Figure 5. Activation of NF-κB due to FoxO6 inactivation by LPS.
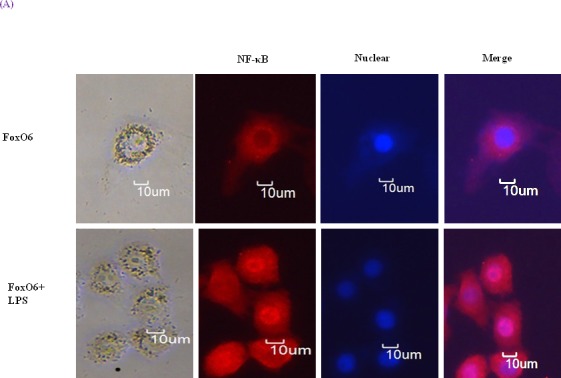
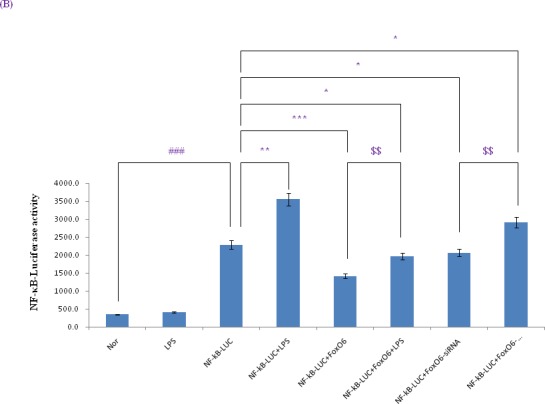
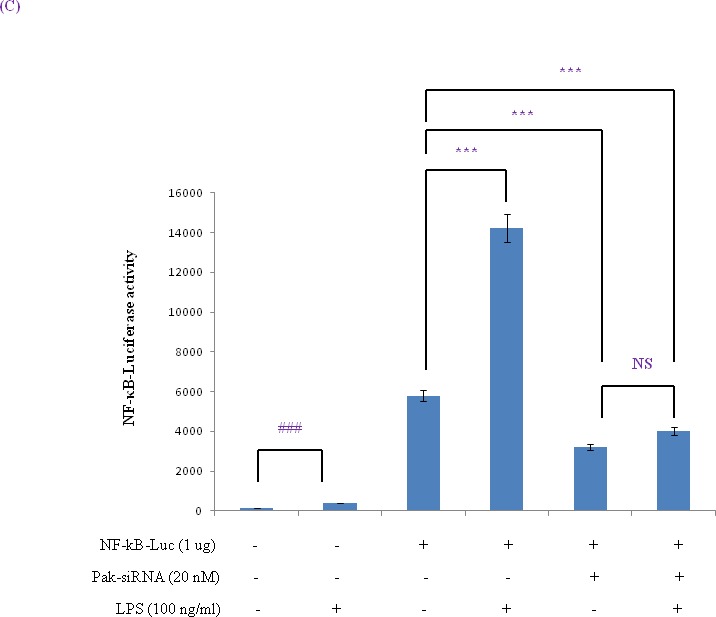
A. HepG2 cells were pretransduced with 100 MOI of FoxO6 vector for 24 hr and then treated with or without LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 hr. Cells were immunostaining using rabbit anti-NF-κB antibody followed by IgG conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (Red). Bar = 10 μm. B. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with a NF-κB-containing plasmid linked to the luciferase gene, pre-incubated with FoxO6 (100 MOI) or FoxO6-siRNA (100 MOI) for 24 hr and then treated with LPS for 2 hr. Results are presented in relative luminescence units (RLU). Results were obtained using one-factor ANOVA: ###p < 0.001 vs. untransduced cells; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. NF-κB-luciferase transduced cells; $$p < 0.01 vs. NF-κB-luciferase transduced cells pre-incubated with FoxO6 virus or FoxO6-siRNA. C. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with a NF-κB-containing plasmid linked to the luciferase gene, pre-incubated with Pak-siRNA (20 nM) for 48 hr and then treated with LPS for 2 hr. Results are presented in relative luminescence units (RLU). Results were obtained using one-factor ANOVA: ###p < 0.001 vs. untransduced cells; ***p < 0.001 vs. NF-κB-luciferase transduced cells.
