Figure 3. Functional defects associated with novel missense variants.
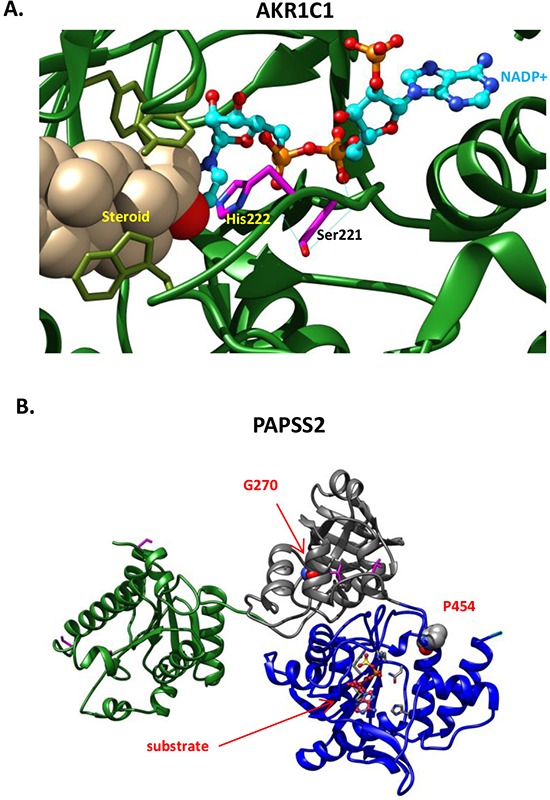
A. AKR1C1, S221N. AKR1C1 catalyzes the inactivation of progesterone to the less potent 20α-hydroxyl-pregn-4-ene-3-one. The reaction is NADPH dependent with an obligatory requirement for the cofactor to bind before the steroid substrate can bind to form the central complex. The progesterone is maintained in a steroid binding site at H222; an H222I mutation decreases the Km value for NADPH 95-fold [102]. Here, AKR1C1 (PDB code: 1MRQ) is shown with bound steroid 20alpha-hydroxy-progesterone, and the cofactor, NADP+ in ball-and-stick representation with cyan carbons, and orange phosphorus atoms. S221 and adjacent catalytic residue H222 of AKR1C1 are shown with magenta sticks. S221 is involved in 2 hydrogen bonds (shown with cyan thin lines) with adjacent residues and one with the NADP+ cofactor. Though predicted to be benign by several conservation based servers, the S221N substitution disrupts the hydrogen-bonding network required to maintain the catalytic active site configuration. B. Shown are the PAPSS2 kinase domain in green, PUA (PseudoUridine synthase and Archaeosine transglycosylase) domain in gray and sulfate adenylyltransferase domain in blue. The position of the P454L and G270D missense variants are indicated.
