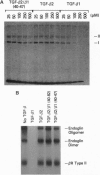
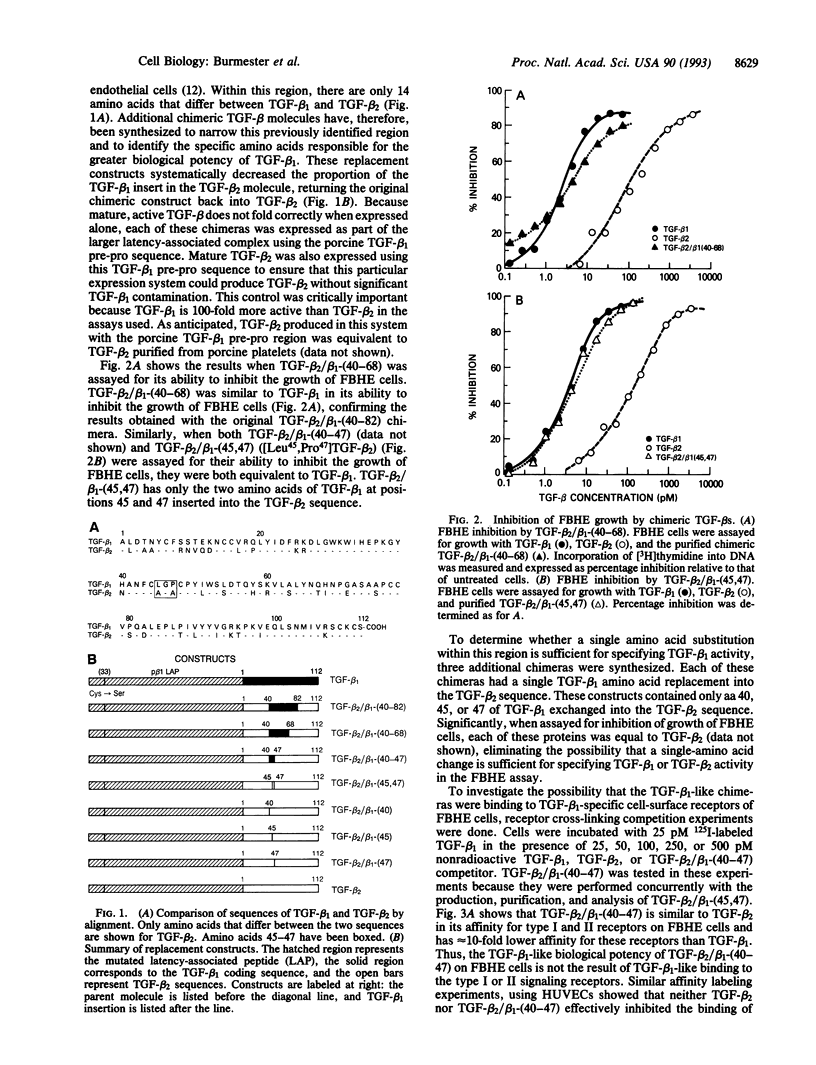
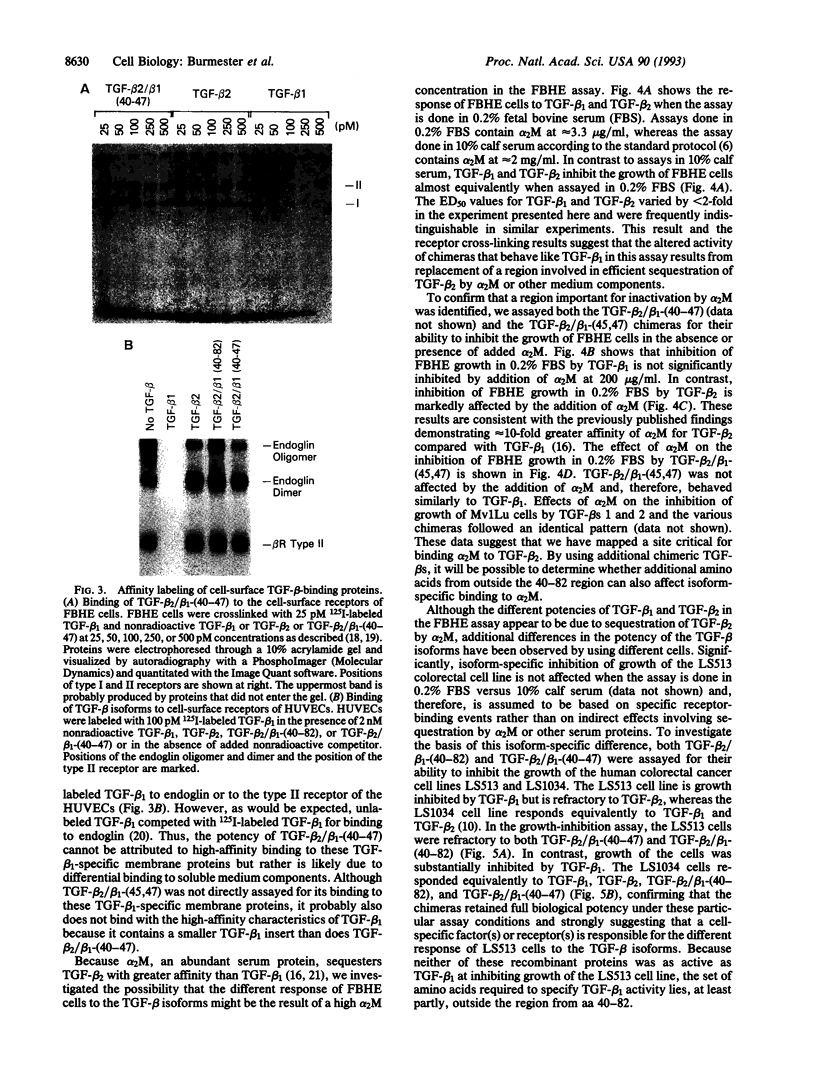
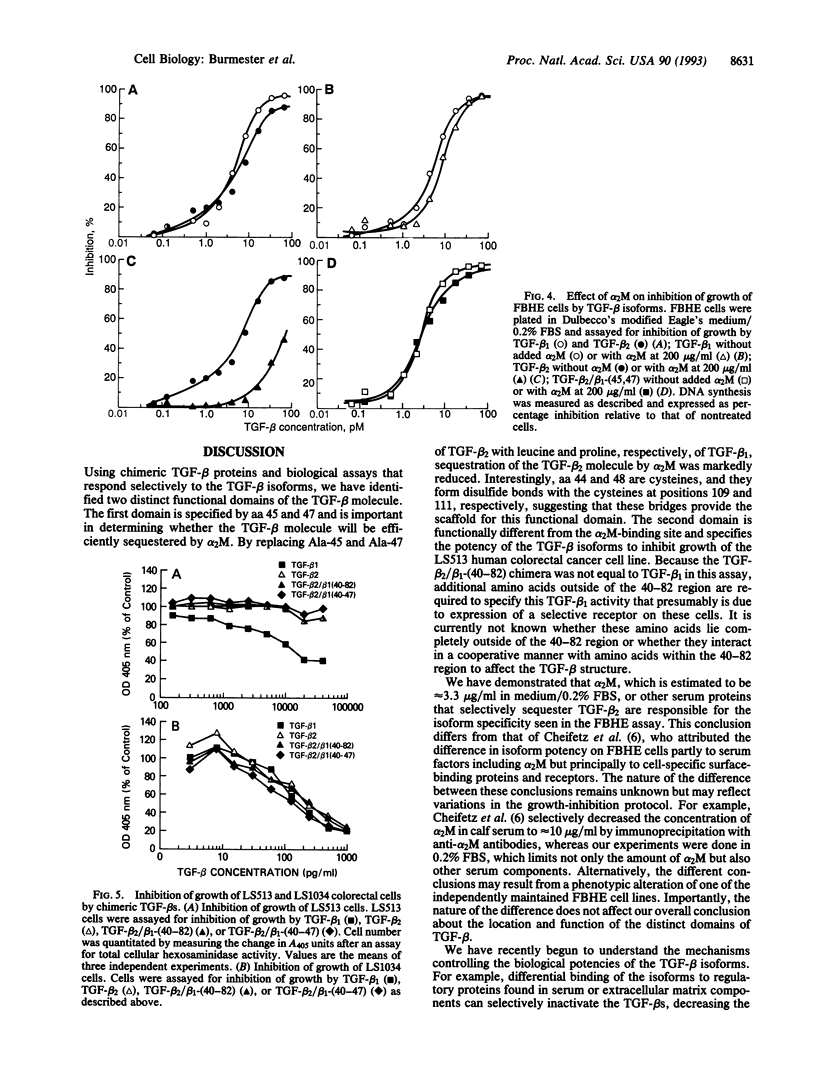
Three distinct isoforms of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) are expressed in mammalian cells. Although many cells respond equivalently to all three isoforms, certain cells respond selectively. Using chimeric proteins in which selected regions of the different isoforms were interchanged, we have identified two distinct functional domains of TGF-beta involved in determining the biological potencies and functions of the molecule. The first domain is important for determining whether TGF-beta can be sequestered by alpha 2-macroglobulin. By replacing aa 45 and 47 of TGF-beta 2 with the corresponding amino acids of TGF-beta 1, sequestration of the TGF-beta molecule by alpha 2-macroglobulin was markedly reduced. The second domain is functionally different from the alpha 2-macroglobulin sequestration site and is important for determining the potency of TGF-beta to inhibit growth of the LS513 human colorectal cancer cell line. Neither the TGF-beta 2/beta 1-(40-47) replacement construct nor a chimera containing aa 1-39 of TGF-beta 2, aa 40-82 of TGF-beta 1, and aa 83-112 of TGF-beta 2 was equivalent to TGF-beta 1 in inhibiting growth of LS513 cells. This fact suggests that additional amino acids outside of the aa 40-82 region are required to specify TGF-beta 1 activity with these cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer S. J., Bax A., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Ogawa Y., Piez K. A., Weatherbee J. A., Tsang M. L., Lucas R., Zheng B. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1: secondary structure as determined by heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1164–1171. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Bellón T., Calés C., Vera S., Bernabeu C., Massagué J., Letarte M. Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth factor-beta receptor system in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19027–19030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Hernandez H., Laiho M., ten Dijke P., Iwata K. K., Massagué J. Distinct transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor subsets as determinants of cellular responsiveness to three TGF-beta isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20533–20538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Isoform-specific transforming growth factor-beta binding proteins with membrane attachments sensitive to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20767–20772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Ebner R., Derynck R. Inactivation of the type II receptor reveals two receptor pathways for the diverse TGF-beta activities. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.8388126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D., Sporn M. B. Differential inhibition of transforming growth factor beta 1 and beta 2 activity by alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6973–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daopin S., Piez K. A., Ogawa Y., Davies D. R. Crystal structure of transforming growth factor-beta 2: an unusual fold for the superfamily. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):369–373. doi: 10.1126/science.1631557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanders K. C., Lüdecke G., Engels S., Cissel D. S., Roberts A. B., Kondaiah P., Lafyatis R., Sporn M. B., Unsicker K. Localization and actions of transforming growth factor-beta s in the embryonic nervous system. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):183–191. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser A. G., Burmester J. K., Webbink R., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Inhibition of growth by transforming growth factor-beta following fusion of two nonresponsive human carcinoma cell lines. Implication of the type II receptor in growth inhibitory responses. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2588–2593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings J. C., Mohan S., Linkhart T. A., Widstrom R., Baylink D. J. Comparison of the biological actions of TGF beta-1 and TGF beta-2: differential activity in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):167–172. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Nathans D. Proliferin secreted by cultured cells binds to mannose 6-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3521–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Wang X. F., Ng-Eaton E., Weinberg R. A., Lodish H. F. Expression cloning of the TGF-beta type II receptor, a functional transmembrane serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Cheifetz S., Doody J., Andres J. L., Lane W. S., Massagué J. Structure and expression of the membrane proteoglycan betaglycan, a component of the TGF-beta receptor system. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Like B. Cellular receptors for type beta transforming growth factor. Ligand binding and affinity labeling in human and rodent cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Receptors for the TGF-beta family. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90627-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwin J. R., Newman W., Beall L. D., Tucker A., Madri J. Vascular cells respond differentially to transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2 in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):37–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. J., Fitz-Gibbon L., O'Connor-McCourt M. D. Subtypes of betaglycan and of type I and type II transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptors with different affinities for TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 are exhibited by human placental trophoblast cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Feb;150(2):334–343. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. J., O'Connor-McCourt M. D. A transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) receptor from human placenta exhibits a greater affinity for TGF-beta 2 than for TGF-beta 1. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4350–4356. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor-McCourt M. D., Wakefield L. M. Latent transforming growth factor-beta in serum. A specific complex with alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14090–14099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Greenberger J. S., Anklesaria P., Bassols A., Massagué J. Two forms of transforming growth factor-beta distinguished by multipotential haematopoietic progenitor cells. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):539–541. doi: 10.1038/329539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottmann O. G., Pelus L. M. Differential proliferative effects of transforming growth factor-beta on human hematopoietic progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2661–2665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S. W., Burmester J. K., Merwin J. R., Madri J. A., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Identification of a structural domain that distinguishes the actions of the type 1 and 2 isoforms of transforming growth factor beta on endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Physiological actions and clinical applications of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta). Growth Factors. 1993;8(1):1–9. doi: 10.3109/08977199309029129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlunegger M. P., Grütter M. G. An unusual feature revealed by the crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of human transforming growth factor-beta 2. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):430–434. doi: 10.1038/358430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Roberts A. B., Rosen D. M., Seyedin S. M. Membrane binding characteristics of two forms of transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14655–14662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta: recent progress and new challenges. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1017–1021. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suardet L., Gaide A. C., Calmès J. M., Sordat B., Givel J. C., Eliason J. F., Odartchenko N. Responsiveness of three newly established human colorectal cancer cell lines to transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3705–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. F., Lin H. Y., Ng-Eaton E., Downward J., Lodish H. F., Weinberg R. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the TGF-beta type III receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]