Abstract
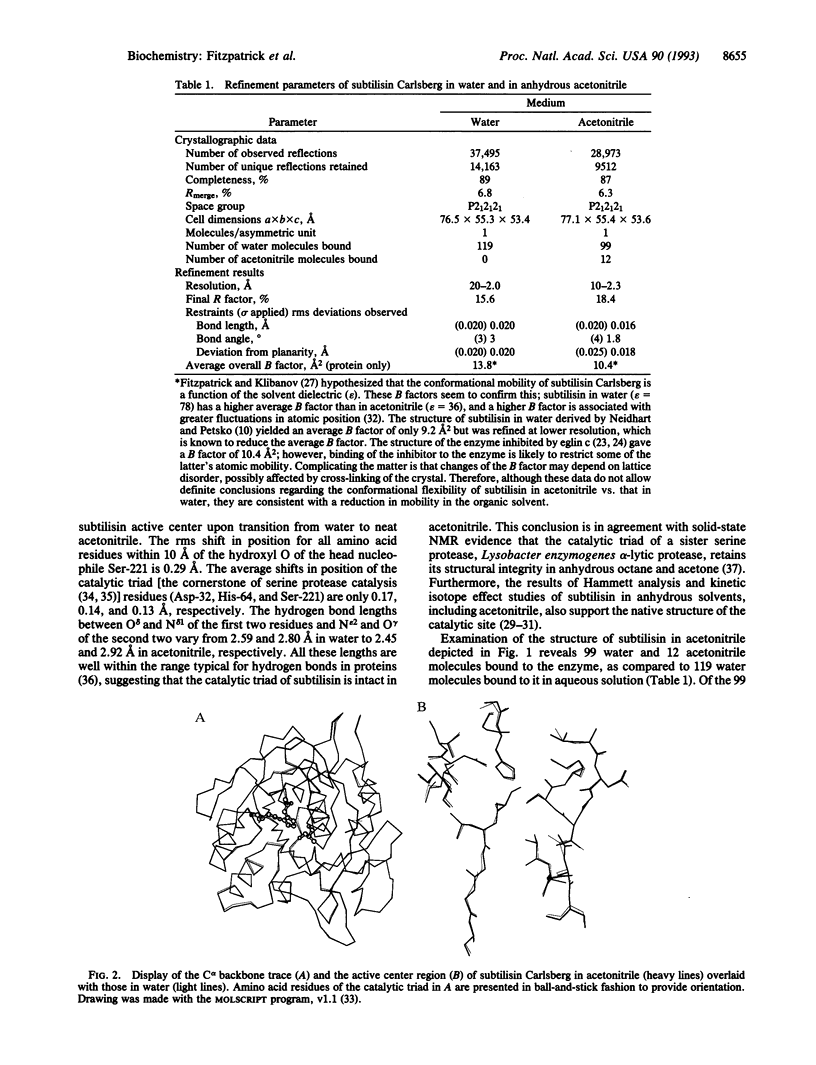
The crystal structure of the serine protease subtilisin Carlsberg in anhydrous acetonitrile was determined at 2.3 A resolution. It was found to be essentially identical to the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme in water; the differences observed were smaller than those between two independently determined structures in aqueous solution. The hydrogen bond system of the catalytic triad is intact in acetonitrile. The majority (99 of 119) of enzyme-bound, structural water molecules have such a great affinity to subtilisin that they are not displaced even in anhydrous acetonitrile. Of the 12 enzyme-bound acetonitrile molecules, 4 displace water molecules and 8 bind where no water had been observed before. One-third of all subtilisin-bound acetonitrile molecules reside in the active center, occupying the same region (P1, P2, and P3 binding sites) as the specific protein inhibitor eglin c.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affleck R., Xu Z. F., Suzawa V., Focht K., Clark D. S., Dordick J. S. Enzymatic catalysis and dynamics in low-water environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Birktoft J. J., Hartley B. S. Role of a buried acid group in the mechanism of action of chymotrypsin. Nature. 1969 Jan 25;221(5178):337–340. doi: 10.1038/221337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Papamokos E., Musil D. The high-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the complex formed between subtilisin Carlsberg and eglin c, an elastase inhibitor from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Structural analysis, subtilisin structure and interface geometry. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):673–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N., Hen S. J., Klibanov A. M. Protein separation and purification in neat dimethyl sulfoxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1462–1468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90451-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Principles that determine the structure of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:537–572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):849–857. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta M. N. Enzyme function in organic solvents. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A. Diffraction methods for biological macromolecules. Interactive computer graphics: FRODO. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:157–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klibanov A. M. Enzymatic catalysis in anhydrous organic solvents. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhalen C. A., James M. N. Structural comparison of two serine proteinase-protein inhibitor complexes: eglin-c-subtilisin Carlsberg and CI-2-subtilisin Novo. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6582–6598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranker A., Karplus M. Functionality maps of binding sites: a multiple copy simultaneous search method. Proteins. 1991;11(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhart D. J., Petsko G. A. The refined crystal structure of subtilisin Carlsberg at 2.5 A resolution. Protein Eng. 1988 Oct;2(4):271–276. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.4.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petsko G. A., Tsernoglou D. The structure of subtilopeptidase A. I. X-ray crystallographic data. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):453–456. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUIOCHO F. A., RICHARDS F. M. INTERMOLECULAR CROSS LINKING OF A PROTEIN IN THE CRYSTALLINE STATE: CARBOXYPEPTIDASE-A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:833–839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringe D., Petsko G. A. Mapping protein dynamics by X-ray diffraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(3):197–235. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. J., Klibanov A. M. Inhibitor-induced enzyme activation in organic solvents. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11624–11626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. J., Trudel L. J., Skipper P. L., Groopman J. D., Tannenbaum S. R., Klibanov A. M. Antibody-antigen binding in organic solvents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of subtilisin BPN' at 2.5 angström resolution. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):235–242. doi: 10.1038/221235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaks A., Klibanov A. M. Enzymatic catalysis in nonaqueous solvents. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3194–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]